Many testers assume XPath in Selenium is easy—inspect an element, copy the XPath, and move on.
I thought the same until a minor UI update broke half my tests in one run. Suddenly, every copied XPath failed, and I spent hours regenerating locators that kept breaking again.
After trying absolute paths, relative paths, and every quick fix I could think of, nothing stuck.
That’s when I realized the problem wasn’t XPath itself—it was not knowing how to write stable, flexible locators.
Overview
XPath in Selenium is a locator strategy used to navigate the HTML structure of a webpage and find elements based on their hierarchy, attributes, or text. It’s especially useful when elements don’t have unique IDs or stable CSS selectors.
How to Find XPath in Chrome
- Right-click the element and select Inspect to open DevTools.
- In the Elements panel, right-click the highlighted HTML node.
- Choose Copy → Copy XPath for the full XPath (absolute) or Copy → Copy full XPath depending on Chrome’s version.
- Prefer manually crafting relative XPath for stability instead of relying on auto-generated ones.
How to Find Elements by XPath in Selenium
- Use driver.findElement(By.xpath(“your_xpath_here”)) for locating a single element.
- Use driver.findElements(By.xpath(“your_xpath_here”)) to fetch multiple matching elements.
- Apply functions like contains(), starts-with(), and text() to build flexible, robust XPaths.
- Combine attributes (e.g., //button[@type=’submit’ and contains(@class,’primary’)]) for more reliable targeting.
This guide breaks down how to find elements with XPath the right way, with examples you can apply immediately.
Understanding XPath
XPath is a query language used to navigate and extract information from XML documents—and because HTML is structured similarly, it works seamlessly for locating elements in Selenium tests.
It allows testers to traverse the DOM and identify elements using paths, conditions, and attributes, making it especially useful when elements lack unique IDs or stable selectors.
As David Auerbach, a software tester with over 10 years of experience, explains, XPath gives testers the flexibility to pinpoint elements through logical paths and conditions, making it an essential tool when modern web applications don’t provide reliable or unique selectors.
Syntax of XPath
Below is the syntax for Xpath:
Xpath =//tagname[@Attribute=’value’]
Where:
- // selects nodes anywhere in the document.
- tagname is the name of the HTML tag you want to target.
- @ refers to an attribute of that tag.
- attribute is the attribute name.
- value is the value assigned to that attribute.
To dive deeper into XPath fundamentals, check this article on Effective ways to use XPath in Selenium.
Before diving into XPath functions, here’s a simple example:
To locate a button like this:
<button class="login-btn">Login</button>
You can use the following XPath:
//button[@class='login-btn']
This selects the <button> element whose class attribute is login-btn.
As you apply XPath in real Selenium test suites, validating your locators across different browsers becomes essential. XPath behavior and page structure can vary subtly between environments.
Platforms like BrowserStack Automate lets you run Selenium tests on real browsers and devices, ensuring your XPath locators stay reliable under true user conditions.
How to find XPath in Chrome
Follow the steps below to find the XPath in Chrome.
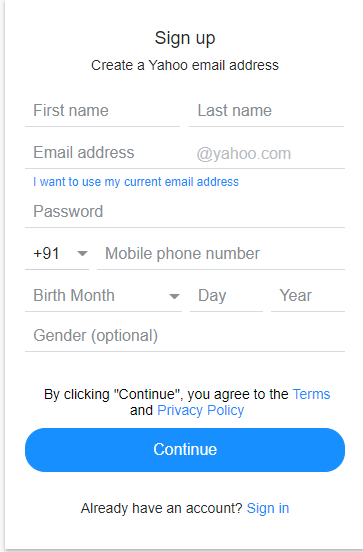
- Launch Google Chrome and navigate to yahoo.com to create a yahoo account and locate the fields using XPath.
