Images are vital to websites and applications irrespective of the device that they are accessed.
They are added to the website banner, logo, product descriptions, etc. It is critical to load the entire website without compromising quality and content..
Overview
What is a Lazy Loading Image?
A lazy loading image is an image that loads only when it enters the user’s viewport, improving page load speed and performance.
Why use Lazy Loading of Images?
- Faster initial page load
- Reduces bandwidth usage
- Improves website performance
- Enhances user experience
- Saves server resources
Techniques for Lazy Loading Images in Javascript
1. Using EventListeners
2. Using Intersection Observer API
This article describes what lazy loading of an image is, its significance, techniques, best practices and more.
What is JavaScript Lazy loading?
JavaScript Lazy Loading is a performance optimization technique that delays the loading of non-critical resources, such as images, videos, or scripts, until they are actually needed on the page.
Instead of downloading all content upfront, the browser only loads what is required for the initial viewport, and additional elements are fetched as the user scrolls or interacts with the page.
By implementing lazy loading, developers can:
- Reduce initial page load time.
- Save bandwidth by loading resources only when necessary.
- Improve user experience with faster, more responsive pages.
How Lazy Loading in JavaScript Works?
Lazy loading works by deferring the download and rendering of resources until they are needed. Instead of fetching all images, videos, or scripts when the page first loads, placeholders are used, and the actual resources are requested only when the user scrolls near them or triggers an interaction.
The process typically involves:
- Placeholder Assignment: Lightweight placeholders (like blank images or low-resolution previews) are displayed initially.
- Viewport Detection: JavaScript checks whether an element is visible within the user’s viewport using events or APIs like IntersectionObserver.
- On-Demand Loading: Once the element comes into view, the actual resource (image, video, or script) is fetched and rendered.
- Progressive Rendering: The resource replaces the placeholder, ensuring a seamless user experience without blocking page load time.
Techniques for Lazy Loading Images in Javascript
Images on a webpage can be loaded either using <img> tags or CSS background property.
Images are loaded using the <img> tag. The browser uses the src attribute to trigger image load. The images are loaded as soon as the browser receives the src attribute. You specify the image URL in the data-src attribute. This avoids loading all images upfront.
1. Using EventListeners
To trigger the load of the images, you can use event listeners such as scroll, resize, and Orientation Change.
- Scroll: The scroll event is triggered when the webpage is scrolled.
- Resize: This occurs when the browser size changes.
- Orientation Change – The event is triggered when the device’s orientation is changed from portrait to landscape or vice versa.
document.addEventListener(“scroll”, lazyload);
window.addEventListener(“resize”, lazyload);
window.addEventListener(“orientationChange”, lazyload);
EventListener can be easily added and removed using addEventListener() and removeEventListener().
The first image fold must be added upfront for a better experience. The first image fold will have an src attribute, whereas the folds below will later load data-src.
Once you have added these elements it is essential that you test them. Using Percy, one can calculate the height of the page, by scrolling to the end of the page and then taking a screenshot for each screen scrolled.
2. Using Intersection Observer API
The Intersection Observer API asynchronously observes the changes and loads images as the element enters the viewport. The prior approach requires to bind events, consider performance, and build a mechanism to determine if an element was in the viewport or not. This is relatively straightforward, arithmetic is avoided, and excellent performance is provided through the Intersection Observer API.
You can add the observer to every image that will be loaded slowly. Using the isIntersecting property, you can select the URL from the data-src attribute and shift it to the src attribute so that the browser can load the image when the API determines that the element has entered the viewport. Once this is finished, you can take the observer and the lazy class out of the image.
