When it comes to browser automation, Puppeteer and Selenium are two widely used tools, each with distinct strengths.
Overview
What is Puppeteer?
Puppeteer is a Node.js library developed by Google to control headless or full Chrome/Chromium browsers via the Chrome DevTools Protocol.
What is Selenium?
Selenium is an open-source tool for automating web browsers, widely used for testing web applications and other browser tasks.
Key Differences: Puppeteer vs Selenium
- Developer & Release: Puppeteer, developed by Google, was released in 2017; Selenium, developed by the Selenium Project, was released in 2004.
Core Language & Platform Support: Puppeteer supports Node.js and Chrome/Chromium; Selenium supports multiple languages and browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge). - Automation Scope & Use Case: Puppeteer is focused on web automation, web scraping, and headless tasks, while Selenium is used for full-scale web and mobile automation (via Appium).
- API & Flexibility: Puppeteer offers a high-level API for Chromium; Selenium offers both high and low-level APIs for broad browser control.
- Screenshot Capability: Puppeteer captures screenshots and PDFs; Selenium provides similar functionality, with PDF generation available in Selenium 4.
This article explores the core differences between Puppeteer and Selenium to help you determine which tool aligns best with your project needs.
Puppeteer vs Selenium: Core Differences
Here is a key comparison between Puppeteer and Selenium:
| Parameter | Puppeteer | Selenium |
|---|---|---|
| Developer | Developed by Google | Developed by the Selenium Project (originally by ThoughtWorks) |
| Release Year | 2017 | 2004 |
| Core Language | Node.js only | Supports multiple languages: Python, Java, JavaScript, Ruby, C#, etc. |
| Platform Support | Works only with Chrome and Chromium | Cross-platform; supports Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and Internet Explorer |
| Type | Node.js library for headless browser automation | Web testing framework for automating browser interactions |
| Browser Compatibility | Chrome/Chromium only | Multi-browser support |
| Automation Scope | Web automation only | Supports both web and mobile automation (via Appium) |
| Screenshot Capability | Can capture screenshots and generate PDFs | Similar support, but PDF generation is available from Selenium 4 onwards |
| Use Case Focus | Lightweight tasks, web scraping, headless automation | Full-scale automated testing across browsers and platforms |
| API Level | High-level API built for Chromium | High-level and low-level APIs for broad control and flexibility across browsers |
Introduction to Puppeteer
Puppeteer is a Node.js library developed by Google that provides a high-level API to control headless or full Chrome/Chromium browsers through the Chrome DevTools Protocol.
It’s primarily used for automating web page interactions such as testing, scraping, and generating screenshots or PDFs.
Key Features of Puppeteer
- Controls headless and full Chrome/Chromium browsers
- Captures screenshots and generates PDFs of web pages
- Automates form submissions, UI interactions, and navigation
- Performs web scraping with ease
- Supports performance and rendering tests
- Integrates easily into CI/CD workflows
- Offers full access to Chrome DevTools features
Advantages of Puppeteer
Puppeteer stands out for its speed, simplicity, and direct integration with Chrome, making it a go-to tool for modern web automation tasks.
- Direct access to Chrome’s DevTools Protocol, allowing precise control over browser behavior.
- Single browser and language support streamlines performance, making automation faster and more efficient than multi-language, multi-browser setups.
- No need for separate browser drivers, reducing setup complexity and maintenance overhead.
- Built-in features for performance tracking, including automated screenshots and page load monitoring.
Limitations of Puppeteer
While Puppeteer offers speed and simplicity, it also has limitations that may not suit every automation need.
- Limited to JavaScript/Node.js, which can be restrictive for teams working with other programming languages.
- Supports only Chrome and Chromium-based browsers, making it less flexible for cross-browser testing.
- Lacks broader ecosystem support, as tools like Selenium offer more versatility across browsers and platforms.
- Firefox support is experimental, and full compatibility is still under development, limiting options for non-Chrome environments.
Introduction to Selenium
Selenium is a powerful open-source tool designed to automate web browsers. While it is widely used for testing web applications, its capabilities extend to various browser automation tasks across different environments.
With support for multiple programming languages and operating systems, Selenium allows for flexible and scalable testing. It also enables cross browser compatibility by supporting major browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and Internet Explorer.
Key Features of Selenium
- Cross-browser testing on Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and more
- Multi-language support, including Java, Python, JavaScript, C#, Ruby, and Kotlin
- Integration with testing frameworks like TestNG, JUnit, and NUnit
- Support for parallel and distributed test execution via Selenium Grid
- Active community and regular updates through the Selenium Project
- Open-source and highly customizable for diverse automation needs
Advantages of Selenium
Selenium remains a leading choice in automation testing due to its flexibility, wide compatibility, and active community support.
