Most Selenium testers trust what they see in DevTools. Inspect the element, copy the XPath, paste it into a script, and the locator should work. The logic feels solid because the element is visible, the DOM shows it, and tests usually pass.
Then a build fails. The same element is on the page, nothing in the code changed, yet NoSuchElementException appears. The test may pass after a reload or fail without explanation.
I went through the same cycle until it became obvious. The XPath I copied was accurate only for the initial DOM, not the rendered state after scripts, styles, and interactions.
Once I started using Chrome extensions, I saw the DOM the way Selenium sees it. Dynamic attributes, hidden nodes, runtime inserts. The extensions reveal how elements behave after rendering, help generate resilient XPath, and reduce the trial-and-error of finding a locator that survives UI changes.
Overview
7 Best Chrome Extensions to find XPath in Selenium
- SelectorsHub: Generate reliable XPath and CSS selectors with automatic suggestions for dynamic web elements.
- XPath Finder: Locate unique XPath for elements and copy them easily for Selenium automation.
- Scraper: Extract data and XPath from web pages quickly to use in automation or analysis.
- Relative XPath Helper: Quickly create relative XPath expressions for elements without relying on absolute paths.
- Xpath Helper: Test and validate XPath expressions directly in the browser for immediate feedback.
- Xpather: Highlight elements and generate XPath in real time, supporting dynamic and complex DOM structures.
- TruePath: Find accurate and stable XPath for elements, even in highly dynamic or nested DOMs.
In this article, I will show the top Chrome extensions that make XPath discovery faster and more reliable.
What is XPath
XPath is a way to identify and navigate elements inside a webpage’s DOM. It describes the path to a specific node, so a test script can interact with it.
Testers use XPath because many elements do not have stable IDs or class names, especially in modern frameworks. XPath lets them locate elements based on text, attributes, structure, or relationships, which makes it useful for dynamic UIs where other locators fail.
How to Find XPath in Chrome Using Selenium?
To find XPath in Chrome, testers usually inspect the element directly in DevTools. Chrome shows the DOM structure and attributes, so the locator can be copied or refined. This is the fastest way to understand how an element is represented on the page.
