What is Section 508 Compliance?
Section 508 Compliance refers to the requirement that all electronic and information technology developed, procured, maintained, or used by federal agencies be accessible to individuals with disabilities.
The goal of this compliance is to ensure equal access to information and services for all users, regardless of disability, through adherence to technical criteria and functional performance requirements defined by the U.S. Access Board.
Understanding Section 508 is essential for organizations that create, manage, or procure technology used by federal agencies.
What is 508 Compliance?
Section 508, refers to the U.S Workforce Rehabilitation Act of 1973, which ensures federal agencies make their electronic and information technology accessible to people with disabilities.
The law applies to all federal agencies when they develop, procure, maintain, or use electronic and information technology.
Amended in 1998, Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 focuses on setting accessibility standards for EIT, including websites, software applications, hardware, and other electronic content.
The standards are designed to make technology accessible to individuals with disabilities, including those with visual, auditory, cognitive, and motor impairments.
Section 508 standards were updated in 2017 to align with the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.0, which is an internationally recognized set of guidelines for web accessibility developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).
Read More: Web Accessibility Best Practices
Scope of 508 Compliance
Section 508 Compliance applies to all electronic and information technology (EIT) developed, procured, maintained, or used by federal agencies in the United States.
The scope of Section 508 extends beyond federal agencies themselves. It also includes contractors, vendors, and any organizations that develop digital tools or content for federal government use. This includes a wide range of technologies and digital assets, such as:
- Websites and web applications
- Software and mobile applications
- Electronic documents (e.g., PDFs, Word files, Excel spreadsheets)
- Multimedia content (e.g., videos, webinars)
- Telecommunications products
- Computers and peripheral equipment
- Information kiosks and self-service terminals
While Section 508 specifically applies to federal entities, many state and local governments, educational institutions, and private organizations voluntarily adopt these standards to promote broader digital accessibility and mitigate legal and reputational risk. Additionally, any organization seeking to contract with federal agencies must ensure that their products or services meet Section 508 requirements.
Why is 508 Compliance Important?
Section 508 Compliance is important because it ensures equitable access to digital content and technology for individuals with disabilities, supporting both legal obligations and inclusive design principles. Its significance can be understood through several key dimensions:
- Legal Obligation: Compliance with Section 508 is mandatory for federal agencies and their contractors. Failure to meet these standards can result in legal consequences, including complaints, investigations, and potential loss of federal contracts.
- Equal Access and Inclusion: Section 508 promotes digital equity by enabling individuals with visual, auditory, cognitive, or motor impairments to interact with technology in meaningful ways. It upholds the civil rights of people with disabilities by removing barriers to information and services.
- Improved Usability for All Users: Designing with accessibility in mind often results in cleaner, more navigable interfaces that benefit all users, not just those with disabilities. Features such as keyboard navigation, captioned videos, and readable text improve overall user experience.
- Reputational and Ethical Considerations: Organizations that prioritize accessibility demonstrate a commitment to diversity, equity, and social responsibility. This can enhance public trust, brand reputation, and stakeholder confidence.
- Broader Market Reach: Accessible products and services can reach a wider audience, including the estimated 1 in 4 U.S. adults living with a disability. For vendors and developers, compliance opens opportunities to engage with the federal market and other accessibility-conscious institutions.
What are the 508 compliant website requirements?
Section 508 outlines that Electronic content must adhere to the Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements outlined in Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.0. This means all the federal websites should conform to Level A and AA of WCAG 2.0 to meet Section 508 compliance requirements.
