Modern mobile apps rely on natural gestures like swipes, pinches, long presses, and taps to create smooth user experiences. These interactions differ across platforms, devices, screen sizes, and OS versions. Testing them is essential to ensure your app works as expected for every user.
Overview
Natural app gestures and interactions include common touch actions like swiping, tapping, pinching, and dragging that users rely on to navigate mobile apps. To ensure a consistent and intuitive experience across devices, it’s essential to test gestures on mobile thoroughly under real-world conditions.
Why testing gestures on real mobile devices matters:
- Ensures accurate touch response across screen sizes and resolutions
- Captures device-specific behavior and performance
- Identifies OS-level gesture conflicts
- Validates smooth animations and transitions
- Helps detect latency or misfires in real user conditions
Key Gestures to Test:
- Swipe/Scroll: For navigating screens, scrolling lists, and dismissing items
- Pinch/Zoom: For zooming in and out on images, maps, and visuals
- Rotate: For adjusting the orientation of images or UI elements
- Drag and Drop: For moving items within the app interface
- Long Press: For revealing additional options or context menus
- Tap: For selecting, activating, or interacting with elements
Methods to Test Gestures:
- Live Testing Platforms: These platforms allow you to test on real iOS and Android devices, interact with your app using actual touch gestures, and validate gesture performance across various device and OS combinations.
- Automated Testing Tools: Tools like Appium and Espresso let you simulate gestures through scripts, run tests across multiple devices in parallel, and integrate gesture testing into your CI/CD pipelines for continuous validation.
This article explores what natural app gestures and interactions are, how they differ, and the key interaction elements to consider for iOS and Android. It also covers why testing on real devices is important, the challenges involved, and practical methods to test gestures on mobile accurately.
What Are Natural App Gestures and Interactions?
Natural app gestures and interactions are touch-based movements that users intuitively perform to navigate and control mobile apps. These gestures replicate real-world motions, making digital experiences more fluid and user-friendly.
They are generally categorized into:
- Single-finger gestures include common actions like tap (to select or activate), swipe (to navigate or dismiss), and long press (to reveal additional options).
- Multi-finger gestures involve pinch, zoom (to scale content), and rotate (to change the orientation of elements like images or maps).
These gestures form the core of how users interact with modern mobile apps and must function smoothly across all devices and platforms.
Difference between App Gestures and Interactions
App gestures and interactions are often assumed to be the same, but serve distinct purposes. While the terms are used interchangeably, understanding the difference is essential for accurate and thorough gesture testing.
App Gestures:
App gestures refer to the touch-based actions users perform on a mobile screen to trigger specific responses within an app. They are fundamental UI elements that allow users to send commands through gestures, which the app then interprets and responds to accordingly.
Example:
If a user taps the menu icon in the top-right corner of an app to open a navigation panel, that tap is recognized as a gesture. The resulting action, displaying the menu, is the app’s response to the user’s input.
Common gestures across Android and iOS include tap, swipe, scroll, pinch, rotate, long press, and drag.
App Interactions:
App interactions represent a broader layer that builds on gestures and varies based on the operating system (Android or iOS). While gestures are physical inputs, interactions encompass how the app responds based on platform-specific UI patterns, behavior, and feedback mechanisms.
Example:
The same gesture, such as a swipe, may trigger different responses on Android and iOS due to differences in system design and user expectations.
Interactions also include elements like haptic feedback, sound, or visual cues, which differ from one platform to another.
For comprehensive testing of these gestures and interactions across a wide range of real devices, BrowserStack App Live provides the perfect solution. It allows testing app gestures and interactions on actual iOS and Android devices in the cloud, ensuring an accurate user experience on every platform.
App Interaction Elements to Consider for iOS & Android
Certain UI components within mobile apps are highly gesture-sensitive and behave differently across Android and iOS. To ensure consistent performance, these elements must be thoroughly tested during mobile gesture testing:
- Graphics-Based Elements: Visual components like buttons, icons, and image galleries rely on taps, swipes, and pinches for interaction. Testing ensures these gestures trigger the right responses across platforms.
