Flaky tests are tests that returns success as well as failures although there are no changes made to the code or the test.
Overview
What is a Cypress Flaky Test?
A Cypress flaky test gives unreliable pass/fail results despite no test code or application changes. This inconsistency masks real issues and damages confidence in your automated tests.
How to Fix and Prevent Cypress Flaky Tests:
- Identify and address root causes like timing sensitivities, unstable selectors, or inconsistent test data.
- Implement intelligent synchronization using explicit waits, assertions, and network request interception.
- Employ stable and unique element selectors for robust interactions, preferably data-* attributes.
- Effectively leverage Cypress’s built-in features, such as Test Retries and configurable timeouts.
- Adopt solid test design principles, ensuring tests are atomic and independent and the state is managed properly.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding, systematically identifying, debugging, and ultimately resolving flaky tests in your Cypress test suite.
What is a Cypress Flaky Test?
A flaky test in Cypress inconsistently passes or fails without any codebase, environment, or test logic changes. These tests produce unreliable results, making it difficult for developers to trust the outcomes of their test suite.
Flakiness typically arises due to timing issues, unhandled asynchronous behavior, test interdependence, or environmental instability.
In Cypress, flakiness often stems from timing issues, unhandled async behavior, or incorrect use of commands like cy.intercept() or cy.get(). Even minor oversights can lead to inconsistent test results, undermining confidence in your test suite.
Common Mistakes That Causes Flaky Tests in Cypress
Identifying flaky tests in Cypress can be tricky. Because of the nature of flaky tests, it becomes difficult to discover the cause or reproduce the error. This becomes frustrating.
That said, there are a few common mistakes that one makes which might result in the test becoming flaky.
- Hard coded wait: Using fixed cy.wait() commands introduces unreliability as application load times can vary significantly.
- Poorly designed selectors: Relying on unstable or overly complex selectors causes tests to break easily with minor UI changes.
- Less understanding in retry-ability: Overlooking or misinterpreting Cypress’s automatic retry mechanisms leads to adding unnecessary manual waits or assertions.
- Not using network wait: Tests proceed without confirming critical background API calls have completed, leading to checks against incomplete data.
- Less understanding in how the state of an element changes in application: Interacting with or asserting against elements before they are fully loaded, visible, or enabled causes unexpected failures.
These are the quite commonly made mistakes as seen from user complaints across platforms.
Learn More: How to find Flaky Selenium Test Suite
How to Systematically Identify Flaky Tests in Your Cypress Suite
Discovering flaky tests is the first crucial step towards a more stable and trustworthy automation suite.
Employ the following systematic approaches to pinpoint these inconsistent tests within your Cypress projects:
- Monitor CI/CD reports for tests with inconsistent pass/fail patterns over time.
- Re-run the entire test suite or specific suspicious tests multiple times locally.
- Utilize the Cypress Dashboard, if integrated, for its flaky test detection features.
- Investigate tests that frequently fail in CI environments despite passing locally.
- To confirm inconsistent outcomes, execute a suspected flaky test in a loop (e.g., 10-20 iterations).
- Tag and closely observe tests that show any slight variation in behavior or timing.
Effective Techniques for Debugging Flaky Cypress Tests
Once a flaky test is identified, pinpointing the exact cause requires careful investigation and the right tools.
The following techniques can help you effectively debug and understand the root of the flakiness in your Cypress tests:
- Insert cy.pause() commands to inspect the application and DOM state at various points.
- Use .debug() on specific Cypress commands to log detailed information to the console.
- Analyze screenshots and videos automatically captured by Cypress on test failure.
- Check the browser’s developer console for JavaScript errors or warnings during test execution.
- Examine network requests and responses using cy.intercept() or browser dev tools.
- Simplify the test by commenting out sections to isolate the problematic command(s).
- Compare DOM structures or element states between a successful and a failed run.
Core Strategies for Fixing and Preventing Flaky Tests in Cypress
Effectively tackling flaky tests involves resolving inconsistencies and proactively building more resilient automation.
The following core strategies combine Cypress-specific features with general best practices to help you achieve a more stable and reliable test suite.
Understanding retry-ability in Cypress
Cypress is smart. If you are querying for an element, it ensures the element exists in DOM before proceeding to the next chained command.