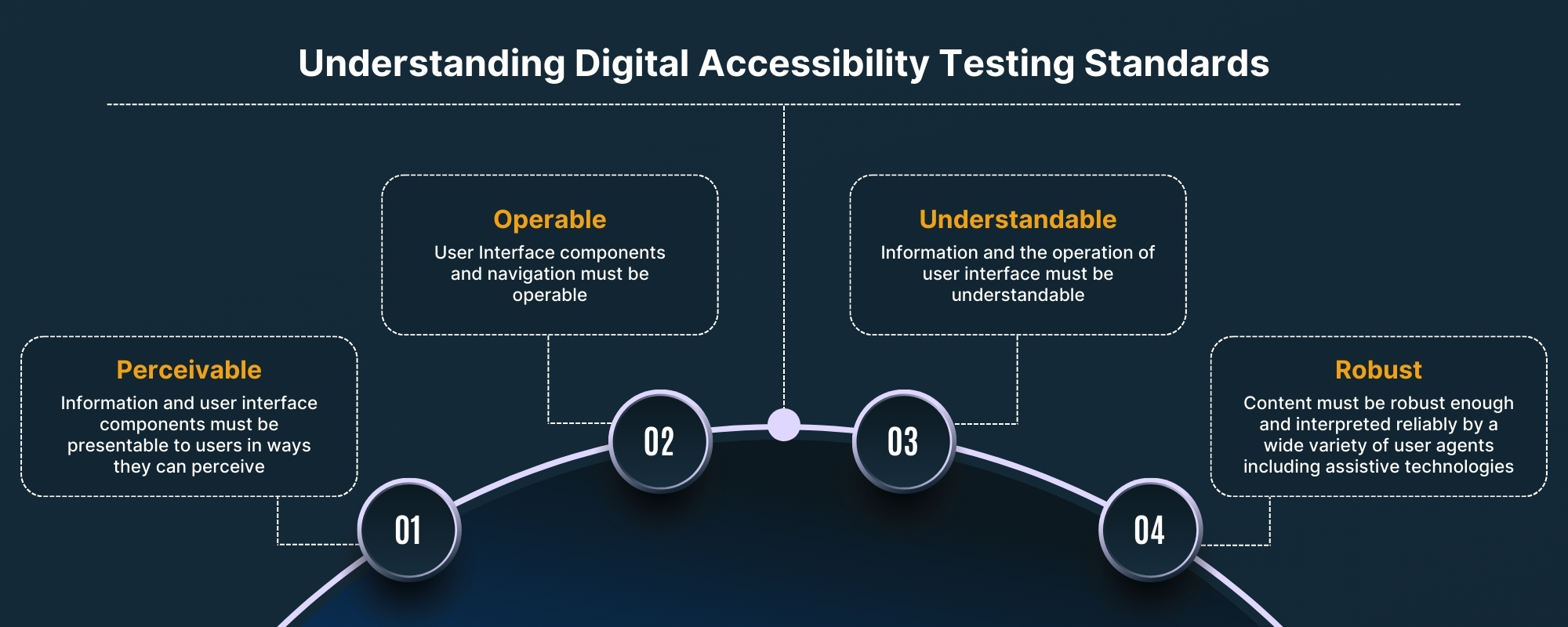
WCAG is a set of guidelines developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), which influences global web accessibility policies like Section 508 and ADA Compliance. WCAG compliance is based on 4 Key Principles:
- P- Perceivable
- O- Operable
- U- Understandable
- R- Robust
These principles further classify into actionable guidelines that should be followed for Section 508 WCAG compliance. Here are the WCAG guidelines:
| 1. | Perceivable | |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Text Alternatives | Provide Text Alternatives to different non-text content forms so that it can be used by assistive technology such as screen readers, braille, large print, symbols, or easy language. |
| 1.2 | Time-based Media | Provide Captions, alternatives or audio descriptions for pre-recorded and live time-based media such as audio or video. |
| 1.3 | Adaptable | Create content that is adaptable to different forms without losing out on the information or its structure. |
| 1.4 | Distinguishable | Make content easier for the user to see and hear so that they can separate the foreground from the background. |
| 2. | Operable | |
| 2.1 | Keyboard Accessible | Make all the functionality of the website accessible from a keyboard without requiring specific timings for individual keystrokes. |
| 2.2 | Enough Time | Give the users enough time to read and act on the content. |
| 2.3 | Seizures | Content design should not have anything that flashes more than 3 times to avoid causing seizures due to photosensitivity. |
| 2.4 | Navigable | Help users navigate through the workflows and webpages, find content, and determine where they are on the website. |
