What is ADA Testing?
What is ADA Testing?
ADA testing checks whether a website, application or other digital content complies with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) regulations, which aim to ensure equal access to information and services for people with disabilities.
To check if ADA compliance is successfully met, ADA testing typically involves evaluating various aspects such as:
- Keyboard accessibility
- Screen reader compatibility
- Alternative text for images
- Color contrast
- ARIA Tags
- Compatibility with Assistive Technologies to improve usability for individuals with disabilities.
This often involves using assistive technologies, automated testing tools, and manual inspection to identify and address any accessibility barriers.
The goal is to ensure equal access to information and services for all users, regardless of their abilities.
ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990) is a civil rights law in the US that prohibits discrimination based on disability. It advocates inclusiveness by ensuring that people with disabilities have equal access to various aspects of public life, including employment, public services, public accommodations and telecommunications.
ADA testing is typically conducted through a combination of:
- Automated tools,
- Manual inspection, and
- User testing.
Different Techniques of ADA Testing
Here’s a brief overview of how ADA compliance is checked:
- Automated Testing using automated accessibility testing tools to scan the digital content for common accessibility issues, such as missing alternative text for images, improper use of headings, inadequate color contrast, and keyboard navigation issues.
- Manual Inspection of the digital content to identify accessibility barriers that may not be detected by automated tools. This involves ensuring interactive elements are accessible (and in the right order) via keyboard navigation.
- Assistive Technology Testing of screen readers, screen magnifiers, and voice recognition software to interact with the digital content from the perspective of users with disabilities. This helps identify any usability issues and ensures compatibility with assistive technologies.
- User Testing by users with disabilities to check the accessibility and usability of the digital content and provide feedback. This real-world testing helps uncover any accessibility challenges that may have been overlooked during automated and manual testing.
By employing these testing methods in combination, organizations can effectively assess ADA compliance and identify areas for improvement to ensure that their digital content is accessible to all users.
Why is ADA Compliance Testing important?
Did you know: 90% of websites are inaccessible to people with disabilities relying on assistive technology. Only 3% of the internet is fully accessible to people with disabilities.
ADA compliance testing is important because it ensurequirements for ADA res legal adherence, promotes inclusivity, enhances user experience, boosts reputation, and expands market reach by making digital content accessible to individuals with disabilities.
| Year | Number of ADA Lawsuits |
|---|---|
| 2018 | 10,163 |
| 2019 | 11,053 |
| 2020 | 10,982 |
| 2021 | 11,452 |
| 2022 | 8,694 |
| 2023 | 8,227 |
| 2024 | 8,800 |
ADA Testing helps businesses with,
- Larger Target Audience
- Avoiding Lawsuits and Penalties
- Establishing Brand Recognition
Larger Target Audience
Approximately 1.3 billion people, or around 16% of the global population, live with significant disabilities as of 2025. About 86% of people with disabilities in the EU and approximately 75% of Americans with disabilities use the internet daily.
This makes ADA compliance for web accessibility essential for websites to follow.
Avoiding Lawsuits and Penalties
Failure to comply with the ADA may lead to penalties that range from $55,000 to $150,000, as well as legal actions initiated by impacted individuals.
In 2024, over 4,000 lawsuits were filed in federal and state courts against organizations for inaccessible websites and mobile apps, highlighting the serious legal exposure of digital non-compliance.
By prioritizing ADA testing and early accessibility fixes, businesses can substantially reduce the risk of legal problems and uphold their commitment to inclusivity.
Establishing Brand Recognition
Accessibility efforts signal to users that your brand is trustworthy and values the needs of all its users. Consumers are increasingly valuing businesses that prioritize accessibility and inclusivity. Performing ADA Testing can enhance your brand’s image, fostering a positive perception among customers and the general public.
User Experience
Accessibility improvements made during ADA Testing often enhance the user experience for all users, not just those with disabilities. Optimizing digital content for accessibility can improve usability, navigation, and overall satisfaction for a broader range of users.