document.addEventListener(“DOMContentLoaded”, function() {
var lazyloadImages;
if (“IntersectionObserver” in window) {
lazyloadImages = document.querySelectorAll(“.lazy”);
var imageObserver = new IntersectionObserver(function(entries, observer) {
entries.forEach(function(entry) {
if (entry.isIntersecting) {
var image = entry.target;
image.src = image.dataset.src;
image.classList.remove(“lazy”);
imageObserver.unobserve(image);
}
});
});
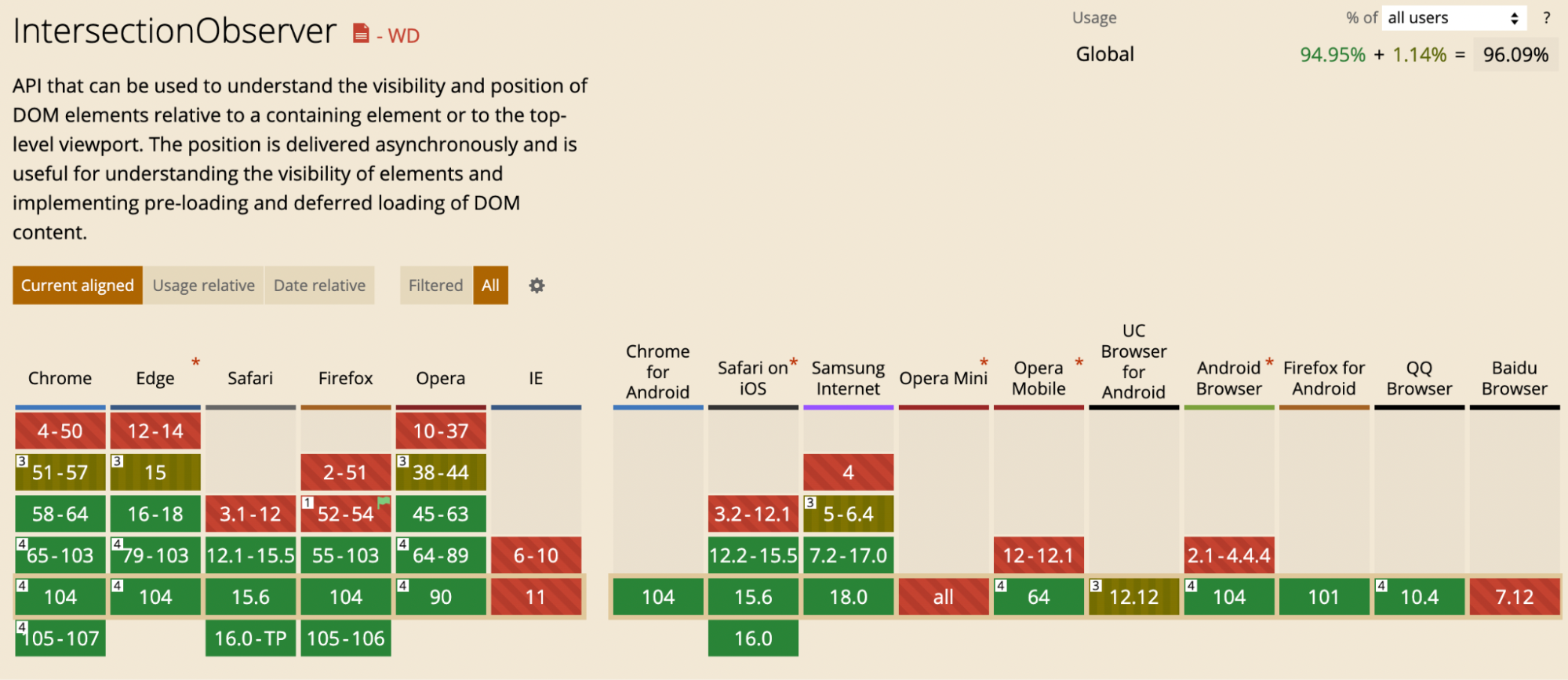
Images load faster in Intersection Observers when compared to event listeners. However, some browsers may not support Intersection Observer API and might have to opt for event listeners.
To know the list of browsers that support Intersection Observer API, refer to caniuse website.
