Mobile applications are evolving faster than ever, and so are user expectations. With rapid release cycles, growing device fragmentation, and the need for high performance, ensuring app quality on Android is becoming increasingly complex.
Manual testing alone can’t keep up, it’s time-consuming, error-prone, and simply doesn’t scale. That’s where Android automation testing tools and frameworks come in.
Overview
Android automation testing tools are software frameworks or platforms designed to automatically test Android applications for functionality, performance, and usability.
Top tools and frameworks include:
- Appium: Cross-platform tool for automating Android and iOS apps using WebDriver, supports native, hybrid, and web apps.
- Nightwatch: Node.js-based framework using Selenium and Appium for mobile end-to-end testing.
- Selendroid: Selenium-based tool for automating native and hybrid Android apps, supports real devices.
- Calabash: BDD framework using Cucumber for writing Android UI tests in plain English.
- Espresso: Google’s native Android UI testing framework, fast and tightly integrated with Android Studio.
This article explores the top Android Automated Testing Tools and Frameworks that can help QA teams keep up with the evolving Android ecosystem.
Why is Android preferred amongst the User and Developer Community?
Here are some of the reasons why users and developers prefer Android operating system:
- Android is an open-source system that makes it easily accessible, customized, and development-friendly.
- It has a large user base as it caters to multiple audiences owning smartphones of different budgets and functionalities.
- A more extensive user base means a more significant market share.
- Learning app development on the Android platform is easy with an open-source community and contribution forum.
- Simultaneously, developers and testers have adopted tools and techniques for Android Automated Testing.
Android Testing must be performed diligently to deliver high-quality apps for the best results.
What is Android Automation Testing?
Android app automation testing is the process of using software tools and frameworks to automatically test the functionality, performance, and usability of Android applications. It involves different types of testing and requires creating scripts and automated tests that simulate user interactions with the app, such as tapping buttons, entering text, and swiping screens.
Various tools and frameworks are available for Android automation testing, which this guide covers in detail. However, as Android ecosystems grow more fragmented and release cycles become faster, many teams now rely on cloud-based real device platforms to execute automation at scale.
This enables testing across a wide range of physical devices and OS versions without the overhead of maintaining in-house device labs, while delivering more reliable insights into real-world app behavior.
The Role of Cloud-Based Device Testing in Android Automation
Modern Android automation has shifted toward cloud-based real-device platforms for several reasons:
- Eliminating False Positives: Emulators often fail to replicate real-world hardware behavior, such as battery drain, thermal throttling, or GPS accuracy. Cloud-based real devices ensure that if a test passes, it works on the hardware your customers actually use.
- Massive Parallelization: Running a test suite on one device takes hours, but testing parallelly across 100 devices simultaneously will only take minutes. Cloud platforms enable this scale without the overhead of maintaining physical hardware.
- Accessibility to Fragmented Hardware: Android fragmentation is a moving target. Cloud platforms provide instant access to everything from legacy models to the latest flagship devices and various OS versions, ensuring zero gaps in your testing matrix.
- Seamless CI/CD Integration: Modern cloud testing is headless and integrated. It allows developers to trigger automated tests directly from their CI/CD pipelines (like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or GitLab), receiving AI-powered feedback and debugging insights in real-time.
Why opt for Android Automation Testing?
Android fragmentation is one of the major concerns for those seeking to create an Android app. It must work flawlessly on thousands of Android devices with different hardware specifications and OS versions.
Manually testing an app on thousands of Android devices would take enormous time and effort. You’d have to hire many testers to work through every user scenario on every Android device, at least the popular ones. This is where you opt for Android app automation testing.
- Instead of running every scenario manually, automate as many of them as possible, create test scripts that emulate user actions, and establish benchmarks by which tests will pass or fail.
- Additionally, you can use parallel testing to run tests simultaneously on multiple Android devices, thus reducing time and effort even further.
Of course, one cannot completely do away with manually testing mobile applications. Human perception and judgment are essential because the success of an app does, in the end, depend on what users think of it. However, except for the most necessary test cases, QAs must aim to automate the bulk of their test scenarios.
