Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment are two common practices in modern software development. These help teams automate the release process, reduce manual effort, and deliver features to users faster with consistent quality.
Overview
What is Continuous Delivery?
Continuous Delivery is a development practice in which every code change undergoes automated builds and tests and is always ready for production. The release happens only after manual approval, which gives teams control over when to deploy.
What is Continuous Deployment?
Continuous Deployment is a practice where every code change that passes automated tests is immediately released to users. There is no manual approval step, so updates go live as soon as they are validated.
Continuous Delivery vs Continuous Deployment: Core Differences
Here are the core differences between continuous delivery and continuous deployment.
| Feature | Continuous Delivery | Continuous Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Release trigger | Manual | Automatic |
| Production readiness | Always ready | Always deployed |
| Human intervention | Required for deployment | Not required |
| Risk level | Lower due to the manual gate | Higher if not well-tested |
| Feedback loop | Fast | Fastest |
This article explores continuous deployment vs continuous delivery in detail. It also highlights when to use continuous delivery vs deployment in DevOps.
What is Continuous Delivery?
Continuous Delivery is a software development practice where code changes are automatically built, tested, and prepared for a production release. Each change moves through a standardized pipeline that handles compilation, unit testing, integration testing, and deployment to a staging environment.
Although the process automates everything up to production, the deployment step requires manual approval. This gives teams complete control over when to release features, which helps reduce risks and align deployments with business goals.
What is Continuous Deployment?
Continuous Deployment (CD) is a software development and DevOps practice where every code change that passes automated tests and quality checks is automatically deployed to production without any manual intervention. In other words, when code changes are ready and meet the predetermined criteria, they are released to end-users or customers automatically and immediately.
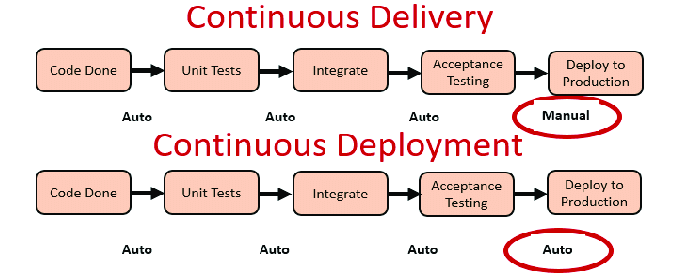
Difference between Continuous Delivery vs Continuous Deployment
The main differences between Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment can be tabulated as below:
| Aspect | Continuous Delivery | Continuous Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Code changes are automatically prepared for release to production | Code changes are automatically released to production without manual approval |
| Automation Level | Automated testing and staging, but manual approval for production release | Fully automated process from commit to production |
| Manual Intervention | Yes, human approval is required before deployment | No, every successful change is deployed automatically |
| Risk Level | Lower risk due to manual gatekeeping | Slightly higher risk without manual checks, mitigated by robust testing |
| Speed of Delivery | Fast, but depends on release schedules or approvals | Fastest possible since changes go live after passing tests |
| Use Case | Teams needing control over what and when to release | Teams that are confident in their test coverage and need to iterate quickly |
| Rollback Strategy | Manual rollback is often available | Must have automated rollback or rapid fix mechanisms |
| Example | Deploying weekly or on demand after tests pass | Deploying multiple times a day automatically |
Benefits of Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment
Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment improve software release cycles by introducing automation, consistency, and speed. Both help teams release updates faster, reduce errors, and respond to user needs more effectively.
Benefits of Continuous Delivery
Continuous delivery automates the path to production and ensures code is always in a deployable state. Teams still control the release timing to align deployments with business goals.
- Ready-to-Release Builds: Every code change is automatically built, tested, and pushed through staging. This keeps the codebase in a deployable state so teams can confidently release anytime.
- Controlled Releases: Teams manually decide when to push changes to production. This control allows better coordination with business timelines, user readiness, or external dependencies.
- Early Bug Detection: Automated tests run at every stage of the pipeline. This catches issues early during integration or staging and reduces the chance of defects reaching production.
Read More: How to find Bugs in Software?
- Easier Rollbacks: Smaller and more frequent releases help teams pinpoint issues faster and roll back changes without affecting unrelated features.
- Stronger Dev Workflow: Developers get fast feedback through automated builds and tests triggered after each commit. This helps them identify issues early and maintain clean, stable code.
Benefits of Continuous Deployment
Continuous deployment takes automation further by releasing every passing change to production automatically. This removes the manual approval step and delivers features directly to users.
