Selenium with CodeceptJS
Your guide to running tests using CodeceptJS on BrowserStack’s Selenium Grid of 3000+ real devices and desktop browsers.
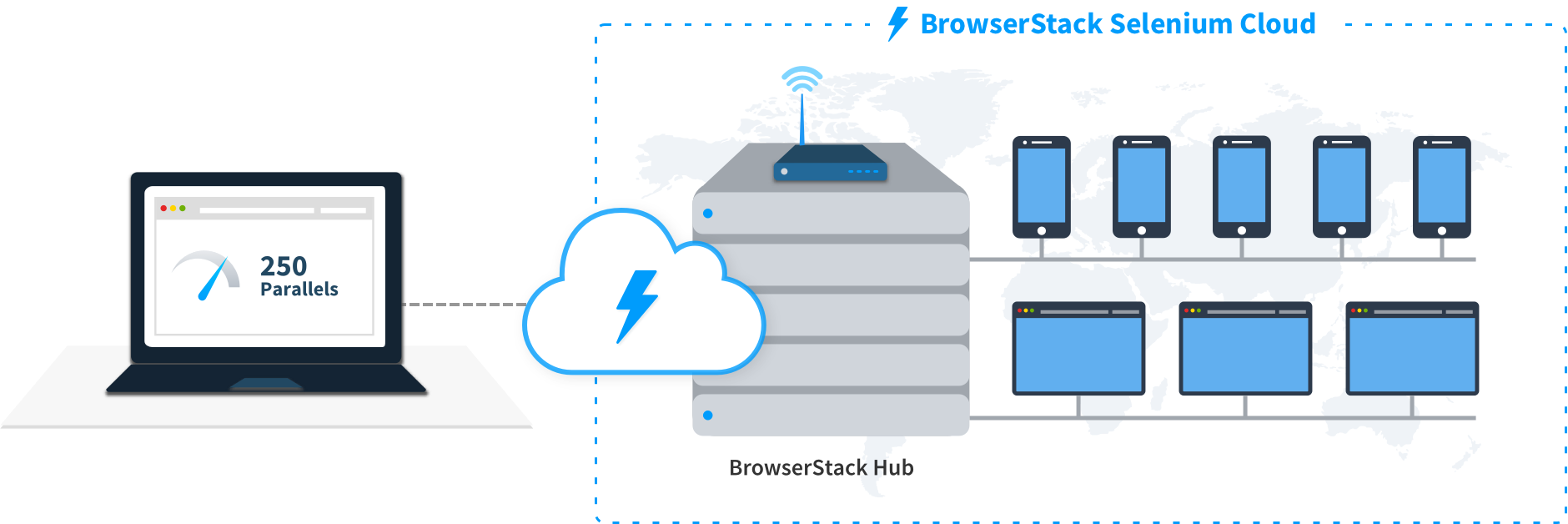
This section covers running your first build with BrowserStack’s sample repo. To run builds with your existing test suite(s), skip to integrate your test suite.
Prerequisites
- You need to have BrowserStack Username and Access key, which you can find in your account profile. If you have not created an account yet, you can sign up for a Free Trial.
- Node v12+ installed on your machine.
Run a sample build
Run a sample CodeceptJS test build on BrowserStack:
Get our sample project
Get our sample project using one of the following options:
Option 1: Download the project
Option 2: Clone the sample repository
Clone our sample repository and install the dependencies.
Configure the config file
Configure the following parameters in the browserstack.yml config file to run the sample build.
Set access credentials
Use the userName and accessKey variables to set your BrowserStack access credentials in the browserstack.yml file to authenticate your tests.
Configure browser or device combinations
Choose from 3000+ real mobile devices and browsers available on BrowserStack:
Copy and replace the browserstack.yml config file
Replace the contents of browserstack.yml situated in the root directory of this project with the given config.
Execute the build on BrowserStack
You are now ready to run your build on BrowserStack. From the root directory of this project, run the given command.
After you run your test, visit the Automate dashboard to view your test results.
After you have successfully run your first test on BrowserStack, try integrating your test suite with BrowserStack.
We're sorry to hear that. Please share your feedback so we can do better
Contact our Support team for immediate help while we work on improving our docs.
We're continuously improving our docs. We'd love to know what you liked
- RESOURCES
We're sorry to hear that. Please share your feedback so we can do better
Contact our Support team for immediate help while we work on improving our docs.
We're continuously improving our docs. We'd love to know what you liked
Thank you for your valuable feedback!