- Completely open-source and free to use, making it accessible for individuals and organizations alike
- Easily integrates with CI/CD tools and supports Agile testing workflows for continuous development
- Compatible with multiple browsers, operating systems, and programming languages, ensuring broad coverage
- Backed by a large community, offering extensive libraries, plugins, and troubleshooting resources
Limitations of Selenium
Despite its versatility, Selenium has certain limitations that may impact ease of use and specific testing scenarios.
- Requires a steep learning curve, especially for beginners or teams without prior automation experience
- Lacks built-in support for image-based testing, such as visual regression or direct image comparison
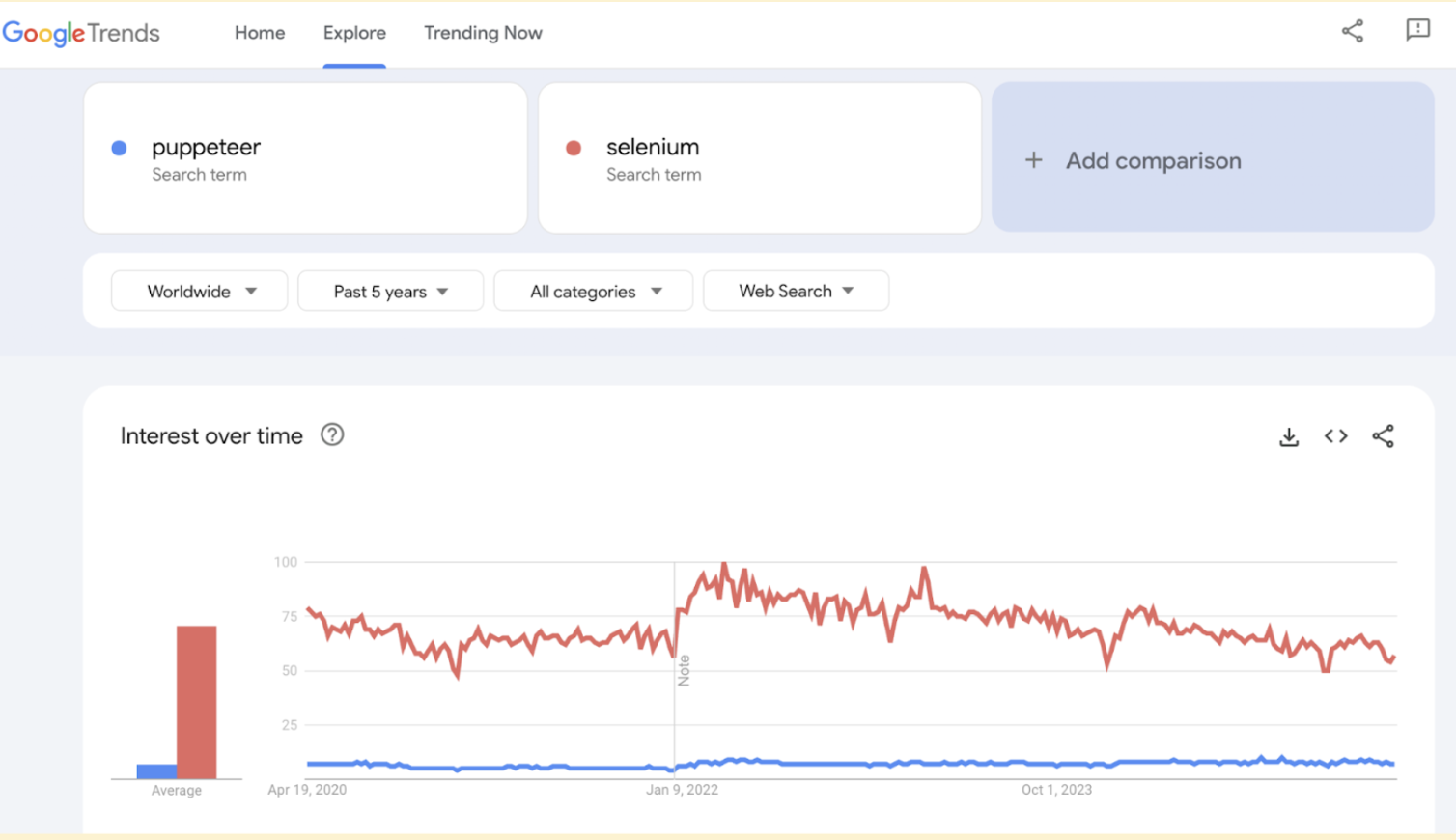
Market Trends on Selenium and Puppeteer
The graph below highlights Selenium’s long-standing and growing popularity in the automation testing space.
