findElement and findElements in Selenium are methods used to locate web elements. These methods help interact with web elements during automation testing and enable precise actions on a webpage.
Overview
Key Differences between findElement vs findElements in Selenium
In Selenium, findElement and findElements are used to locate web elements, each serving a distinct purpose.
- Single vs. Multiple Elements: findElement locates a single element, while findElements finds multiple elements matching the given locator.
- Return Type: findElement returns a WebElement, whereas findElements returns a List containing all matched elements.
- Exception Handling: findElement throws a NoSuchElementException if no matching element is found, whereas findElements returns an empty list when no elements match.
This article explains what findElement() and findElements() are, their key differences, and how to use the methods with examples.
Introduction to Selenium Find Element
Interaction with a web page requires the driver to locate a web element, and either trigger a JavaScript event like a click, enter, select, etc., or type in the field value. Usually, one starts automated testing of any web app by finding relevant web elements on the web page. Such automated testing is often executed using frameworks like Selenium WebDriver.
Selenium defines two methods for identifying web elements:
- findElement: A command to uniquely identify a web element within the web page.
- findElements: A command to identify a list of web elements within the web page.
Why Do You Need FindElement(s) Command?
The findElement and findElements commands are important tools in Selenium for locating web elements. They help automate interactions with a webpage, like clicking buttons or entering text, to ensure accurate test results. Here’s why Selenium findelement is essential for automation testing.
- Find a single element: findElement is used when you need to interact with just one element, like clicking a button or filling out a form.
- Find multiple elements: findElements is used when you want to work with several elements simultaneously, such as checking all links or images on a page.
- Reliable tests: These Selenium commands help make your tests more reliable by ensuring the correct elements are interacted with, even when the page’s content or design changes.
- Handle dynamic pages: They allow you to manage changes on web pages, like content loading or element updates, without errors.
Difference Between findElement and findElements in Selenium
While both findElement and findElements are designed to locate elements, they cater to different use cases. Here’s a table that highlights the key differences between findElement and findElements.
| Method | findElement | findElements |
|---|---|---|
| Return Type | Returns the first matching web element | Returns a list of multiple matching web elements |
| When No Element Found | Throws NoSuchElementException | Returns an empty list |
| Best For | Detecting a unique web element for specific actions | Handling cases where multiple elements need to be interacted with |
| Use Case | Useful when you know there will be only one match, like logging in with a specific button | Useful when you need to interact with all matching elements, like validating all links on a page |
| Performance | More efficient for single-element detection | Can be slower when dealing with large numbers of elements |
Find Element in Selenium command Syntax (with explanation)
The findElement command returns an object of the type WebElement. It can use various locator strategies such as ID, Name, ClassName, link text, XPath, etc.
Below is the syntax:
WebElement elementName = driver.findElement(By.LocatorStrategy("LocatorValue"));Locator Strategy comprises the following values:
- ID
- Name
- Class Name
- Tag Name
- Link Text
- XPath
Locator Value is the unique method to identify the web element quickly.
Example: Find Element in Selenium:
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='gh-ac']")).sendKeys("Guitar");Find Elements in Selenium command Syntax (with explanation)
The findElements command returns an empty list if no elements are found using the given locator strategy and locator value.
Below is the syntax of findElements command
List<WebElement> elementName = driver.findElements(By.LocatorStrategy("LocatorValue"));Read More: Selenium WebElement Commands
Example: Find Elements in Selenium
List<WebElement> listOfElements = driver.findElements(By.xpath("//div"));Now, let’s delve deeper into understanding how to find web elements with the help of various locators. One can refer to different types of locators in Selenium.
How to use Selenium findElement
You can use different strategies to locate elements using findElement and findElements in Selenium. Below are the commonly used methods.
1. Find by ID
ID is uniquely defined for each element and is the most common way to locate elements using ID Locator. If a website has dynamically generated ids, then this strategy cannot be used to find an element uniquely. However, it will return the first web element which matches the locator.