Follow these steps to find XPath in Chrome for Selenium:
- Open the page in Chrome
- Press Right-click > Inspect on the target element
- In DevTools, highlight the element in the Elements panel
- Right-click the element node
- Select Copy > Copy XPath or Copy > Copy full XPath
- Paste the locator into Selenium code for testing
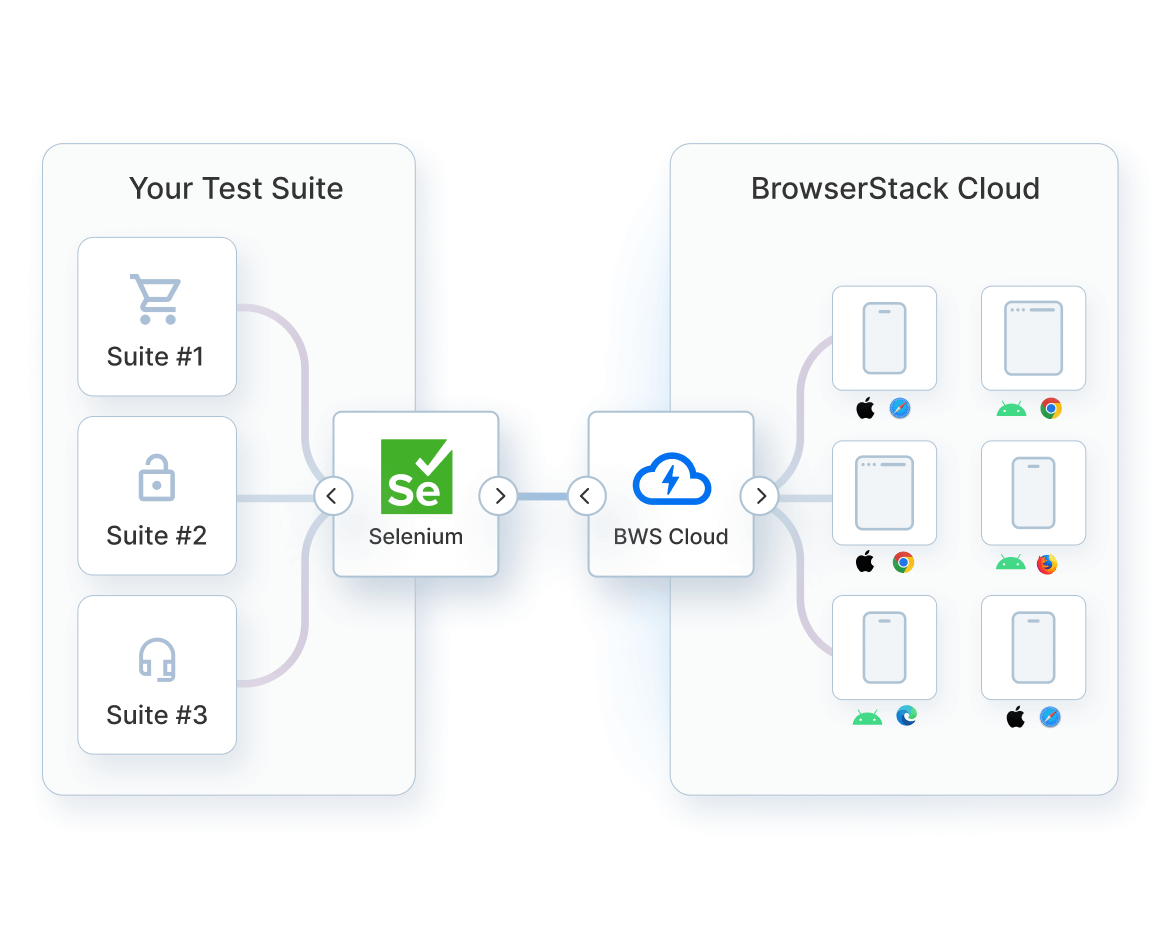
Finding the XPath in Chrome is only the first step. The real challenge is whether the same locator holds up across different Chrome versions, OS combinations, and device types.
That is where tools like BrowserStack make a difference. The same XPath can be executed on real browsers and real devices, so any variation in loading, layout, or rendering becomes visible before the script reaches production.
Top 7 Chrome Extensions to find Xpath in Selenium in 2026
XPath is a crucial locator in Selenium, essential for identifying dynamic and complex elements in the DOM like ID, Name, Class name, Link text, etc. It comes in two types: Absolute and Relative, each suitable for different scenarios. To simplify XPath generation, various Chrome extensions can efficiently locate elements, reducing manual effort.
The below-mentioned Chrome Extension tools reduce the manual effort required, allowing for quicker and more accurate XPath generation.
December 2025 Update: We have fact checked the entire article and updated the Chrome Extensions list to reflect the best options.
1. SelectorsHub
SelectorsHub is a free XPath and CSS selectors plugin. It is one of the best plugins for generating XPath, CSS selectors, JS path, JQuery, Playwright selectors, and various other types of possible selectors. SelectorsHub has various features where it helps to generate and verify our XPath.
It can deal with iframes, nested iframes, shadow DOM, nested shadow DOM, SVG elements, and dynamic and invisible elements. It also helps to generate XPath manually by auto-suggesting.
Steps to install and use SelectorsHub Plugin:
- Download the SelectorsHub plugin from their official website.
- Add the plugin to your browser and restart the browser.
- Navigate to a website, right-click on an element, and select inspect. SelectorsHub will be the last tab in the dev tools.
- Copy and paste the desired XPath in your automation code.