Comprehensive ADA Testing is a good way to avoid Lawsuits, ensure better user experience, enhance brand recognition and improve business growth with a larger target audience.
Who needs to perform ADA Testing?
ADA testing should ideally be conducted by various stakeholders involved in the development and maintenance of digital content, including:
- Web Developers for creating and coding websites, applications, and other digital content need to ensure that the products they produce meet ADA accessibility standards.
- Quality Assurance (QA) Teams for testing digital content for ADA compliance. They perform thorough checks to identify accessibility issues and ensure that the final product meets accessibility standards.
- UX/UI Designers create user interfaces that are intuitive and accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. They should consider accessibility principles during the design phase and collaborate with developers to implement accessible solutions.
- Content Creators, Writers, and editors need to ensure that text-based content, including articles, documents, and multimedia captions, is accessible to individuals with disabilities.
- Project Managers oversee the entire development process and ensure that ADA compliance is integrated into project requirements and timelines. They are responsible for prioritizing accessibility and allocating resources for ADA testing.
- Compliance Officers/Legal Advisors provide guidance on ADA regulations and ensure that digital content complies with relevant laws and standards to avoid any litigations.
What are WCAG requirements for ADA-compliant Website Test?
ADA Title III does not explicitly outline the specific requirements for ensuring website accessibility. Nevertheless, in cases related to ADA violations, U.S. courts commonly refer to the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.0 as the recommended standard that websites should follow.
WCAG compliance is used as a baseline criterion when performing ADA Testing.
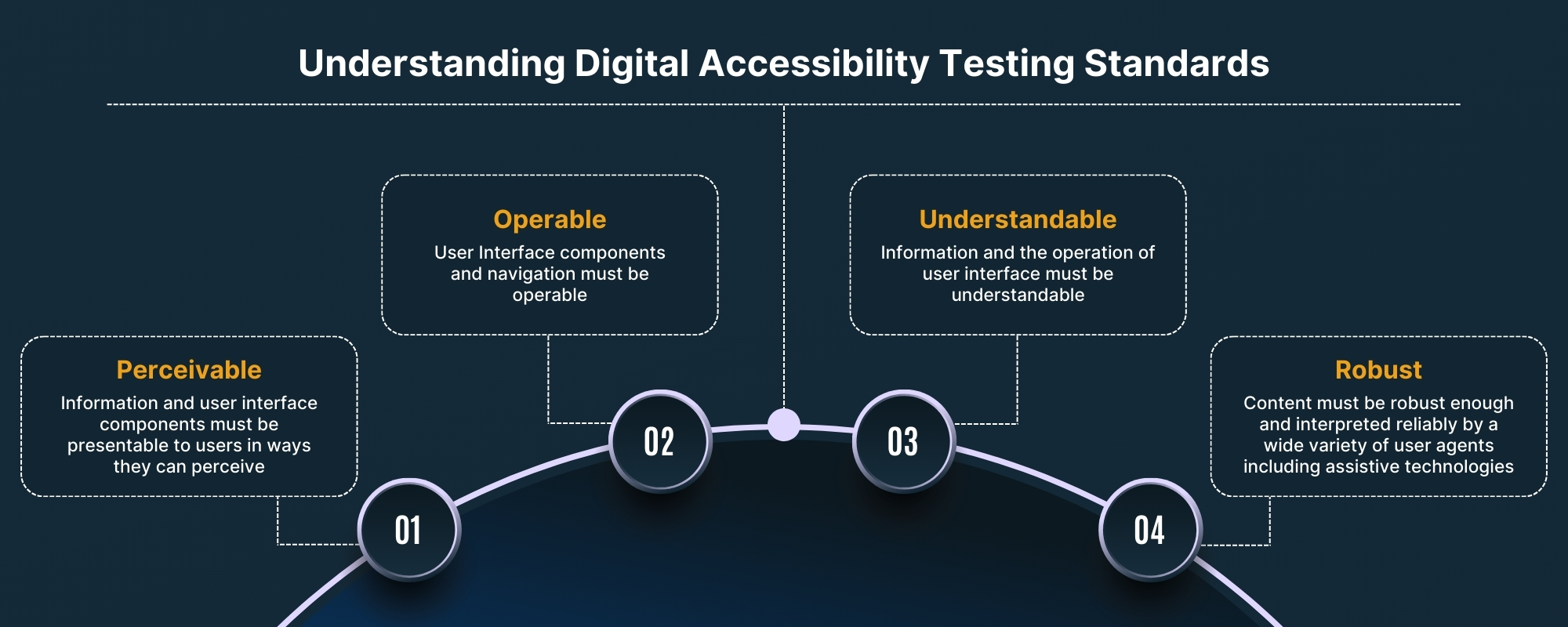
4 Key Principles of WCAG Compliance
WCAG compliance is based on the 4 Key Principles:
- P- Perceivable
- O- Operable
- U- Understandable
- R- Robust
1. Perceivable
- Provide text alternatives for non-text content (e.g., images, videos).
