With the rising popularity of web applications, there has also been an increase in security breaches, which is why CyberSecurity has become an essential part of the software development process. Several measures like Security Testing are being taken to secure user data and privacy. Sandboxing is necessary to ensure a website’s and computer resources’ security. It isolates programs, preventing malicious or malfunctioning programs from damaging the rest of our computers.
What is Sandboxing?
Sandboxing is the practice where an application, a web browser, or a piece of code is isolated inside a safe environment against any external security threat. The idea of sandboxing is to enhance security.
Like the physical sandbox at a playground where kids can create anything they want within the boundary without making a mess elsewhere, the application code is free to execute within a restricted environment in limited contact with the external environment.
For example, in a sandbox, JavaScript can add and modify elements on the page but might be restricted from accessing an external JSON file. This is because of a sandbox feature called same-origin.
Organizations leverage sandboxing in different ways, such as Application Sandboxing, Web Browser Sandboxing, and Security Sandboxing.
What is an online Browser Sandbox?
An online browser sandbox is a virtualized and isolated environment that allows users to run and test web applications or execute potentially unsafe code within a controlled setting.
- It provides a secure and separate space for users to experiment, evaluate, or develop software without the risk of damaging their computer systems or compromising their privacy and security.
- The primary purpose of an online browser sandbox is to provide a controlled environment for running untrusted code, such as JavaScript applications or plugins, in a way that minimizes potential risks.
- Developers can use a sandbox to test their code in different browser versions or configurations.
What are the different types of Sandboxing?
Sandboxing can be classified into three different types:
- Application Sandbox: An application sandbox allows running untrusted software in a safe location and observing it to detect malicious components.
- Web Browser Sandbox: A web browser sandbox allows running web applications in isolated environments to prevent browser-based malware from spreading to the network.
- Security Sandbox: A security sandbox lets you observe and analyze threats in an isolated, safe environment.
Why is Sandboxing Essential?
Sandbox provides a tightly controlled environment for programs to run. In Sandboxing, the scope of action for a code is limited, providing it just the permissions it needs to function without adding additional permissions that could be abused.
For example, a web browser essentially runs web pages we visit in a sandbox. They’re restricted to running in our browser and accessing a limited set of resources — they can’t view our webcam without permission or read our computer’s local files. If the websites visited weren’t sandboxed and isolated from the rest of the system, then visiting any malicious website would be as bad as installing a virus directly.
Use cases for Sandbox Browser
There are several use cases for sandbox browsers. Here are a few examples:
- Web Development and Testing: Developers can ensure their code functions correctly across different browsers, operating systems, and configurations without affecting their local machines.
- Security and Malware Analysis: By running suspicious elements within a sandboxed environment, they can observe their behavior and identify malicious activities.
- Online Privacy and Security: Sandbox browsers can be used by individuals concerned about online privacy and security to try out new software without exposing their data or risking malware infections.
What is Browser Sandboxing?
Browser Sandboxing is a security model that physically isolates Internet users’ browsing activity from the infrastructure, local computers, and networks. There are two main browser isolation techniques:
- Local browser isolation works by running the browser in a container or virtual machine.
- Remote browser isolation involves running a browser on an organization-hosted or cloud-based server such as BrowserStack, allowing users to browse web applications in a cloud-based environment.
Read More: How to test on older browser versions easily
Local Browser Isolation: Virtual Browser
Virtual browsers run the websites in an isolated environment, as a protective barrier between external threats on web and user machines connected to a corporate network. In such as case, if the user visits any malicious site or downloads a malicious file, these threats cannot reach the endpoint.
Virtual browsers significantly improve security and allow organizations to leverage old and unsupported versions of browsers.
Remote Browser Isolation (RBI)
Remote browser Isolation is sandboxing that can be hosted over the cloud by an organization or by third-party providers. As users browse the Internet, the remote server starts a browser in a container to keep it safe from the external environment.
Remote isolation is expensive as it requires the allocation of resources for running a large volume of containerized browsers. But using third-party providers can be cost-effective.
Test on Secured Real Device Cloud for Free
Sandboxing with Different Browsers
Most browsers already have a sandbox to enhance your computer protection. Let’s see how it differs regarding different types of web browsers.
Firefox Sandbox
To protect your computer against any malicious activity, Firefox runs any untrusted code in a sandbox. Firefox runs the code in two parts i.e. the Parent and the Child processes. While browsing the internet, all the untrusted processes are run in the Firefox sandbox.
This activity helps limit the contamination from any malware in case any suspicious activity occurs. The Parent part of the code mediates between the computer resources and the child processes run in the Sandbox. This way, the computer resources are not fully exposed to the code.
