What is WCAG Compliance?
What is WCAG Compliance?
WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) is a set of guidelines that are formulated by the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI) of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). It ensures that the web content is accessible to all, including people with disabilities.
WCAG covers a wide spectrum of disabilities under its guidelines, such as visual, auditory sensory, speech, physical, cognitive, linguistic, learning, and neurological disabilities.
There are three different versions of WCAG compliance in popular use:
- WCAG 2.0
- WCAG 2.1
- WCAG 2.2
- WCAG 3.0 (development in-progress).
Why is WCAG Compliance important?
An Accessibility audit of Fortune 100 corporate websites identified 815,600 WCAG 2.1 accessibility issues, out of which, the majority were Level A issues. This shows that Fortune 100 companies are failing to meet basic criteria for accessibility compliance. This apart, 90% of websites are inaccessible to people with disabilities relying on assistive technology.
This indicates how WCAG testing is essential. Web Accessibility not only holds moral responsibility, but it also holds business implications.
Web Accessibility helps businesses to:
- Target Larger Audience
- Increase Awareness and Avoiding Legal Ramifications
- Enhance Brand Recognition
Target Larger Audience
Did you know an estimated 1.3 billion people – or 1 in 6 people worldwide – experience significant disability as per WHO.
WCAG helps target a larger audience who otherwise would not be able to consume the web content due to one or the other disability. Gartner suggests that, digital products that fully conform to WCAG 2.0 compliance are expected to outperform their market competitors by 50%.
The Digital Accessibility Software Market was estimated at $0.80 billion in 2025. This market is projected to grow to $1.08 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.31% during the forecast period.
Increase Awareness and Avoid Legal Ramifications
More than ever, there is a pressing need for an increased sense of awareness towards web accessibility with assistive tools in the market. In 2024, over 4,000 digital accessibility lawsuits were filed in the US, with rising cases in states like New York and California. This upward trend is expected to continue, especially with the European Accessibility Act taking effect on June 28, 2025.
Enhance Brand Recognition
Demonstrating a commitment to WCAG compliance reflects an inclusive approach, ensuring that individuals with disabilities can access and engage with your digital content. This inclusivity contributes to a positive brand image and showcases a commitment to diversity.
Being WCAG compliant is a good way to avoid Lawsuits and ensure business growth with a larger target audience.
Who should follow WCAG Compliance
WCAG guidelines must be followed to have an accessibility compliance website by:
- Developers to build a website that considers easy access to all, fix the accessibility issues, and debug for any failing accessibility standards and criteria.
- QAs to test whether all the accessibility guidelines and criteria are successfully met by thoroughly testing the application against the success criteria prescribed by WCAG.
- UX Designers for creating an all-inclusive interface design that is accessible and usable by as many people as possible, regardless of their age, ability, or status.
- Product Managers evaluate accessibility pre-requisites, verify accessibility with ease, and access WCAG-mapped issues to create VPAT reports and monitor them.
4 Key Principles of WCAG Compliance
WCAG compliance is based on the 4 Key Principles:
- P- Perceivable
- O- Operable
- U- Understandable
- R- Robust
Perceivable
Users should be able to perceive the information mentioned on the website. It should be presented in a format which can be easily read/ processed by the reader. The website should have text that is clearly visible to the users with issues such as:
- Visually impairment: The website content must be consumable by screen readers and assistive technologies meant for the visually impaired.
- Color-blindness: Ensure a good contrast between the foreground and background of the website for better readability of the content.
- Hearing impairment: Add text/subtitles for every audio/video to help them consume the content easily.
Operable
Websites should be easy to use, irrespective of disabilities. Components of the UI should be designed in a way that they can be operated with ease.
- Users with motor disabilities might have issues using the mouse, so alternative options for the keyboard should be provided.
- For people with cognitive disabilities, animations and media should be controllable, and time limits for completing an action should be generous.
- Options to cancel, go back, alerts and warnings should be available to make sure people make fewer mistakes and operate with ease.
- Any time-bound activities should be designed in a way so that persons with cognitive disabilities can operate it.
Understandable
Although users might successfully perceive or operate the website, they might still not be able to understand its context. A website should have content that can be understood easily. For users to easily comprehend, content should be presented using concise and clear language.
A clear set of instructions/guidelines should be available to help users perform actions. The connection between the action and the result should be clear and obvious.
This can be done using meaningful and logical workflows that are clearly indicated by well-marked navigation. Usability must be well taken into consideration, such as:
- If a user must go through a critical process like a checkout — adequate guidance should be provided.