Top Android App Automation Testing Tools & Frameworks in 2026
Automation Testing of Android Apps is pivotal in a software release cycle. Here are some of the top Android App Automation testing tools and framworks:
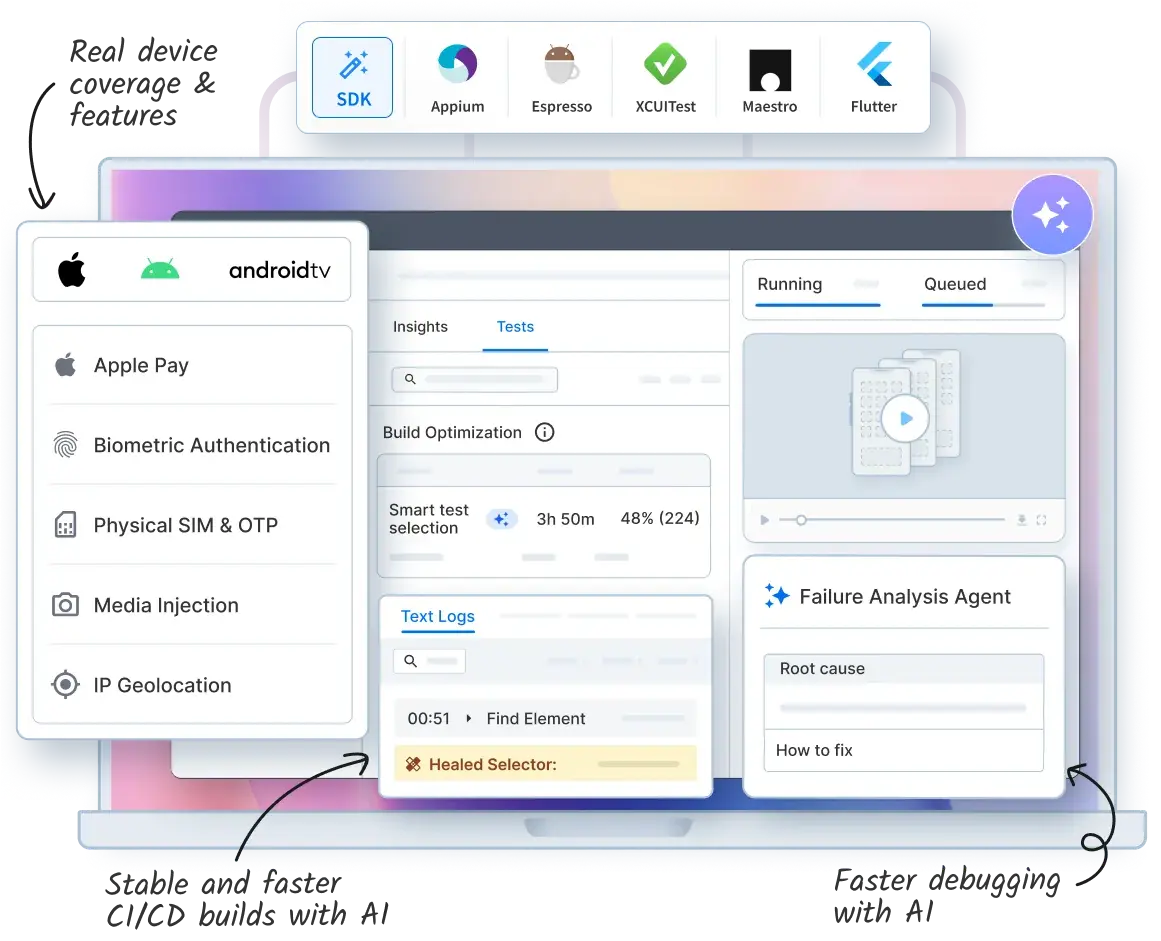
1. BrowserStack App Automate
BrowserStack App Automate is an AI-powered platform designed to scale your automation on a real device cloud of 30,000+ real Android and iOS devices and 3500+ browser combinations . It removes the flakiness of emulators by providing a stable, high-performance environment for every build.
It streamline pipelines with Agentic AI Features such as:
- Self-Healing: Automatically detects and fixes broken locators at runtime to keep your builds green.
- AI Failure Analysis: It automatically processes logs, video, and stack traces to categorize failures and suggests actionable remediation steps, reducing debugging time by 95%.
- Test Selection: Intelligently runs only the tests relevant to your code changes, cutting infrastructure costs by up to 50%.
Its key features also include:
- Effortless SDK Integration: The BrowserStack SDK allows you to migrate existing test suites to the cloud with zero code changes.
- Native Feature Support: Automate complex scenarios like FaceID/TouchID, Camera Image Injection (QR codes), SMS/OTP 2FA, and Network Throttling.
- Unified Debugging: Get high-definition video recordings, device logs, and network (HAR) logs in one dashboard for every test run.
- App Frontend Performance: Automatically capture critical metrics during test runs, including UI rendering time, CPU/memory usage, and battery consumption to catch regressions early.
- Enterprise-Grade Custom Device Lab: Access a private cloud of dedicated devices for strict security requirements, allowing for persistent device states, custom MDM profiles, and SOC2/GDPR compliance.
2. Appium
Appium is a widely used open-source app testing tool. It is a cross-platform testing framework known for its flexibility, allowing QAs to create test scripts against numerous platforms, such as iOS, Windows, and Android, using the same API.
