Test logging is a critical part of the Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC). A test log records every detail of test execution—results, environment, defects, and root cause analysis (RCA)—to support reporting, traceability, and collaboration.
Overview
What is a Test Log?
- A chronological record of test case execution, environment details, and outcomes.
- Helps QAs diagnose failures and verify software quality standards.
Importance of Test Logs in the Testing Process
- Ensures traceability of testing activities across iterations.
- Aids defect tracking with severity and priority.
- Acts as an audit trail for compliance-heavy industries.
- Promotes collaboration and transparency across teams.
Core Components Included in a Test Log File
- Unique test case ID and description.
- Test environment details and input data.
- Execution results (Pass/Fail/Skipped).
- Screenshots, logs, and error messages for failed runs.
- Comments and observations for context.
How to Create, Analyze, and Share Test Logs Effectively
- Create: Capture execution details during test runs.
- Analyze: Review logs to detect patterns, errors, and process gaps.
- Share: Distribute via collaboration tools (Slack, Confluence) or test management systems (Jira, TestRail).
- Store: Maintain historical logs for audits, debugging, and future releases.
This guide covers the definition, components, advantages, creation, analysis, sharing, and storage of test logs with practical examples.
What is a Test Log?
Test logging refers to the process of documenting the details of the testing process, including the test case execution results, the environment configuration, and the issues encountered during testing with proper RCA.
The prime purpose of test logging is to keep a record of the testing process so that the testing team can review the results and determine whether the software under test meets the expected quality standards. The focus is to enable post execution diagnosis of failures and defects in the software.
What are testing artifacts?
Test artifacts are nothing but a set of documents that are created or generated while performing testing. Test artifacts are required to develop transparency between the project team and client to avoid the communication gap and maintain a healthy relation. These test artifacts are shared within the team, clients, product managers, project managers, team leaders, and other stakeholders associated with the project. Due to this transparency, it becomes easy to identify and track changes and also be aware of recent progress of activities of testing from requirement.
Below are 7 main test artifacts used in Software Testing:
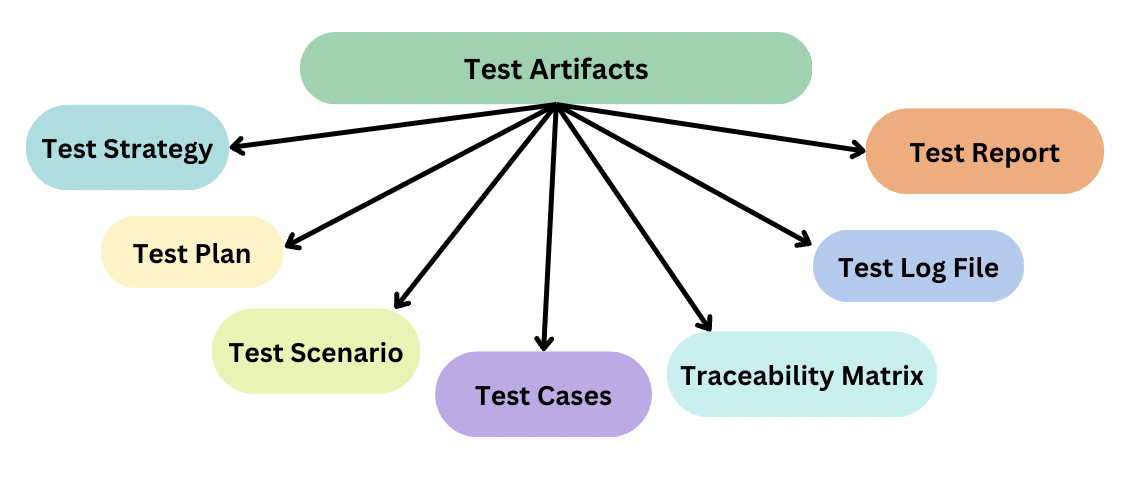
1. Test Strategy: Test Strategy is a high-level document mostly developed by the project manager that outlines the overall approach to be taken for software testing. This document is created at the planning phase that defines testing objectives, test scope, methodologies, tools, infrastructure, and test resources to be used. It is mostly derived from Business Requirement Specification (BRS).
2. Test Plan: While, Test Strategy is just an outline for the whole project, a Test Plan is a detailed document which outlines the testing strategy, objectives, scope, test deliverables, risk, objectives, and activities for a particular project or product. It is a dynamic document that has minute details about how the whole testing phase will work. The main purpose of a test plan is to ensure that testing is conducted in a systematic and organised manner, and that the testing activities align with the project goals and objectives.
