A successful software launch relies on quality, performance, and user experience, making it crucial for product managers to understand product management testing and ensure the product is thoroughly tested and free of critical issues.
Overview
Effective product management testing guarantees high-quality software and aligns the product with business goals. Product Managers play a crucial role in defining testing strategies, collaborating with teams, and leveraging insights for informed decision-making.
Things every product manager should know about testing:
- Choosing the Right Testing Strategy: Align testing with product goals, user needs, and release timelines.
- Types of Testing: Understand functional, usability, performance, security, and regression testing.
- Modes of Testing: Balance manual vs. automated testing and real device vs. emulator-based testing.
- Testing in DevOps Process: Integrate testing into CI/CD pipelines for faster, more reliable releases.
- Testing Business With Users: Conduct user acceptance testing (UAT), A/B testing, and gather real-world feedback.
- Roles and Perspectives of Different Stakeholders: Collaborate with developers, QA teams, and business leaders to align testing with product objectives.
- Understanding the Role of Automation in Testing: Use automation to improve efficiency, reduce manual effort, and accelerate testing cycles.
This guide explores essential things every product manager must know, including strategies, testing types, challenges, and best practices for product management testing.
Why Testing is Crucial in Product Management
Testing is important in delivering high-quality products that meet user expectations and business objectives. Here’s why testing must be included in product management:
- Ensures Product Quality: It helps detect bugs, performance issues, and usability gaps before a product launches.
- Reduces Risks: Testing helps identify potential failures early, which helps prevent costly fixes later.
- Enhances User Experience: Ensures smooth functionality, meeting customer expectations.
- Supports Business Goals: Aligns product performance with market demands and company objectives.
- Improves Development Efficiency: Integrates with CI/CD pipelines for faster, more reliable releases.
- Builds Customer Trust: Delivers a stable, high-performing product that users can rely on.
- Prevents Post-Launch Failures: Avoids major issues that can harm the brand reputation and revenue.
Read More: Testing in Production: A Detailed Guide
Things Every Product Manager Must Know about Testing
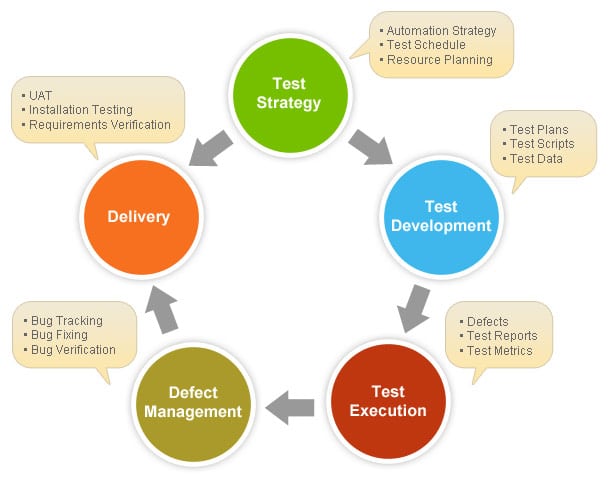
Establishing a robust testing infrastructure that works seamlessly alongside the design and development phases is essential. It provides a systematic approach to capturing, documenting, sharing, and resolving issues within a software application collaboratively.
This process helps prevent problems that could lead to business losses or poor user experiences.
Source: Software Testing Help
Software testing, when done correctly, ensures quality and prevents business failure and customer unhappiness.
Read More: Setting Goals for Software Quality
1. Choosing The Right Testing Strategy
How and what to test during the SDLC depends mainly on the particulars of the business use case. Developing the most efficient automated testing pyramid is not a trivial task. It is easy to get lost in the sea of online advice and waste time, but you can prevent that if you understand the fundamentals.
Testing is a broad field of study, and there are many different ways to classify types, but these are the basic layers at which tests are usually implemented:
- Unit Testing: It involves verifying individual components or functions of the codebase by running dedicated test code, typically integrated within the same project as the application itself.