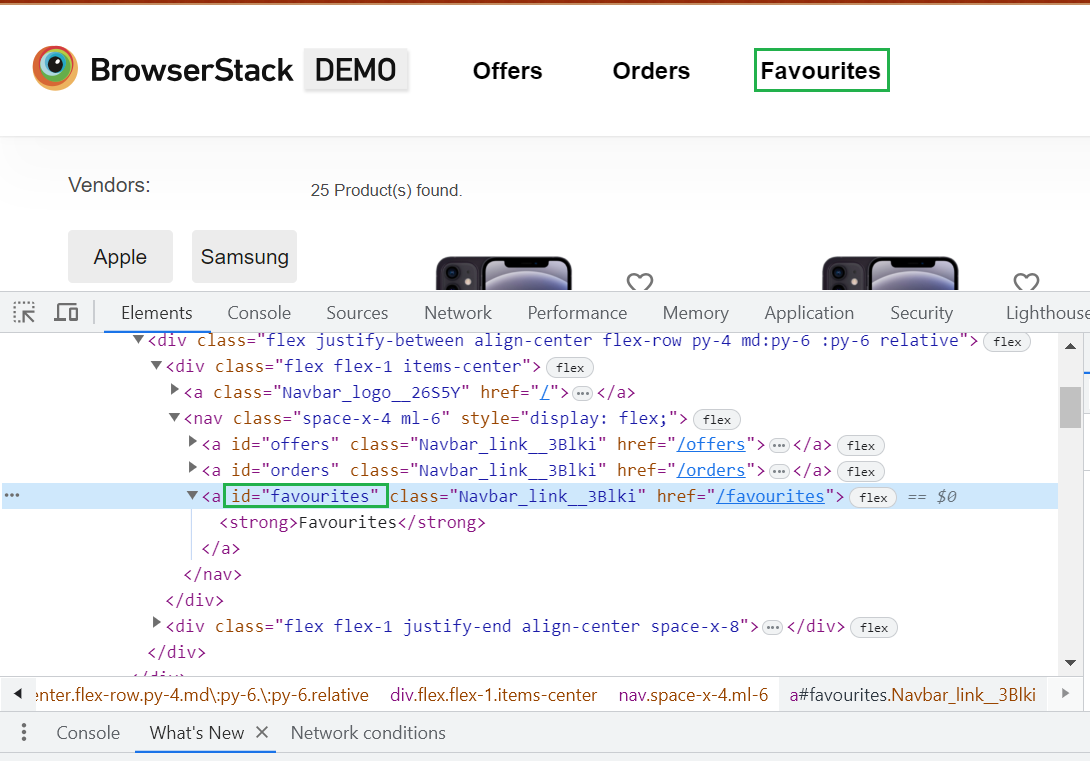
Example: Let’s take bstackDemo for automating and finding the elements. When we open the website, there is one link button “Favourites”, as shown below.
As you can see, it comprises an ID locator whose value is favourites.
The code snippet for find element in Selenium uses the same locator value to write a program:
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import service
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
service = Service("path/to/driver")
options = Options()
driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=service, options=options)
#instance of Chrome | Firefox | IE driver
driver.get(https://bstackdemo.com/)
elementID = driver.findElement(By.id("favourites"))
# will raise NoSuchElementException if not foundRead More: How to Find Elements by ID in Selenium
2. Find by Name
This is similar to Find By ID, except the driver will locate an element by the “name” attribute instead of “id”.
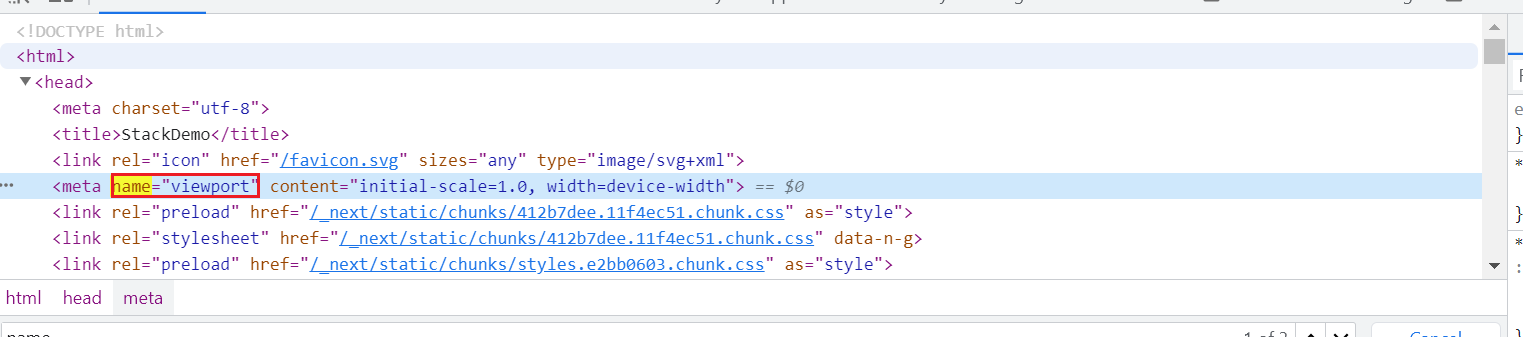
Example: Consider the same bstackdemo webpage. After successful login, we have one field with name “viewport” value shown as the given image.
