When testing mobile applications with Appium, interacting with off-screen elements is a common challenge.
Overview
What is Scroll in Appium?
Scrolling in Appium automates screen movement to reveal hidden elements, enabling interaction through simulated gestures or platform-specific commands.
Different Types of Appium Scroll
- Scroll by Coordinates: Scrolls between defined screen points; fast but less adaptable to dynamic layouts.
- UiScrollable (Android Only): Scrolls within Android views to locate elements by text or description.
- Mobile JSON Wire Protocol: Cross-platform scrolling using mobile:scroll commands based on direction or element attributes.
- Touch Actions (Gesture-Based Scroll): Simulates press-move-release gestures for custom scrolling when defaults fall short.
- Flick (Swipe) Gesture: Performs rapid, momentum-driven swipes for fast navigation through long lists or carousels.
This article explains how to scroll to a specific element in Appium and perform actions on it during test execution..
What does scroll down to the element mean?
In mobile app automation, certain elements may exist in the app’s layout but aren’t immediately visible on the screen. To interact with them, like clicking a button or verifying content, you need to scroll until the element appears.
For example, in a food delivery app, you might scroll to see all available dishes or browse a range of shows and movies in an OTT app.
In such scenarios, Appium allows you to automate the scrolling action so your test can locate and interact seamlessly with off-screen elements.
Importance of Scrolling in Mobile Apps
Scrolling is essential in mobile app testing due to the limited screen size and dynamic content loading patterns typical of mobile interfaces:
- Revealing Off-Screen Elements: Some UI components, like buttons or input fields, may not be immediately visible. Scrolling allows tests to interact with these hidden elements as a user naturally would.
- Testing Dynamic and Lazy-Loaded Content: Many mobile apps load additional content as the user scrolls. Verifying scroll behavior ensures that elements like feeds, lists, or tables load and render correctly.
- Simulating Real User Behavior: Scrolling is a core gesture in mobile navigation. Including it in automated tests helps confirm that the app reacts properly to common touch interactions.
Different Types of Appium Scroll Strategies
Appium supports multiple scroll methods, depending on the app’s structure and platform behavior, to help testers interact with off-screen elements.
Below is an explanation of the different types of Appium scroll strategies.
Also Read: How to perform Drag and Drop using Appium
1. Scroll by Coordinates
This method scrolls the screen by specifying start and end coordinates. It is a simple and fast approach but may lack flexibility for dynamic layouts or devices with varying screen sizes.
2. UiScrollable (Android Only)
UiScrollable is an Android-specific technique that programmatically scrolls through views. It is especially effective for finding elements based on text, description, or other attributes in complex UI structures.
3. Mobile JSON Wire Protocol
Using Appium’s Mobile JSON Wire Protocol, testers can perform scrolling through the mobile:scroll command. This cross-platform method allows for clear and straightforward scrolling by specifying direction or target elements.
4. Touch Actions (Gesture-Based Scroll)
Touch Actions simulate realistic user gestures by defining sequences like press, move, and release. It is ideal when customized scroll behavior is needed or when default scrolling methods do not suffice.
5. Flick (Swipe) Gesture
The Flick Gesture mimics fast, momentum-driven swipes across the screen. It is particularly useful for rapidly navigating long lists, carousels, or content-heavy interfaces.
How to Scroll until Element is Visible in Appium using visibleUiScrollable
While several Mobile Test Automation tools are available in the market, the most popular among them is Appium. Appium comes up with a rich class UiScrollable, which makes it possible to scroll down to the page and perform actions on elements.
It is a powerful Android class that performs element lookups in scrollable layouts. scrollIntoView class performs scroll action until the destination element is found on the screen.
UiScrollable is a UiCollection and provides support for searching for items in scrollable layout elements. This class can be used with horizontally or vertically scrollable controls.
You can use UiScrollable swipe to search elements in a list or search elements outside of the screen like input field, text or button. ScrollIntoView has UiSelector as a search criteria input that allows it to find elements by text or id.
Prerequisites:
- Appium desktop client
- Android studio
- JDK
- Development IDE/Eclipse
Make sure you have all software installed and running in your system.