However, users can alter the strictness or ease of the sandboxing level in Firefox. Firefox is least restrictive when the Sandbox runs at Level 0, while at level 2, it stands balanced. At level 3, Firefox behaves to be very restrictive. To check the Sandboxing level of Firefox, enter the following command in the address bar of Firefox.
about:config
This returns the Firefox configurable variables on the webpage. Upon this, press CTRL+F when the cursor is placed on the config page. Enter the following command in the Find input field box.
security.sandbox.content.level
This function returns the value of the current sandboxing level of Firefox.
Chromium Browser Sandbox
Chromium Browser Sandbox is used by both Microsoft Edge and Google Chrome browsers. It is similar to that of Firefox Browser Sandbox.
It also runs in two parts just as Firefox Sandbox. These parts run the broker process and the target process of the code. While, the parent process here, is termed as broker process, the child processes are named as target processes. All codes that are run by the target processes run within the sandbox. The broker process acts as a mediator between the child process and computer resources to maintain the required supply of the resources.
Microsoft Edge Sandbox
Starting the Windows 10 Sandbox will give you a new desktop with only Recycle Bin and Edge shortcuts. It shows Start Menu and other icons. However, these icons don’t work in the sandboxed environment. Opening them in the main Windows 10 instead of sandboxed Windows 10 is recommended.
Run Edge from the sandboxed Windows 10 environment to ensure maximum browsing security. Once the sandbox is closed, no one can trace your browsing activities. However, your ISP might create a log of the activities, but no one can check the actions performed using Edge in the sandbox. If any website downloads malware to your system, the malware too will disappear upon closing the sandbox.
Note: In Windows 10 Pro and above editions, you can use Windows Sandbox for running Microsoft Edge.
How to turn off Google Chrome Sandbox?
To turn off the Google Chrome Sandbox, right-click on its icon. Click on Properties and then on the Shortcut tab in the dialog box.
Add the following to the app path shown in the Target:
--no-sandbox