- Integration Testing It involves testing sections of the codebase as interdependent functions or modules through test code or other tools.
- System Testing: Testing the workings of an application at the level of features like login, signup, and other supported flows, which validates parts of the application working together.
- Acceptance Testing: This is usually the final stage of testing in which the fully assembled application with data is tested in a live or pre-production environment. This involves testing with actual or mock users.
- Performance Testing: With an increase in users, it becomes vital to ensure that the servers can handle the request loads at peak usage times. Also, maintaining end-to-end security at each point of contact between the app and user.
- Manual Testing: It relies on human testers to explore and validate the product, ideal for usability and exploratory checks.
- Automated Testing: It uses scripts and tools to run repetitive tests quickly and consistently, perfect for regression and large-scale testing.
Both modes complement each other, and the best approach depends on project needs, timelines, and resources.
2. Testing DevOps Process
Development Operations or DevOps is a widely used term that refers to a range of activities, including the coding, testing, building, and deployment of software applications. For a product team, the main task is to implement a unit and integration testing plan as part of the technical architecture. Depending on the level of test automation, teams use:
- Continuous Integration (CI): It refers to automated workflows that validate code commits from individual contributors and seamlessly merge them into the main repository, ensuring consistent integration and reducing integration issues.
- Continuous Delivery/Deployment (CD): This is when a code commit is validated, merged with the parent, and deployed to a testing or production server in the same flow.
Testing in a CI/CD workflow usually involves:
- Writing unit tests: These tests focus on verifying the smallest parts of an application, individual functions or components, to ensure they work correctly in isolation. For product managers, understanding the importance of unit testing ensures better communication with developers and a clearer view of the product’s code quality and reliability.
- Testing source code and build: This involves running unit tests in batches, with other tests on the code to test functionality and code quality. After coding, the next task is to bundle the application into a deployable format as specified by the technical architecture. It involves post-processing the source code and installing packages and dependencies as needed. All major cloud hosts like Github, Gitlab, Bitbucket have native CI/CD support.
- Testing backend and database: For APIs and backend applications like micro-services, integration testing is a very crucial step. Because of complicated architecture and many dependencies, it is vital to ensure proper documentation, performance, and security of REST APIs. Also, the data being passed along needs to be tested to ensure proper values, constraints, etc. Testing DB schema, tables, triggers, etc., separately through specially designed queries and tools is sometimes referred to as Database Testing.
- Testing UI: Testing the application UI in depth is the job of QA teams, but most developers will have a test deployment setup on their dev machine for a brief round of validations that can be performed before code commits. The main goal is to ensure proper integration between the database, APIs, dependencies, and the user interface.
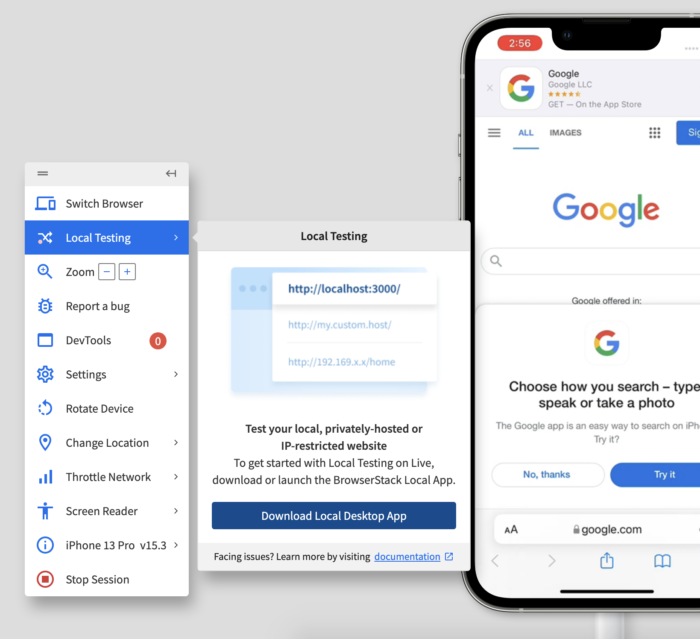
UI tests are best executed on real browsers – devices – OS combinations. Obviously, testing in real user conditions allows the tester to analyze the website or app behavior used by actual customers. If they do not have access to an in-house device lab, they can simply use BrowserStack’s Real Device Cloud.