The entire code remains similar to that of ID locator, except that the difference will be in the findElement syntax.
elementName = driver.findElement(By.name("viewport"))3. Find By LinkText
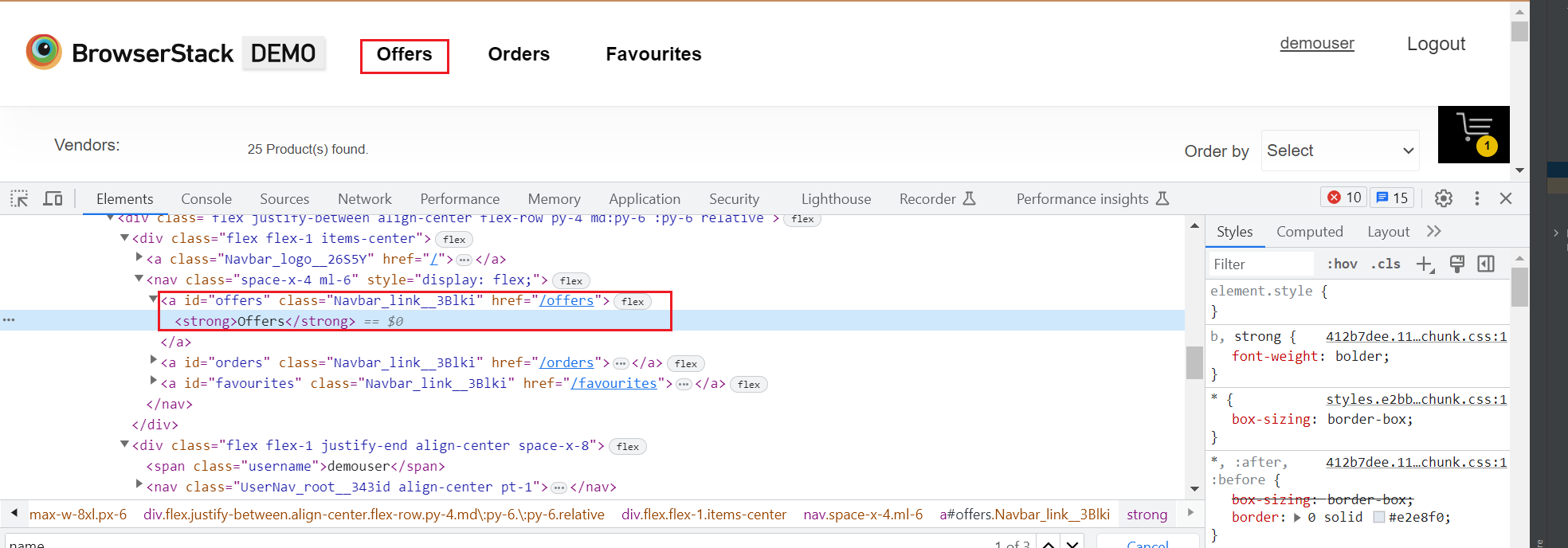
LinkText helps find links in a webpage. It is the most efficient way of finding web elements containing links.
When the tester hits that link and inspects it, it locates the link text Returns, as shown in the snapshot below.
This can be located simply by using Selenium findElement with the syntax below:
elementLinktext = driver.findElement(By.linkText(“Offers”))
4. Find By CSS Selector
CSS Selector is used to provide style rules for web pages and can identify one or more web elements.
Example: Consider the website’s homepage; there is an ”Add to cart” button for all products. Using the same value, the Find elements in Selenium method can locate the element.
elementcss= driver.findElement(By.cssSelector('div[id='1'] div[class='shelf-item__buy-btn']'))5. Find By XPath
XPath is a Selenium technique to navigate through a page’s HTML structure. XPath enables testers to navigate through the XML structure of any document and can be used on both HTML and XML documents.