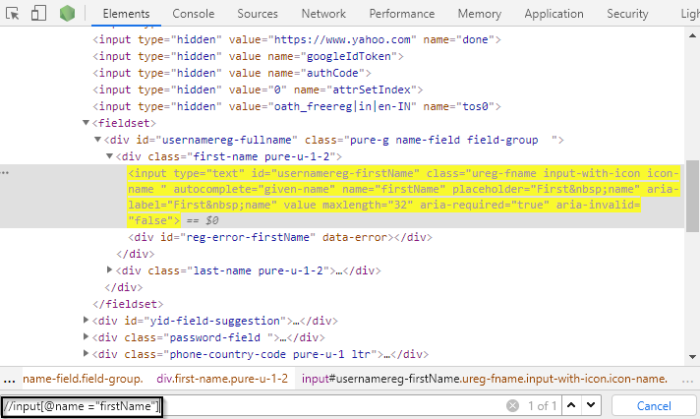
- Go to the First name tab and Right-click >> Inspect.
- On inspecting the web element, it will show an input tag and attributes like class and id.
- Use the id and these attributes to construct XPath, which, in turn, will locate the first name field.
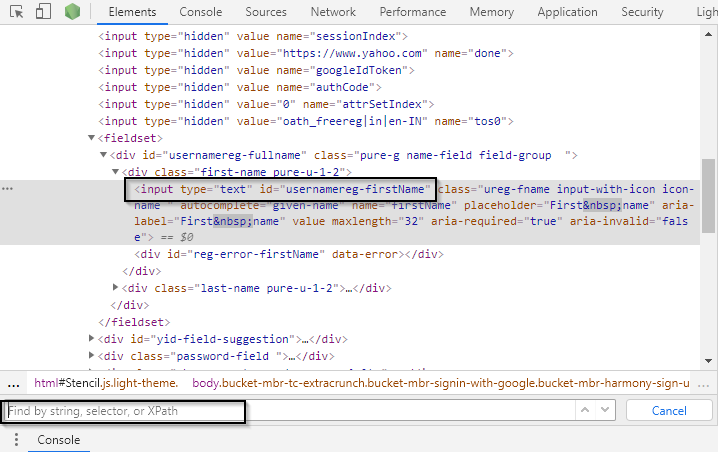
- Let’s write XPath in the elements tab.
Note: Use Ctrl+F to write XPath in the elements tab, as shown below.
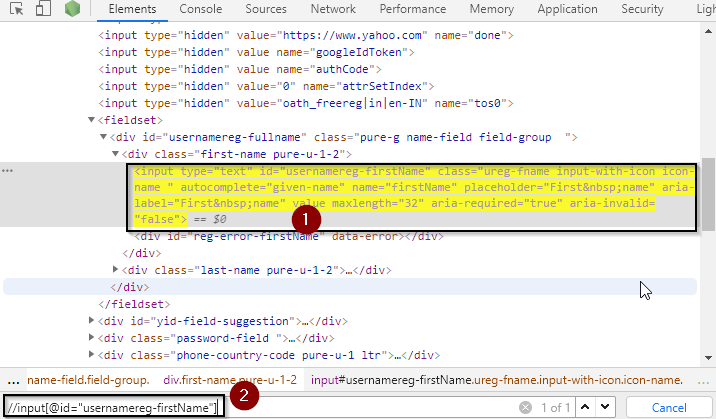
As seen above, a simple XPath is used to locate the firstName tab. Based on the XPath syntax, first use // which means anywhere in the document. Here, input is the tag name that has an id attribute with the value “usernamereg-firstname”.
On writing the XPath, it has highlighted the element, which implies that this particular element was located using XPath.
Note: One can also locate the same element using the name attribute, as it has a locator value for the name tag as well. Using the name locator, the XPath is:
//input{@name=”firstname”]Refer to the snapshot below for clarity:
How to find elements by XPath in Selenium: Example
Now let’s try automating this using Selenium. Here is the Java program written in Eclipse for the same:
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
public class XPathexample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "Your-Chrome-Driver-Path"); // Provide the path to your chrome driver. Make sure your chrome driver version is updated.