Try Testing on Real Device Cloud for Free
3. Testing the Product
Once an application is deployed, the QA team begins system and acceptance-level testing. This process starts with a detailed test plan that outlines expected application behavior across various business scenarios. The test plan highlights all mission-critical workflows, helping testers deeply understand business requirements.
Here’s how the process unfolds:
Step 1 – Document test cases: For manual testing, test cases are documented on collaborative platforms, and testers handle execution and reporting. In automated testing, these cases are encoded into scripts using tools like Selenium or similar frameworks.
Step 2 – Prepare mock data: Test scenarios often require user input. To replicate real-world behavior, mock data is generated and used during testing. Tools like Visual Studio, Devart, and DTM can assist in creating this data.
Step 3 – Test execution:
With the appropriate test scripts and data, the tests are carried out. Finally, a detailed report is generated, capturing key metrics to evaluate the results. It is also crucial to execute tests across a broad range of devices and browsers to ensure compatibility and accessibility.
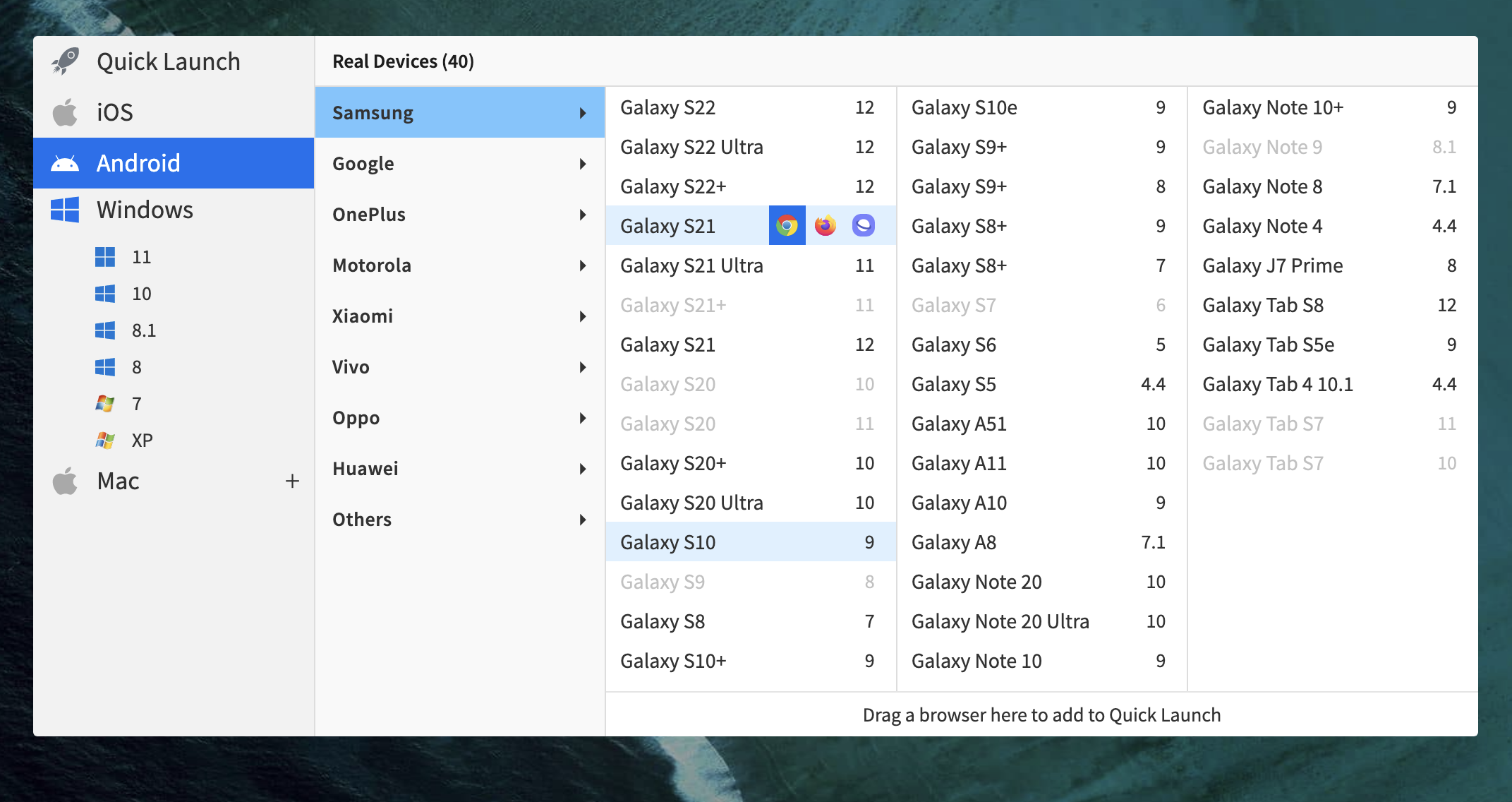
BrowserStack offers a powerful testing ecosystem to cover both manual and automated needs. With BrowserStack Live, testers gain instant access to over 3,500+ real devices and browsers for interactive, manual testing, including local and private environments, along with real-time debugging tools that simplify issue identification.