- Forms should nudge users to provide the relevant information using clear labels.
Robust
With multiple options available, users are free to choose their own agent such as browser, OS, platforms, and devices to access a website. Any website which restricts the user to a specific technology does not conform to accessibility standards.
A website should be compatible with different agents including assistive technologies like screen readers. This would help all users get a consistent user experience irrespective of which set of technologies and agents they use to access the content on the website.
WCAG Guidelines
WCAG 2.0 has 12 guidelines classified under the 4 key Principles (POUR) discussed above. Each of these guidelines has success criteria defined under them based on the conformance levels. On the other hand, WCAG 2.1 is backward compatible with WCAG 2.0, with 1 additional guideline mentioned below:
| 1. | Perceivable | |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Text Alternatives | Provide Text Alternatives to different non-text content forms so that it can be used by assistive technology such as screen readers, braille, large print, symbols, or easy language. |
| 1.2 | Time-based Media | Provide Captions, alternatives or audio descriptions for pre-recorded and live time-based media such as audio or video. |
| 1.3 | Adaptable | Create content that is adaptable to different forms without losing out on the information or its structure. |
| 1.4 | Distinguishable | Make content easier for the user to see and hear so that they can separate the foreground from the background. |
| 2. | Operable | |
| 2.1 | Keyboard Accessible | Make all the functionality of the website accessible from a keyboard without requiring specific timings for individual keystrokes. |
| 2.2 | Enough Time | Give enough time to the users to read and act on the content. |
| 2.3 | Seizures | Content design should not have anything that flashes more than 3 times to avoid causing seizures due to photosensitivity. |
| 2.4 | Navigable | Help users navigate through the workflows and webpages, find content, and determine where they are on the website. |
| 2.5 | Input Modalities (WCAG 2.1 & WCAG 2.2) | Make it easier for the users to operate functionalities using different inputs apart from the keyboard. |
| 3. | Understandable | |
| 3.1 | Readable | Create content that is readable and easy to understand using clear and simple language. |
| 3.2 | Predictable | Design content and pages in a predictable way, where users can easily predict how to operate. |
| 3.3 | Input Assistance | Help users provide correct information and correct mistakes through ways like clear instructions and error prevention techniques. |
| 4. | Robust | |
| 4.1 | Compatible | Create a website with maximum compatibility with the current and future user agents such as browsers, devices, and platforms, including assistive technologies. |
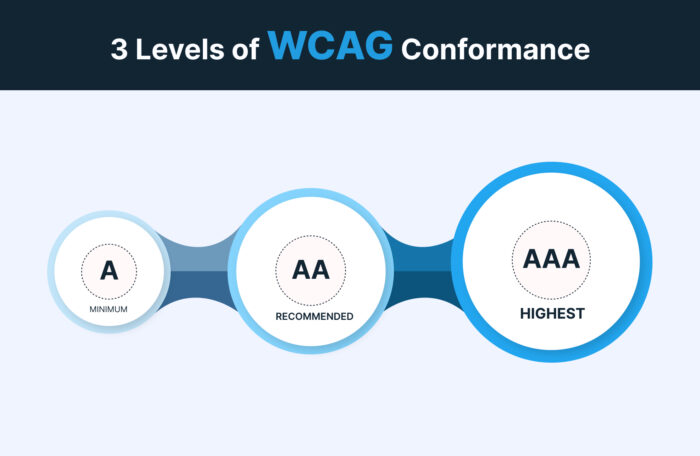
WCAG Conformance Levels
WCAG has three conformance levels as given below:
- A is the minimum level of conformance. It is designed to ensure that web content is accessible to most users with disabilities.
- AA is a higher level of conformance than Level A. It is designed to ensure that web content is accessible to a broader range of users with disabilities, including those with more severe disabilities.
- AAA is the highest level of conformance. It is designed to ensure that web content is accessible to all users, regardless of disability.
How to perform WCAG Testing using BrowserStack Accessibility Testing?
BrowserStack Accessibility Testing is a single platform to identify basic and complex accessibility issues at blazing speed. It is a one-Stop Solution to
- Test,
- Report, and
- Monitor Web Accessibility Health.