In this example, taking a sample APK to automate using Appium. You can get some sample test apk’s on your system on below path:
C:\Users\singe\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk\system-images\android-25\google_apis\x86\data\app
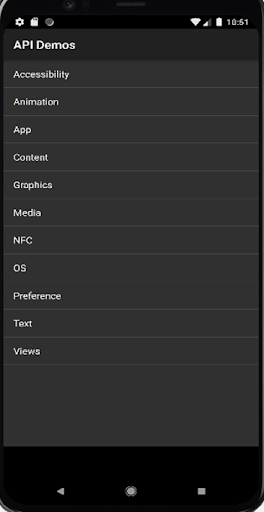
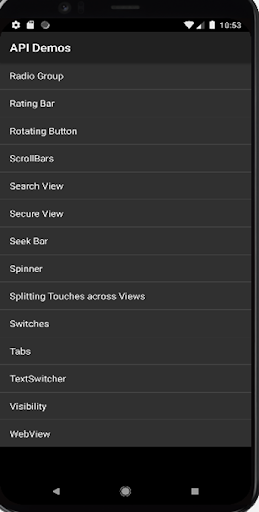
Using one such apk ‘API Demos’ for this article. Automation test will launch the app, click on ‘Views’ and will locate ‘WebView’ by scrolling down the list and clicking over it as seen in the image below.
Make sure you have all the Appium and testing dependencies configured on your system such as:
- Create a new java project.
- Create a package and a class
- Add all required capabilities
- Function to scroll down and take action
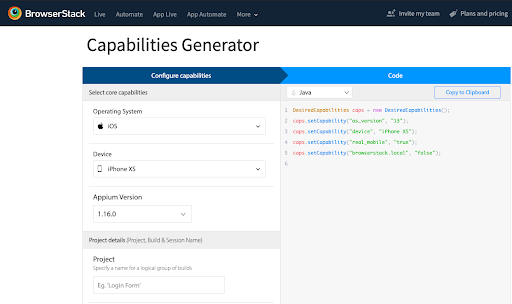
Pro Tip: Use BrowserStack’s Capabilities Generator for Appium to add all the capabilities
Code to Scroll Down until Element is Visible in Appium
The following code uses UiScrollable(), scrollIntoView(), UiSelector(), and scrollable() to scroll down to an element until it is visible using Appium.
package testing;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.DesiredCapabilities;
import io.appium.java_client.android.AndroidDriver;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class scrolldown {
@Test
public void scroll() {
try {
DesiredCapabilities caps = new DesiredCapabilities();
caps.setCapability("deviceName", "Google pixel 4"); //Give your device/emulator name
caps.setCapability("udid", "emulator-5554"); // Go to adb location i.e. C:\Users\singe\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk\platform-tools in command prompt and execute ‘adb devices’ to get udid
caps.setCapability("platformVersion", "8.1.0"); //Give android version of your device. (Check ‘about phone’ section)
caps.setCapability("appPackage", "com.hmh.api"); //provide app package name. Apkinfo can be used or execute dumpsys window windows | grep -E ‘mCurrentFocus’ command in adb shell in cmd in C:\Users\singe\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk\platform-tools
caps.setCapability("appActivity", "com.hmh.api.ApiDemos");
AndroidDriver driver = new AndroidDriver(new URL("http://127.0.0.1:4723/wd/hub"), caps); //Create driver object
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS); //Implicit wait of 10 seconds
driver.findElementByXPath("//*[contains(@text,'Views')]").click();
driver.findElementByAndroidUIAutomator("new UiScrollable(new UiSelector().scrollable(true).instance(0)).scrollIntoView(new UiSelector().textContains(\"WebView\").instance(0))").click(); //scroll down to the element and click
Thread.sleep(10000); //wait of 10 seconds
driver.quit(); //closes the driver session
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}You can automate any scroll scenario in Appium using the above methods. Run tests across various OS versions and real devices for better accuracy and coverage.
BrowserStack Real Device Cloud lets you scale effortlessly by integrating Appium with thousands of real Android and iOS devices via App Automate.
Run Appium Tests on Real Devices
After integration with BrowserStack App Automate, the code will look like below:
package testing;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import io.appium.java_client.MobileBy;
import io.appium.java_client.android.AndroidDriver;
import io.appium.java_client.android.AndroidElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.DesiredCapabilities;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class BrowserStackSample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws MalformedURLException, InterruptedException {
DesiredCapabilities caps = new DesiredCapabilities();
// Set your access credentials
caps.setCapability("browserstack.user”, <user-name>);
caps.setCapability("browserstack.key", <access-key>);
// Set URL of the application under test
caps.setCapability("app", "bs://d74ed9c2bd06fb02d7b863b3f1a7f8dfe97092b7" );
// Specify device and os_version for testing
caps.setCapability("device", "Samsung Galaxy S5");
caps.setCapability("os_version", "4.4");
// Set other BrowserStack capabilities
caps.setCapability("project", "First Java Project");
caps.setCapability("build", "browserstack-build-1");
caps.setCapability("name", "first_test");
// Initialise the remote Webdriver using BrowserStack remote URL
// and desired capabilities defined above
AndroidDriver<AndroidElement> driver = new AndroidDriver<AndroidElement>(
new URL("http://hub.browserstack.com/wd/hub"), caps);
// Test case for the BrowserStack sample Android app.
// If you have uploaded your app, update the test case here.
