Many Selenium WebDriver users assume that once a script works on their local browser, it will run reliably across other browsers and environments.
However, even a script that passes locally can fail instantly on another browser due to element timing differences, dynamic content, or minor environment variations.
But don’t worry, you can also create robust, maintainable tests that handle dynamic content, synchronization, and cross-browser quirks.
In this article, I will show you how to write resilient WebDriver scripts with Java and adopt practical strategies that make your automation reliable in real-world scenarios.
What is Selenium?
Selenium refers to a suite of tools that are widely used in the testing community when it comes to cross-browser testing. Selenium cannot automate desktop applications; it can only be used in browser automation. It supports a number of browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, Safari, Opera and operating systems such as Windows, Mac, Linux/Unix.
Selenium also provides compatibility with different programming languages – C#, Java, JavaScript, Ruby, Python, PHP. Testers can choose which language to design test cases in, thus making Selenium highly favorable for its flexibility.
Selenium Components
The Selenium test suite comprises four main components:
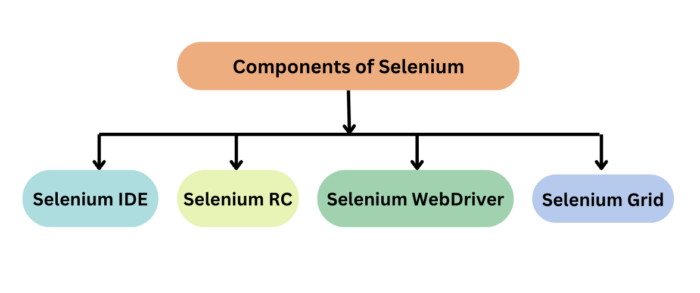
- Selenium Integrated Development Environment (IDE) is a browser extension for Firefox and Chrome that generates tests quickly through its record and playback functionality. The IDE records the user actions on the browser and exports them as a reusable script in different languages such as Java, C# and JavaScript.
Read More: Selenium IDE Alternatives
- Selenium WebDriver is the core component of Selenium which provides a programming interface for driving the web browsers. It allows to write tests in different programming languages to interact with the web elements, simulate user interactions and perform assertions.
- Selenium Grid is a tool that is used for concurrent execution of test cases on different browsers, machines, and operating systems simultaneously. It allows parallel test execution making it faster to run large test suites.
- Selenium RC is obsolete. It is being replaced by Selenium Webdriver due to its complex architecture and limitations. It allows you to develop responsive design tests in any scripting language of your choice. Server and client libraries are the two main components of Selenium RC.
What is Selenium WebDriver?
Selenium WebDriver is a web framework that permits you to execute cross-browser tests. This tool is used for automating web-based application testing to verify that it performs expectedly.
Selenium WebDriver allows you to choose a programming language to create test scripts. As discussed earlier, it is an advancement over Selenium RC to overcome a few limitations. Selenium WebDriver is not capable of handling window components, but this drawback can be overcome by using tools like Sikuli, Auto IT, etc.
To scale your Selenium testing effortlessly, BrowserStack Automate provides a cloud-based infrastructure that lets you run WebDriver tests across thousands of real browsers and devices, ensuring faster execution, higher accuracy, and better test coverage.
Get Expert QA Guidance Today
Schedule a call with BrowserStack QA specialists to discuss your testing challenges, automation strategies, and tool integrations. Gain actionable insights tailored to your projects and ensure faster, more reliable software delivery.
Core Features of Selenium WebDriver
Selenium WebDriver provides a low-level interface to control browsers and simulate real user interactions. Its core features focus on reliability, flexibility, and cross-browser support.
- Direct Browser Control: WebDriver communicates directly with the browser using native automation APIs, which allows tests to interact with the UI as a real user would without relying on JavaScript workarounds.
- Cross-Browser Support: The same WebDriver test can run across Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Safari, making it easier to validate consistent behavior across browsers.
- Multi-Language Support: Selenium WebDriver offers language bindings for Java, Python, C#, JavaScript, and more, enabling teams to write tests using their preferred programming language.