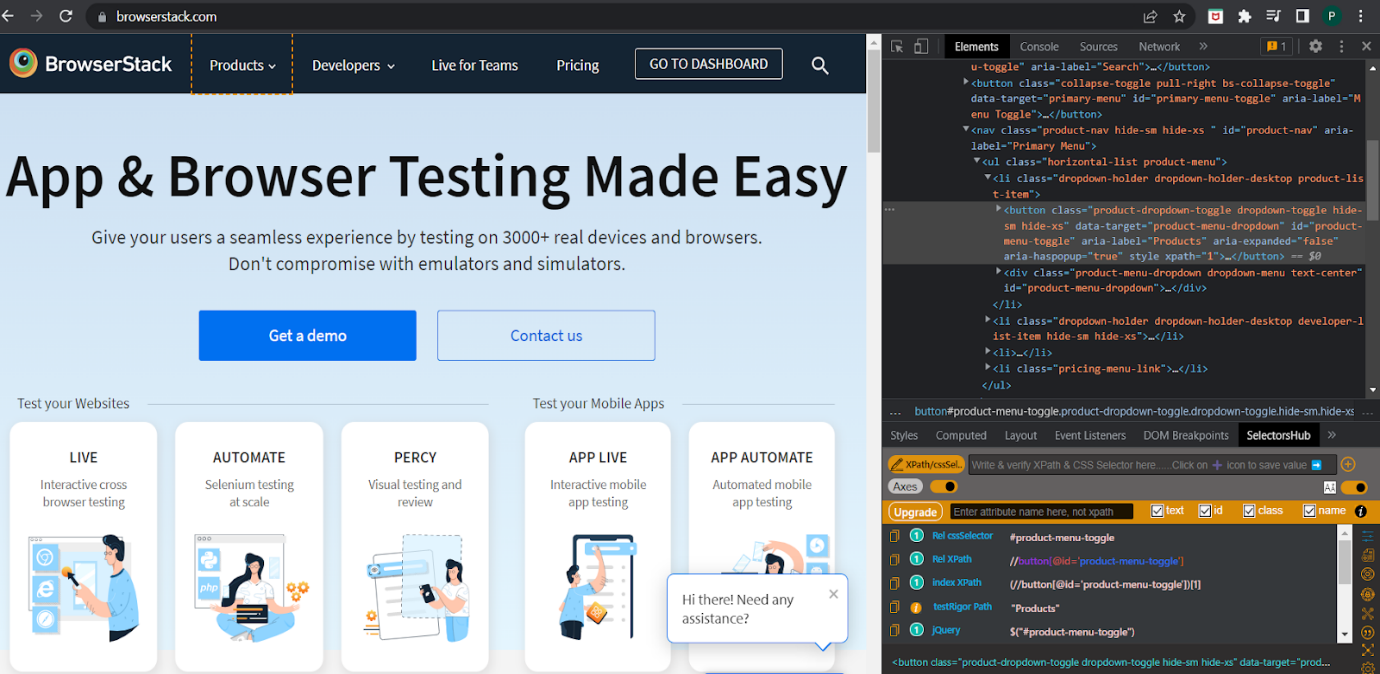
2. XPath Finder
XPath Finder helps locate unique XPath expressions for elements on a webpage. It highlights the selected node in real time and shows the XPath clearly, so testers can copy it directly into Selenium scripts. It is useful when elements do not have stable IDs or when other locators fail.
Steps to install and use XPath Finder:
- Open Chrome Web Store
- Search for XPath Finder
- Click Add to Chrome
- Confirm by selecting Add Extension
- Once installed, refresh the page and start inspecting elements
Read More: Quick XPath Locators Cheat Sheet
3. Scraper
Scraper acts like a web scraper used to extract data from web pages and store them into Google spreadsheets. Scraper is simple and easy to use. It is a Google Chrome extension and it comes with two options to extract data from any part of a web page, Xpath or JQuery selector.
Steps to install and use Scraper Plugin :
- Add the plugin to your browser from Chrome Web Store
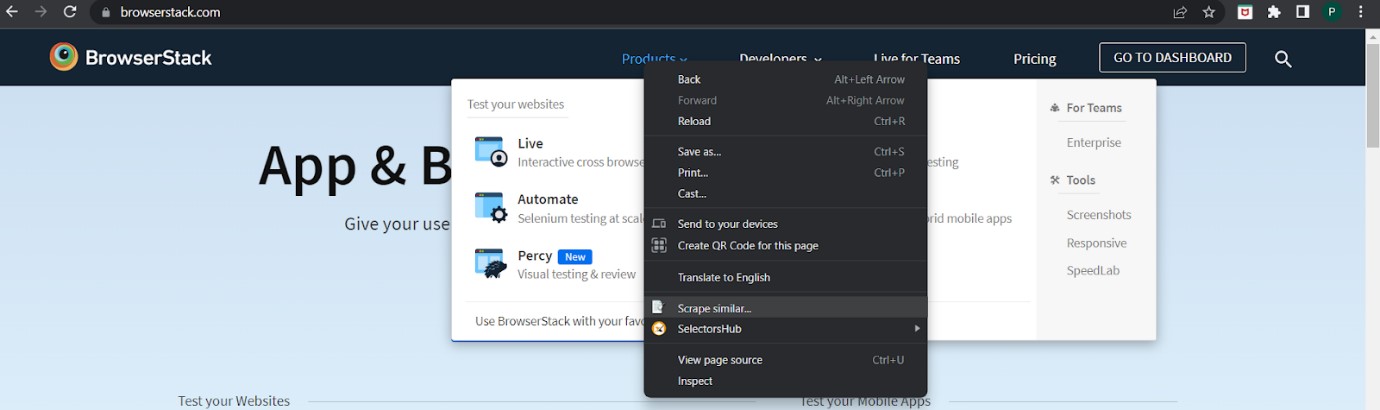
- Right click on an element you want to inspect and click on scrape similar
- A Scraper window gets and then you can generate the xpath of the selected element.
