According to a study by Businesswire, 86% percent of consumers will abandon a brand after two poor customer experiences. Since your website usability and UX elements integrate into the larger chunk of the overall customer experience, it is critical to keep a website in good condition.
Usability issues need to be kept at bay from your website, to boost customer retention and lead generation.
Conducting website usability testing is therefore no negotiable. This guide discusses in detail about website usability testing and its various aspects. Dive in.
What is Website Usability?
Simply, usability refers to how easy or hard something is to use. Website usability refers to the ease with which the average user or visitor can navigate and operate a website, meet their goals, and find what they want.
A few key factors to judge website usability are:
- Learnability: How easily can new visitors maneuver the site and get what they want?
- Efficiency: How smoothly can users complete tasks/actions on the website?
- Satisfaction: How happy are users with the website’s design, functionality, and offerings?
- Errors: How many errors are showing up in usability testing? How severe are the errors? Can the errors be resolved quickly and with minimum effort?
Determining and improving the overall website usability requires the execution of website usability testing.
What is Website Usability Testing?
Website usability testing is the process of evaluating the user-friendliness and intuitiveness of a website for its end users. The objective of this test is to ensure that users can seamlessly interact and navigate through the website.
Importance of Website Usability Testing
Here’s why usability testing is important:
- It improves user satisfaction and increases retention rates.
- By helping you simplify sign-up and purchasing processes, it boosts conversion rates.
- Builds brand image, trust and credibility through a well-functioning and appealing website.
- Helps fulfill legal and ethical standards, particularly with respect to accessibility.
How does Website Usability Testing work?
In website usability testing or web usability testing, QAs put the website through several user scenarios likely to be encountered when using it. It involves performing several user actions that first-time website visitors generally enact.
While user actions are being executed, another QA monitors the same to judge how usable the site is. Feedback is immediate, as the observer can immediately notice and note any difficulties revealed in the test process.
Note that web usability testing must be conducted by individuals not connected to that website’s development. Ideally, this should include actual users who would potentially use the site when it goes public. However, if not feasible, usability tests can be conducted by QAs from another team in the same organization to avoid any bias in the ultimate goal of making a website user-friendly.
Steps to Conduct Website Usability Testing
Here are the steps to conduct website usability testing:
1. Define Goals
Understand and identify what you want to achieve through the website usability test.Example: Improve overall user experience, easy navigation, etc.
2. Identify Target audience
Identify your website users, their requirements, pain points, behaviors and objectives.
3. Choose the Testing Method
Select a testing method that aligns with your objectives. This method could be moderated, unmoderated, remote, or in-person testing.
- Moderated Testing: It involves live interaction with a facilitator
- Unmoderated testing: Tools are used to test independently
- Remote Testing: This test is conducted online
- In-person Testing: Performed in a controlled environment
4. Test Scenarios
Prepare realistic test scenarios and tasks that align with your testing objectives.
5. Set up Testing Environment
Choose tools and platforms needed for testing like cross-browser testing platforms, accessibility testing tools, screen recording tools, usability testing platforms and more.
6. Conduct a Pilot Test
Run a pilot test at a small scale to spot errors or flaws in your instructions or set up.
7. Conduct and Monitor the Testing Session
Observe, manage, and track the assigned tasks during test sessions. Identify pain points in the process and find solutions.
8. Gather Data
Collect quantitative and qualitative data like user feedback, completed tasks, success and error rates.
9. Analyze Results
Detect trends and patterns in user behavior, challenges, and areas for improvement. You can use metrics like error frequency, success rate etc. You can then group these findings into critical, moderate, and low-priority issues. Accordingly, you can come up with an action plan to address the issues.
10. Retest
Once the changes are made, run one more round of usability tests to confirm that the issues are resolved.
11. Documentation
Now, you can document all the key findings, implemented changes, and patterns observed for future reference. This report can then be shared with the stakeholders.