| 2.5 | Input Modalities (WCAG 2.1 & WCAG 2.2) | Make it easier for the users to operate functionalities using different inputs apart from the keyboard. |
| 3. | Understandable | |
| 3.1 | Readable | Create content that is readable and easy to understand using clear and simple language. |
| 3.2 | Predictable | Design content and pages in a predictable way, where users can easily predict how to operate. |
| 3.3 | Input Assistance | Help users provide correct information and correct mistakes through ways like clear instructions and error prevention techniques. |
| 4. | Robust | |
| 4.1 | Compatible | Create a website with maximum compatibility with the current and future user agents such as browsers, devices, and platforms, including assistive technologies. |
Read More to know about WCAG Compliance and Guidelines in detail
How to perform 508 Compliance Testing using BrowserStack Accessibility Testing Tool
BrowserStack Accessibility Testing is a unified platform for swiftly detecting both fundamental and intricate accessibility issues. It is a one-Stop Solution to
- Test,
- Report, and
- Monitor Web Accessibility Health
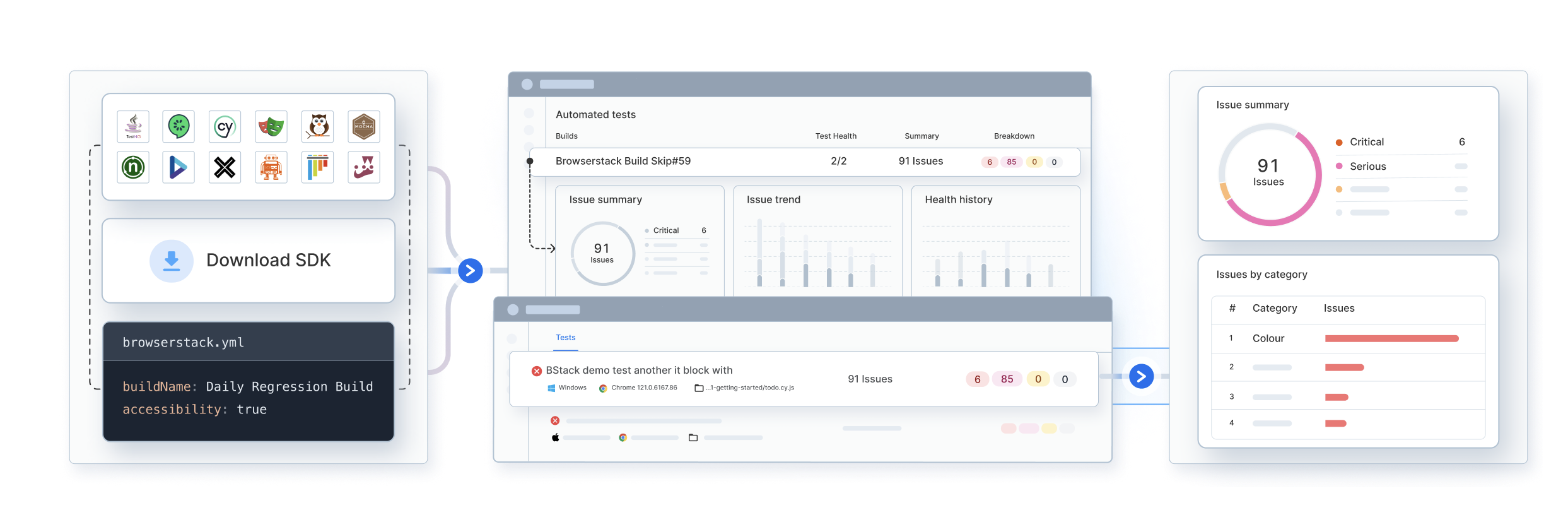
Test: Automated Accessibility Tests
BrowserStack’s accessibility testing platform offers a comprehensive suite of tools to identify Section 508 compliance issues efficiently and accurately. Key testing capabilities include:
- Screen Reader Support: Validate accessibility with built-in support for popular screen readers like NVDA, VoiceOver, and TalkBack across real devices and browsers.
- Workflow Analyzer: Automatically scans complete user flows, such as onboarding or checkout journeys, to uncover issues across multiple pages.