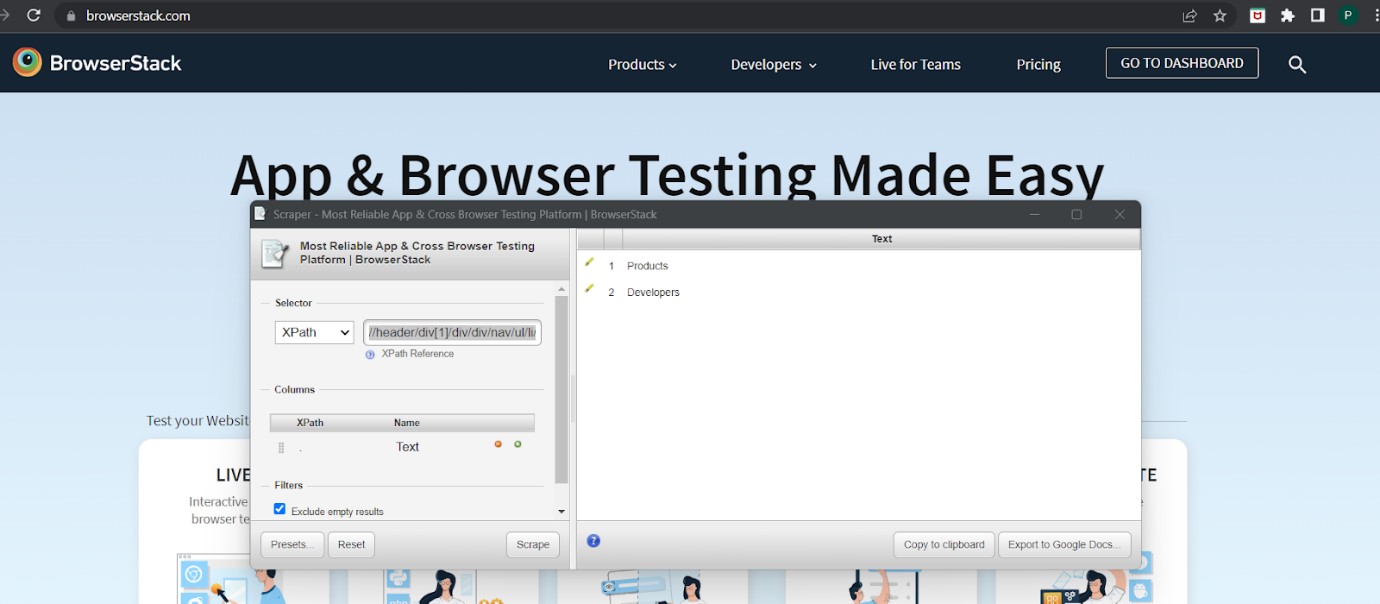
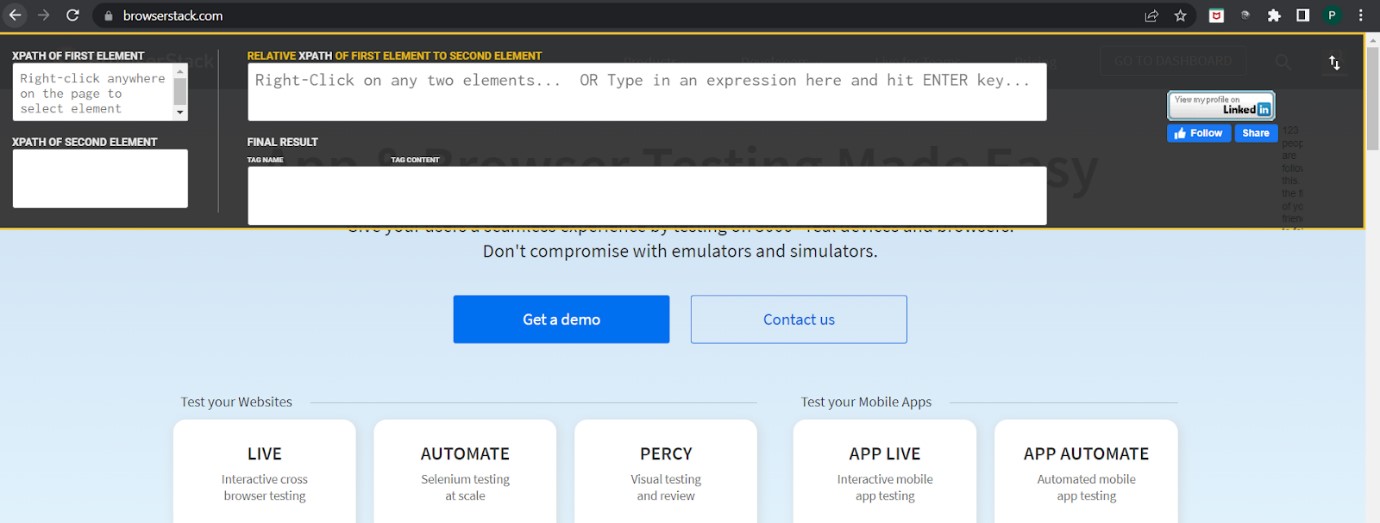
4. Relative XPath helper
The Relative XPath Helper plugin helps to find the relative Xpath between two web elements.