- Provide alternatives for time-based media.
- Create content that can be presented in different ways without losing meaning.
- Make it easier for users to see and hear content.
2. Operable
- Ensure that all functionality is available from a keyboard.
- Provide users enough time to read and use content.
- Do not use content that causes seizures.
- Help users navigate and find content.
3. Understandable
- Make text content readable and understandable.
- Make web pages appear and operate in predictable ways.
- Help users avoid and correct mistakes.
4. Robust
- Maximize compatibility with current and future user agents, including assistive technologies.
Read More to know about WCAG Compliance and Guidelines in detail
WCAG 2.0 has 12 guidelines classified under the 4 key Principles (POUR) discussed above. Each of these guidelines has success criteria defined under them based on the conformance levels. On the other hand, WCAG 2.1 is backward compatible with WCAG 2.0, with 1 additional guideline mentioned below:
| 1. | Perceivable | |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Text Alternatives | Provide Text Alternatives to different non-text content forms so that it can be used by assistive technology such as screen readers, braille, large print, symbols, or easy language. |
| 1.2 | Time-based Media | Provide Captions, alternatives or audio descriptions for pre-recorded and live time-based media such as audio or video. |
| 1.3 | Adaptable | Create content that is adaptable to different forms without losing out on the information or its structure. |
| 1.4 | Distinguishable | Make content easier for the user to see and hear so that they can separate the foreground from the background. |
| 2. | Operable | |
| 2.1 | Keyboard Accessible | Make all the functionality of the website accessible from a keyboard without requiring specific timings for individual keystrokes. |
| 2.2 | Enough Time | Give enough time to the users to read and act on the content. |
| 2.3 | Seizures | Content design should not have anything that flashes more than 3 times to avoid causing seizures due to photosensitivity. |
| 2.4 | Navigable | Help users navigate through the workflows and webpages, find content, and determine where they are on the website. |
| 2.5 | Input Modalities (WCAG 2.1 & WCAG 2.2) | Make it easier for the users to operate functionalities using different inputs apart from the keyboard. |
| 3. | Understandable | |
| 3.1 | Readable | Create content that is readable and easy to understand using clear and simple language. |
| 3.2 | Predictable | Design content and pages in a predictable way, where users can easily predict how to operate. |
| 3.3 | Input Assitance | Help users provide correct information and correct mistakes through ways like clear instructions and error prevention techniques. |
| 4. | Robust | |
| 4.1 | Compatible | Create a website with maximum compatibility with the current and future user agents such as browsers, devices, and platforms, including assistive technologies. |
To conduct ADA testing, you would evaluate the website against these principles and success criteria, ensuring that it meets the specified criteria for accessibility.
How to perform ADA Testing using BrowserStack Accessibility?