- Test Automation: Integrates with CI/CD pipelines to run accessibility checks during every build, ensuring early detection of issues.
- Assisted Testing: Enables manual, guided evaluations on real devices, allowing testers to verify keyboard navigation, screen reader behavior, and custom UI component accessibility.
These features work together to ensure that both technical and functional accessibility requirements are thoroughly tested throughout the development lifecycle.
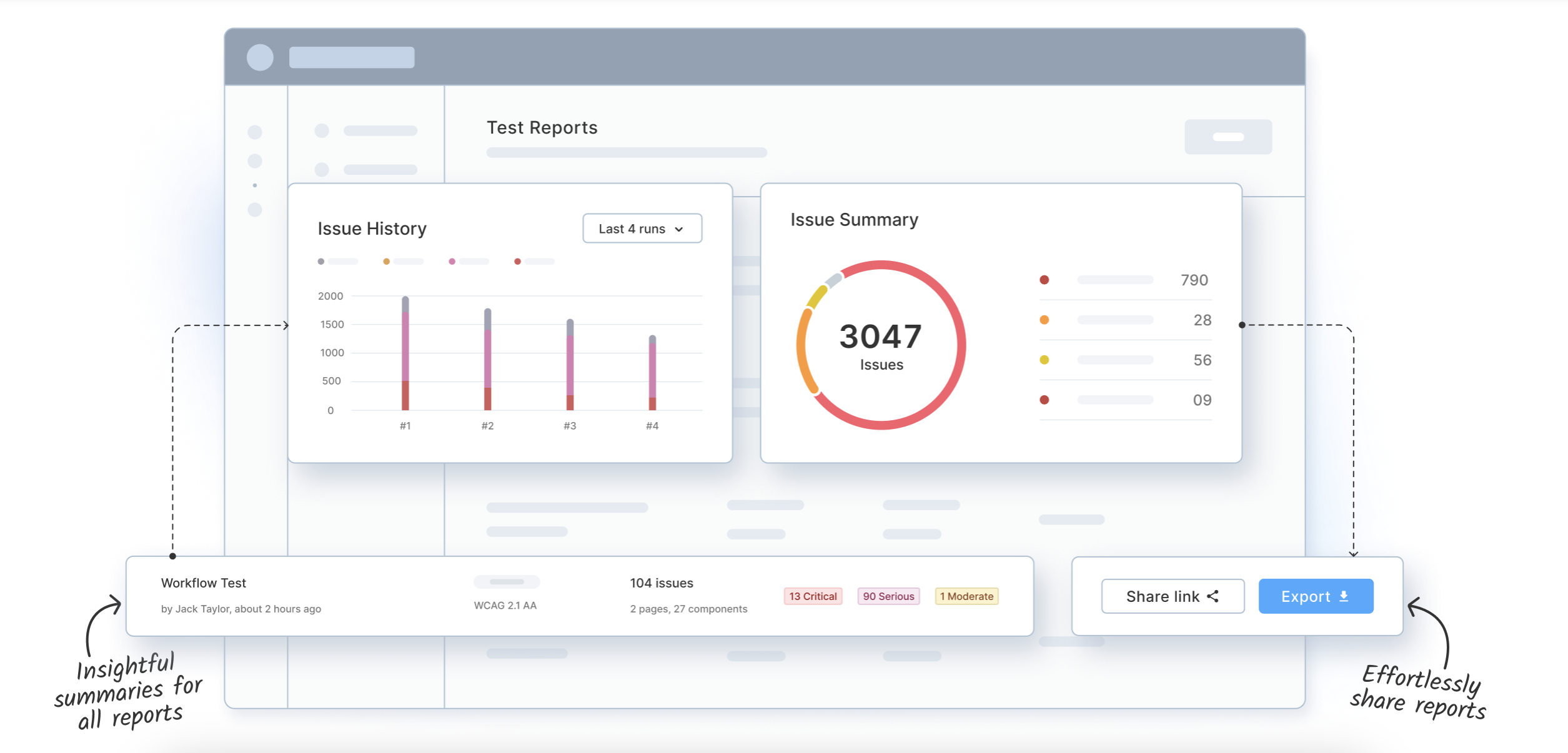
Report: Centralized Reporting Dashboard
BrowserStack provides a centralized accessibility dashboard that aggregates test results into one unified view for easy analysis and action. This dashboard helps teams quickly identify, categorize, and prioritize accessibility issues found during automated or manual testing.