- Faster Releases: Every code change that passes tests is deployed automatically, so users receive features and fixes without delays.
- Less Manual Work: The release process runs end-to-end without human input, so developers and ops teams spend less time managing deployments.
- Quick Feedback from Users: Changes reach real users immediately, allowing teams to observe behavior, gather data, and make adjustments faster.
- Fewer Release Errors: Automation removes manual steps that often cause mistakes, making releases more consistent and reliable.
- Shorter Development Cycles: Teams deliver continuously and quickly respond to issues or feedback so development stays agile and aligned with user needs.
Continuous Delivery vs Continuous Deployment: When to use which
The decision to use Continuous Delivery or Continuous Deployment depends on several factors, including the organisation’s requirements, risk tolerance, team maturity, and the nature of the software being developed. Let’s explore when each approach is most suitable:
When to Use Continuous Delivery
It is better to use Continuous Delivery when:
- There is a need for frequent releases: If your organisation wants to release software changes to production frequently but prefers to have human intervention to control when those changes are deployed, Continuous Delivery is a good fit.
- High regulatory or compliance requirements: In industries with strict regulatory or compliance standards, Continuous Delivery allows for thorough testing and review before releasing to production, giving stakeholders confidence in the process.
Read More: ADA Standards for Accessible Design
- Manual approval is preferred: If the organisation prefers to have a manual approval step before deploying changes to production, Continuous Delivery provides the flexibility to control the release timing.
- Limited automation maturity: If the team is still transitioning to an automated deployment process, starting with Continuous Delivery can be a stepping stone before fully adopting Continuous Deployment.
When to Use Continuous Deployment
It is better to use Continuous Deployment when:
- Rapid and frequent releases are crucial: In fast-paced industries or markets where continuous updates are essential to stay competitive and respond to customer needs quickly, Continuous Deployment is an ideal choice.
- High confidence in automated testing: Continuous Deployment requires a high level of trust in automated testing to ensure that code changes will not introduce critical issues in production.
- Streamlining deployment process: If the organisation wants to minimise manual intervention and reduce the potential for human errors during deployment, Continuous Deployment automates the entire process.
- Continuous feedback loop: If the organisation aims to gather continuous feedback from users and iterate rapidly based on that feedback, Continuous Deployment allows for faster turnaround of feature updates and bug fixes.
Read More: How to improve DevOps Feedback Loop
- Agile and DevOps maturity: Continuous Deployment is a natural progression for organisations that have already embraced agile development practices and have a mature DevOps culture.
Also Read: Agile vs DevOps: What’s the Difference?
Ultimately, the decision between Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment will depend on the organisation’s specific goals, its existing development and deployment processes, and its readiness for a higher level of automation and continuous release. It’s also possible for an organisation to start with Continuous Delivery and gradually move towards Continuous Deployment as their automation and testing practices mature.
Why Use BrowserStack for Test Automation in Continuous Delivery or Continuous Deployment?
BrowserStack is an ideal platform for testing in continuous delivery and deployment environments due to its ability to integrate seamlessly with automated workflows and support cross-browser and cross-device testing. It enhances the speed and reliability of testing by offering instant access to over 3,500+ real devices and browsers without the need for complex infrastructure.
- Real Device Cloud: BrowserStack enables testing on real devices and browsers to ensure that tests reflect actual user experiences and catch issues specific to real-world environments.
- Test Automation: BrowserStack supports full test automation in the cloud to reduce manual setup and support faster release cycles.
- Cross-Browser Testing: BrowserStack supports parallel testing across multiple browsers and versions to ensure consistent performance and user experience on a wide range of browsers.
- Seamless CI/CD Integration: BrowserStack integrates with popular CI/CD tools like Jenkins, CircleCI, and GitHub Actions to trigger tests automatically during the build and deployment process.
- Scalable and Reliable Infrastructure: BrowserStack’s cloud-based platform scales easily to handle test automation across different environments to reduce the need for infrastructure management.
- Faster Debugging with Screenshots and Videos: BrowserStack provides detailed logs, screenshots, and video recordings of test executions to help quickly identify and resolve issues.
Conclusion
Continuous delivery and deployment streamline the release process and improve software quality, but they serve different purposes. Continuous delivery offers more control over release timing, while continuous deployment enables faster delivery with fully automated releases. Choosing between them depends on your team’s risk tolerance, business needs, and automation maturity.
BrowserStack supports both approaches by providing real device testing, CI/CD integrations, and scalable automation infrastructure. It also offers parallel testing, visual logs, and instant feedback to keep releases fast, stable, and aligned with delivery goals.