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.manage().window().maximize();
driver.manage().deleteAllCookies();
driver.manage().timeouts().pageLoadTimeout(40, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
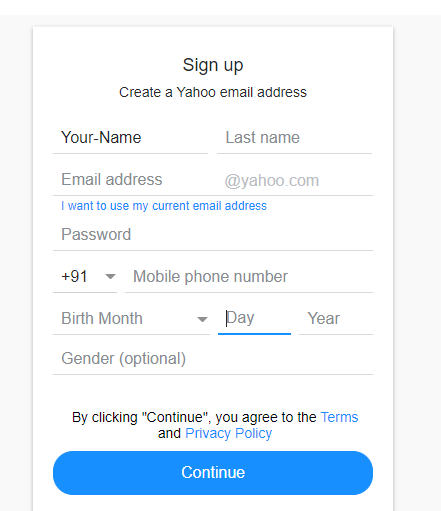
driver.get("https://login.yahoo.com/account/create");
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='usernamereg-firstName']")).sendKeys("Your-Name"); // Will send values to First Name tab
}
}On executing the code above, Chromedriver will launch Google Chrome, navigate to Yahoo signup page and enter the value for first name tab as shown below.
Read More: findElement vs findElements in Selenium
Similarly, fill in all the details and find elements by XPath in Selenium.
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
public class XPathexample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "Your-Chrome-Driver-Path"); // Provide the path to your chrome driver. Make sure your chrome driver version is updated.
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.manage().window().maximize();
driver.manage().deleteAllCookies();
driver.manage().timeouts().pageLoadTimeout(40, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
driver.get("https://login.yahoo.com/account/create");
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='usernamereg-firstName']")).sendKeys("Your-Name"); // Will send values to First Name tab
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='usernamereg-lastName']")).sendKeys("Your-Last_name"); //xpath for last name box
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='usernamereg-yid']")).sendKeys("email@yahoo.com"); //xpath for email box
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='usernamereg-phone']")).sendKeys("123456789"); //xpath for phone number box
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//select[@id='usernamereg-month']")).click(); //xpath for usermonth box
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='usernamereg-day']")).sendKeys("01"); //xpath for userday box
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='usernamereg-year']")).sendKeys("1999");// xpath for user year
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//button[@id='reg-submit-button']")).click();// xpath for submit button
}
}On executing the above code, it will fill in all the details and hit the Continue button to complete the form submission.
Once you understand how to locate elements with XPath, the next step is ensuring these locators behave consistently across real browsers and devices.
Why Test Elements in Selenium on Real Device Cloud?
Testing elements in Selenium on a real device cloud is essential for several reasons:
- Realistic Testing Conditions: Real device clouds provide access to a broad spectrum of devices and environments, ensuring tests reflect actual user conditions accurately.
- Enhanced Security: Maintained with high security standards, real device clouds offer secure, isolated testing environments, minimizing data breach risks.
- Broad Browser and OS Coverage: Helps identify compatibility issues across various browsers and operating systems, enhancing user experience.
- Performance Insights: Real devices yield authentic performance data essential for optimizing application responsiveness.
- Scalability and Accessibility: Facilitates scalable and accessible testing, suitable for distributed teams.
- CI/CD Integration: Integrates smoothly with CI/CD pipelines for continuous testing and early issue detection.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Although initially more costly, it saves on long-term expenses related to fixes and support.
Enhance Your Selenium Testing with BrowserStack Automate
XPath reliability can vary across browsers, devices, and rendering engines, which means local testing alone often isn’t enough.
BrowserStack Automate helps you validate XPath locators under real user conditions by running your Selenium tests on real browsers and real devices in the cloud.
With BrowserStack Automate, you can:
- Test XPath locators across a wide range of real browsers, devices, and OS versions.
- Identify flaky or environment-specific locator issues early in the pipeline.