Retry Command
Here is an example
cy.get(".shelf-item__buy-btn").invoke("text").should("eq", "someText")Use the get() command of Cypress for querying the element. The get() command ensures that the element being queried exists in DOM before proceeding to invoke() command.
This ensures that you don’t encounter the missing element exception when there is delay in elements loading in the application.
Do refer to Cypress’ API documentation to understand how you can use cy.get() command based on your test design.
Commands Chained with Assertion Retry
cy.get(".shelf-item__buy-btn").invoke("text").should("eq", "someText")The above example of Retry Command uses get() query command for the element and should() assertion. Cypress will first wait until the element exists in DOM which is good, but since we are checking for all the elements with the selector class matching, which is 25, there could be a delay in application rendering these elements?
Cypress understands this scenario and retry the first immediate chained command with the assertion command. In our case it is get, cypress will retry the get() command until its length becomes 25 up-to defined timeout.
Understanding Interception To Make Tests Stable
As Cypress runs within the browser, it has total control over the network calls and can listen, modify, and wait for those calls.
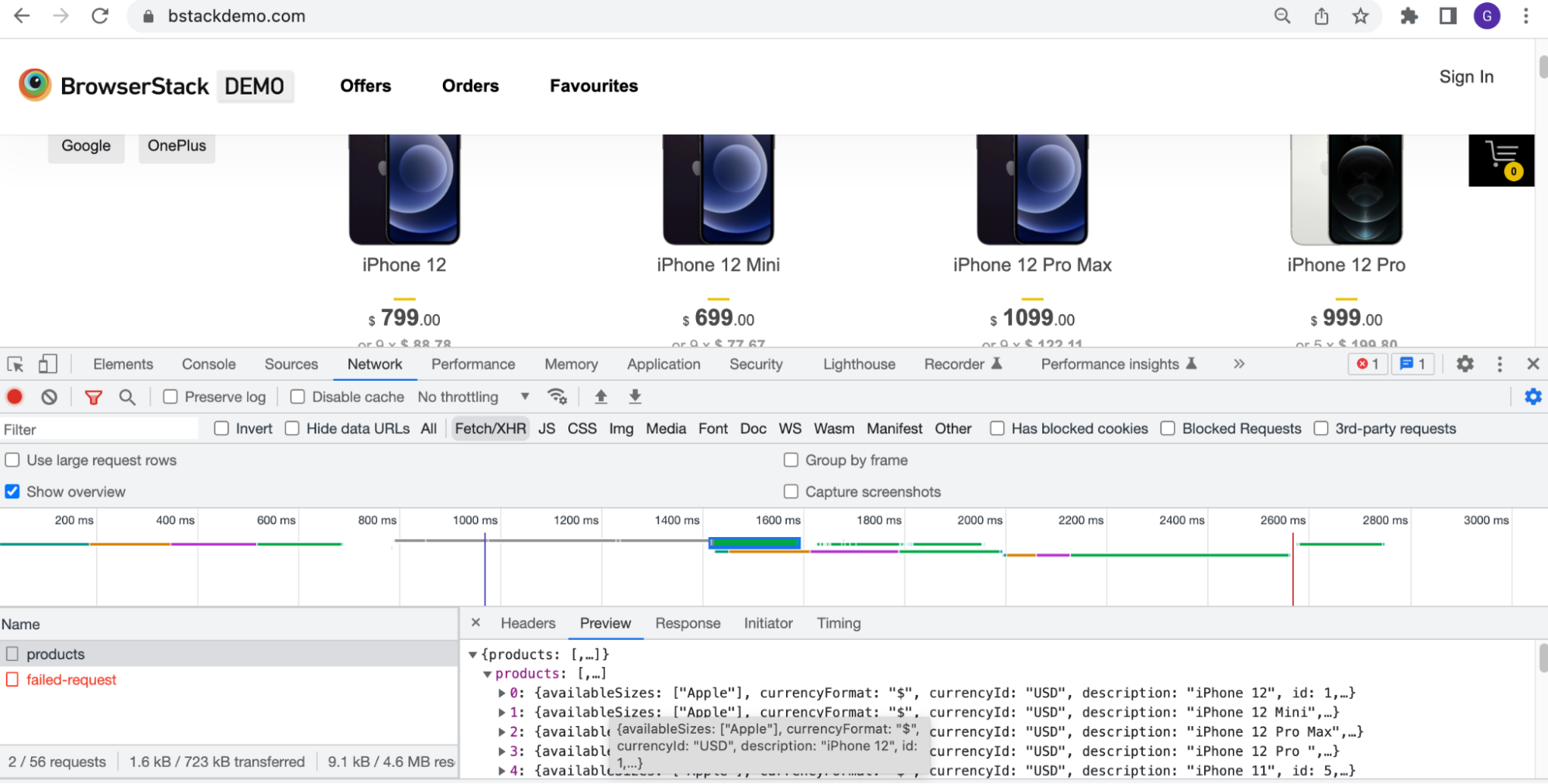
To understand how you can leverage this to write our tests, let’s use the BrowserStack’s demo application
To see the network activity, Open Dev tools (Click on F12 key) > Network. You can see that BrowserStack’s demo website uses an API call to retrieve the product details.