- Real User Interaction Simulation: Actions such as clicking, typing, scrolling, and form submissions are executed as actual browser events, helping uncover UI and behavior issues that unit tests cannot detect.
- Advanced Element Handling: WebDriver supports complex interactions including alerts, iframes, dynamic elements, and multiple windows or tabs, which are common in modern web applications.
- Framework Integration: Selenium WebDriver integrates seamlessly with testing frameworks like TestNG, JUnit, and pytest to support structured execution, reporting, and scalable test suites.
Benefits of Selenium WebDriver
Here are some of the benefits that come with using Selenium WebDriver
- Cross-browser compatibility: It is one of the most popular Open-Source tools and is easy to get started with for testing web-based applications. It also allows you to perform cross browser compatibility testing.
- OS Support: Supports multiple operating systems like Windows, Mac, Linux, Unix, etc.
- Language Support: It provides compatibility with a range of languages, including Python, Java, Perl, Ruby, etc.
- Browser Support: Provides support for modern browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Internet Explorer.
- Quick Execution: Selenium WebDriver completes the execution of test scripts faster when compared to other tools
- Concise API: More Concise API (Application Programming Interface) than Selenium RC’s
- Supports specialized WebDriver implementations: It also provides compatibility with iPhoneDriver, HtmlUnitDriver, and AndroidDriver
Limitations of Selenium WebDriver
Here are some limitations of Selenium WebDriver:
- Delayed Browser Support: Support for new browsers is not readily available when compared to Selenium RC
- Lack of Built-in Reporting: It doesn’t have a built-in command for automatically generating test results and requires third-party tools for this purpose.
- Resource-Intensive: Running multiple tests can be slow with increased resource consumption
Use Cases of Selenium WebDriver in 2026
Selenium WebDriver continues to play a critical role in modern test automation, especially as applications become more dynamic, distributed, and browser-dependent.
- Cross-Browser Regression Testing: WebDriver is widely used to validate critical user flows across browsers and versions, ensuring consistent behavior as web standards and browser engines continue to evolve.
- End-to-End Workflow Validation: Selenium automates complete user journeys such as login, checkout, and form submissions, making it effective for verifying business-critical paths in production-like environments.
- Continuous Integration and Delivery Pipelines: Teams integrate Selenium WebDriver with CI/CD tools to run automated tests on every code change, enabling faster feedback and safer releases.
- Testing Dynamic and JavaScript-Heavy Applications: WebDriver handles modern frameworks that rely on dynamic DOM updates, client-side rendering, and asynchronous behavior.
- Real-Device and Real-Browser Testing: Selenium is used alongside real device and browser platforms to validate behavior under real-world conditions that cannot be replicated accurately in local environments.
- Accessibility and Visual Validation Workflows: Selenium supports automation for accessibility checks and visual comparisons by integrating with specialized tools, helping teams catch usability issues early.
- Legacy Application Automation: Many organizations rely on Selenium WebDriver to automate older web applications where newer testing tools are not compatible or practical.