Post this, whenever you click the Chrome icon, it will load Chrome without a sandbox.
Beyond Browser Sandboxing: Test on Secured Real Device Cloud
However, one must understand that using a sandboxed environment for browsers won’t make it 100% safe. Some browser parts may extend beyond the sandbox, mainly if they still use Flash and ActiveX elements. These can still be compromised, and cybercriminals can access the computers. But, it is essential to adopt the best possible ways to safeguard applications, and Sandboxing is one of those ways.
- Using a secure Real Device Cloud for testing web applications is a way to ensure complete security.
- BrowserStack’s Real Device Cloud follows standard security protocols and compliances like SOC2 Type2, where external attacks cannot compromise the web application.
- Besides, one can test the applications on all the browsers versions under real user conditions on devices across different platforms.
Browser Sandboxing with BrowserStack Live: Example
BrowserStack Live offers a SOC2 Type 2 secured Browser sandbox with real mobile and desktop devices. You can test on 3500+ real device and browser combinations. It allows you to test under real user conditions with features like geolocation testing, local testing, network simulation.
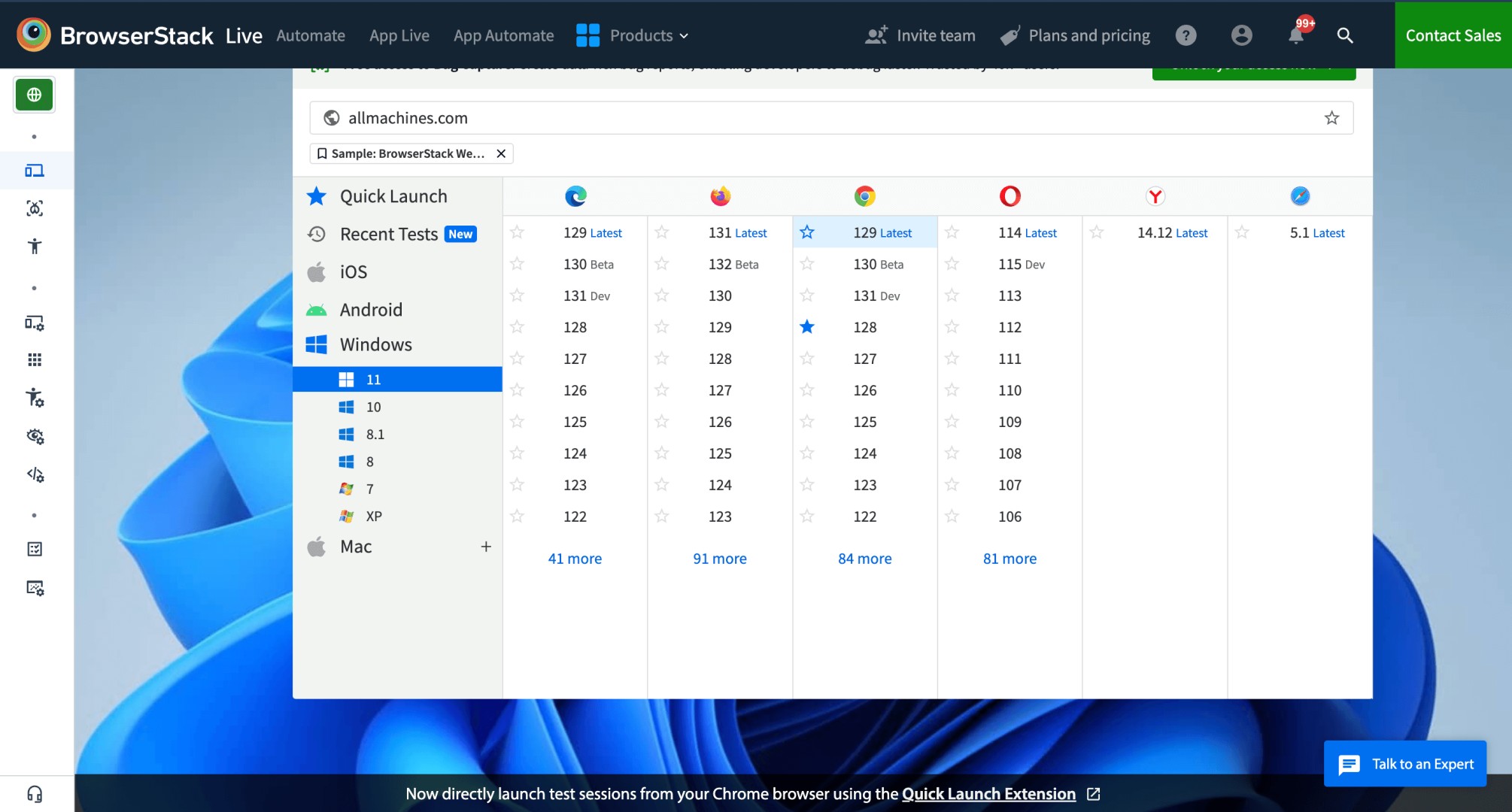
Here’s how you can use browser sandbox with BrowserStack Live. In this example, testing allmachines.com website on Windows 11 desktop with Google Chrome 129.
Step 1. Signup on BrowserStack. Login if you are an existing user.
Step 2. Add allmachines.com URL in the field. Select Windows 11 device with Google Chrome 129 Browser to test on browser sandbox online.
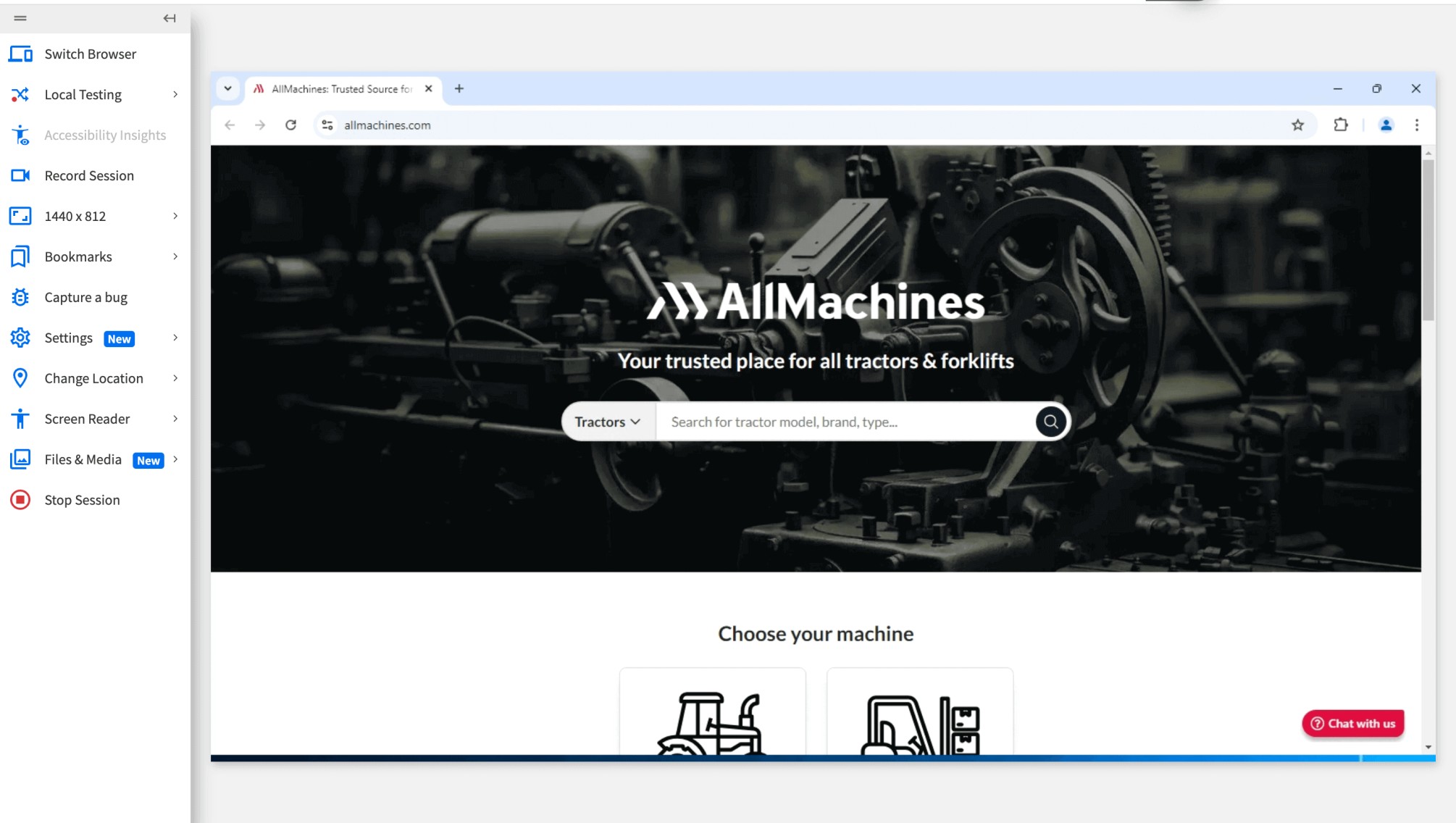
BrowserStack Live opens real Chrome 129 on Windows 11 in a secured environment.
Step 3. Testing allmachines.com on Windows 11 and Chrome 129 device browser combination.
BrowserStack Live not only offers you secured Browser Sandbox online to test on but it also allows you to test under real user conditions.
You can test your website on Local Environment, Record Session, Debug in Real Time, Capture a Bug for a comprehensive Testing Experience.
Why use BrowserStack for Browser Sandboxing Online?
