An integration test with Cypress checks how multiple parts of an application (like components, services, or APIs) work together. It ensures that connected features behave as expected in a real browser environment.
Learn how to execute integration tests in Cypress and how tools like BrowserStack can enhance your Cypress testing efforts.
What is an Integration Test?
In integration testing, the individual parts tested in the unit testing phase are combined in a sophisticated way to form a single module of an interconnected and integrated part of the application. This module is then tested for the interconnectivity of the separated components. Integration testing tests the functionality of the small systems made up of the application’s unit-tested components and their interconnectivity.
What is Cypress?
Cypress framework is a testing tool that facilitates JS and browser-based testing. With Cypress, the testers can directly manipulate the DOM, as the Cypress test can access the browser directly.
How is Cypress used in Integration Testing?
When using Cypress to do the integration testing, there are two main keywords to be considered. ‘describe’ and ‘ít’ keywords will be the main structure for the test flow of the integration test.
- The ‘describe’ keyword usually defines a test suite, while ‘it’ defines a single test case.
- So the testing module for the integration test can be considered a testing suite and mentioned under describe keyword.
- In contrast, all the testing scenarios under that module can be mentioned and written under it keywords under the describe blocks so that the describes can be run to execute the integration tests.
With Cypress’s powerful and convenient structure, we can always boost up the process of integration testing while following a few basic norms:
- The first one will be writing short and simple test scenarios.
- Even though the test is moduled, it is better to use simpler scenarios rather than complex and long scenarios as they can be hard to execute, and bug localization will also be hard, sometimes impossible.
- Another uses descriptive test names, as it helps greatly in bug localization and in threat assessment in various degrees.
- So by adhering to these basic norms, the Cypress integration tests can be easily and conveniently executed with the optimum results output.
Must-Read: Cypress Best Practices for Test Automation
Planning your Integration Test
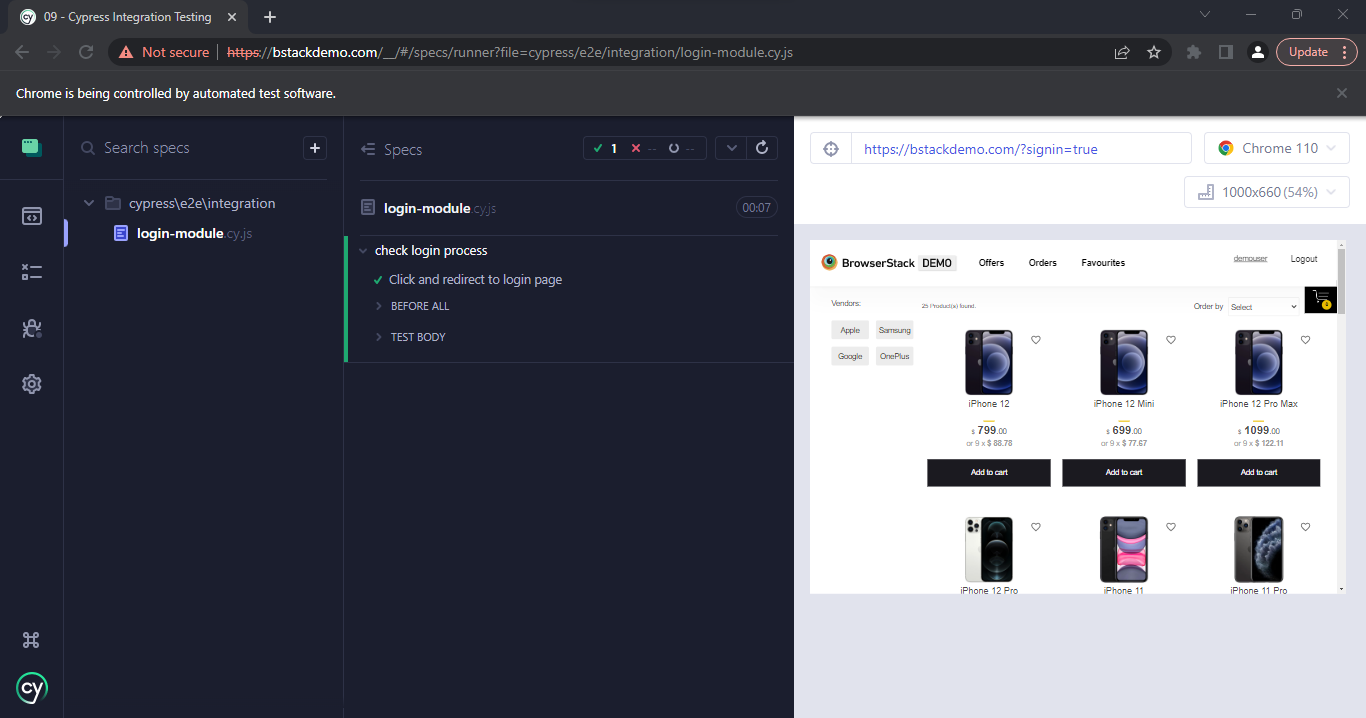
As part of the integration testing, a test scenario needs to be planned. As an example, the login module of the demo site is to be tested.
