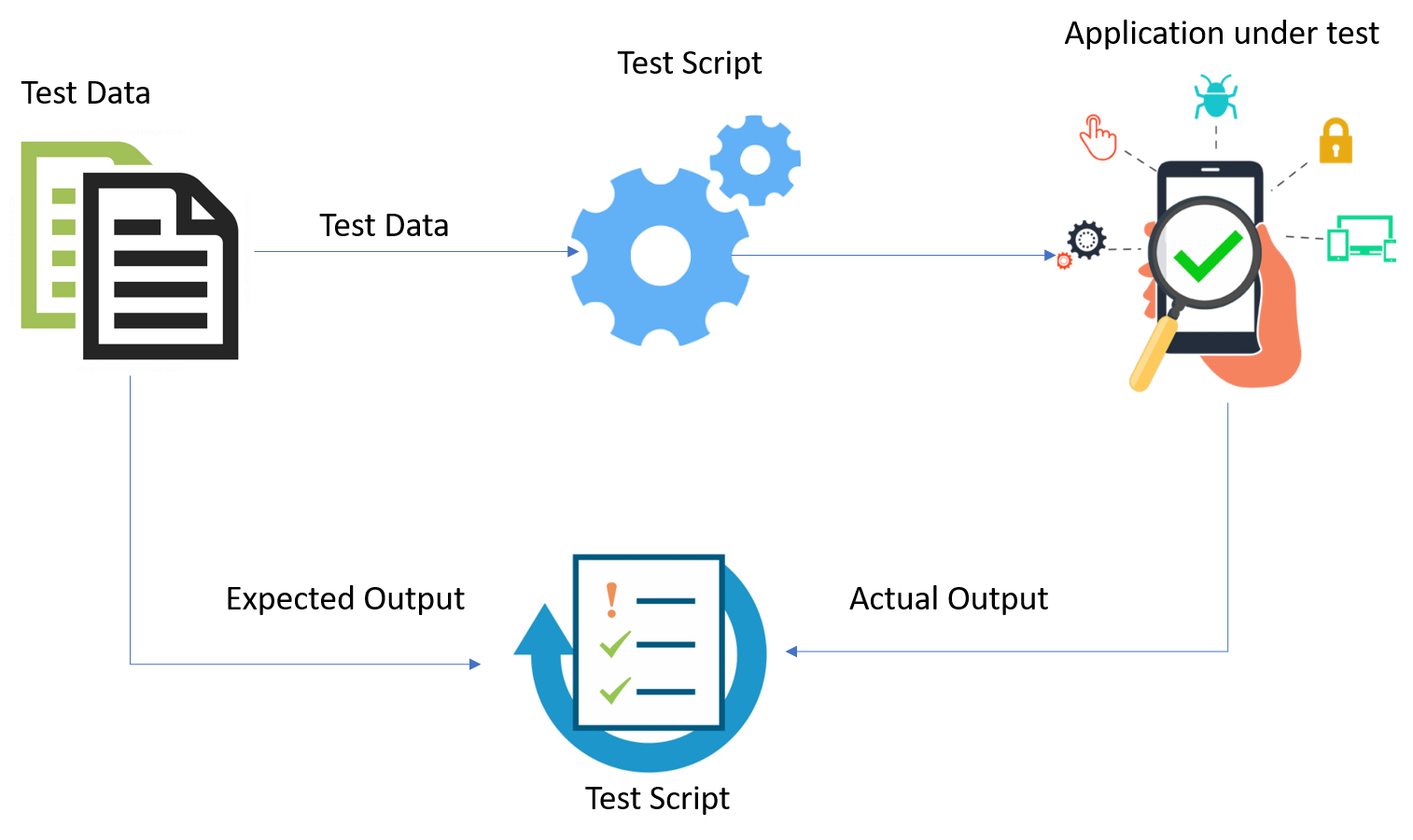
As new code is added, the number of required tests grows to ensure smooth functionality. This can quickly become overwhelming, leading testers to reduce coverage and risk introducing defects. Data-driven testing helps prevent this by streamlining the process and maintaining thorough validation.
Overview
A Data-Driven Framework in Selenium is a testing approach where test data is separated from the test scripts, allowing the same test logic to run with multiple data sets.