While Puppeteer also enjoys strong adoption, particularly for Chrome browser automation, Selenium maintains a broader user base and wider usage across different browsers and environments.
Each tool has its strengths, but Selenium remains the more universally adopted choice.
Source: Google Trends
Setup and Test Implementation of Puppeteer and Selenium
Selenium and Puppeteer are the two automation testing tools that can be directly installed using npm.
- To install Selenium, type the following command in the terminal:
npm install selenium-webdriver
Another way is to study and use the Selenium Installation here.
Here, creating a driver and using it is easy—the syntax is verbose compared to the alternatives but still pretty straightforward:
The example below located the Yahoo sign up page using the Xpath locator.
driver.get("https://login.yahoo.com/account/create");
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='usernamereg-firstName']")).sendKeys("Your-Name"); // Will send values to First Name tab
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='usernamereg-lastName']")).sendKeys("Your-Last_name"); //xpath for last name box
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='usernamereg-yid']")).sendKeys("email@yahoo.com"); //xpath for email box
- Now, on to Puppeteer. To install Puppeteer, type the command below in the terminal:
npm install puppeteer
Now, let’s locate the same sign-up page using the Puppeteer syntax:
await page.goto(‘https://login.yahoo.com/account/create’); await page.click(‘button’); await page.type(‘#sign-up’, ‘your_name’); await page.type(‘[type=email]’, ‘your_email’);
People also read: How to Build and Execute Selenium Projects
Selenium or Puppeteer: Which is the preferred one?
Below is a clear bifurcation of when you should prefer Selenium and when Puppeteer is the better option.
Here are some key use cases of Puppeteer:
- You’re working exclusively with Google Chrome or Chromium.
- Deep Chrome integration for tasks like PDF generation, screenshots, or headless testing.
- Project demands lightweight automation with a quick setup.
Below are the key situations where you need to use Selenium:
- To perform cross-browser testing across Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, etc.
- Your team works with multiple programming languages like Java, Python, C#, or Ruby.
- You require features like record-and-playback, reusable test suites, or CI/CD integration.
- You need a scalable, community-supported solution with rich documentation.
Testing on Real Device Cloud with BrowserStack
For accurate and efficient test execution, run Selenium tests on real devices and browsers through BrowserStack Automate. With instant access to 3500+ real desktop and mobile environments, teams can validate user experiences on real device cloud under real user conditions.
BrowserStack also supports easy integration with popular CI/CD tools, allowing teams to scale test automation effortlessly.
Conclusion
In summary, Puppeteer is ideal for Chrome-specific testing, while Selenium stands out for its cross-browser and multi-language support, making it the preferred tool for comprehensive automation testing.
Leveraging BrowserStack Automate enhances Selenium’s capabilities by providing access to a vast cloud of real devices and browsers, enabling testers to achieve more accurate and scalable test coverage with minimal setup.
Together, these tools empower development and QA teams to deliver high-quality web applications efficiently.
Useful Resources for Puppeteer
Understanding Puppeteer:
- Puppeteer Framework Tutorial: Basics and Setup
- How to start with Puppeteer Debugging
- How to install and setup Puppeteer with npm (NodeJS)
- Puppeteer Type Command: How to type a text in input box in Puppeteer
- Cross Browser Testing in Puppeteer: Tutorial
- Understanding Puppeteer Headless
- How to run UI Automation Testing using Puppeteer
- How to capture Lazy Loading Images for Visual Regression Testing in Puppeteer
- How to use Proxy in Puppeteer?
- How to run Tests in Puppeteer with Firefox
- How to Perform Visual Regression Puppeteer
- Handling Alerts and Popups in Puppeteer
- Pyppeteer Tutorial: Guide to Puppeteer in Python (with Examples)
Tools Comparisons:
- Puppeteer vs Selenium: Core Differences
- Cypress vs Selenium vs Playwright vs Puppeteer: Core Differences
- Cypress vs Puppeteer: Core Differences
- Playwright vs Puppeteer: Which to choose in 2024?
- Top 10 Puppeteer Alternatives
Useful Resources for Selenium
Methods, Classes, and Commands
- Selenium Commands every Developer or Tester must know
- Selenium WebElement Commands
- Desired Capabilities in Selenium Webdriver
- Assert and Verify Methods in Selenium
- Understanding System setProperty in Selenium
- Select Class in Selenium : How to select a value in dropdown list?