- Sliding Interfaces: Features like image sliders, carousels, and eBook readers often require horizontal or vertical swipe gestures. These should be tested for responsiveness and consistency on both platforms.
- Overflow Menus: Tapping menu icons often triggers pop-up menus or side drawers. These interactions may differ slightly in animation, layout, or behavior between iOS and Android and must be validated.
- Contextual Menus via Long Press: Long-press gestures frequently reveal additional options (e.g., edit, uninstall, app info). Testing ensures these menus appear and function correctly across different devices.
- Sound Feedback: Audio cues such as shutter sounds, alert tones, or confirmation beeps help users understand when an action is completed. These interactions should be checked to ensure they’re triggered at the right moments.
Read More: Mobile App Performance Testing Checklist
Challenges of Testing Natural Gestures & Interactions
Testing mobile gestures comes with several challenges that can impact app functionality and user experience if not addressed properly:
- Device fragmentation: Variations in screen size, resolution, and hardware affect gesture behavior across Android and iOS devices.
- Inconsistent gesture recognition: Different operating systems and devices may interpret the same gesture differently.
- Touch sensitivity issues: Subtle differences in touch response can cause gestures to fail or behave unexpectedly.
- Environmental factors: Real-world conditions like network speed, battery state, or background processes can impact gesture performance.
- Complex gesture flows: Multi-step or multi-finger gestures are harder to automate and verify across all devices.
Why Test Natural App gestures & Interactions on Real devices?