Highlights include:
- Grouped issues by severity and WCAG/Section 508 rule: Helps teams understand the impact of violations.
- Visual documentation: Screenshots and DOM-level issue highlights help developers locate and fix problems faster.
- Historical data tracking: Enables comparisons over time to monitor improvement or regression.
- Exportable reports: Facilitates communication with stakeholders and simplifies compliance documentation and VPAT creation.
This centralized approach streamlines team collaboration and supports consistent accessibility improvements.
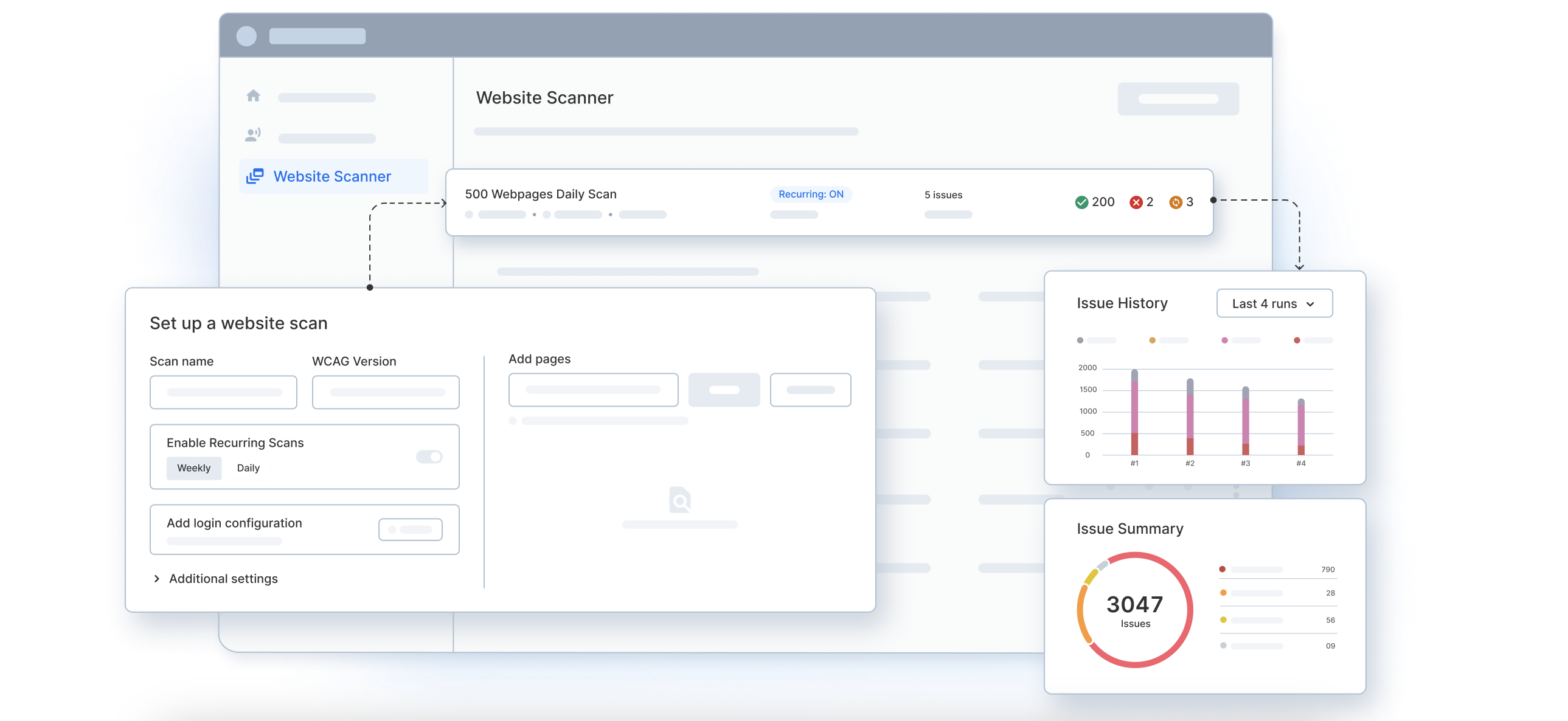
Monitor: Website Scanner for Accessibility Health
The Website Scanner feature offers a real-time, continuous solution to monitor accessibility health across entire websites. It is designed for proactive maintenance and ensures sustained compliance with Section 508 and WCAG standards.