- SendKeys in Selenium WebDriver
- getAttribute() method in Selenium: What, Why, and How to use
- How does Selenium isDisplayed() method work?
- findElement vs findElements in Selenium
- Types of Listeners in Selenium (with Code Examples)
- How to set Proxy in Firefox using Selenium WebDriver?
Configuration
- How to set up Selenium on Visual Studio
- How to configure Selenium in Eclipse
- Maven Dependency Management with Selenium
- How to Build and Execute Selenium Projects
XPath
- How to use XPath in Selenium?
- How to find element by XPath in Selenium with Example
- Top Chrome Extensions to find Xpath in Selenium
Locators and Selectors
- Locators in Selenium: A Detailed Guide
- CSS Selector in Selenium: Locate Elements with Examples
- How to Create Object Repository in Selenium
Waits in Selenium
- Wait Commands in Selenium C and C#
- Selenium Wait Commands: Implicit, Explicit, and Fluent Wait
- Understanding Selenium Timeouts
- Understanding ExpectedConditions in Selenium
- Understanding Role of Thread.sleep() in Selenium
Frameworks in Selenium
- Data Driven Framework in Selenium
- Implementing a Keyword Driven Framework for Selenium: A Practical Guide
- Hybrid Framework in Selenium
Miscellaneous
- How to create Selenium test cases
- How to set Proxy in Selenium?
- Difference between Selenium Standalone server and Selenium server
- Exception Handling in Selenium WebDriver
- How to use JavascriptExecutor in Selenium
- How to run your first Selenium test script
- Parallel Testing with Selenium
Best Practices, Tips and Tricks
- Top 5 Challenges Faced During Automation Selenium Testing
- 5 Selenium tricks to make your life easier
- 6 Things to avoid when writing Selenium Test Scripts
- Best Practices for Selenium Test Automation
- Why you should pay attention to flaky Selenium tests
- How to start with Selenium Debugging
- How to make your Selenium test cases run faster
- How to upgrade from Selenium 3 to Selenium 4
- Why you should move your testing to a Selenium Cloud?
Design Patterns in Selenium: Page Object Model and Page Factory
- Design Patterns in Selenium
- Page Object Model and Page Factory in Selenium
- Page Object Model and Page Factory in Selenium C#
- Page Object Model in Selenium and JavaScript
- Page Object Model and Page Factory in Selenium Python
Action Class
- How to handle Action class in Selenium
- How to perform Mouse Hover Action in Selenium
- Understanding Click Command in Selenium
- How to perform Double Click in Selenium?
- How to Drag and Drop in Selenium?
- How to Scroll Down or Up using Selenium Webdriver
- How To verify Tooltip Using Selenium
TestNG and Selenium
- Database Testing using Selenium and TestNG
- How to use DataProvider in Selenium and TestNG?
- All about TestNG Listeners in Selenium
- How to run parallel test cases in TestNG
- How to use TestNG Reporter Log in Selenium: Tutorial
- Prioritizing tests in TestNG with Selenium
JUnit and Selenium
- Understanding JUnit assertions for Selenium Testing with Examples
- How to run JUnit Parameterized Test in Selenium
- How to write JUnit test cases
- JUnit Testing Tutorial: JUnit in Java
- How to create JUnit Test Suite? (with Examples)
Use Cases
- Handling Login Popups in Selenium WebDriver and Java
- How to Launch Browser in Selenium
- How to handle Alerts and Popups in Selenium?
- How to get Selenium to wait for a page to load
- How to Find Element by Text in Selenium: Tutorial
- How to Read/Write Excel Data using Apache POI Selenium
- How to handle Captcha in Selenium
- How to handle multiple windows in Selenium?
- How to handle Multiple Tabs in Selenium
- How to find broken links in Selenium
- How to handle Cookies in Selenium WebDriver
- How to handle iFrame in Selenium
- How to handle Web Tables in Selenium
- How To Validate Text in PDF Files Using Selenium Automation
- Get Current URL in Selenium using Python: Tutorial
Types of Testing with Selenium
- Different Testing Levels supported by Selenium
- How to perform UI Testing with Selenium
- Regression Testing with Selenium: Tutorial
- UI Automation using Python and Selenium: Tutorial
- How to Run Visual Tests with Selenium: Tutorial
- How to perform ETL Automation using Selenium
- Cross Browser Testing in Selenium : Tutorial