3. Test Scenario: Test scenario is a statement used to describe the functionality of the software under test. It is derived from Use Case which is used to validate end to end feature testing in linear statements. Testers have to think from the customer’s perspective to test the software to ensure it meets the needs of the users.
Also Read: Use Case vs Test Case: Core Differences
4. Test Cases: Test Cases are derived from Test Scenarios and are a set of instructions or steps that are designed to verify a specific functionality or feature of the software under test. It is a detailed document consisting of test case name, preconditions, steps, input data, and expected result. Developing test cases helps in identifying problems in requirement or design of the software.
Read More: Test Plan vs Test Case: Core Differences
5. Traceability Matrix: It is a document that provides a mapping between the requirements, design, and testing phases of a software development project. It is a matrix table that visualises many to many relationships among client requirements and test cases. It is used to track the development and testing of each requirement. It helps to ensure transparency and completeness of products of software testing.
6. Test Log File: Test log file also known as a test log or test execution log, is a record of the activities performed during the execution of software testing. It provides a chronological account of the testing process, including details such as test case execution results, defects encountered, test environment information, and other relevant information.
Test management tools often provide built-in capabilities to generate test logs automatically or enable testers to export the log information in a specific format.
The test log file serves as a valuable source of information for test reporting, tracking progress, identifying trends, and analyzing the overall quality of the software under test. It can also facilitate collaboration among team members and provide a historical record for future reference or audits.
7. Software Test Report: A software test report is a document that provides a comprehensive overview of the testing activities and results performed on a software system or application. It serves as a formal record of the testing process, outcomes, and any issues encountered during testing. The test report is typically prepared by the testing team or quality assurance (QA) team and shared with relevant stakeholders, such as project managers, developers, and clients.
Why is test log necessary?
Creating test log is a time-consuming activity however it is essential to create them for the following reasons:
- It can be used as a test record as it captures a detailed record of the testing process, including what was tested, who tested it, when it was tested, and the results of the test cycle. This can be used as a reference or to assist with debugging.
- It can be used to troubleshoot issues that arise during the testing process. One can identify the root cause of issues and take steps accordingly to address them by reviewing the test logs.
- It provides an audit trail which is important for compliance purposes. For e.g: In healthcare and finance sectors it is necessary to have a detailed record of the testing process to ensure that all requirements have been met and the software is compliant with required standards.
- It promotes collaboration as test logs can be shared with the cross functional teams. This ensures that everyone is on the same page and there is no communication gap.
Advantages of Test Log
- Traceability: All the test activities and results can be tracked with a test log. This helps to ensure that all the required test activities were performed and completed for a particular iteration as a proof to show the required audience whenever it is demanded. Also, any issues identified during testing can be accurately traced back to their source.
- Defect tracking: Issues found during testing can be tracked with details such as severity, priority and status. This helps the QA team to prioritise the issues which need early resolution before release.
- Documentation: Test artifacts and deliverables are the fundamental part of the Software Testing Lifecycle (STLC). A test log consists of all the necessary test execution details which can be used as a formal record. It also helps to provide a historical record of the testing process which can be referred to in future.
- Transparency between teams: A test log facilitates communication between QA members as well as with the development and product team. For example- Test logs can be uploaded on Confluence or Sharepoint and can serve as a common platform which can be referred by any team to view test logs.
- Test analysis and improvement: The historical test log data can be reviewed by the testing team to identify trends (w.r.t issues), patterns, and areas for improvement. This helps to enhance the testing process and upgrade the quality of software/ application under test.
Read More: Defect Management in Software Testing
Various Components of Test Log
Test logs created after every test execution should have a trail of entries that should precisely describe the execution activities in detail. Below are the components of a typical test log however this may vary depending on the testing approach or tool used.