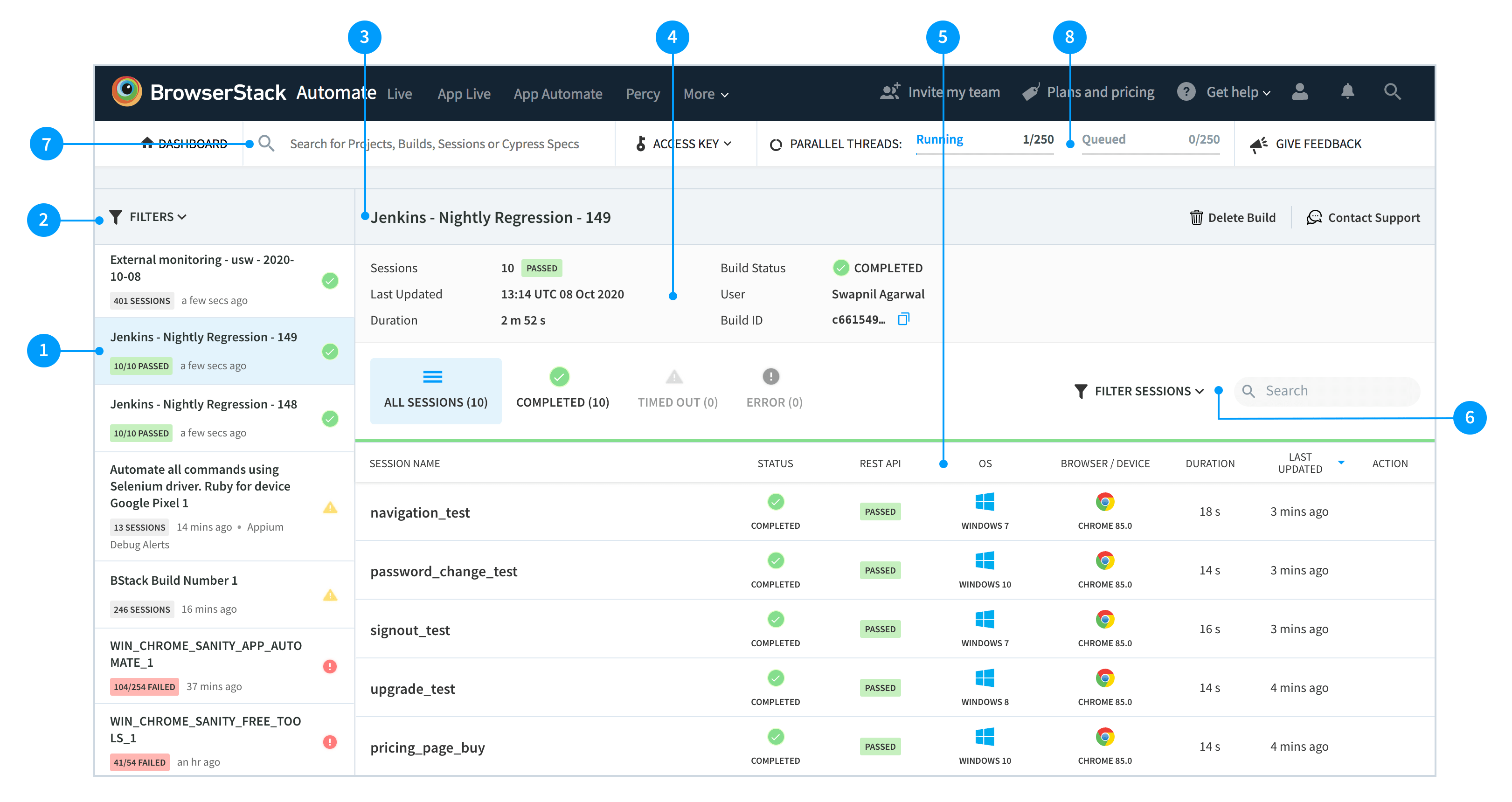
BrowserStack Automate enables scalable automated testing across the same real device cloud, supporting popular frameworks like Selenium and Appium. It provides parallel test execution, detailed reports, and seamless CI/CD integration, accelerating regression and cross-browser testing while ensuring comprehensive coverage and faster releases.
Step 4- Documenting issues and exceptions: Any unexpected behavior or bugs are captured in the tracking tool, along with details such as date, time, location, screenshots or videos, steps to reproduce, severity, and assigned ownership.
Step 5 – Iterate until fixed: Developers address logged issues, and the QA team re-tests until all critical defects are resolved, ensuring the application is ready for release.
This iterative process ensures that the product aligns with business expectations and delivers a seamless experience to users.
Read More: Testing in Production: A Detailed Guide
4. Roles and Perspectives of Different Stakeholders
Understanding the roles and perspectives of various stakeholders helps Product Managers align testing efforts with business objectives, technical requirements, and user needs.
Business Leadership
Business leaders expect the testing process to ensure the application is deployed smoothly and delivers optimal performance, accessibility, and user experience. All documented business requirements and design standards must be fully implemented without discrepancies.
Core workflows, such as sign-up, login, booking, and product purchase, should function flawlessly in the hands of users to meet business goals.
Technical Leadership
From the perspective of technical leaders, including Product Managers, the primary goal is to maintain a continuous development and integration pipeline (CI/CD). Continuous integration combined with Agile methodologies is widely recognized as the industry standard in Product Management today.
Technical leaders oversee a robust QAOps workflow, ensuring that automated test scripts run as scheduled and generate timely, relevant reports. They closely monitor these reports to guarantee that the entire application ecosystem supports the business objectives.
Developers
For developers, testing focuses on validating new code additions or changes before and after deployment. This includes identifying and fixing bugs in development, testing/staging, and production environments.
Developers follow shared testing guidelines and write unit tests to cover any new functions or modifications within their modules.
QA/QC Team
Once initial checks are complete on the development side, the QA/QC team takes over further testing. This process may involve manual testing, automated testing, or a combination of both.
Testers carefully document application behavior and log any anomalies or defects in a reporting portal, where issues are assigned, tracked, and resolved.