In order to make our tests effective/stable and reliable instead of just waiting for the element state, you can wait for this API call to be successful.
it("Intercept test", () => {
cy.intercept("api/products").as("products");
cy.visit("https://www.bstackdemo.com/");
cy.wait("@products", {timeout: 4000} );
});The intercept function has to be added before the line of code which triggers the api call. In our case, we need to add the API call for the product before visiting the BrowsertStack’s demo application and then wait for that call to complete successfully.
Defining Timeouts
Cypress allows users to control the timeout global/Command level which ensures the various actions complete within a given time and anything exceeding throw timeout error.
Below are the global timeouts that you can set in Cypress config file or pass it via command line
- defaultCommandTimeout
- execTimeout
- taskTimeout
- pageLoadTimeout
- requestTimeout
- responseTimeout
Best Practices for Writing Reliable Cypress Tests
Consider incorporating these general best practices into your workflow:
- Prioritize data-* attributes (e.g., data-cy, data-testid) for unique and resilient element selectors.
- Ensure each test is atomic and independent, setting up and tearing down its specific conditions.
- Implement a consistent strategy for managing test data to avoid conflicts and ensure predictability.
- Explicitly verify the application is correct before performing actions or making assertions.
- Keep test logic focused and straightforward, aiming to verify one specific functionality per test.
- Design tests to reliably clean up any state they create, such as new records or user sessions, after execution.
- Regularly review and refactor your test suite to remove redundancy and adapt to application changes.
Conclusion
Effectively managing flaky tests in Cypress transforms them from a common frustration into a solvable challenge.
By understanding their causes and diligently applying strategies for identification, debugging, and prevention as outlined in this guide, you pave the way for a more stable and reliable automated testing process.
BrowserStack Automate provides a robust real device cloud platform for your Cypress tests to ensure consistent test outcomes across diverse real user conditions.
Useful Resources for Cypress
Understanding Cypress
- Cross Browser Testing with Cypress : Tutorial
- Run Cypress tests in parallel without Dashboard: Tutorial
- Handling Test Failures in Cypress A Comprehensive Guide
- Cypress Test Runner: Tutorial
- Handling Touch and Mouse events using Cypress
- Cypress Automation Tutorial
- CSS Selectors in Cypress
- Performance Testing with Cypress: A detailed Guide
- Cypress Best Practices for Test Automation
- Test React Native Apps with Cypress
- Cypress E2E Angular Testing: Advanced Tutorial
- Cypress Locators : How to find HTML elements
- Maximizing Web Security with Cypress: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Conditional Testing in Cypress: Tutorial
- Cypress Web Testing Framework: Getting Started
- Cypress Disable Test: How to use Skip and Only in Cypress
- What’s new in Cypress 10? How it will change your current testing requirements
Use Cases
- How to Record Cypress Tests? (Detailed Guide)
- How to run your first Visual Test with Cypress
- How to Fill and Submit Forms in Cypress
- How to Automate Localization Testing using Cypress
- How to run Cypress Tests in Chrome and Edge
- How to use Cypress App Actions?
- How to Run Cypress Tests for your Create-React-App Application
- How to Run Cypress Tests in Parallel
- How to handle Click Events in Cypress
- How to Test React using Cypress
- How to Perform Visual Testing for Components in Cypress
- How to run UI tests in Cypress
- How to test redirect with Cypress
- How to Perform Screenshot Testing in Cypress
- How to write Test Case in Cypress: (with testing example)
Tool Comparisons