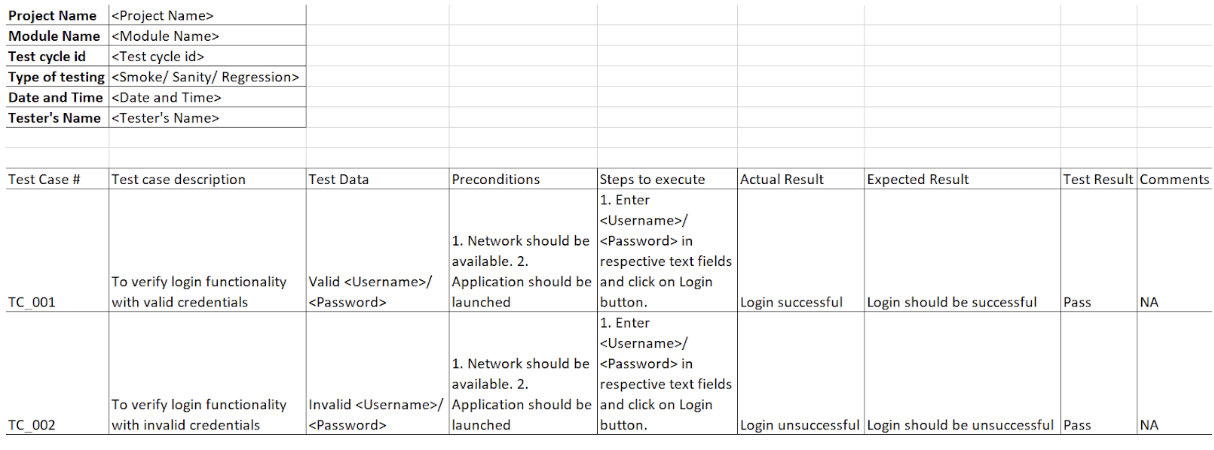
- Test case ID: A unique identifier for the test case being executed.
- Test case description: A short summary of the test case being executed.
- Test environment: The hardware and software environment details in which the test case was executed.
- Test data: The input data used for a test execution.
- Test result: The result of test execution as Passed/ Failed/ Skipped.
- Date and Time of execution: Date and time when the test case was executed.
- Tester’s name: Name of the tester who executed the test case.
- Test logs: Relevant test logs, error messages, crash logs, failure screenshots generated during test execution.
- Test artifacts: Any artifacts used during test execution such as System Requirement Specifications (SRS)/ Business Requirement Specifications (BRS)
- Comments: Any comments or observations about the test execution.
Test Log Template
Here’s how a test log template looks like
How to create a Test Log
A test log is created mainly by the software testers, quality assurance engineers, or other testing professionals. Below are some general steps to create a test log.
- Identify the test cases and create a list of these test cases.
- Decide among the team and define the components that should be included in a test log such as test case id, test case description, date and time of execution, tested by, etc.
- Execute the test cases and record the results along with relevant logs and screenshots.
- Review the test log and identify any issues and use this to improve the testing process.
It is essential to share the test logs with the cross functional teams and the stakeholders as needed and maintain the test log on some shared drive.
How to analyse Test Log
Analysing a test log helps in identifying issues that may need to be addressed. Below are some common steps to analyse a test log.
- Review the test results to identify any issues or areas of concern.
- Review each test case to identify specific issues or areas of improvement. For e.g: A particular feature was restructured however the test case was not modified accordingly and hence the test case failed/ skipped.
- Analyse the test logs to look for error messages or warnings that may help to find the cause of the problem.
- Identify root causes by gathering the information from the test log and performing some additional testing and debugging.
- Based on the analysis of the test log, give recommendations to alter the software testing process by providing compelling reasons and benefits to the test system by adopting this change.
- After the recommendation is approved by the team collectively, update the test log with new information or analysis. Finally, circulate the updated test log to the cross functional teams so that everyone gets well acquainted with the updated test log.
Test Log Report
A test log report is a document that provides a summary of the testing activities and results for a particular software application. This report contains information such as test cases executed, test results, test environment, bugs encountered, and any other relevant data.
Test log report caters to provide a historical record of the testing process which can be used by the testing, development, product team and other stakeholders.
Below are some of the general elements of a test log report:
- List of test cases executed.
- Test results with Passed/ Failed/ Skipped/ NA status.
- Severity and Priority of test result.
- Any supporting data or logs or screenshots captured for failed test cases.
- Test environment details. (Software and hardware used for test execution)
How to share a Test Log with the team?
Depending on the organisation’s preference and tools used, one can share test logs by following common methods:
- The simplest way to share a test log is via email.
- Test logs can also be shared via collaborative tools such as Microsoft Teams, Slack, and SharePoint.
- Any version control system such as Git, SVN, Bitbucket can be used to share the test log. Dump all the information on a shared repository and share with the team. This ensures that everyone has access to the same version of the report.
- Test Management tools can also be used to share the test log such as Jira, Confluence. By using tools such as Confluence one can keep all the testing related information in one place and ensure that all the team members are referring to the latest version of the test log.BrowserStack’s Test Management Tool allows you to integrate with Jira and write and manage your test cases and test log files for a streamlined testing process.
Try BrowserStack Test Management Tool for Free
Roles of Software Testers in Test Log Management
Software tester’s role is paramount as the test log is created, maintained and updated by them. Software tester has to be technically sound in order to understand the domain and product requirements. Below are some of the salient activities performed by software tester:
- Testers are responsible for creating and updating the test log which includes all the principal details such as test cases, test results, test artifacts included, bugs identified with status, priority and severity.