Key Characteristics of a Data-Driven Framework in Selenium
- Separation of Test Data and Scripts: Test data is stored externally (Excel, CSV, DB), independent of test logic.
- Reusability: The same test script can run with multiple sets of input data.
- Scalability: Adding new test data does not require changing the test code.
- Maintainability: Centralized data handling reduces script duplication and simplifies updates.
- Flexibility: The framework can work with various data sources such as Excel, JSON, or databases.
- Improved Test Coverage: Running tests with diverse data sets helps uncover defects that might otherwise be missed.
This article explains the importance of data-driven tests, outlines the steps to implement them, and highlights key dos and don’ts to follow.
Importance of Data-Driven Tests
Data-driven tests provide efficiency, scalability, and stronger coverage by separating test logic from test data. Here are the key benefits:
- Reduced Test Scripts: A single script can run with multiple data sets, minimizing duplication.
- Better Test Coverage: Running the same test with varied inputs helps identify edge cases and hidden defects.
- Improved Efficiency: Test creation, updates, and execution become faster.
- Easy Maintenance: Any change in test data requires updates only in the external data file, not in the script.
- Reusability: Test scripts can be reused across multiple scenarios without rewriting code.
- Scalability: Adding new test cases becomes simple by just extending the data set.
- Consistency and Accuracy: Automated execution with structured data reduces human error in repetitive testing.
What is Data Driven Testing Framework in Selenium?
A Data-Driven Framework is used to drive test cases and suites from external data sources such as Excel (xls, xlsx) or CSV files. In Selenium, this framework separates the test data from the actual test script, allowing flexibility and easier maintenance.
Since the test logic is independent of the data set, testers can modify or extend test cases without altering the underlying code. For instance, if changes are required in the login functionality, only the login-related test data needs to be updated, without affecting other features dependent on the same code.
Additionally, new test parameters can be added effortlessly by including more usernames and passwords in the external data file. This approach improves reusability, scalability, and coverage.
To scale these data-driven tests across thousands of real browsers and devices, teams can leverage BrowserStack Automate. It enables seamless execution of Selenium tests in parallel, ensuring broader coverage, faster feedback, and more reliable results in real-world environments.
Data Driven Testing Example
This example will demonstrate how to read the data from excel files and perform data driven testing using Selenium. WebDriver does not directly support data reading of excel files. Therefore, one needs to use a plugin such as Apache POI for reading/writing on any Microsoft office document.
- To download Apache POI Jar files click here. Download the zip file or tar file as per requirement and place them along with the set of Selenium JARs and configure your build path.
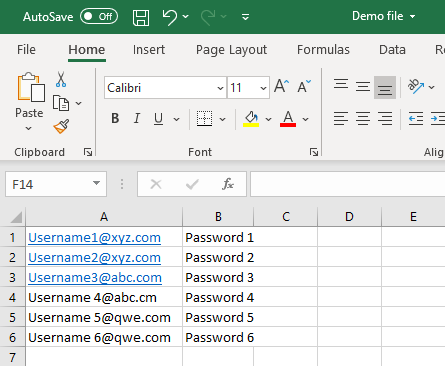
Here is an example that includes using an Excel file as the data source. The sheet contains multiple combinations of usernames and passwords, which are read and executed during the test.
The task here is to enter all the combinations of username and passwords into the login field in order to test the functionality. Here’s how to do that.
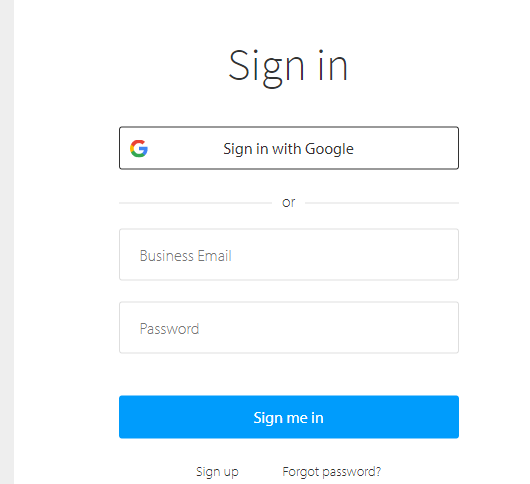
Here, the target is to enter all these combinations of username and password into the Browserstack Sign in page as shown below.
Let’s write a code snippet to read the data files.