Difference between Event Listeners and Intersection Observers
Explore the key differences between event listeners and intersection observers for tracking user interactions and element visibility on your web pages.
| Event Listeners | Intersection Observers |
| Manually calculate when an element enters the viewport | Asynchronously Observe changes |
| Required to fire off at even the smallest scroll movement | When the threshold is reached, or the target element enters the viewport, executes its callback function once. |
For most businesses moving online, the need for Lazy Loading Image has peaked. The e-commerce website needs to showcase all its products to the customers without compromising the image quality or the number of images on a page. The Lazy Loading Images technique will boost the e-commerce website’s performance.
Image Place Holders
Now that images are lazily loaded, what will appear when the images are still loading? You need to add image placeholders to avoid the emptiness of the webpage. You can either have block colors or low-quality image placeholders. The block colors will be aligned to the image loaded in the place. However, a better option would be to blur or add low quality of the actual image, which will give the user a better idea of what is still loading.
That said, one should not lazy load all the images on a web page if the page isn’t too long, if there are fewer images on a webpage, or if the images are present close to the viewport. The ability of the user’s browser to execute Javascript is a requirement for lazy loading to work. Although native lazy loading claims to eliminate this reliance, with browser support remaining at or near 70%, JavaScript libraries are still required to deliver the same experience across all browsers.
Advantages and Disadvantages of JavaScript Lazy Loading
Like any performance optimization technique, JavaScript Lazy Loading has its own advantages and disadvantages. Here are the key points to consider:
Advantages:
- Improved Page Speed: Loads only visible content first, reducing initial page load time.
- Optimized Bandwidth Usage: Downloads images, videos, or scripts only when required, saving data.
- Better User Experience: Delivers a faster and smoother browsing experience by prioritizing critical content.
- Enhanced SEO Performance: Helps improve Core Web Vitals and search rankings through faster loading.
Disadvantages:
- Delayed Content Visibility: Non-visible elements may take extra time to load when users scroll to them.
- SEO Limitations: Improper implementation can prevent search engines from indexing lazy-loaded content.
- Increased Complexity: Requires additional coding or configuration compared to standard loading.
- Compatibility Issues: Older browsers or certain devices may not fully support lazy loading.
Best practices for lazy loading images using Javascript
To ensure efficient implementation and avoid common pitfalls, here are some best practices for lazy loading images using JavaScript:
- Use the Intersection Observer API: Utilize the Intersection Observer API to efficiently detect when an image enters the viewport. This approach minimizes resource consumption and avoids the performance issues associated with scroll event listeners.
- Implement Fallbacks: Ensure that your lazy loading mechanism gracefully degrades on older browsers by providing fallback behavior or polyfills so that all users receive a consistent experience.
- Optimize Placeholder Images: Use low-resolution placeholders or lightweight loading animations to indicate that content is being loaded. This improves perceived performance and enhances the user experience.
- Prioritize Above-the-Fold Content: Preload critical images that appear in the viewport on initial load to ensure that the most important visuals render quickly, enhancing overall page performance.
- Set Appropriate Image Dimensions: Specify width and height attributes for images to reserve layout space and avoid content shifting during the load process, which contributes to a smoother user experience.
- Monitor and Test Performance: Regularly test your lazy loading implementation across different devices and network conditions. Tools like BrowserStack Percy can help capture full-page screenshots and ensure that images load as expected across all environments.
Conclusion
Lazy loading images in JavaScript is a powerful way to optimize performance, reduce page load times, and deliver a smoother user experience. By loading only the resources that matter in the moment, teams can save bandwidth while keeping web applications fast and responsive.
To ensure these optimizations work consistently across all browsers and devices, testing in real user conditions is essential. BrowserStack provides a robust testing platform that makes this possible.
With BrowserStack Percy, teams can go a step further by running visual regression tests, automatically scrolling through full-page content and capturing screenshots to verify that every element is rendered correctly.
This combination of performance optimization and comprehensive testing ensures that your lazy loading implementation not only speeds up your site but also maintains flawless user experiences.