It is easy to use as all you have to do is right-click on the elements for which you want the relative xpath and create or edit the xpath as per the requirement.
Steps to install and use Xpath Helper Plugin :
- Add the plugin to your browser from Chrome Web Store
- Open the application to inspect and click on the relative Xpath helper plugin
- Right click on the element for which Xpath has to be generated.
5. Xpath Helper
Xpath Helper is another top Chrome extension that generates, edits and evaluates Xpath. It is the easiest plugin to use compared to other plugins. You just have to click on the console and edit or generate your xpath.
Steps to install and use Xpath Helper Plugin :
- Add the plugin to your browser from the Chrome Web Store and restart the browser
- Open the application you want to inspect and Press Ctrl+Shift+X or Press Xpath helper button in toolbar
- Press Shift button and mouse hover the elements you want to inspect. Xpath is generated in the console . We can also edit the xpath as required and see the desired xpath in the results window.
- Again press Ctrl+Shift+X to close the console
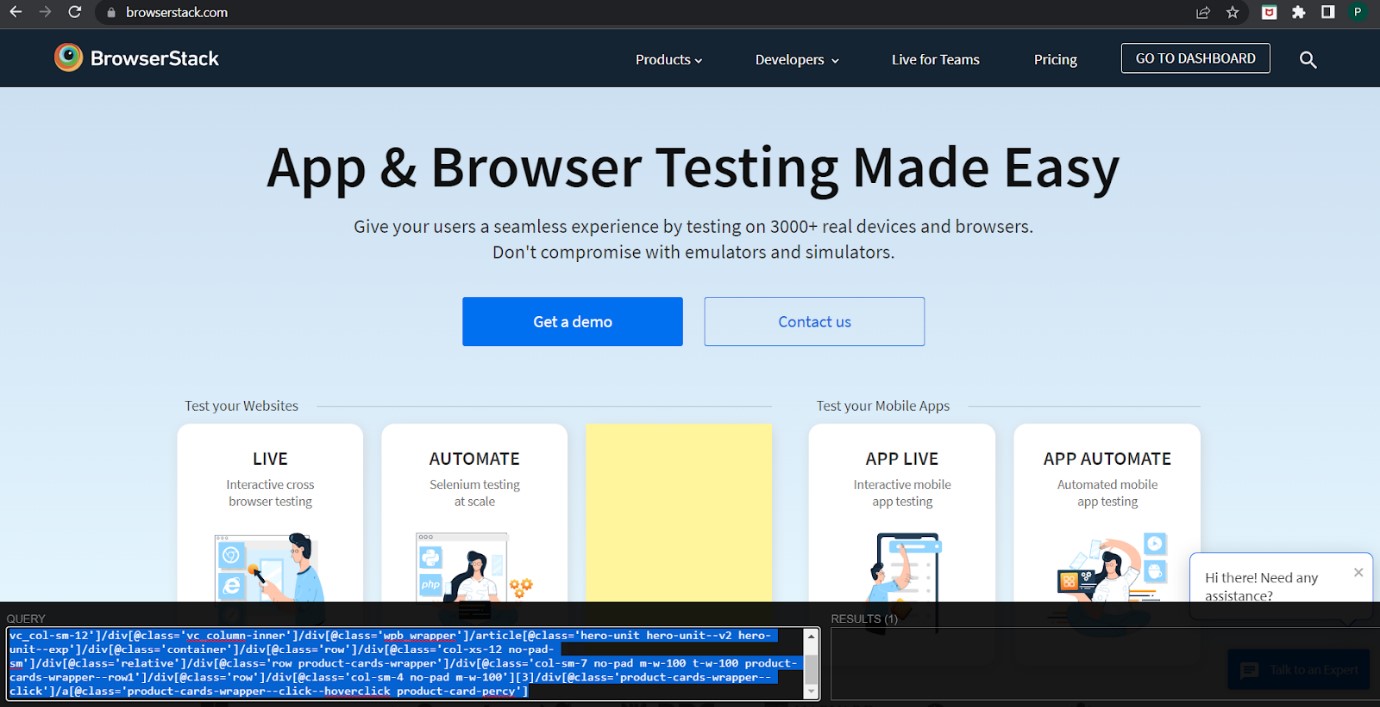
6. Xpather
Xpather plugin operates on the current document and highlights the matched element. It also displays all the matched elements on the right side bar. It supports Xpath 2.0.