Key features:
- Full-site scanning: Automatically crawls and scans all public URLs to identify accessibility violations.
- Health scores: Assigns scores based on compliance levels, helping organizations benchmark and prioritize improvements.
- Issue trend monitoring: Visualizes how accessibility issues evolve over time, making it easier to detect regressions after content updates or deployments.
- Scheduled scans: Runs periodic scans to ensure ongoing monitoring and compliance without manual intervention.
This monitoring capability supports long-term accessibility strategies and early detection of new or recurring issues.
Section 508 vs ADA Compliance
Both Section 508 and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) promote digital accessibility, but they differ in legal scope, enforcement, and technical focus.
Below is a side-by-side comparison:
| Aspect | Section 508 | ADA (Title II & III) |
|---|---|---|
| Applicability | Federal agencies and federally funded organizations | State/local governments (Title II) and private businesses/public accommodations (Title III) |
| Focus | Electronic and information technology (EIT) | Physical access and digital accessibility (websites, mobile apps) |
| Enforcement | Overseen by the U.S. Access Board; subject to audits and reviews | Enforced by the Department of Justice; subject to civil litigation |
| Standards Referenced | WCAG 2.0 Level AA (Section 508 Refresh) | No fixed legal standard, but WCAG 2.1 Level AA is commonly used |
| Testing Requirements | Requires formal accessibility testing and documentation for compliance | Testing is recommended but not explicitly defined; legal actions often evaluate WCAG compliance |
| Legal Obligation | Mandatory for federal procurements and IT systems | Mandatory for public-facing websites and services under civil rights law |
Schedule Website Scan for 508 Compliance Now
Who needs to comply with Section 508?
Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act requires that all federal agencies ensure their electronic and information technology (EIT) is accessible to individuals with disabilities. Compliance is mandatory for the following entities:
- Federal Government Agencies: All federal departments, agencies, and offices across the executive, legislative, and judicial branches must meet Section 508 requirements for websites, software, documents, and other digital tools.
- Contractors and Vendors: Any company or individual providing technology-related products or services to the federal government must ensure those offerings are Section 508 compliant. This includes software, websites, mobile applications, and hardware.
- Federally Funded Organizations: Organizations that receive federal funding are also required to comply. This includes public universities, research institutions, and local or state programs supported by federal grants.
- Technology Providers: Vendors that develop or distribute digital tools, platforms, or content used by federal agencies must design their products to meet 508 standards. This applies to both off-the-shelf and custom-built solutions.
While Section 508 directly applies to U.S. federal entities, private organizations may choose to adopt these standards to improve accessibility, reduce legal risk, and enhance the user experience for a broader audience.
How to make website 508 compliant?
Here are some of the key best practices to make website 508 compliant:
- Understand and Implement WCAG Standards
- Track WCAG 2.0 using a 508 Compliance checklist based on WCAG standards.
- Use HTML Markup in the content as per the accessibility standards.
- Create workflows that users can easily understand and follow.
- Make easy-to-use Design Navigation.
- Check the compatibility with Assistive Technology such as Screen Readers.
- Create interactive elements that are easy to identify.
- Create designs for different viewport sizes.
- Perform cross-browser compatibility tests on the website regularly.
- Regularly audit your digital content, including websites, documents, and applications, to identify and address accessibility issues by performing WCAG Testing
- Run usability tests with users across the disability spectrum.
- Create VPAT reports and track Web Accessibility conformance regularly.