After QA approval, the application is released to a controlled group of users for acceptance testing. This phase verifies that the product meets real-world user expectations and business requirements before a full-scale launch.
Read More: Difference between Testing and Debugging
5. Reporting and Communications
Once a sound testing strategy, the right tools, and a team are in place, clear and continuous communication becomes essential. Dashboards, emails, and notifications serve as streams of relevant information, providing real-time updates on test progress, bug fixes, and overall application health.
The process typically flows as follows:
- The business team evaluates the current state of application performance, overlays future business goals, and communicates the vision through business requirement documents.
- Technical leadership and QA collaboratively update the test plan, involving all stakeholders to align on testing priorities.
- The QA team updates the traceability matrix and test cases in the bug tracker, assigns ownership, and hands off tasks to developers.
- Manual and automated test scripts are updated to reflect new cases, followed by mock runs to validate changes.
- Reports summarizing test results, such as dashboards, emails, and notifications, are shared regularly to keep all stakeholders informed and aligned.
- Effective communication ensures that issues are identified and addressed promptly. By maintaining this flow of information, teams can monitor application health, drive continuous improvement, and stay on track to meet business goals.
6. Common Testing Challenges for Product Managers
Product managers are essential in ensuring software quality, but testing comes with several challenges.
Here are some common testing challenges they face:
- Ensuring Comprehensive Test Coverage: It is tough to test every scenario, and even if a single test case is missed, it can lead to unnoticed issues in production.
- Managing Cross-Team Collaboration: Developers, testers, and stakeholders often have different priorities, which can cause miscommunication and slow down the testing process.
- Interpreting Test Results & Reports: If the product managers do not have a technical background, it can be difficult for them to understand complex testing data.
- Handling Resource Constraints: Issues like limited budgets, small teams, or poor testing tools can impact product testing.
- Balancing Speed & Quality: Product managers often get tight release deadlines, making it challenging to conduct thorough testing without slowing down the product delivery.
Read More: Software Testing Challenges with Solutions
7. Best Practices for Product Managers in Testing
Product managers can improve the testing process by setting clear goals, fostering collaboration, and leveraging automation.
Here’s how they can optimize testing:
- Define Clear Testing Goals: Setting clear goals and objectives can help teams prioritize their tasks and align testing with business needs.
- Improve Cross-Team Collaboration: Proper communication should be maintained with developers, testers, and business teams.
- Encourage Early Testing: It is always better to detect and fix bugs in the early stage of development, as this helps to reduce costs and prevent last-minute issues.
- Stay Updated on Testing Trends & Tools: Adopting automation frameworks enhances efficiency and keeps the process up to date.
- Leverage Test Automation: Automating repetitive tasks improves accuracy and ensures consistent results, which helps speed up the release process.
- Monitor Key Testing Metrics: Product managers should track defects, test coverage, and efficiency to make better data-based decisions.
8. Understanding the Role of Automation in Testing
Product managers need efficient testing solutions to ensure faster releases without compromising quality. Automation helps to transform software testing by making it faster, more accurate, and highly scalable.
Here’s why automation plays a crucial role in modern testing for effective product management:
- Improves Testing Efficiency: Automation eliminates repetitive test cases, allowing teams to focus on more complex testing scenarios.
- Enhances Accuracy & Consistency: Automated tests eliminate human errors, ensuring that the same test case produces consistent results.
- Supports Agile & CI/CD Workflows: When combined with automation, continuous testing provides quick feedback on software quality. This makes it easier to integrate testing in fast development cycles.
- Expands Test Coverage: Automation enables testing across multiple devices, browsers, and operating systems, ensuring a seamless user experience.
- Optimizes Resource Utilization: By automating time-consuming tests, teams can allocate resources to exploratory testing and innovation.