Test Web Accessibility for WCAG Compliance
You can perform WCAG Testing for your website using BrowserStack Accessibility Testing Tool. It provides core features to:
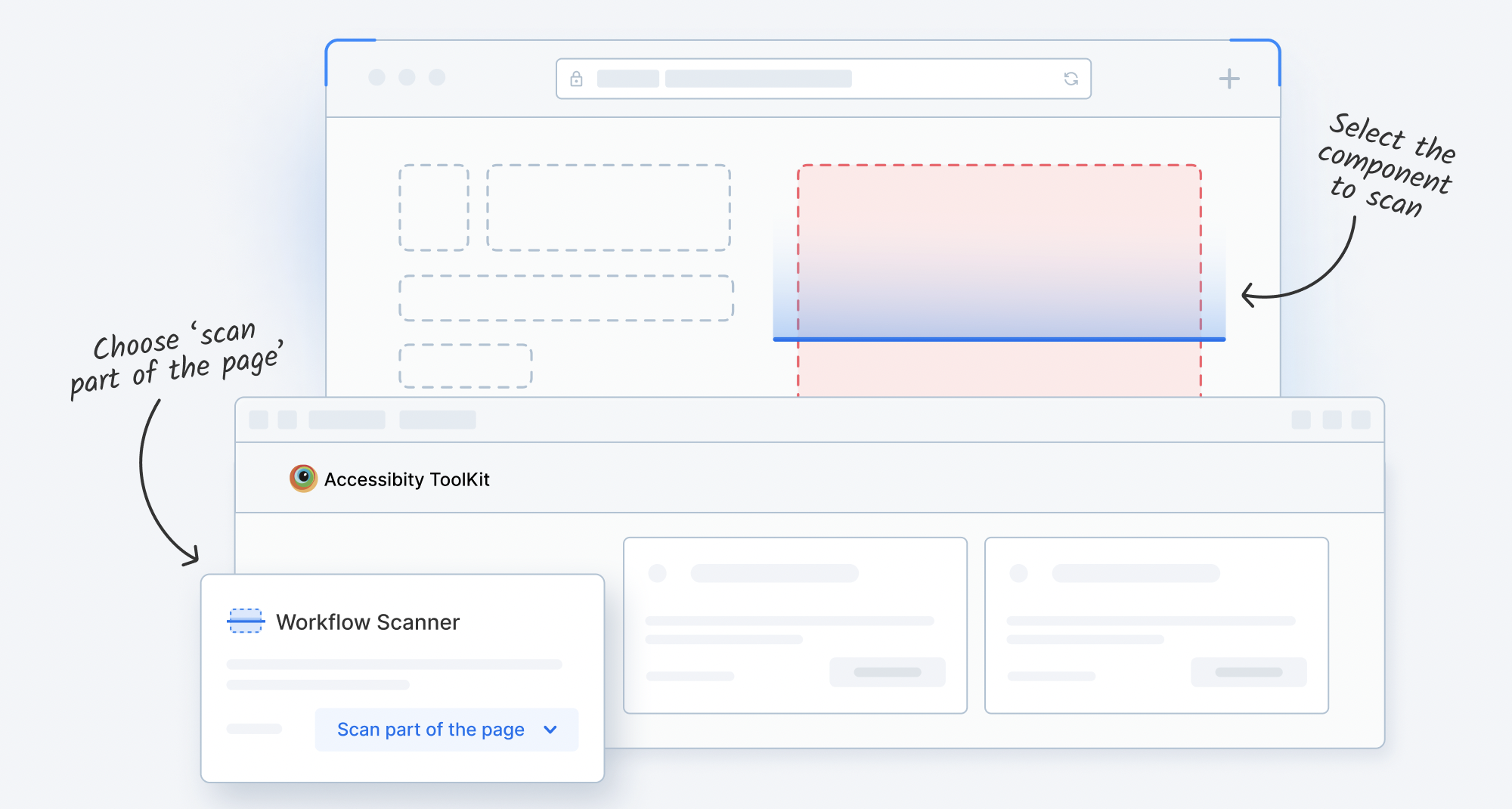
- Test any user workflow in a single scan using Workflow Scanner
- Identify complex accessibility issues by answering simple, auto-generated questions using Assisted Tests
- Precisely locate issue sources using Screen Readers on Real Devices
You can run Workflow Scanner to Scan user flows across full page scan or test part of a page for accessibility. Use the Workflow scanner to automatically identify and report basic issues such as missing alt text, insufficient color contrast, among others at blazing speed.
Try BrowserStack Accessibility Testing
It allows you to choose the required WCAG versions and its conformance level, for example, WCAG 2.0 AA. Upon running the scanner it highlights all the Web Accessibility Issues along with its details.