Step 1: Go to the Eclipse IDE and create a project. Add all the dependencies for TestNG, Selenium and Apache POI.
Step 2: Create a class file to write the functionality.
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterMethod;
import org.testng.annotations.DataProvider;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class ExcelExample{
@Test(dataProvider="testdata")
public void demoClass(String username, String password) throws InterruptedException {
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "Path of Chrome Driver");
Webdriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.get("<a href="https://www.browserstack.com/users/sign_in</a>");
driver.findElement(By.name("user[login]")).sendKeys(username);
driver.findElement(By.name("user[password]")).sendKeys(password);
driver.findElement(By.name("commit")).click();
Thread.sleep(5000);
Assert.assertTrue(driver.getTitle().matches("BrowserStack Login | Sign Into The Best Mobile & Browser Testing Tool"), "Invalid credentials");
System.out.println("Login successful");
}
@AfterMethod
void ProgramTermination() {
driver.quit();
}
@DataProvider(name="testdata")
public Object[][] testDataExample(){
ReadExcelFile configuration = new ReadExcelFile("Path_of_Your_Excel_File");
int rows = configuration.getRowCount(0);
Object[][]signin_credentials = new Object[rows][2];
for(int i=0;i<rows;i++)
{
signin_credentials[i][0] = config.getData(0, i, 0);
signin_credentials[i][1] = config.getData(0, i, 1);
}
return signin_credentials;
}
}In the above code, there is a “TestDataExample() method” in which the user has created an object instance of another class named “ReadExcelFile”. The user has mentioned the path to the excel file. The user has further defined a for loop to retrieve the text from the excel workbook. But to fetch the data from the excel file, one needs to write a class file for the same.
Try Running Selenium Tests on Cloud for Free
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class ReadExcelFile{
XSSFWorkbook work_book;
XSSFSheet sheet;
public ReadExcelFile(String excelfilePath) {
try {
File s = new File(excelfilePath);
FileInputStream stream = new FileInputStream(s);
work_book = new XSSFWorkbook(stream);
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
public String getData(int sheetnumber, int row, int column){
sheet = work_book.getSheetAt(sheetnumber);
String data = sheet.getRow(row).getCell(column).getStringCellValue();
return data;
}
public int getRowCount(int sheetIndex){
int row = work_book.getSheetAt(sheetIndex).getLastRowNum();
row = row + 1;
return row;
}In the code above, the user has used Apache POI libraries to fetch the data from the excel file. Next, it will point to the data present in the excel file and then enter the relevant username and password to the sign in page.
Note: The same thing can be done using a Data provider in TestNG. But to fetch the data from the Excel sheet, the user needs Apache POI jar files.
Note: Please enter one valid credential to test.
Advantages of Data Driven Testing Framework
A Data-Driven Testing Framework offers multiple benefits that enhance efficiency, scalability, and accuracy in test automation:
- Allows testing of the application with multiple sets of data values during regression testing
- Separates the test case data from the executable test script
- Allows reusing of Actions and Functions in different tests
- Generates test data automatically. This is helpful when large volumes of random test data are necessary
- Results in the creation of extensive code that is flexible and easy to maintain
- Lets developers and testers separate the logic of their test cases/scripts from the test data
- Allows execution of test cases several times which helps to reduce test cases and scripts
- It does not let changes in test scripts affect the test data.
By incorporating data-driven testing using Selenium, testers can refine their test cases for more efficient execution. This shortens timelines, makes their lives easier and results in more thoroughly tested and better quality software.
Conclusion
A Data-Driven Testing Framework in Selenium simplifies test automation by separating data from scripts, making tests more reusable, scalable, and easier to maintain. By enabling the same script to run across multiple data sets, it ensures broader test coverage, improved efficiency, and faster detection of defects.
To amplify these benefits, teams can leverage BrowserStack Automate. It enables execution of Selenium tests on over 3500+ real browsers and devices, ensuring true cross-platform coverage.
With powerful parallel testing, test cycles run significantly faster, while seamless CI/CD integrations with tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and Azure DevOps make automation part of the delivery pipeline.
Backed by a secure, reliable cloud infrastructure, BrowserStack also provides advanced debugging tools such as logs, screenshots, and video recordings, helping teams identify and resolve issues quickly.
By combining data-driven testing with BrowserStack Automate, teams can release software with greater speed and real-world reliability.