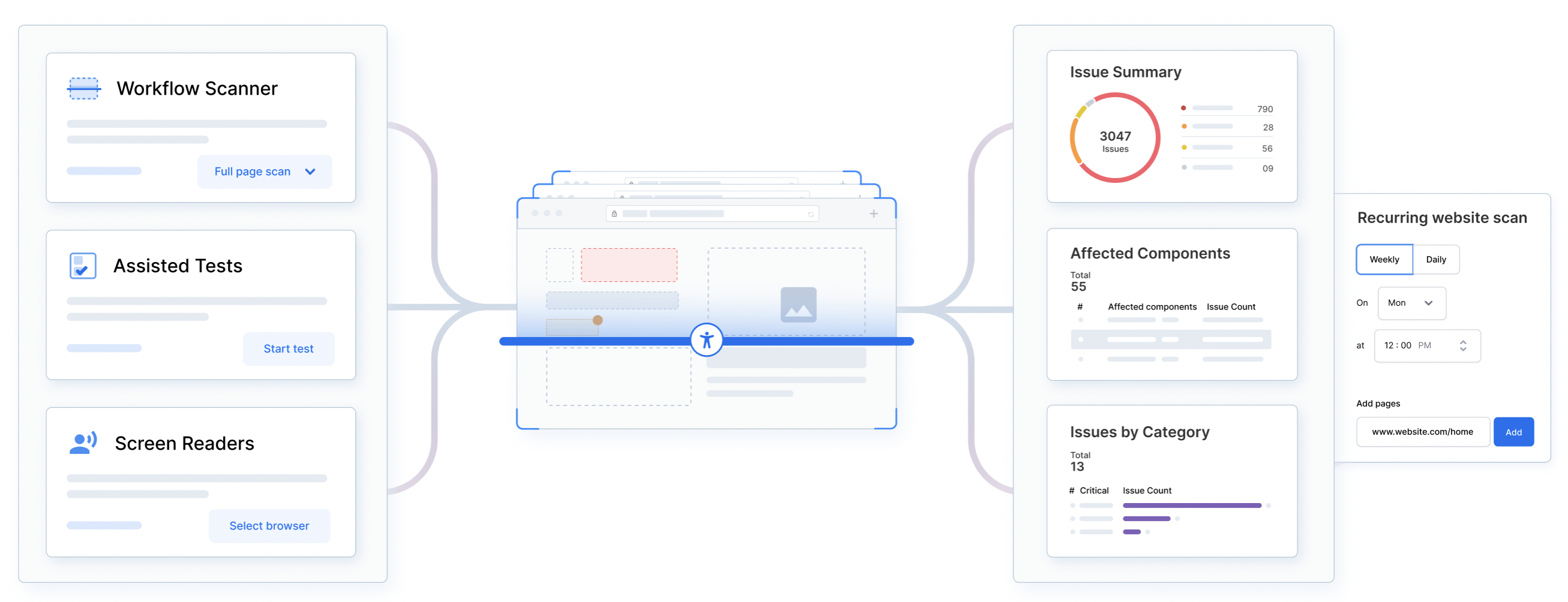
Performing ADA compliance testing using BrowserStack Accessibility involves the following steps:
- Sign up for BrowserStack
- Launch BrowserStack Accessibility Toolkit
- In the Workflow Scanner tile, choose the test scope, i.e. Full Page Scan or Part of the Page.
- Choose the required WCAG versions and its conformance level, for example, WCAG 2.0 AA.
- It scans the website as per the scope to detect any accessibility issues and presents it in the Issue Summary and Workflow Log.
- Click Save report to save a report of the detected issues. Click Share link to copy the Accessibility Dashboard link to the report. To download the report in CSV format, click Export.
Why prefer BrowserStack Accessibility Testing as an ADA Testing tool?
If your website or app isn’t accessible, you risk excluding users and facing legal consequences. This is why standards like WCAG, ADA, and Section 508 are essential.
BrowserStack Accessibility Testing supports global compliance and helps teams catch and fix issues early, before they affect users or lead to lawsuits. Here is why you must choose BrowserStack for ADA compliance testing:
- Real-Device Coverage: Run tests across 3,500+ real browsers and devices—not just Chrome or simulators.
- Automated Accessibility Tests: Quickly identify WCAG violations with high-speed, reliable tests on real browsers and devices—ensuring compliance right at the code level.