Report Web Accessibility Issues for WCAG Compliance
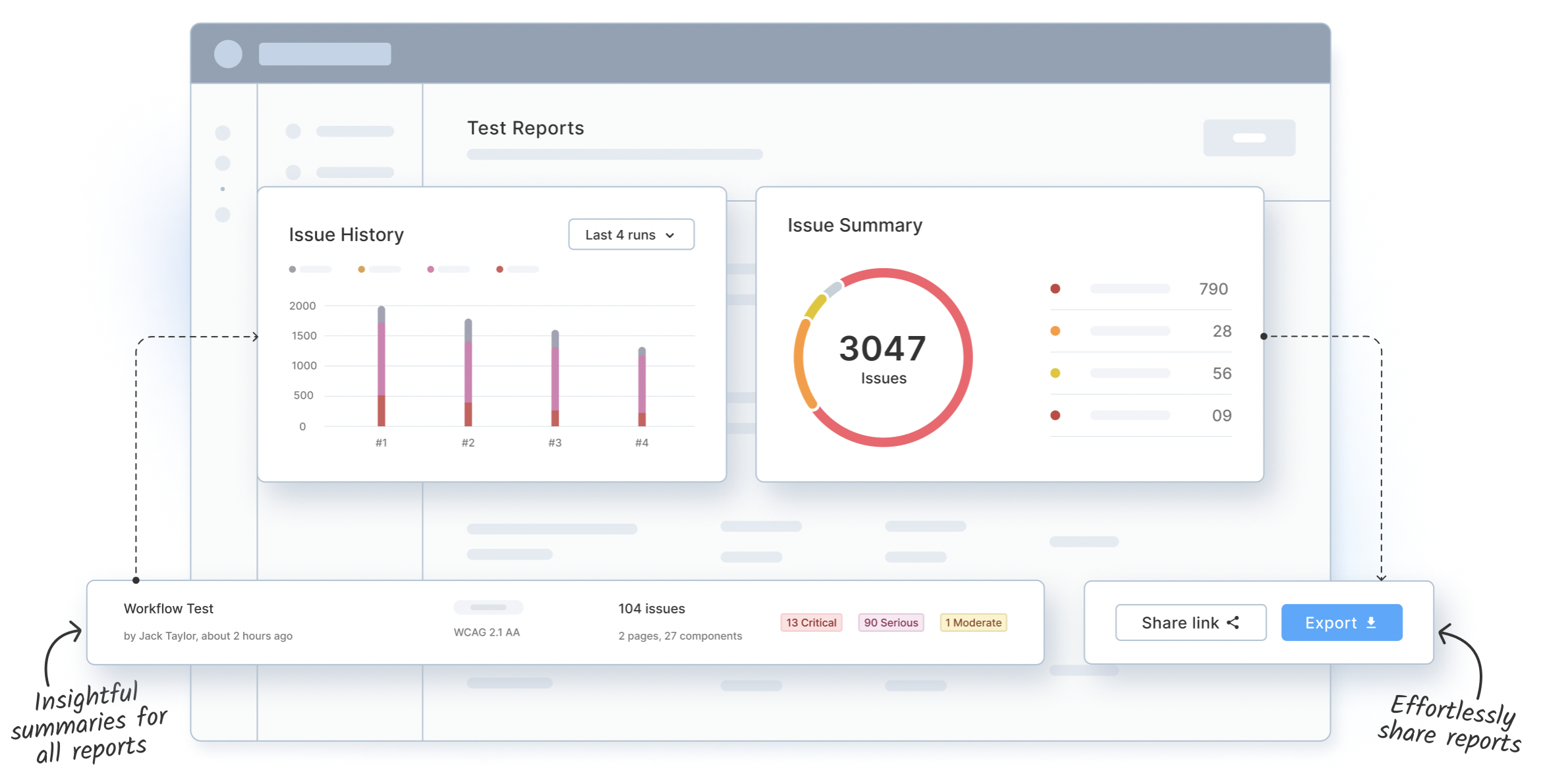
BrowserStack Accessibility Testing Tool provides you access to all reports from the past and present on one single dashboard. Combine multiple reports into one in seconds, and use insightful issue summaries to better inform debugging.
You can get details on Issue Summary and Workflow Log Reports within the dashboard. All reports contain issues that are grouped on the basis of violating WCAG guidelines. It enables easier VPAT report creation.