Here’s a handy 508 compliance checklist that can help you check web accessibility standards are duly followed to make the website 508 compliant:
- Insert alternative text tag on visual assets.
- Use headlines and descriptions in a clear hierarchy with well-defined structure.
- Use sufficient color contrast to make content perceivable.
- Keep text font and size easy to view.
- Ensure Hyperlinks in documents have descriptive text.
- Accommodate keyboard navigation.
- Add subtitles and captions to videos.
- Avoid seizures due to photosensitivity by avoiding any flashing lights or blinking bright elements on the website.
- Use clear labels in form elements, along with proper instructions for a better understanding.
- Use pop-ups and alerts to help users avoid mistakes.
- Make it easy to correct mistakes if they occur using options like Back and Edit.
- Use concise language in text content for easy understanding.
- Ensure the website is compatible with screen readers and other assistive technologies.
Why Choose BrowserStack for Accessibility Testing?
Ensuring digital accessibility is not just a matter of ethics, it’s a legal and business imperative. Non-compliance with accessibility standards such as WCAG, ADA, or Section 508 can exclude users with disabilities and expose organizations to significant legal risks.
BrowserStack Accessibility Testing helps teams detect and resolve accessibility issues early in the development process, before they escalate. With support for WCAG 2.1/2.2, ADA, EAA, AODA, and more than 10 global accessibility standards, it enables proactive compliance across a wide range of digital environments.
Powered by its advanced Spectra Rule Engine, the platform identifies significantly more accessibility gaps than traditional tools. Combined with rapid, automated workflow scans, it supports fast-paced development and continuous integration without compromising on accessibility rigor.
Key Benefits
- Extensive Device Coverage: Tests run on over 3500+ real browsers and devices, not just Chrome or emulators, ensuring true cross-platform accessibility.
- CI/CD Integration: Seamlessly fits into development pipelines, allowing teams to perform shift left testing and catch issues early.
- Real Screen Reader Testing: Supports real-world testing with assistive technologies like NVDA, JAWS, and VoiceOver.
- AI-Powered Insights: Leverages BrowserStack AI to highlight patterns, prioritize issues, and streamline large-scale audits.
- Collaborative Reporting: Offers a centralized dashboard for managing logs, sharing test results, and maintaining team alignment with role-based access.
- Compliance Coverage: Supports ADA, Section 508, WCAG 2.1/2.2, AODA, and more, ensuring global readiness.
- No Overlays or Shortcuts: Focuses on genuine accessibility improvements rather than superficial UI fixes.
- Trusted by Industry Leaders: Integrated into the broader BrowserStack QA ecosystem, used by over 50,000 teams globally.
Core Features of BrowserStack Accessibility Testing
BrowserStack is designed not only to check for compliance but also to support remediation, collaboration, and inclusive design practices:
- Automated Accessibility Tests: Perform high-speed, accurate scans on live devices and browsers to detect WCAG violations.
- Assisted Tests: Use guided workflows to uncover issues like keyboard traps, improper focus management, or dynamic content updates.
- Workflow Analyzer: Analyze entire user flows, such as account creation or checkout, to ensure accessibility at every step.
- Real Screen Readers: Test with actual assistive technologies to validate user experience for individuals relying on screen readers.
- Central Reporting Dashboard: Monitor issues across pages, track team progress, and generate compliance documentation with ease.
- Accessibility Design Toolkit: Enables designers to test contrast, font size, and interactive components early in the design phase, supporting accessibility from the ground up.
- BrowserStack AI for Accessibility: Automatically groups related issues and recommends remediation steps to help teams resolve problems faster.
Conclusion
508 compliance ensures that federal electronic and information technology is accessible to all. It ensures all-inclusion and clearly specifies the requirements of web accessibility for all electronic content, including websites, software applications, and hardware.
To follow 508 compliance, WCAG 2.0 should be conformed to. WCAG has set a detailed framework to test accessibility with its 4 Principles and Guidelines. It ensures that the website has an all-inclusive design.
By running Accessibility Tests based on the WCAG you can check 508 compliance for the website and follow all the guidelines to deliver electronic content that is accessible to all.