- Workflow Analyzer: Evaluate complete user journeys—like sign-ups and checkouts—to ensure accessibility across dynamic, multi-step experiences, not just static screens.
- CI/CD Integration: Built for shift-left testing with support for Appium, Espresso, and XCUITest.
- AI-Powered Fix Suggestions: BrowserStack AI for Accessibility flags patterns, prioritizes issues, and suggests fixes at scale.
- Spectra™ Rule Engine: Detects edge cases that other tools miss.
- End-to-End Journey Testing: Analyze multi-step flows like sign-ups, checkouts, and navigation—not just static pages.
- Screen Reader Testing: Validate with real screen readers like NVDA and JAWS on real devices.
- Assisted Testing: Catch complex issues like keyboard traps and focus problems with guided testing.
- Centralized Dashboard: Track, manage, and collaborate across teams with unified reporting and role-based access.
- Accessibility by Design: Validate contrast, typography, and components early with the Accessibility Design Toolkit.
- Part of a Trusted Ecosystem: Used by 50,000+ teams worldwide for high-impact, high-scale testing.
Try ADA Testing with BrowserStack Accessibility
Best Practices for ADA Testing
Here are some best practices for conducting ADA testing efficiently:
- Familiarize with ADA Guidelines and WCAG standards.
- Use automated tools for quick issue identification.
- Conduct manual inspections for nuanced accessibility issues.
- Test across diverse devices and browsers.
- Involve users with disabilities for insights.
- Document findings for efficient issue resolution.
- Regularly monitor and update accessibility.
- Provide training on accessibility best practices.
- Seek expert guidance for a thorough evaluation.
- Stay informed about evolving accessibility standards.
- Create workflows that are easy to understand and follow
- Design Navigation that is easy to use
Why choose BrowserStack for ADA Testing?
BrowserStack Accessibility Testing is a robust solution designed to help teams ensure their websites and applications are fully accessible, meeting compliance standards such as ADA, WCAG 2.1/2.2, Section 508, and AODA.
The tool integrates seamlessly into your CI/CD workflows, enabling real-time accessibility testing on over 3,500 real devices and browsers, ensuring a true user-centric experience.
Here are the reasons why you must choose BrowserStack for ADA Testing:
- Comprehensive Compliance Coverage: Supports ADA, WCAG, Section 508, AODA, and other global accessibility standards, ensuring your site meets legal and user needs.
- Real Device Testing: Tests on 3,500+ real devices and browsers for authentic user experiences beyond simulators.
- Faster, Smarter Testing: BrowserStack’s exclusive Spectra engine identifies 66% more issues and runs tests 8X faster, speeding up your development cycles.
- True Screen Reader Testing: Utilizes real screen readers like NVDA and JAWS, ensuring accessibility testing reflects real-world use.
- Seamless CI/CD Integration: Automates accessibility checks early in the development process, preventing costly issues later.
- AI-Driven Insights: BrowserStack’s AI features for accessibility helps prioritize and group issues for quick resolution, focusing on high-impact problems first.
- Visual Issue Detection: Provides contextual guidance to help you quickly address accessibility issues with ease.
- Collaborative Workflows: Enables team collaboration with role-based access, test logs, and reports for better tracking and remediation.
- True Accessibility Focus: Focuses on genuine accessibility, not just quick fixes or UI overlays.
- Design-First Tools: BrowserStack’s Accessibility Design Toolkit is built into your Figma designs with features like color contrast and component validation.
- Easy monitoring: Ensure ongoing WCAG compliance and remain audit-ready with the Website Scanner. Easily configure URLs for testing, schedule scans in advance, and receive auto-generated, insightful reports.
Conclusion
ADA testing is essential for ensuring the accessibility of digital content to all users, regardless of abilities. Adhering to ADA guidelines and utilizing tools like BrowserStack Accessibility Testing are crucial. Similarly, WCAG compliance is integral, offering a detailed framework to test accessibility.
By prioritizing accessibility and continuous improvement, businesses can meet legal requirements, enhance reputation, and create an inclusive online environment for all users.