Steps to install and use Xpather Plugin:
- Add the plugin to your browser from the Chrome Web Store
- Open the application to inspect and click on the Xpather plugin
- Enter the Xpath on the text box and search. It will highlight the matched element and display all the matched elements at the right sidebar.
7. Truepath
Truepath Chrome extension generates relative Xpath based on various attributes like Id, href,src,class, name,title,index etc. It is efficient as it provides relative Xpaths based on multiple attributes.
Steps to install and use Truepath Plugin :
- Add the plugin to your browser from Chrome Web Store
- Open the application to inspect and click on the Truepath plugin
- Right click on the element to inspect and click on Relative xpath
- A Truepath window will display once a matching element or elements are found. If no matching element is found then no window will be displayed.
Way Ahead: How to Use XPath in Selenium?
Before you learn how to use XPath in Selenium, understand its types.
- Absolute XPath: Direct path from the root, less adaptable to changes.
- Relative XPath: Starts from any point in the document, more robust and flexible.
Here’s how you can use XPath in multiple ways in Selenium to locate elements:
- Using Attributes: Locate elements robustly with attributes in XPath, e.g., //form[@id=’loginForm’]/input[3]. Use multiple attributes for precise targeting, like //input[@name=’name’][@value=’Last Name’].
- Logical Operators: Enhance selection flexibility using logical operators, such as //input[@id=’name’ or @name=’name’] to handle multiple possible attribute values.
- Using Text: Search for elements based on their text content, for example, //a[text()=’Click Me’], and use wildcards to broaden the search, like //*[text()=’Click Me’].
Why Validate XPath on Real Browsers and Devices
XPath that works in local Chrome can still break on real user environments. Browsers handle layout, rendering, and timing differently, especially on devices with smaller screens or slower CPUs. Even a tiny shift in the DOM can cause Selenium to lose the element and fail the test.
Validating XPath on real browsers and devices shows how the locator behaves when pages load differently, animations delay elements, or components render in a different order. The more conditions it survives, the more stable the tests become.
Tools like BrowserStack make this validation practical at scale. You can run the same script across many Chrome versions, operating systems, and device profiles without changing the code. This reveals where XPath holds up and where it needs refinement, long before the failures reach CI or production.
Here are some core features of BrowserStack that help validate XPath on real browsers:
- Selenium Grid on Cloud: Run Selenium tests on multiple real devices and Chrome versions without maintaining your own grid.
- Parallel testing: Execute the same XPath across multiple environments at once to see where it breaks.
- Local environment testing: Test staging or localhost builds without deploying, which speeds up validation.
- Location and device settings: Switch screen sizes, orientations, and network conditions to see how rendering affects XPath.
- Test reporting and analytics: View failures, screenshots, and logs to understand how DOM and timing affected the locator.
Conclusion
Finding the right XPath is critical for stable Selenium tests. Modern web pages render dynamically, change attributes, and introduce delays that make copied locators unreliable. Using tools and techniques to inspect the DOM carefully ensures that your XPath is accurate and resilient, reducing flaky tests and saving hours of debugging.
Testing these locators on BrowserStack takes stability a step further. By running scripts across real browsers, devices, and configurations, you can see how XPath behaves in production-like conditions. This not only uncovers hidden issues early but also ensures that your Selenium tests remain robust, reliable, and ready for any environment.