You can also select multiple reports to create a consolidated report that can be shared or exported as a CSV file.
Learn More about Accessibility Testing
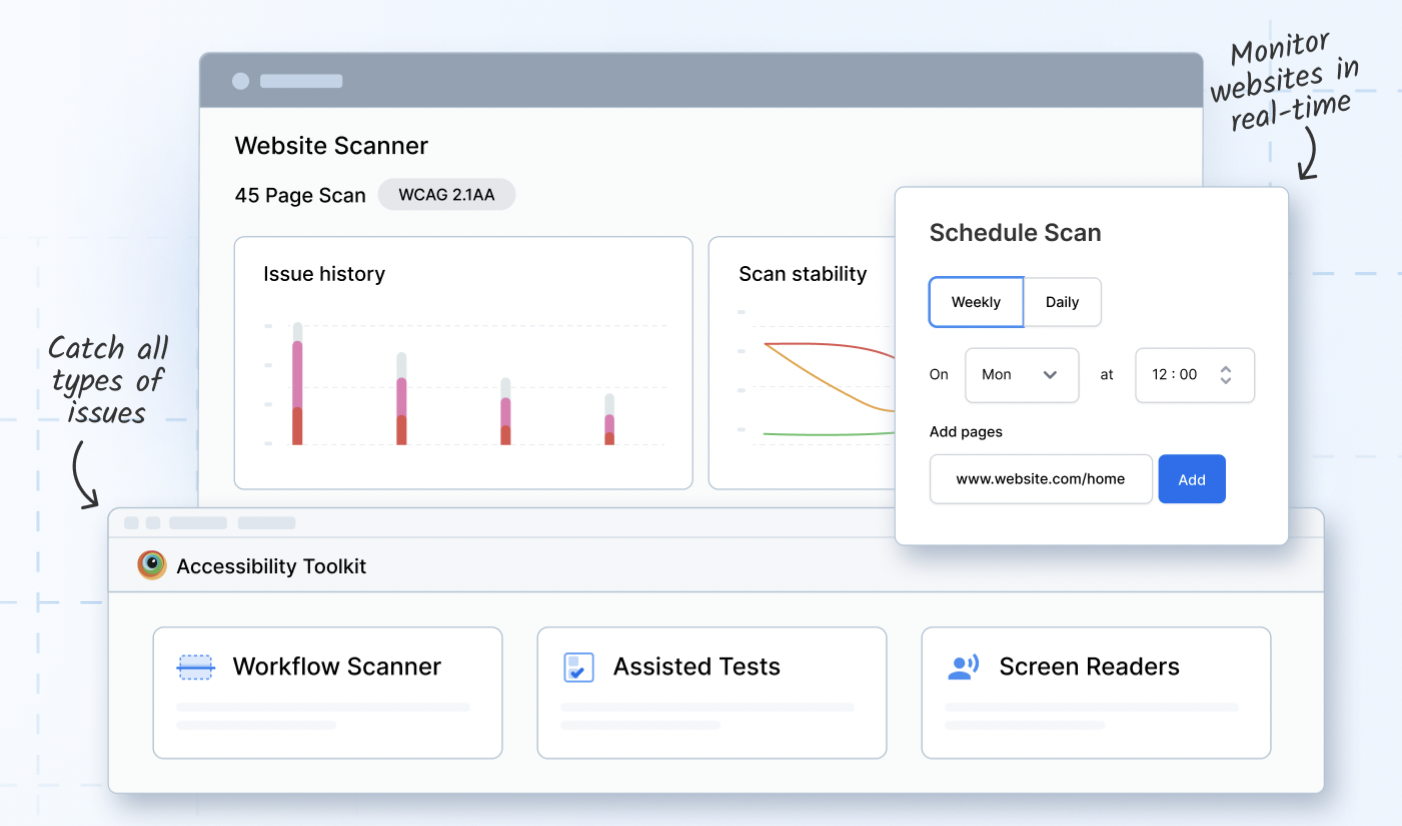
Monitor Web Accessibility for WCAG Compliance
It also allows you to schedule scans at regular intervals and get a detailed Accessibility report. Upon the completion of the workflow scan, you can get details on Issue Summary and Workflow Log Reports within the dashboard.
Schedule Website Scan for WCAG Compliance Now
Why use BrowserStack for WCAG Compliance Testing?