Selenium WebDriver Framework Architecture
WebDriver Architecture is made up of four major components:
- Selenium Client library
- JSON wire protocol over HTTP
- Browser Drivers
- Browsers
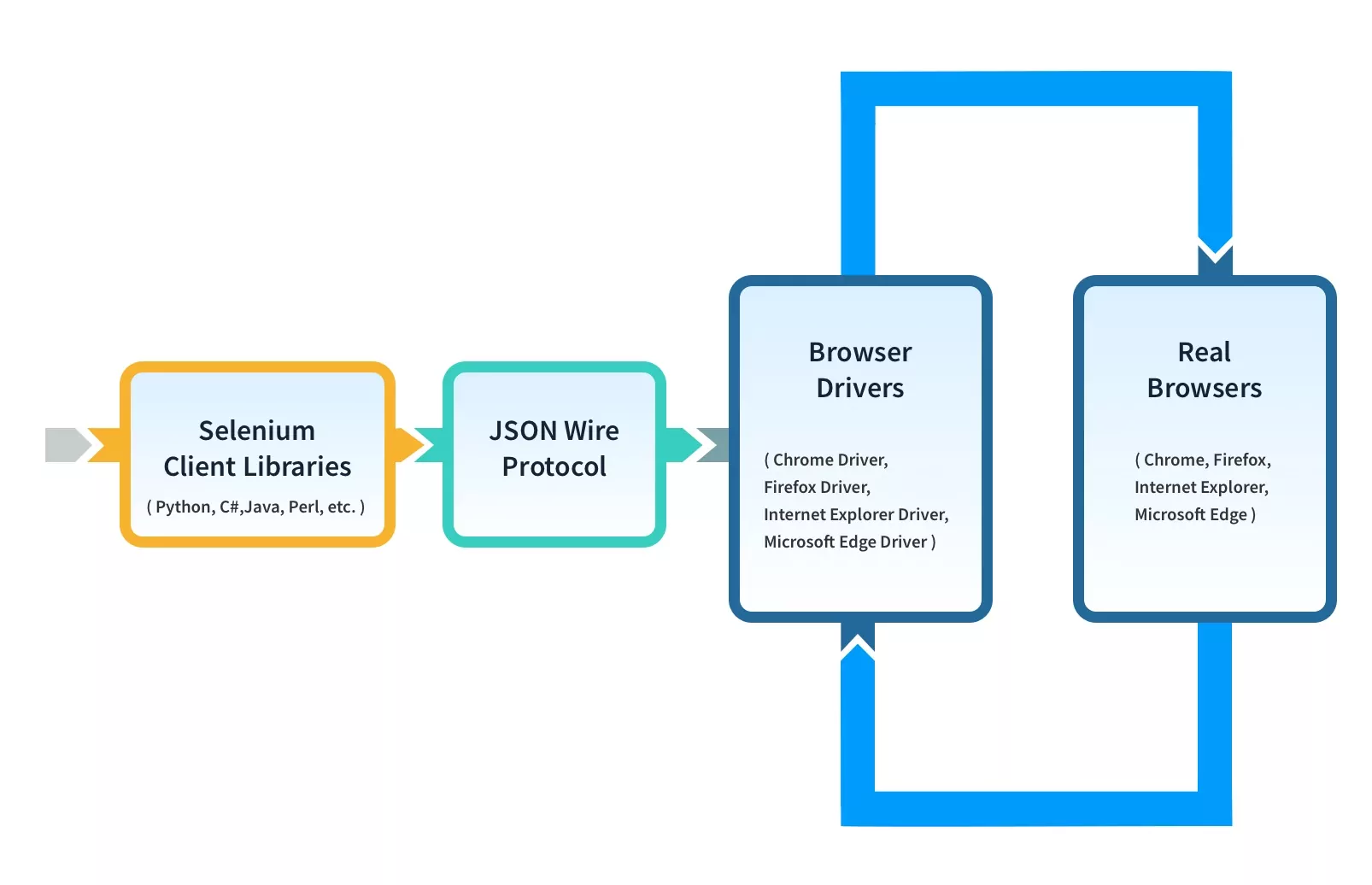
1. Selenium Client Libraries/Language Bindings
Selenium provides support to multiple libraries such as Ruby, Python, Java, etc as language bindings have been developed by Selenium developers to provide compatibility for multiple languages.
For instance, if you want to use the browser driver in Python, use the Python Bindings. You can download all the supported language bindings of your choice from the official site of Selenium.
2. JSON Wire Protocol
JSON is an acronym for JavaScript Object Notation. It is an open standard that provides a transport mechanism for transferring data between client and server on the web. It provides support for various data structures like arrays and objects which makes it easier to read and write data from JSON.
JSON serves as a REST (Representational State Transfer) API that exchanges information between HTTP servers. Learn more about REST API for accessing Selenium
3. Browser Drivers
Selenium provides drivers specific to each browser and without revealing the internal logic of browser functionality, the browser driver interacts with the respective browser by establishing a secure connection. These browser drivers are also specific to the language which is used for test case automation like C#, Python, Java, etc.