BrowserStack Live is a go-to tool for using BrowserSandbox online. It offers advanced features to ensure a seamless and detailed testing experience along with security.
Here’s why you should use BrowserStack Live for Browser Sandboxing Online:
- No Setup Required: BrowserStack Live does not require any setup on your system. All you need to do is Signup on BrowserStack and start accessing Live dashboard.
- Test on Real Devices & Browsers: You can test on 3500+ real devices and browser combinations. You can Test on latest or legacy browser versions of different browsers available for your sandbox.
- Supports Browser Sandboxing for Mobile: You can use online Browser Sandbox for iOS and Android mobile devices. It allows you to test on real mobile browsers seamlessly for a real-like experience.
- Real-time debugging: BrowserStack Live integrates with various debugging tools, allowing you to inspect elements, capture screenshots and videos of bugs, and streamline the troubleshooting process, all while your tests are running.
- Network Simulation: Test the app under real user conditions by simulating network conditions from 2G to custom scenarios to identify performance issues in various internet environments.
- Real Device Network Testing: Leverage physical SIM card features to test cellular network-dependent functionalities, such as SMS verification and two-factor authentication.
- Screen Readers Testing: Use built-in screen readers like VoiceOver or TalkBack to test web app accessibility, ensuring usability for users with disabilities.
- Geolocation Testing: You can replicate website and mobile behaviors by choosing IP addresses from over 60 countries to validate scenarios such as localized pricing, languages, and product listings.
Conclusion
Browser sandboxing is a crucial technique that enhances security and user privacy by isolating web applications from the main operating system. By creating controlled environments, it minimizes the risk of malware, data breaches, and other vulnerabilities.
As web technologies evolve, the importance of browser sandboxing continues to grow, offering developers and users alike a safer browsing experience.
However, it is always best advised to use an online Browser Sandbox like BrowserStack Live for better security and real like experience without the hassle of any additional setups.