DevOps and Agile have brought development and QA closer together, but the steps in between can sometimes lead to friction between developers and testers.
Overview
Benefits of Collaboration between developers and testers
- Early Issue Detection: Problems are identified early, saving time and cost.
- Improved Communication: Ensures clear alignment on goals and requirements.
- Efficient Test Planning: Collaborative planning leads to comprehensive test coverage.
- Better Code Quality: Feedback from testers helps developers optimise code.
- Faster Feedback Loops: Speeds up the development cycle.
- Continuous Improvement: Knowledge sharing leads to improved processes.
- Shared Understanding: Ensures alignment on project objectives across teams.
Key Aspects of Collaboration between developers and testers
- Understanding Requirements: Testers must clearly grasp requirements to design effective test cases.
- Risk Assessment: Collaborative risk analysis identifies defect-prone areas to guide testing.
- Early Involvement: Testers should engage early in design and requirements discussions.
- Communication: Open and transparent communication builds trust and strengthens teamwork.
- Shared Responsibility: Developers and testers both play a role in ensuring software quality.
- Collaboration Tools: Platforms like MS Teams, Slack, or bug tracking software enhance communication and collaboration.
This guide offers a comprehensive overview of developer-tester collaboration, focusing on key benefits, best practices, and tools for high-quality software delivery.
Why is Collaboration Important between Developers and Testers?
Collaboration between developers and testers plays a major role in ensuring that the final product is reliable, high-quality, and meets user expectations.
Here are several other reasons why collaboration is important between developers and testers:
- Early Detection of Bugs: When testers are involved early in the development process, they can help identify potential issues before code is written. Developers get quick feedback on their work, which helps catch bugs sooner, reducing rework and cost.
- Shared Understanding of Requirements: Collaborating closely ensures that both developers and testers understand the project requirements in the same way. This minimizes misunderstandings or incorrect assumptions about functionality.
- Faster Delivery: Testing can happen continuously when developers and testers work in sync (e.g., through CI/CD pipelines). This speeds up the development cycle and drives quicker releases without sacrificing quality.
- Improved Test Coverage: Testers can provide valuable input on edge cases and user scenarios developers might miss. At the same time, developers can help testers understand technical limitations, enabling more focused and practical testing.
- Better Communication: Regular interaction encourages a culture of openness and mutual respect. Developers understand the value of testing, and testers feel more empowered to raise concerns, leading to a more collaborative and less siloed team.
- Enhanced Product Quality: Ultimately, when both roles collaborate well, it leads to a better user experience. Code becomes more robust, tests more aligned with real-world usage, and the final productis more reliable and stable.
- Shift-Left Testing: Collaboration supports a “shift-left” approach. Testing earlier in the development lifecycle. This reduces the cost of fixing bugs later and promotes continuous quality improvement.
- Efficient Use of Tools and Automation: When developers and testers collaborate, they can better integrate tools for automated testing, CI/CD, and bug tracking, streamlining workflows and reducing redundancy.
Common Complaints in the Product Development Process
Given what was discussed above, there are a number of complaints that crop up in the product development team.
- Complaints about the project being finished according to guidelines but QA teams moving goalposts
It’s seen to happen to the best of teams and after working hard on a project, and completing everything to the best of their ability. While the development team might feel that the job is complete, the QA process has only kicked off and starts to find defects and issues.
Sometimes, this may be due to things breaking down in regression, or integration issues between individually well-tested modules.
- Complaints about the Dev team being unable to recreate issues raised by QA personnel.
One of the most frequent complaints of any developer is “It works fine at my end”. This can be caused by the Dev and QA teams not communicating clearly and objectively enough to understand the root cause of a problem.
Oftentimes, different deployment environments, devices, or Browser/OS configurations can lead to chaos and unreplicated bugs.
- The issues have been discovered too late to be resolved in time for the launch
DevOps is all about speed and fast feedback loops. Bugs need to be identified early enough and communicated to the dev team for a fix to be made and regression tests to run in order to get the code ready for production.
Poorly coupled processes create roadblocks to the smooth functioning of software teams.
- The QA team receives too many modules with buggy codes
QA teams are often under enormous pressure to test and verify code for production or merge. Developers might often fall into a pattern of delivering buggy code and correcting them once the QA team comes back.
This can be both a roadblock in terms of accelerating release velocity and lead to inter-departmental tension as well.
Must Read: How to Accelerate Product Release Velocity
Stakeholders of Software Development
The underlying solution to all the common challenges mentioned above is to increase collaboration and cooperation between the teams and to create a common language they can all speak. BDD is all about enabling collaboration and communication, and hence achieving advanced BDD in software development can be a good way to help QAs and Developers work together.
Before, that it is important to learn about the stakeholders of software development.
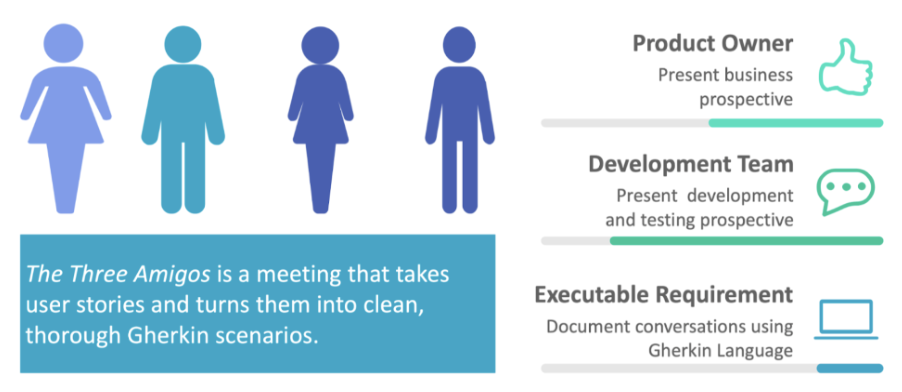
The three main stakeholders in any software development project are the Business Team, the Development Team, and the QA team who are called the “Three Amigos”.