BrowserStack Accessibility stands out as a leading tool for WCAG compliance testing. Here are some of the reasons why it you must choose it for an accessibility compliance website:
- Automated Accessibility Testing at Scale: Run accessibility tests across a wide array of real browsers and devices to save time and reduce manual effort.
- Comprehensive Insights: Go beyond basic WCAG checks to uncover deeper accessibility barriers, including screen reader support and keyboard navigation issues.
- Flexible WCAG Standards: Select from WCAG 2.0, 2.1, or 2.2 to align with your specific compliance goals.
- Conformance Detection: Quickly pinpoint violations against the compliance level your organization requires.
- Real Device Screen Readers: Test with built-in screen readers like VoiceOver (Mac), NVDA (Windows), and TalkBack (Android) on actual devices.
- AI-Driven Prioritization: Use BrowserStack’s AI to intelligently surface high-impact issues and suggest actionable fixes.
- Faster, Smarter Scanning: The Spectra™ Rule Engine identifies more issues with higher speed and accuracy than traditional tools—without slowing development.
- Centralized Reporting & Monitoring: Track accessibility issues across pages, projects, and teams with a centralized dashboard, while scheduling automated scans for ongoing WCAG compliance.
- Design for Accessibility: Utilize the Accessibility Design Toolkit to validate color contrast, typography, and component choices during the design phase, ensuring accessible experiences from the start.
- Assisted Testing: Access guided manual testing workflows to catch complex issues that automation might miss, such as focus states and keyboard traps.
- Automated Monitoring: Use the Website Scanner to schedule recurring scans, monitor WCAG adherence, and receive intelligent reports for ongoing compliance.
Best Practices for WCAG Testing
Some of the key best practices to follow while performing WCAG Testing are:
- Use a checklist to keep track of WCAG Compliance
- Order your content properly using HTML Markup
- Create workflows that are easy to understand and follow
- Design Navigation that is easy to use
- Make interactive elements easy to identify
- Create designs considering different viewport sizes
- Test for cross-browser compatibility
- Use Automation tools to check Accessibility regularly
- Run usability tests with users across the disability spectrum
- Create VPAT reports regularly for Accessibility conformance
WCAG Compliance Checklist
Here’s a handy checklist that can help you follow WCAG Compliance:
- Insert alternative text tag on visual assets.
- Add contrasting colors.
- Accommodate keyboard navigation.
- Resize text to be viewable.
- Interactive elements should be operable.
- Improvise with headlines and descriptions.
- Creating a clear heading hierarchy.
- Add subtitles and captions to videos.
- Avoid flashing lights or blinking bright elements to avoid seizures due to photosensitivity.
- Add clear labels to forms for a better understanding.
- Website is compatible to screen readers.
- Allow users to control time limits on their interaction.
- Help users avoid mistakes using alert messages.
- Make it easy to correct mistakes that do occur.
- Use concise language for easy understanding.
- Website is compatible with current and future user agents (including assistive technologies).
How is WCAG perceived globally?
WCAG forms the baseline for the various Laws and Accessibility Compliances amended in different countries such as:
| Region | Laws / Compliances | Overview |
|---|---|---|
| USA | Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) | It requires public businesses and organizations to provide accessible digital content and services. ADA Testing includes websites, mobile apps, and other online platforms. |
| UK | Equality Act 2010 | It covers disability discrimination and requires online service providers to make reasonable adjustments to ensure accessibility. |
| EU | European Union Web Accessibility Directive | The directive mandates that every website and app in the public sector must have an accessibility statement. It also requires the implementation of a feedback mechanism, which allows users to bring accessibility issues to the attention of website administrators or request access to inaccessible content. |
| Canada | Accessibility for Ontarians with Disabilities Act (AODA) | This is a provincial law in Ontario, Canada that aims to make the province accessible and prohibits discrimination on various grounds, including disability. As a result, government agencies and organizations providing services to the public must ensure their digital content is accessible. |
| Australia | Disability Discrimination Act (DDA) | The DDA requires that public and private sector organizations provide equal access to goods, services, and facilities, including digital content, to individuals with disabilities. |
| India | Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act (RPwD Act) | This mandates that the government, private organizations, and educational institutions make electronic and information technology accessible to people with disabilities. |
Conclusion
WCAG compliance plays a key role in ensuring web accessibility. Through its 4 Principles and Guidelines, it has set a detailed framework to test accessibility and ensure that the website has an all-inclusive design.
By running WCAG Tests, you can keep a check on web accessibility using WCAG compliance and follow all the guidelines to deliver web content that is easily accessible to all.