//driver.findElementByName("Cancel").click();
driver.findElementByXPath("//*[contains(@text,'Views')]").click();
driver.findElementByAndroidUIAutomator("new UiScrollable(new UiSelector().scrollable(true).instance(0)).scrollIntoView(new UiSelector().textContains(\"WebView\").instance(0))").click();
Thread.sleep(5000);
// Invoke driver.quit() after the test is done to indicate that the test is completed.
driver.quit();
}
}Test Results
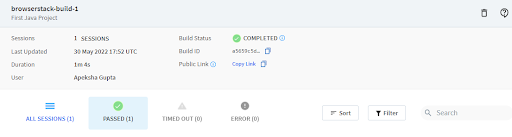
Test results can be viewed on App Automate Dashboard once the test execution is completed. By clicking on individual tests will give you a detailed report for each test including steps, text logs, Appium logs, execution video logs, and other details for better debugging of failed tests.
Testing on Real Mobile Devices with BrowserStack
When automating scroll actions in Appium, it’s important to test in real user conditions.
BrowserStack App Automate lets you run Appium tests on real Android and iOS devices, offering several practical advantages:
- Reliable Gesture Behavior: Scrolling actions behave differently on emulators vs real devices. Testing on actual hardware helps catch inconsistencies in scroll speed, direction, or responsiveness that affect user experience.
- Accurate UI Rendering: Real devices ensure that your app’s layout renders correctly across screen sizes, resolutions, and OS versions, essential for verifying whether scrollable elements are visible and accessible.
- Uncover Device-Specific Bugs: Some scroll-related issues only appear on certain manufacturers or OS builds. Testing across various real devices helps identify and fix these early.
- Test Under Real Network and Performance Conditions: Unlike simulators, real devices replicate real CPU load, memory usage, and network behavior, factors impacting scroll actions and overall performance.
Best Practices for Scrolling to Elements in Appium
To make scroll actions more reliable during test automation, especially when elements are outside the visible screen area, follow these tips:
- Identify scrollable parent containers in the UI to narrow down the correct scroll target.
- Scroll using the nearest scrollable container to the element, rather than deeply nested ones.
- Use native scroll methods (like UiScrollable or Touch Actions) instead of relying on JavaScript-based scrolling.
- Add short waits after scrolls to allow dynamic content to load properly.
- Avoid hardcoding the number of scrolls, scroll until the element becomes visible.
- Implement exception handling if the scroll doesn’t bring the element into view.
- When using coordinate-based scrolling, go slightly beyond the target to reduce test flakiness.
Conclusion
Scrolling to elements in Appium is essential for testing real-world mobile interactions, where content often extends beyond the visible screen. Using the right scroll strategy can ensure stable and reliable automation.
Pairing Appium with real device testing platforms like BrowserStack further boosts accuracy by validating scroll behavior across different devices and OS versions.
Appium Useful Resources
Tutorials
- How to perform Parallel Test Execution in Appium?
- Appium Visual Testing: The Essential Guide
- How to run Appium iOS Tests on Real Devices?
- How to perform Debugging in Appium
- How to Run Your First Appium Test Script
- How to report bugs in Appium UI Testing?
- How to run Appium Tests on macOS?
- XPath in Appium: Tutorial
- How to Analyze Appium Logs
- How to perform Drag and Drop using Appium
- How to test mobile app in Landscape or Portrait mode using Appium
- How to Run Same Script in Multiple Devices using Appium
- How to change Time Zones for Mobile App Testing using Appium
- How to Perform Localization of Mobile Apps using Appium
- What is Appium Inspector? (Benefits & How to Use it?)
- How to run Appium tests on Android devices
- How to scroll down to an element in Appium
- How to Download and Install Appium
- How to set up your Appium Grid
- How to test Biometric authentication using Appium?
- How to use touch actions in Appium?
- How to Automate a Real E2E User Flow involving App and Browser with Appium
- How to Inspect Element using UIAutomatorViewer in Appium
- How to Test Flutter Apps Using Appium Automation
- Understanding Appium Desktop: Tutorial
- Appium Tutorial for Mobile Application Testing
- React Native and Appium Tutorial
- Understanding FindElements in Appium
Best Practices, Tips, and Tricks
- Appium Best Practices Every Developer Must Know
- Effective Locator Strategies in Appium
- Top Appium Commands every Developer must know
- Desired Capabilities in Appium
- Overcoming Top Challenges faced in Appium Automation
Getting Started with
- Getting Started with Appium and NUnit framework
- WebdriverIO Tutorial: Getting started with Test Automation using Selenium and Appium
- Appium with Python: Getting Started with App Automation Testing
- Appium with Java: Getting Started to Run Automated Tests
- Test Windows Desktop App using Appium-Compatible WinAppDriver
Differences and Comparisons