Testing web applications with Selenium often involves interacting with multiple web elements using locators. Hard-coding these locators directly in test scripts leads to code duplication and makes maintenance difficult.
Overview
If a locator changes, updates must be made across multiple scripts, which is time-consuming. This is where an object repository helps.
An object repository is a centralized storage location for web element locators, mapping unique element identifiers (keys) to their corresponding locators (values). It helps manage locators separately from test logic, improving test script maintainability.
Use Cases of Object Repository in Selenium
- Store and manage locators for web elements in a central location.
- Reduce code duplication by separating locators from test scripts.
- Simplify updates when UI changes by updating locators in one place.
- Improve script maintainability, scalability, and readability.
This article explores how to create and use an object repository in Selenium to streamline test automation and improve maintainability.
What is an Object Repository in Selenium?
An object repository is a centralized storage that holds web element locators as objects. In Selenium, QAs typically store these locators in a separate file called a properties file (.properties), which organizes data in key-value pairs. This properties file acts as the object repository for Selenium WebDriver.
Depending on the automation framework, object repositories can also be maintained using XML files or other formats.
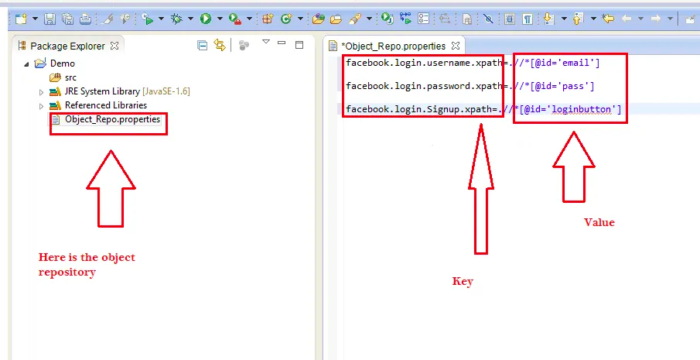
The image below represents a sample Properties file. It has the extension named “.properties”
QAs can create two types of object repositories in Selenium WebDriver:
- Using a properties file in Selenium
- Using an XML file
Types of Object Repository in Selenium
There are two common types of object repositories used in Selenium automation:
1. Properties File-Based Object Repository
- Stores locators as key-value pairs in a .properties file.
- Ideal for small to medium projects.
- Easy to implement and maintain, but may not scale well for large test suites.
2. Object Repository Using Page Object Model (POM)
- Uses Java classes to represent web pages, storing locators as variables within page classes.
- Offers better scalability and maintainability for large projects.
Encourages separation of page structure and test logic, following best practices in test automation design.
Other formats like XML or JSON can also be used for object repositories, depending on the project’s requirements and framework.
For teams looking to enhance their test automation process, platforms like BrowserStack provide a reliable cloud infrastructure to run Selenium tests at scale. BrowserStack’s real device cloud helps ensure your tests run consistently across different browsers and devices, while your object repository keeps your test scripts maintainable and scalable.
How to Create an Object Repository in Selenium
To create an object repository using a properties file in Selenium, follow these key steps:
1. Create a Properties file and add data
Please note: Here, it is assumed that the reader has basic knowledge on how to setup java project structure in Eclipse IDE.
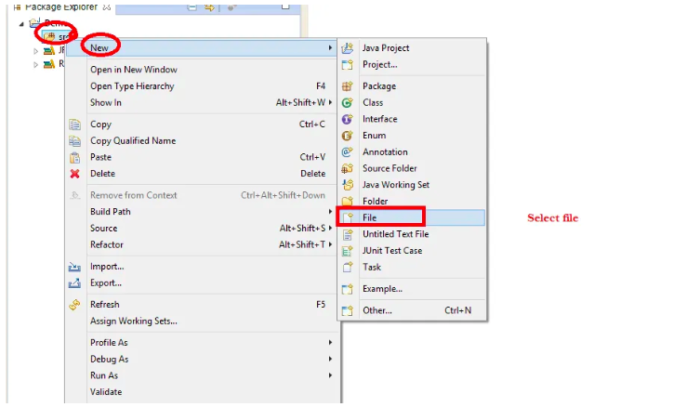
QAs first need to set up a basic project structure on eclipse. To create a property file, one needs to follow the steps below:
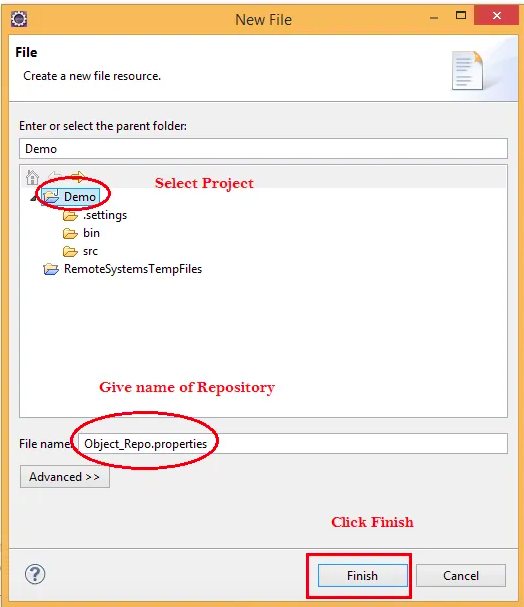
- Right-click on Project folder > New > Other> General > File
- Click Next and then name the file (example: demo_repo.properties) and then click on Finish.