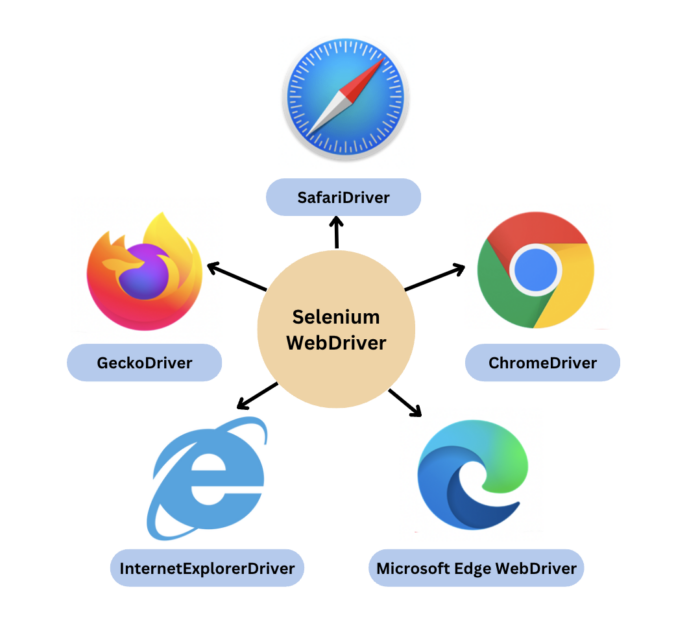
You can download the browser driver of your choice as per your language requirements. For example, you can configure Selenium Web driver for Python on BrowserStack.
| Browser | BrowserDriver | OS Supported |
|---|---|---|
| Google Chrome / Chromium | ChromeDriver | Windows/macOS/Linux |
| Mozilla Firefox | GeckoDriver | Windows/macOS/Linux |
| Microsoft Edge | Microsoft Edge WebDriver | Windows/macOS/Linux |
| Safari | SafariDriver (in-built) | macOS High Sierra and newer |
| Internet Explorer | InternetExplorerDriver | Windows |
When a test script is executed with the help of WebDriver, the following tasks are performed in the background:
- An HTTP request is generated and it is delivered to the browser driver for every Selenium Command
- The HTTP request is received by the driver through an HTTP server
- All the steps/instructions to be executed on the browser is decided by an HTTP server
- The HTTP server then receives the execution status and in turn sends it back to the automation scripts
4. Browsers
As discussed earlier, Selenium provides support for multiple browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Internet Explorer etc.
Curious about Selenium 4? Watch this in-depth webinar on Selenium 4 by Simon Stewart, the Selenium Project’s lead, the creator of WebDriver, and the co-editor of the W3C WebDriver specification.
How Selenium WebDriver Works
Working on Selenium Webdriver varies for Selenium 3 and Selenium 4. Here’s how it works
Selenium 3
In Selenium 3, there is no direct communication between the client libraries (Java, Python, JavaScript, etc) and the browser drivers. Here is how Selenium 3 works:
- Client library connects with browser drivers and browsers using the JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) Wire Protocol.
- JSON protocol provides a transport mechanism for transferring data between client and server on the web through various data structures like arrays and objects used to read and write data from JSON.
- JSON acts as a REST (Representational State Transfer) API to exchange information between HTTP servers.
Selenium 4
The architecture of Selenium 4 is similar to Selenium 3; however, it uses W3C protocol instead of JSON wire protocol for communication between Client Libraries and Browser Drivers. And therefore, WebDriver in Selenium 4 is fully W3C compliant!
Test scripts can communicate directly with the browser drivers (binaries) using the WebDriver protocol. With the removal of JSON Wire protocol, the communication got a lot easier between the client libraries and the browser drivers.
Below WebDriver script would help you understand the execution flow:
1. Initialize a WebDriver instance (for e.g: ChromeDriver or FirefoxDriver)
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
2. Navigate to a URL to start testing the web application.
driver.get(“URL”);
3. Find web elements using different locator strategies.
WebElement element = driver.findElement(By.xpath(“locator value”));
4. Perform actions on web elements like click, sendKeys, getText();
element.click();
5. Run the test
6. Assert the execution with expected result
7. Always close the browser session after the test to free up system resources and avoid leftover processes.
driver.close(); // closes current browser tab driver.quit(); // closes entire browser session
Types of Requests
There are two types of requests you might be familiar with – GET and POST.