Accurately testing natural gestures like swipes, pinches, and long presses requires behavior only real devices can provide. For testing natural app gestures and functionalities, QA testers have three options:
While emulators and simulators are helpful in early development stages, they cannot fully replicate real user conditions. They often lack support for native gestures, sensor input, touch responsiveness, and physical feedback.
Testing gestures on real devices ensures that gestures work as intended across various screen sizes, hardware configurations, and operating system versions. Real device clouds offer scalable access to a wide range of actual iOS and Android devices, allowing teams to identify gesture-related bugs and usability issues more effectively.
How to Test Natural App Gestures and Interactions on Real Android & iOS Devices using BrowserStack?
When it comes to testing gestures and interactions, QA testers must use multiple real Android & iOS devices to test the functionalities. However, mobile device farms can prove to be time-consuming and costly. So instead of spending time, energy, and money, a better alternative would be using BrowserStack App Live.
Interact with your mobile app on the remote device, just as you would with a real device in hand. Use trackpad to scroll, swipe, tap, long press, and pinch to zoom. Follow the step-by-step process to test the app gestures and interactions with BrowserStack App Live:
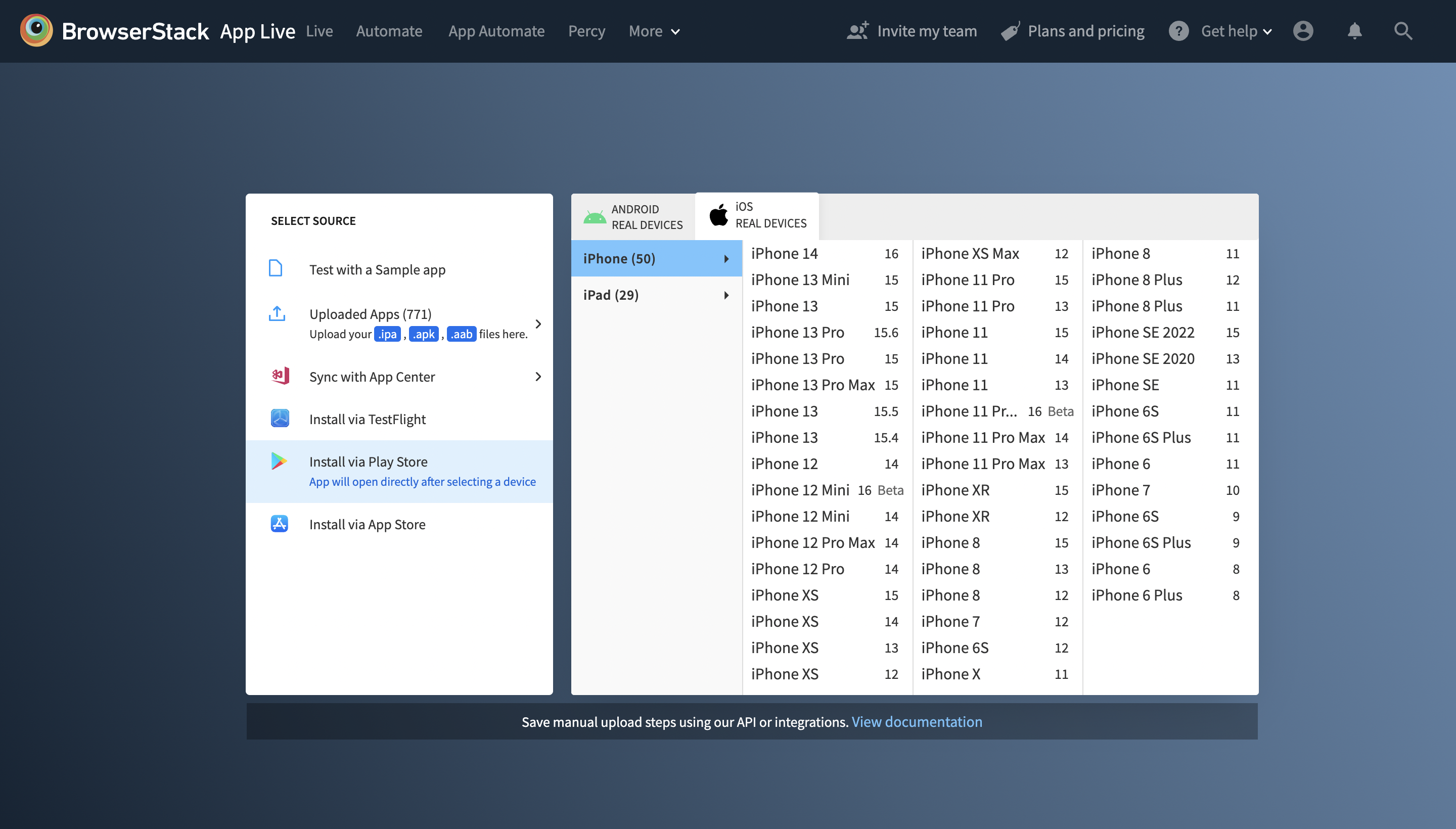
Step 1 – Go to the App Live Dashboard. Choose from any device-OS combination to test the app gestures and interactions from the list of 3500+ real devices & browsers (Android & iOS) on App live.
Step 2 – Upload the “Application” that needs to be gesture tested. You also have the option to test a sample App, Install via TestFlight, App Store, or Play Store.