- Testers need to review the test logs to make sure that all the information has been captured correctly and is complete.
- Testers need to analyse test logs to recognize trends, patterns and issues that may impact the quality of the software being tested.
- Testers need to work in collaboration and closely with different cross functional teams to guarantee that the testing process is smooth, effective and helpful for the entire team.
- Testers are liable to maintain and improve the testing process on a timely basis. They need to review the test logs, improve and implement changes to make the testing process effective.
What is log storage in testing?
Storing and managing the test logs during test execution is termed as Log Storage in Software Testing. As creating a test log is important, storing and accessing it is equally important to allow the testers to access, analyse and modify at any given time. Following are some of the significances of storing test logs:
- It is easy to identify the root cause of the problem by referring to the stored test logs for any software failure as test logs contain all the wealth of information pertaining to the test execution.
- Using stored test logs, testers can create a report and trend of bugs found for the trail of test execution thereby showcasing the health of the software in a graphical manner.
- Stored test logs can be accessed by any team member and it can serve as evidence that the test execution was executed properly and all the important details were captured.
BrowserStack is a cloud-based platform that allows testing of mobile applications and websites across 3000+ on-demand browsers, operating systems and real devices. Along with testing, it also leverages the benefit of viewing and analysing test logs!
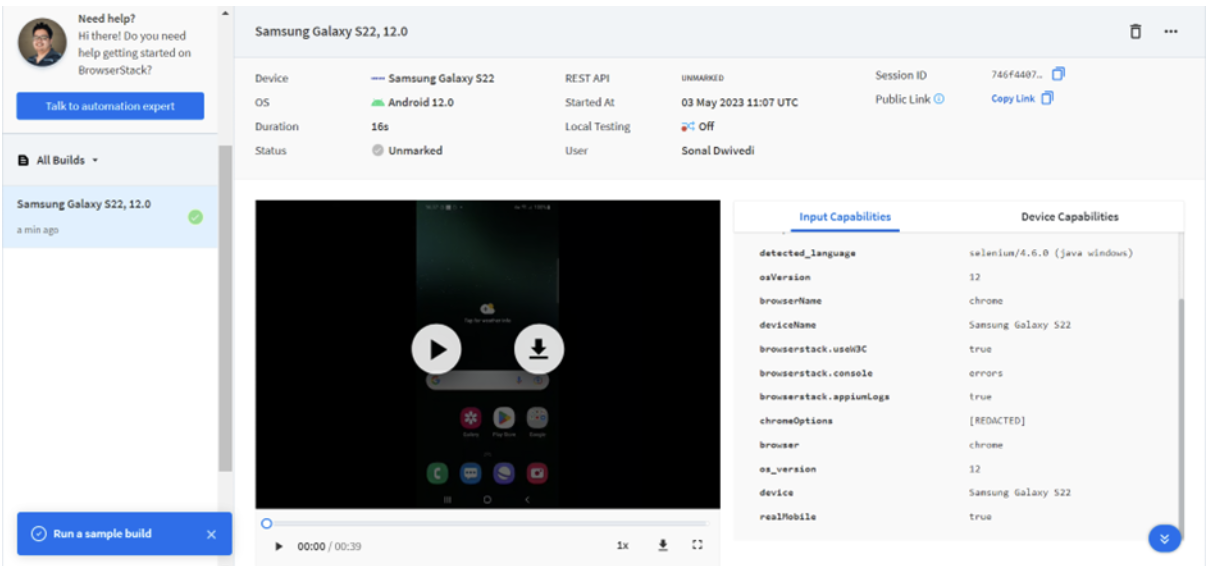
To view the test logs in BrowserStack, you can navigate to the Automate or Live section of the platform and click on the specific test run.