Product Testing Methods for Product Managers
Product Managers work with cross-functional teams to apply a variety of product testing methods throughout the software development lifecycle. Here are key methods, each serving specific goals:
Quality Assurance (QA) Testing
QA Testing is a comprehensive, structured process that identifies defects, performance bottlenecks, and usability issues before the product reaches users. It involves validating core workflows and ensuring the product’s features function as expected. Product Managers rely on QA testing to maintain product quality, meet release criteria, and support customer satisfaction.
Concept Testing
Before investing resources into development, Concept Testing helps validate product ideas or new features by collecting feedback from representative users. This method uncovers whether the concept resonates with the target audience and highlights areas for improvement, helping Product Managers prioritize features that add real value.
User Observation
By directly observing users interact with the product, teams can gain invaluable insights into real-world behavior. This hands-on approach reveals pain points, usability challenges, and unexpected usage patterns that analytics alone might miss, driving more user-centric design and development decisions.
Tree Testing
Tree Testing evaluates how effectively users can navigate the product’s structure or menu hierarchy. It uncovers confusing navigation paths and helps Product Managers refine the information architecture to ensure users find what they need quickly and intuitively.
Card Sorting
This method involves users grouping and labeling information to reflect how they naturally categorize content. Card Sorting informs the design of menus, labels, and categories that align with user mental models, enhancing navigation and overall product usability.
A/B Split Testing
A/B Testing compares two versions of a page or feature to determine which performs better based on specific metrics such as click-through rates, conversions, or user retention. It enables data-driven decision-making for continuous product optimization.
Eye-Tracking and Mouse-Tracking
By monitoring where users focus their gaze and cursor movements, these tools reveal attention patterns and navigation habits. Product Managers use these insights to optimize layout, highlight key actions, and improve overall user experience.
Time-Lapse Testing
Tracking user behavior over time, Time-Lapse Testing shows how feature adoption, engagement, and retention evolve. This longitudinal insight supports Product Managers in making strategic roadmap adjustments and enhancing long-term user satisfaction.
Canary Deployments
Canary Deployments involve releasing new features to a small, controlled user segment before a full rollout. This method reduces risk by allowing early detection of issues and gathering real-world feedback, enabling safer and smoother product launches.
Why Choose BrowserStack to Automate Testing?
Automated testing works best when it runs on a reliable and well-configured platform. However, if the platform is unstable or slow, the tests may not give accurate results.
BrowserStack is a popular cloud-based testing platform that simplifies test automation by providing access to 3500+ real devices and browsers. It enables seamless cross-browser testing without the need to manage physical devices or testing infrastructure.
With features like parallel testing, integration with popular automation frameworks, and advanced debugging tools, BrowserStack helps teams achieve faster feedback loops and more reliable test results.
Here’s why BrowserStack is the ideal choice for automation:
- Test on Real Devices & Browsers: Provides access to 3500+ real mobile devices and desktop browsers across various operating systems for comprehensive testing.
- Seamless CI/CD Integration: Easily integrate with popular CI/CD pipelines for automated testing within your development workflow.
- Parallel Testing: Run multiple tests simultaneously on different devices to accelerate execution and reduce build times.
- Supports all major Frameworks: It works with Selenium, Playwright, Cypress, and other popular testing tools, ensuring compatibility with your existing workflow.
- Advanced Debugging Tools: Get logs, screenshots, and video recordings for quick issue resolution.
Conclusion
It is imperative to set up a system where all participants can effectively collaborate on the testing process. To get the best results, you need the whole team to work together. Armed with the right knowledge and tools, you can effectively improve the quality of deliverables and achieve great things with your product. Although some would argue about the resource-heavy and time-consuming nature of the testing workflow, in a proper development environment, testing provides a unique opportunity to improve the quality of any software application without having to risk any real user or business opportunities.
In an evolving ecosystem of technology, BrowserStack offers an industry-leading testing infrastructure to maximize the productivity of your software testing team and ship quality releases at the speed of Agile. Get onboarded to streamline your product management.