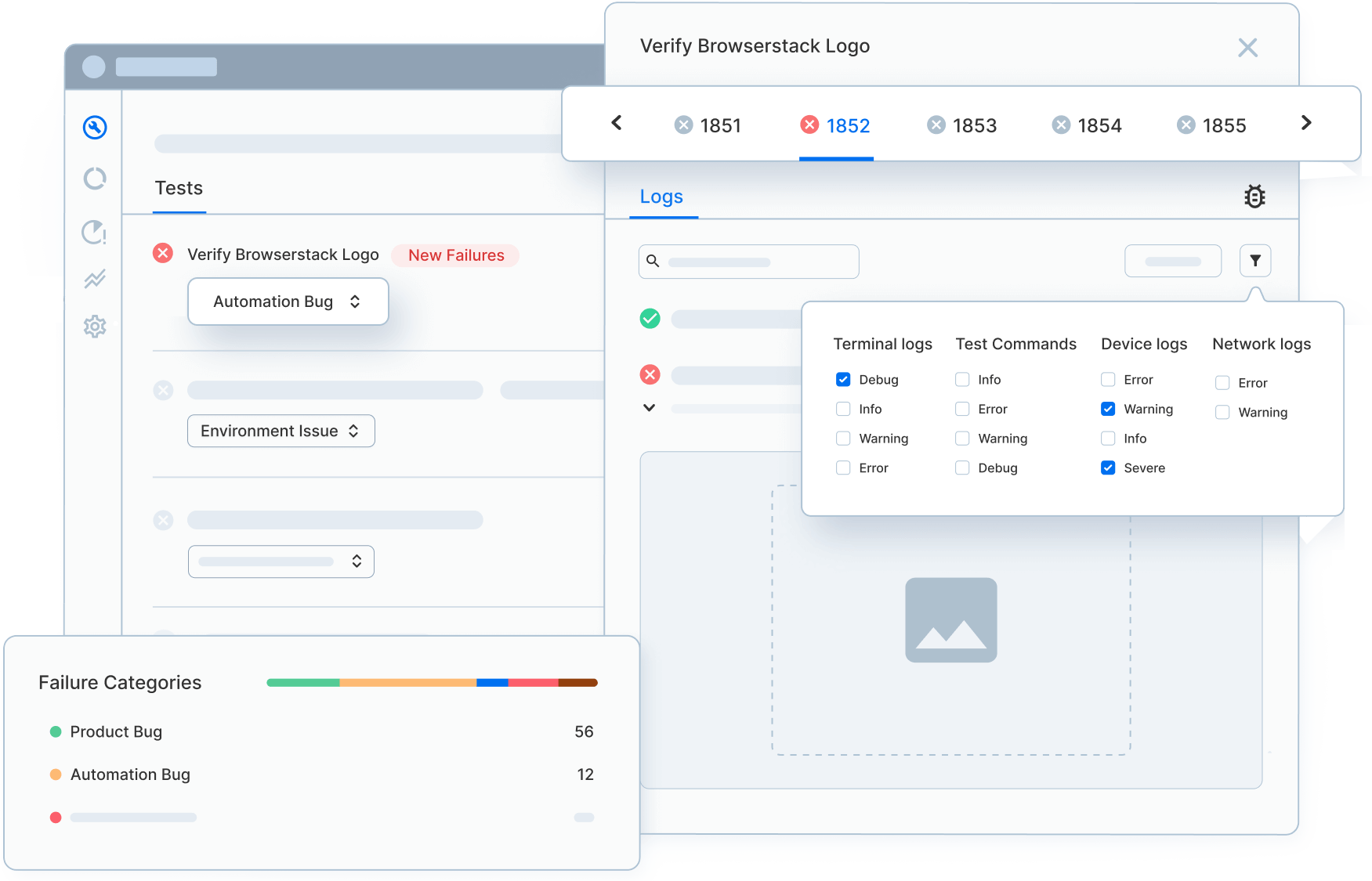
- Debug faster using test artifacts like video recordings, screenshots, console logs, and network logs.
- Validate DOM behavior and page-load timing to ensure XPath remains stable in dynamic applications.
- Scale test execution without maintaining any local infrastructure.
By integrating BrowserStack Automate into your workflow, you ensure your XPath-based tests are reliable, scalable, and production-ready across all real-world environments.
Conclusion
While this post has discussed a variety of ways to locate elements on a web page using the XPath locator in Selenium Webdriver, one should use Occam’s razor – the simplest and logical options while selecting elements to ensure minimal rework in the event of a page redesign.
Try running the code detailed above using Selenium. Bear in mind that Selenium tests must be run on a real device cloud instead of emulators or simulators to get completely accurate results. BrowserStack’s Cloud Selenium Grid of 3500+ real browsers and devices allows testers to automated visual UI tests in real user conditions. Simply sign up, select a device-browser-OS combination, and start running tests for free.
Follow-up Read: How to Find Element by Text in Selenium: Tutorial