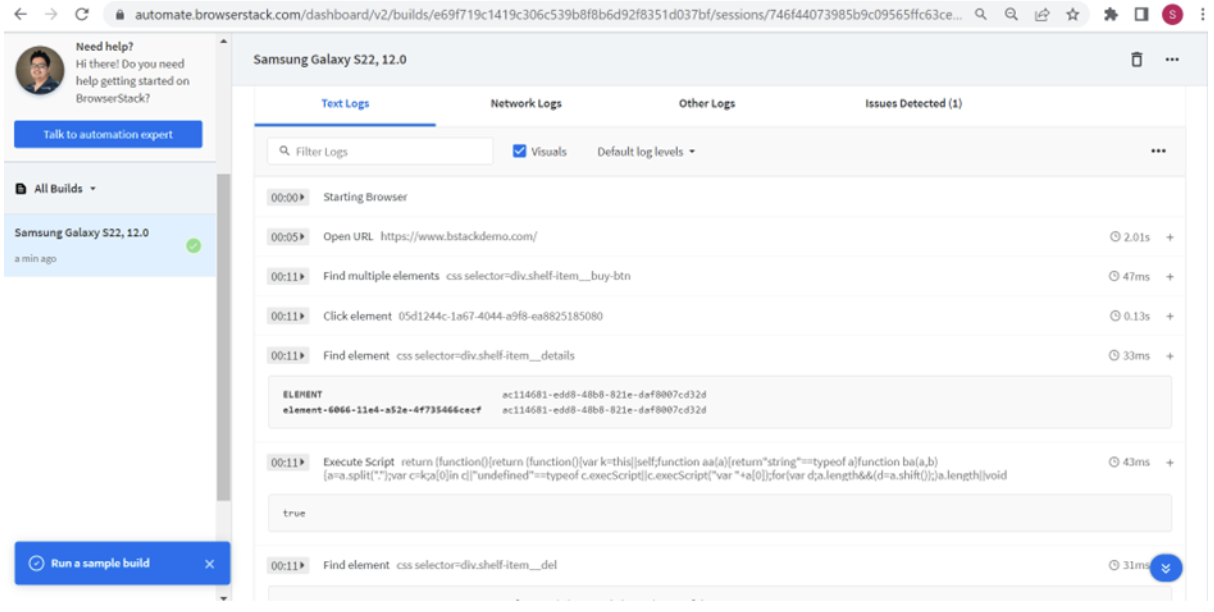
Following image displays the test run details of Samsung Galaxy S22, 12.0 which was run on BrowserStack’s Automate platform. The details of the test execution can be viewed after clicking on the particular test case.
Test log generated by BrowserStack contains detailed information about the test execution such as test case name and description, environment details, steps executed during the run, test results, screenshots and videos of the test run, console and network logs.
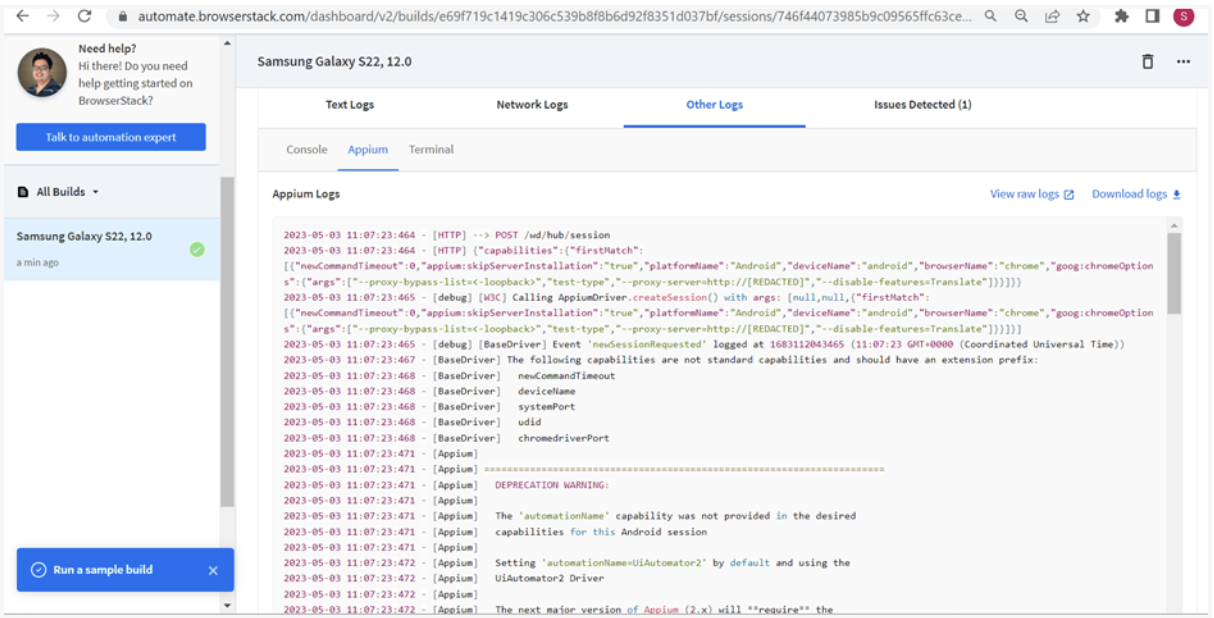
Text logs can be viewed by clicking on the Text Logs tab shown in image below.
BrowserStack also provides integrations with popular test management tools like JIRA, Trello, and TestRail, allowing you to automatically capture and store test logs in your preferred system.