Types of Website Usability Testing
If you’re wondering how to conduct usability testing for a website, it can be executed in three common ways:
- Comparative: This method compares multiple versions of the same website (different designs, features, functions, etc.) and evaluates the pros and cons of each.
- Explorative: This method judges the usability and efficacy of early-stage designs or prototypes. It pays particular attention to users’ intentions, inclinations, needs, and preferences early on to align the site with customer expectations from the beginning. It’s good to be acquainted with exploratory testing in such cases.
- Assessment: This method checks overall usability, usually at specific points during development. Think of these as milestones that periodically check how the website is faring as it is being designed, coded, and consolidated. Generally, real-time trials as part of UI testing are helpful.
Benefits of Website Usability Testing
Fundamentally, website usability analysis is used to detect issues that people familiar with the website are unlikely to identify – generally, the in-depth knowledge of developers, designers, marketers, and product managers miss out on issues that could bother the everyday user.
Some specific benefits of web usability testing are:
1. Prototype Validation
When checking for usability from the early stages of the software release flow, web usability testing helps validate the concept itself. This allows devs, designers, and QAs to plan out features and layout for maximum usability, cutting down on extra work later.
2. Exceeding Customer Expectations
After complete development, another thorough usability test is necessary to check if all aspects of the site work as expected. This is mandatory to ensure complete customer satisfaction, especially if your product team is constantly releasing updates and new features.
Pro-Tip: Regression testing in agile helps fastrack this by checking if new code contradicts or scrambles older features. It ensures that new code enhances, or at least leaves old code unaffected with every build.
3. Recalibrate Complex Workflows
Think of the checkout process on an e-commerce website. It usually requires users to follow many steps to get to what they want. Usability tests are needed to verify that these steps are easy to follow and accomplish. It also helps developers rethink if they could simplify the process as far as possible.
Must-Read: How to Train, Engage and Manage a QA Team
4. Detect Errors
Other forms of testing can overlook minor errors (broken links, site errors, grammatical issues). However, website usability analysis tends to catch these as it is being conducted by new pairs of eyes. Allowing such errors to leak into production can damage users’ perception of the brand’s credibility.