If it’s a GET request then it results in a response that will be generated at the browser end and it will be sent over HTTP to the browser driver and eventually, the browser driver with the help of JSON wire protocol sends it to the UI (Eclipse IDE).
Read More: How to configure Selenium in Eclipse
Common Commands and Interactions in Selenium WebDriver
Selenium WebDriver exposes a simple but powerful API that allows tests to interact with web pages in the same way a real user would. These commands form the foundation of most automation workflows, regardless of application complexity.
- get(String url): Loads the specified web page in the current browser window and waits for the page to finish loading before continuing execution.
- findElement(By locator): Locates the first matching web element on the page using strategies such as ID, name, CSS selector, or XPath, and returns a WebElement for further interaction.
- click(): Simulates a user clicking on an element such as a button, link, checkbox, or menu item.
- sendKeys(CharSequence…): Enters text into input fields, text areas, or editable elements, and can also be used to simulate keyboard actions.
- getTitle(): Retrieves the title of the currently loaded web page, which is commonly used for basic validations.
- quit(): Closes all browser windows and ends the WebDriver session, releasing system resources.
These commands are often combined with waits, assertions, and framework utilities to build reliable and maintainable automation flows.
How to use Selenium WebDriver in Java: Example
Below code launches BrowserStack web application on chrome browser and verifies the page title.
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class BrowserStackDemo {
WebDriver driver;
@Test
public void verifyTitle() {
driver= new ChromeDriver();
driver.get("https://www.browserstack.com/");
Assert.assertEquals(driver.getTitle(), "Most Reliable App & Cross Browser Testing Platform | BrowserStack");
driver.quit();
}
}The code above does the following:
- Create a Selenium WebDriver instance
- Configure browser if required
- Navigate to the required web page and locate the relevant web element
- Perform action on the web element
- Verify and validate the action
Selenium is not just limited to Browser Automation but also supports different testing levels such as Regression Testing, Cross Browser Testing, UI Testing, Database Testing, Visual Testing, and Headless Browser Testing.
On executing the above java code, Selenium will navigate to the Chrome browser and open the BrowserStack Home page. Then, it will also check the test case status using Assert and try to match the URL.
Why Run Selenium WebDriver Tests on Real Devices & Browsers?
Each device and browser render web pages differently, hence, for consistent user experience across different devices and browsers, it is advisable to test it in the real environment set up.
Procuring the latest devices and browsers is challenging. It is best to invest in a real device cloud platform which helps test web apps on a wide range of devices and browser combinations.
BrowserStack Automate is a real device cloud that provides a comprehensive infrastructure for cross-device and cross-browser testing. There’s zero hassle in setting up the device and environment.
Testing in real devices and browsers ensures high-quality user experience.
Here are the features offered by BrowserStack Automate, and that’s why you should use to run Selenium Tests:
- Parallel Testing: BrowserStack Automate lets you test on multiple device and browser combinations at once, speeding up test execution and providing quick feedback.
- Real Devices and Browsers: Testing on real devices and browsers ensures accurate performance insights, unlike emulators. You can test on the latest devices without buying them.
- Dedicated Dashboard: Automate offers a dashboard to track and manage your tests, showing test statuses (Pass/Fail/Pending), device details, test duration, screenshots, and more.
- Custom Reports with Artifacts: Generate detailed, customized reports including test status, device/browser configurations, video recordings, and screenshots.
- Easy Integration with CI/CD: Seamlessly integrate with CI/CD tools like Jenkins, TeamCity, and TravisCI for faster, reliable, and consistent application delivery.
Conclusion
Selenium WebDriver remains a core tool for web automation because it gives testers precise control over browsers and the flexibility to handle real-world application behavior. When used correctly, it enables teams to build maintainable, reliable test suites that cover critical user journeys, adapt to modern web frameworks, and scale with growing application complexity.
To get consistent results from Selenium WebDriver, tests must run in environments that reflect how users actually interact with applications. Platforms like BrowserStack provide access to real browsers and real devices, helping teams validate behavior across browser versions, operating systems, and screen configurations.