- Business Team (BA): Has the Product Owner who analyses the business needs and defines the nature of the problem being addressed by the Product.
- Development Team (DevOps): This has the developers who work on building a product to solve the identified problem.
- QA team: This has the testers who validate whether the product satisfies the business requirements and that it works as expected for the entire range of expected
The Three Amigos
And once the requirements have been consolidated, it is the remaining two amigos, the Dev and the QA team who bear the responsibility to push the code into production.
How to empower QAs and Developers to Work Together
Here are different ways in which you can empower QAs and Developers to work together:
1. Implement Test-Driven Development (TDD)
TDD encourages writing tests before the code is written, making quality an integral part of the development process. Developers and testers can collaborate on defining test scenarios upfront, ensuring that both functional and edge cases are considered early. This proactive approach reduces rework and fosters a shared understanding.
2. Enable a comprehensive team mentality
A test-first approach might help prevent nasty surprises during the development process, but this is not enough to foster closer cooperation between QA and Dev teams.
A step forward is to create a structured system of collaboration for:
- Inferring the requirements, and reaching a consensus on what they actually mean. This helps in Requirements Coverage as a part of Test Coverage and helps the entire team be on the same page when the project is complete.
- Collaboration to create test cases. This is critical for the developers to understand where and how a test can fail and how to avoid these pitfalls. Also, this helps in easier bug replication and resolution.
- Reach an understanding of new features being developed. This is especially key during regression testing and subsequent release as the chance of things breaking and needing a regression fix is minimized.
3. Adopt a Shift-Left mindset
Getting QA involved in the software development process at the earliest is commonly called Shift Left as this moves testing to the conventional “left” of a software development process. This encourages greater collaboration and helps to increase test coverage as testers and developers can work closely to understand the scope of what needs to be tested for product release and the entire plan can be built accordingly
The teams can coordinate together to set up the Definition of Ready (DoR) and the Definition of Done (DoD) which are effectively the entry and exit conditions for a project.
SDLC
4. Use Debugging tools to share bug reports across teams
As mentioned before, one of the major roadblocks to testers and developers working together remains the “unreplicable bug”
Modern tools and systems help in creating real-time detailed test and debugging reports that enable teams to coordinate with each other and sort things out.
Tools like BrowserStack offers real devices for mobile app testing and automated app testing. Simply upload the app to the required device-OS combination and check to see how it functions in the real world.
BrowserStack offers a wide range of debugging tools that make it easy to share and resolve bugs on its products Live, Automate, App Live, and App Automate.
5. Set up feedback loops and regular meetings
Establish structured and frequent communication channels like daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, or bug triage meetings etc., to encourage open dialogue between developers and testers. These feedback loops help surface issues early, clarify misunderstandings, and align both teams on goals, timelines, and quality expectations.
6. Promote Cross-Functional Collaboration
Encourage developers and QAs to participate in each other’s workflows. For example, testers can join requirement discussions or code reviews, while developers can assist in writing or reviewing test cases. This shared involvement reduces knowledge silos, and ensures that quality becomes a collective responsibility.
Collaboration Tools for Software Testing
Here are the top tools that can facilitate collaboration between development and testing teams:
1. BrowserStack Test Management
BrowserStack Test Management is a unified tool designed to streamline test case management for QA teams and developers. It allows teams to create, organize, assign, and track test cases and execution runs efficiently. With built-in integrations for CI/CD pipelines and defect tracking tools like Jira, it promotes seamless collaboration between testers and developers. Real-time updates, visual dashboards, and historical test data ensure everyone is on the same page regarding software quality.
2. Jira
Jira is a widely adopted project management and issue-tracking tool that helps development and QA teams collaborate efficiently. It supports agile methodologies allowing users to create user stories, log bugs, and assign tasks. QA teams can link test cases or test executions, enabling tight alignment between testing activities and development progress. Its comment threads, status tracking, and automation features make it ideal for transparent, traceable collaboration.
3. Slack
Slack is a messaging platform that facilitates fast, informal collaboration among teams. Integrated with testing tools (like Jenkins, BrowserStack, etc.), it can send automated alerts on test failures, deployments, or bug reports. Testers and developers can quickly discuss issues in real time, share logs, screenshots, and links, and resolve blockers faster than through traditional email threads. Its channel-based structure allows for organized discussion per project or team.
Read More: How to use Slack Bug Reporting while Testing
Conclusion
When QA and Dev teams collaborate effectively, they don’t just build better software—they build it faster, smarter, and more reliably. The synergy between these teams drives innovation, removes friction, fosters transparency, and strengthens overall product quality. Investing in this collaboration is no longer an option but a necessity. Tools like BrowserStack Test Management facilitates this collaboration seamless by offering a shared space to manage test cases, track progress, and streamline workflows.