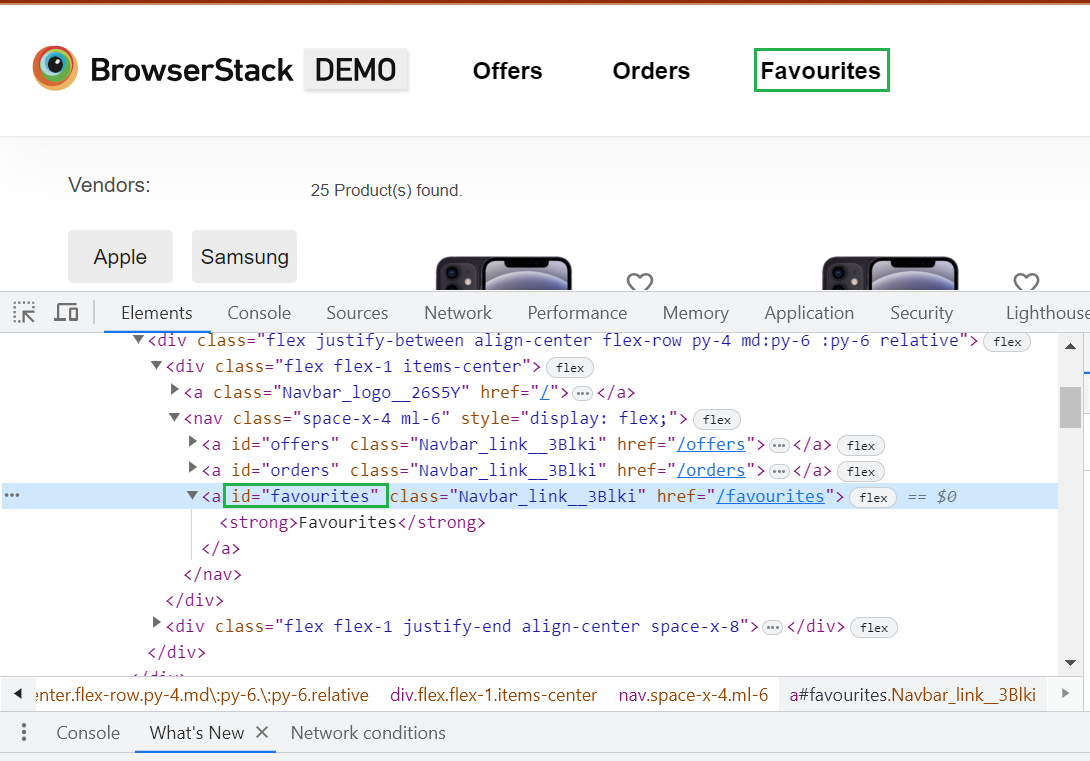
Example: Let’s try to locate the favorites button on the homepage with the help of XPath. The code below shows that it contains an ID locator. Note that relative XPath starts with ‘//’.
In the image below, one can see a Hyperlink tag. Start with //a. Here //a implies a tag name. Use the id attribute and pass favourites in single quotes as its value.
This will give the XPath expression shown below:
//a[@id=’favourites’]
Now, using the Selenium findElement method, execute the code below:
elementxpath = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//a[@id=’favourites’]"))Run Selenium Tests on Real Device Cloud
Locating web elements is the basis of automated Selenium testing of websites and web apps. To learn more about the fundamentals of Selenium, don’t forget to look at Selenium WebDriver Tutorial and what’s new with Selenium Grid 4.
Why You Should Run Selenium Tests on Real Devices
Real devices reflect actual user environments, including hardware behavior, browser rendering, touch gestures, and network conditions. Testing on real Windows, iOS, and Android devices improves accuracy and ensures your web application works as expected across all devices and browser versions.
BrowserStack provides access to over 3,500 real devices, browsers, and OS versions to ensure broad test coverage. It integrates seamlessly with your build pipeline to run automated tests on internal environments. Test results include video recordings and logs so teams can identify and fix issues faster without needing to review the code manually.
Here are additional capabilities of BrowserStack for Selenium testing.
- Test across browsers: Run Selenium tests on Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, Opera, and Yandex to ensure a consistent user experience.
- No device setup needed: BrowserStack hosts physical devices on different servers worldwide so you can run Selenium tests on the cloud without maintaining a device farm.
- CI/CD integration: Integrate Selenium tests with CI/CD tools like Jenkins, CircleCI, and GitHub Actions to enable continuous testing and faster release cycles.
- Reuse existing scripts: Run Selenium WebDriver tests on real devices without changing code.
- Minimal test flakiness: The AI self-heal feature reduces locator test flakiness caused by layout shifts, design changes, or weak locator strategies.
Conclusion
findElement and findElements in Selenium help accurately locate web elements during automation testing. These commands improve test effectiveness and ensure reliable test execution by interacting with the right elements. Testing on real devices further enhances accuracy by providing insights into how your website or app performs in real-world conditions.
BrowserStack Automate gives you access to 3,500+ real devices, browsers, and OS combinations to test under real user conditions. With BrowserStack Cloud Selenium Grid, you can run Selenium tests on multiple devices and browsers in parallel to save time and maximize coverage.
Run Selenium Tests on Real Device Cloud for Free
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the return type of findElement and findElements in Selenium?
findElement() returns one WebElement that matches the locator. If no element is found, it throws an error. On the other hand, findElements() returns a list of matching elements. If no match is found, it returns an empty list.
2. When should we use findElement () and findElements ()?
Use findElement() when you need a single element. Use findElements() when you need to locate multiple elements.
3. How to find elements by ID in Selenium?
To find an element by its id, use driver.findElement(By.id(“elementId”)). This will locate the element with the given ID and return it as a WebElement with which to interact.
4. How to click and find elements in Selenium?
You can click an element by locating it using findElement() and then using the click() method: findElement(By.id(“elementId”)).click().