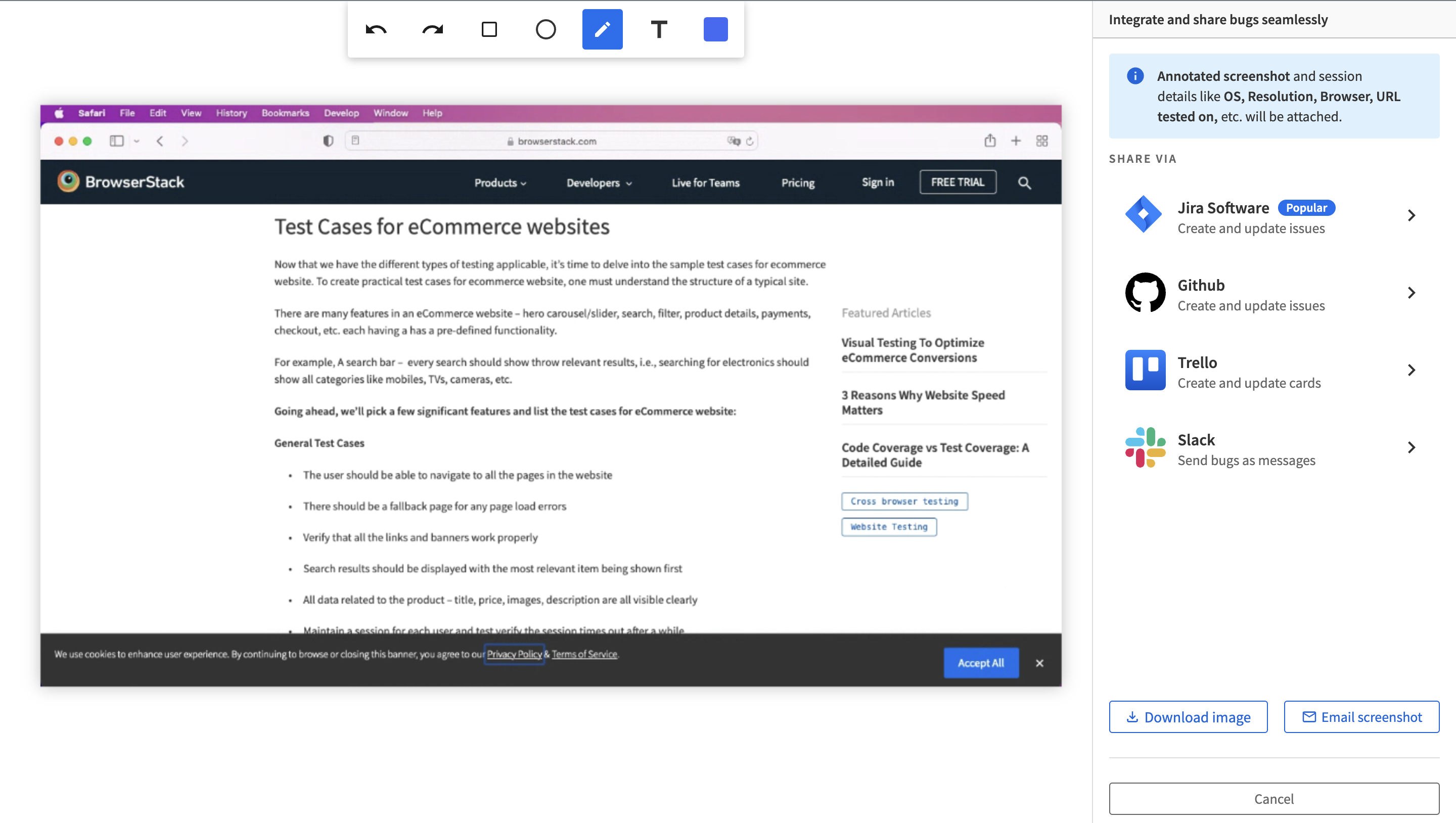
Identify and troubleshoot errors before your users have to deal with them by testing on a real device cloud. BrowserStack provides a robust combination of 3000+ real browsers and devices (latest and legacy) for manual and automated testing.
Best Practices for Website Usability Testing
Here are the best practices for conducting usability test:
- Find volunteers who are not QAs or developers to take the usability tests first. Since the target audience will primarily be composed of people without too much technical knowledge, it is best to find similar individuals for testing purposes. However, if this is not feasible, find individuals in other teams with little to no knowledge about the project. They should have a neutral approach with the mindset of a first-time user.
- Give testers specific tasks they have to accomplish and observe how they go about it. Instead of asking them to file detailed reports, observe as they navigate the website to gauge usability levels. Additionally, ask them to narrate out loud so you can follow their intellectual process.
- Keep tasks as vague as possible. For example, ask them, “If you wanted to buy coffee mugs from this website, how would you do it?” Don’t give them too many hints with “Select a set of coffee mugs from the “Crockery” section on the Navigation Bar.” This approach will help identify more usability bugs and obstacles.
- Website usability testing needs to be run at multiple stages, such as the initial concept and on every subsequent prototype. Use feedback from every test to refine and restructure development operations that follow.
- Use real browsers and devices on BrowserStack. It doesn’t matter what emulator or simulator is being used; they will not offer 100% accurate results as they are not capable of replicating real user conditions.
Conclusion
Website usability testing is an essential step in the website development pipeline. Use it to ensure that website users get exactly what they want with minimal effort.
This form of testing is integral to developing an intuitive UI that does not confuse visitors or waste their time with easily avoidable complications.
Since the customer is always right, ensure that the website will inspire them to approve of it under the best possible customer experience.
To ensure that your website works consistently across all browsers, devices and OS, do test your website on BrowserStack. The platform offers a vast real device cloud that lets your access 3500+ real devices, browsers and OS combinations.