So for this scenario, 3 main test cases will be used.
- The tester is directed to the site, and the home page is loaded.
- When clicked in the login button tester is redirected to the login page.
- The user is redirected to the home page with the logged-in status when the correct credentials are entered.
Example Codebase
/// <reference types="cypress" />
//The login module is tested under the "check login process" test suite
describe('check login process', () => {
//First test case - direct to the site under test
before('Visit the demo site',() => {
cy.visit('https://bstackdemo.com/');
})
//Second test case - click on the login
it('Click and redirect to login page', () => {
cy.get('#signin').click();
//Third test case - user is logged on and redirected to home page
cy.get("#username").click();
cy.xpath("//div[text()='demouser']").click();
cy.get("#password").click();
cy.xpath("//div[text()='testingisfun99']").click();
cy.get("#login-btn").click();
})
})Code Base for the Test
The codebase for the above example can be found here
Do note that to get the most out of integration testing, teams must always perform tests on multiple real devices, platforms, and OS combinations.
Accuracy and comprehensive identification of all possible bugs are possible only in real user conditions, and that is where you can opt for BrowserStack for Cypress testing.
Why Use BrowserStack to Run Cypress Tests
BrowserStack is a cloud-based testing platform that lets you run Cypress tests efficiently across multiple device-OS-browser combinations. Here are a few reasons why you should choose BrowserStack:
- Cross-browser testing: Cypress runs on limited browsers, mainly Chrome-based ones. BrowserStack helps you expand your Cypress tests to many other browsers, such as Safari, Edge, IE, and more.
- Video Recording: The ability to record videos of test execution is a significant benefit of using BrowserStack to execute Cypress tests.
- Cloud Infrastructure: This cloud-based platform does not require setting up or maintaining browsers or physical devices locally.
- Parallel Testing: With parallel testing, you can run multiple Cypress tests concurrently, speeding up test execution and eventually the release cycles.
- Real-device testing: BrowserStack offers you a vast real-device cloud, letting you run Cypress tests on 3500+ real device, browser, and OS combinations, thus allowing you to test under real user conditions.
- Integrations: BrowserStack offers seamless integrations with several CI/CD tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, Circle CI, Bamboo and more.
- Scalability: BrowserStack supports real-device and parallel testing on a cloud-based infrastructure, enabling you to run hundreds of Cypress tests across different environments.
Conclusion
Integration testing with Cypress ensures that different components of your application work seamlessly together. Its fast, browser-based execution and intuitive syntax make it ideal for modern web apps.
Tools like BrowserStack further enhance this by allowing Cypress tests to run across real browsers and devices, helping teams ensure cross-platform consistency and catch environment-specific bugs early.
Useful Resources for Cypress
Understanding Cypress
- Cross Browser Testing with Cypress : Tutorial
- Run Cypress tests in parallel without Dashboard: Tutorial
- Handling Test Failures in Cypress A Comprehensive Guide
- Cypress Test Runner: Tutorial
- Handling Touch and Mouse events using Cypress
- Cypress Automation Tutorial
- CSS Selectors in Cypress
- Performance Testing with Cypress: A detailed Guide
- Cypress Best Practices for Test Automation
- Test React Native Apps with Cypress
- Cypress E2E Angular Testing: Advanced Tutorial
- Cypress Locators : How to find HTML elements
- Maximizing Web Security with Cypress: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Conditional Testing in Cypress: Tutorial
- Cypress Web Testing Framework: Getting Started
- Cypress Disable Test: How to use Skip and Only in Cypress
- What’s new in Cypress 10? How it will change your current testing requirements
Use Cases
- How to Record Cypress Tests? (Detailed Guide)
- How to run your first Visual Test with Cypress
- How to Fill and Submit Forms in Cypress
- How to Automate Localization Testing using Cypress
- How to run Cypress Tests in Chrome and Edge
- How to use Cypress App Actions?
- How to Run Cypress Tests for your Create-React-App Application
- How to Run Cypress Tests in Parallel
- How to handle Click Events in Cypress
- How to Test React using Cypress
- How to Perform Visual Testing for Components in Cypress
- How to run UI tests in Cypress
- How to test redirect with Cypress
- How to Perform Screenshot Testing in Cypress
- How to write Test Case in Cypress: (with testing example)
Tool Comparisons