Now, one needs to store the data in this file in key-value pairs. Just double click on your .properties file and add the key-values.
This example uses the web elements of the Facebook login page. The XPath of the username, password, and login button will be added to the property file.
facebook.login.username.xpath=.//*[@id='email'] facebook.login.password.xpath=.//*[@id='pass'] facebook.login.Signup.xpath=.//*[@id='loginbutton']
The test case scenario includes three basic steps:
- Visiting Facebook login page
- Entering username & password
- Clicking on login button
2. Reading data from the Properties file
To read data from the Properties file, you need to use the built-in Properties class that is available in Java.util.package.
So one needs to create an object of Properties class:
Properties obj = new Properties();
Now you also need to create an object of FileInputStream class with its path pointing to the .properties file:
FileInputStream objfile = new FileInputStream(System.getProperty("user.dir")+"\\<name of the properties file>");Now to integrate the properties file in your test script that includes locators, you need to load the file. To do this, you can use the load method of the property class. Refer to the code snippet below.
Properties obj = new Properties();
FileInputStream objfile = new FileInputStream(System.getProperty("user.dir")+"\\<name of the properties file>");
obj.load(objfile);
String username = obj.getProperty("facebook.login.username.xpath");The string username will contain the XPath to find the username field on the login page.
3. Using the Properties file in Selenium Script
Now to use the locator information available in the properties file, you need to pass the available data as parameters using the findElement method.
driver.findElement(By.xpath(obj.getProperty("facebook.login.password.xpath"))).
sendKeys("adsadasdas");Refer to the complete code below for getting a sense of the program flow:
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.firefox.FirefoxDriver;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class TestFacebook {
@Test
public void TestOR() throws IOException{
// Specify the file location I used . operation here because
//we have object repository inside project directory only
File src=new File(".Object_Repo.properties");
// Create FileInputStream object
FileInputStream objfile=new FileInputStream(src);
// Create Properties class object to read properties file
Properties obj=new Properties();
// Load file so we can use into our script
obj.load(objfile);
System.out.println("Property class loaded");
// Open FirefoxBrowser
WebDriver driver=new FirefoxDriver();
// Maximize window
driver.manage().window().maximize();
// Pass application
driver.get("http://www.facebook.com");
// getProperty Fetches the value of target key from the properties file
// In this case entering username
driver.findElement(By.xpath(obj.getProperty("facebook.login.username.xpath"))).
sendKeys("SeleniumWebDriver@gmail.com");
// getProperty Fetches the value of target key from the properties file
// In this case entering password
driver.findElement(By.xpath(obj.getProperty("facebook.login.password.xpath"))).
sendKeys("adsadasdas");
// getProperty Fetches the value of target key from the properties file
// In this case clicking on login button
driver.findElement(By.xpath(pro.getProperty("facebook.login.Signup.xpath"))).click();
}
}Using object repository in Selenium helps QAs manage their test suite more effectively. The centralized approach of maintaining the web element’s locator information makes it easy for testing teams to make changes quickly, with less effort. Thus, an understanding of Object Repository serves to make QA’s lives easier in a significant way.
Read More: Keyword Driven Framework for Selenium
Advantages of Object Repository in Selenium
Using an object repository in Selenium offers several key benefits:
- Centralized Locator Management: All element locators are stored in a single location, making it easier to manage and maintain tests.
- Reduced Code Duplication: Locators are defined once and reused across multiple test scripts, ensuring cleaner and more organized code.
- Simplified Maintenance: If an element’s locator changes, it only needs to be updated in the object repository, saving time and effort.
- Improved Scalability: Helps scale test automation projects by separating test logic from UI elements, supporting long-term project growth.
- Enhanced Readability and Collaboration: Makes it easier for teams to understand and modify tests, as locators are managed in a structured and consistent format.
By combining an object repository with a reliable testing infrastructure like BrowserStack, teams can ensure their Selenium tests remain maintainable and robust across browsers and devices.
Conclusion
Using object repository in Selenium helps QAs manage their test suite more effectively. The centralized approach of maintaining the web element’s locator information makes it easy for testing teams to make changes quickly, with less effort. Thus, an understanding of Object Repository serves to make QA’s lives easier in a significant way.