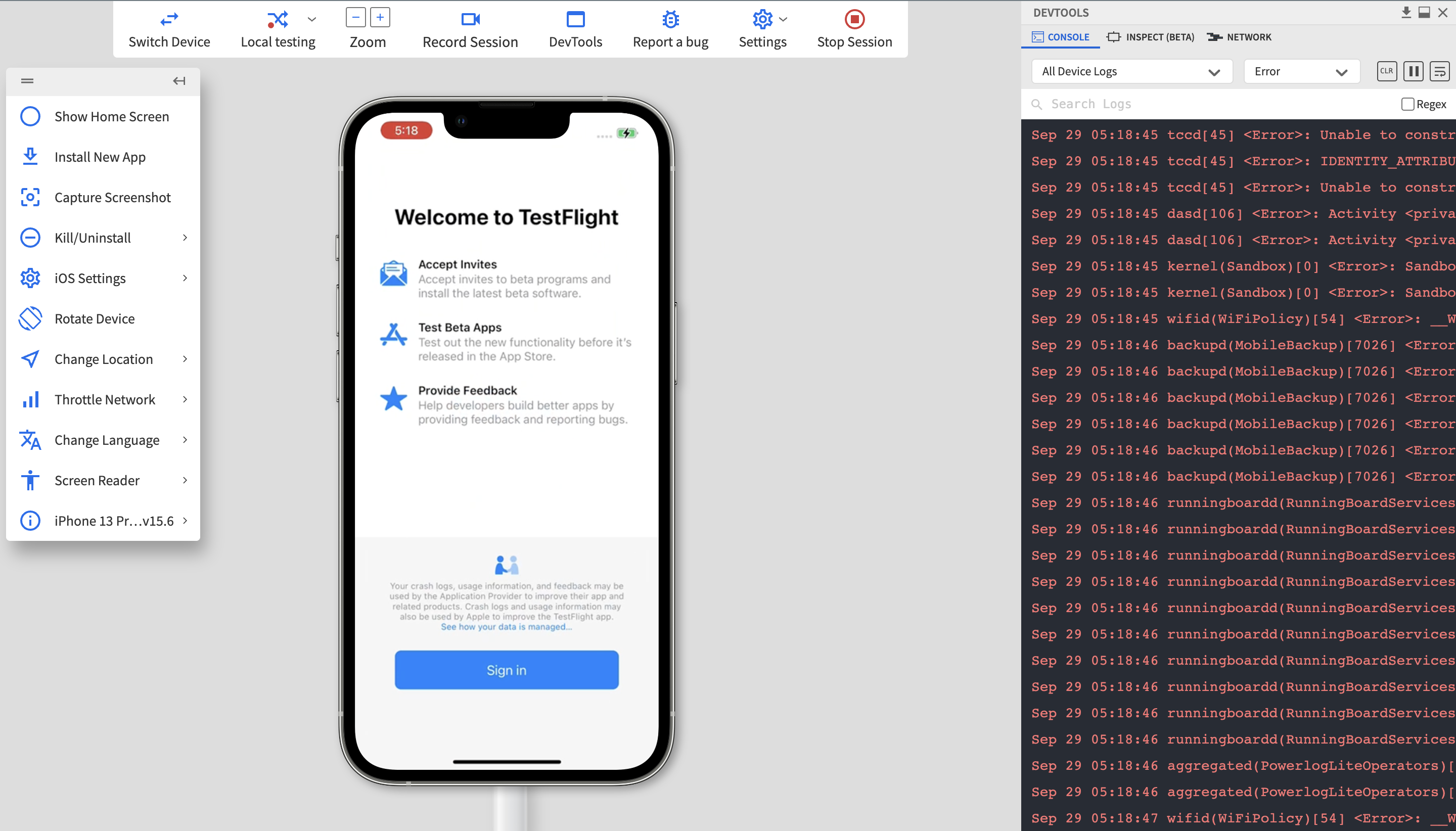
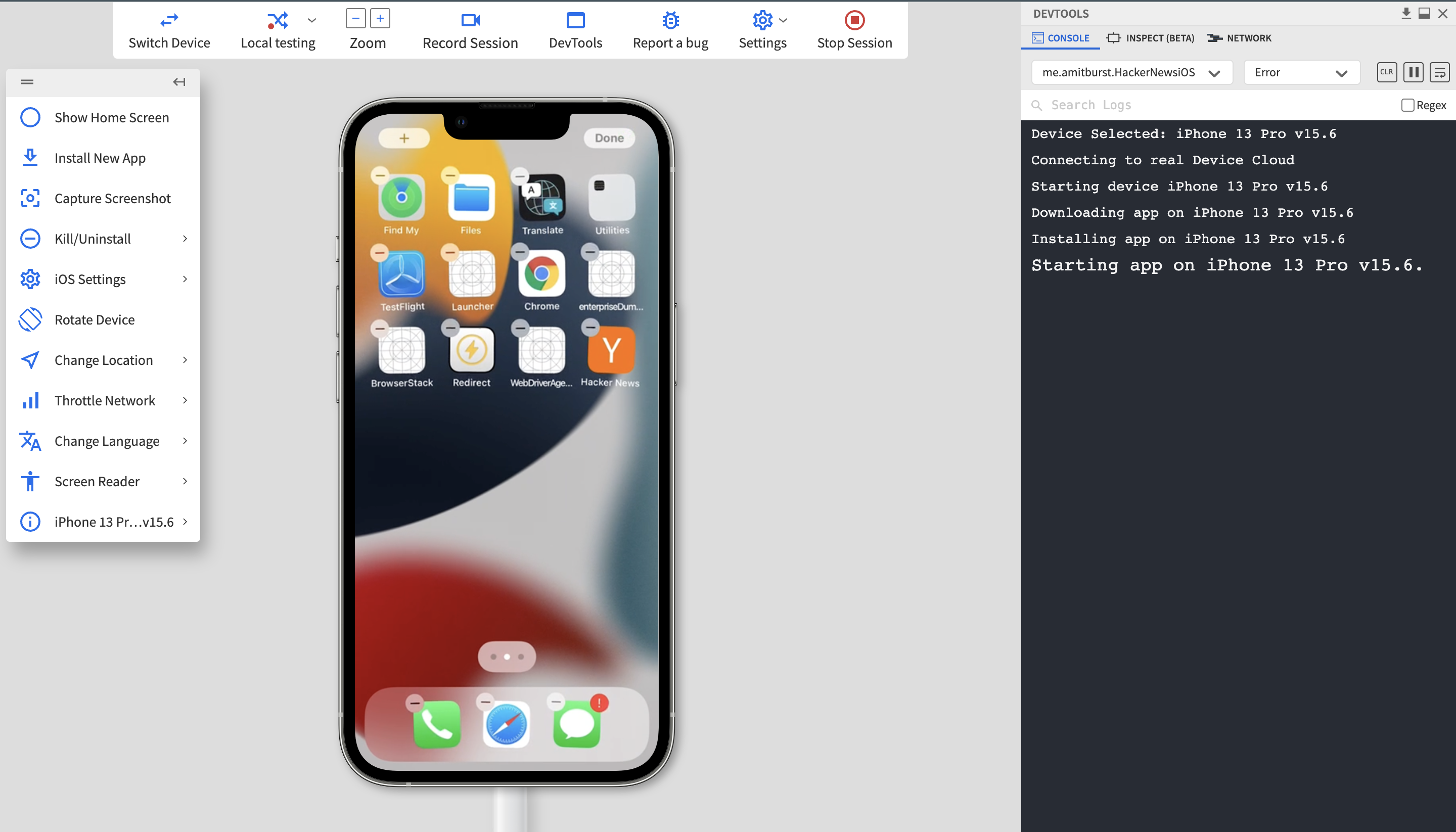
Step 3 – You’ll be now redirected to the testing dashboard, where you can start testing. You can see in the below screen that long-press gesture on an iPhone has been tested directly through App Live without having to buy an actual device.
Step 4: Use the available tools to capture screenshots, record test sessions, view device logs, and document any issues found during testing. This helps QA teams share detailed feedback and reproduce gesture-related bugs efficiently.
BrowserStack App Live offers many more testing options including network throttling, geolocation, screen rotation, installation/uninstall, and many others to test actual usability in real user conditions. Moreover, you can do it on multiple devices-OS combinations.
Conclusion
Gestures and Interactions are the crux of any mobile device and corresponding app functionalities. That’s why gesture testing on real Android & iOS devices is a must for QA testers. Testing gestures and interactions make the user’s experience convenient & smooth which is why product launches these days are incomplete without improving these two elements to enhance the UI.
- By using BrowserStack App Live, testing the gestures and interactions on real devices and browsers, it becomes easier for QA testers to find & fix bugs and enhance the user’s experience.
- Also, it helps QA testers to test the gestures and interactions without buying real physical devices as BrowserStack App Live provides 3500+ real devices and browsers to test the gestures and interactions and identify bugs to resolve.