That means QAs can use the same code for iOS and Android, saving significant time and effort. The Appium Inspector provides a unified interface for inspecting and interacting with elements across iOS and Android as well. This simplifies the testing process for apps running on multiple platforms.
Much like Selenium, Appium also allows testers to write test scripts in multiple programming languages, which include Java, JavaScript, PHP, Ruby, Python, and C#.
You can run Appium tests in parallel using Appium Grid.
Run Android Appium Tests on Real Devices
3. Nightwatch
NightwatchJS is a Node.js based framework that is developed and maintained by BrowserStack. Nightwatch uses Appium under the hood to achieve mobile application automation on virtual simulators & real devices. Nightwatch also takes care of the entire installation with just a single command.
You can run Nightwatch tests in parallel using Appium Grid.
4. Selendroid
Selendroid is based on the Selenium framework, Selendroid is used for Android app testing. Driving UI of native and hybrid apps, Selendroid can be used on android emulators and actual devices. Similar to Selenium, Selendroid offers playback and recording features.
Selendroid can also be combined with other frameworks, such as JUnit. It offers cross-platform support through export options for scripts in other languages such as Java, Python, and Ruby.
5. Calabash
Calabash is an open-source mobile testing framework tool that works with multiple languages, such as Java, Ruby, .NET, etc., to test native and hybrid apps.
Using Calabash, testers can write and execute automated acceptance tests for Mobile apps. It supports actions such as swiping, screen rotate, tap, etc. It has support for the Cucumber framework. Hence, easier to understand by non-technical stakeholders and supports Behaviour Driven Development (BDD).
6. Espresso
Espresso is an open-source app testing tool used to test UI. It is an Android testing framework developed by Google. It is known for its robustness, simplicity, and flexibility.
Its core features are Synchronized test executions, intent validations, and capabilities to run recipes.
Espresso enables developers to test both Android native views and hybrid web-views. It supports test scripts in Java and Kotlin. Espresso supports both black-box testing and testing of individual components during development cycles.
Factors to consider for App Automation Testing
Android apps have evolved, and so have their features and functionalities. With the growing user expectations, adding new exciting features to the Android App is essential for customer retention. Moreover, as the number of Android devices in the market increases, so should the feature support for these devices to ensure a consistent user experience. Thus, the scope of testing has increased as well.
Here are factors to consider when testing an Android app:
Functionality
Every app has some core functionalities that come from the users’ requirements. Functional testing is done to verify whether the app runs for every use case. Take an example of a ride-sharing application (like Uber, Lyft). A tester has to ensure the following test scenarios:
- The maps are working in sync with the user’s location
- The available cab locations shown to the user are accurate
- The driver ratings are functional and verified
- The pricing system is working as per the algorithms defined
- The booking time is optimized
Cross Platform Compatibility
Many new Android devices are launched every year. These include different shapes, sizes, configurations, and even components. Thus, it is essential to understand your app’s requirements and make sure that it is universally accepted and compatible with every Android device. Compatibility is tested based on the device and the version of the Operating system.
Follow-Up Read: Top Android Devices For Mobile App Testing
User Interface (UI)
UI is another essential aspect of any app since it is the critical connection between the user and the functionality. UI includes the visual elements of the app and how well they represent each function. App testing for UI enables the tester to ensure the correct visual representation of buttons and text.
Security
Security has been a significant concern since technology has brought in many more users, which has made the safety of private user data more vulnerable. This is very critical for apps concerning finance and communication. Security testing is thus done to ensure the encryption and decryption of essential data. It also ensures that the data stored is safe and secure from vulnerabilities.
Interface
App development is often done in phases, and once all the stages are completed, the app is tested for any bugs. The app is thoroughly tested for all components essential such as location services, maps, social app integration, location services, maps, voice recording, etc. This is known as interface testing.
Solving Android Automation Challenges with App Automate
As Android automation testing scales, teams often face recurring challenges related to device coverage, test stability, execution speed, and debugging.
The table below highlights common Android automation challenges and how BrowserStack App Automate helps address them.
| Challenge | App Automate Solution | Key Benefit |
| Android Fragmentation | Instant access to 30,000+ physical devices, from legacy models to the latest flagships (Samsung S24, Pixel 9). | 100% real-world accuracy without hardware overhead. |
| Test Flakiness | AI Self-Healing feature detects and fixes broken UI locators at runtime to keep builds green. | Drastically reduced script maintenance. |
| Slow Feedback Loops | Run thousands of tests simultaneously across various device/OS combinations. | Shorter execution time (days to minutes). |
| Complex Debugging | AI-Driven Failure Analysis automatically categorizes failures (product bug vs. system flake) with HD video and logs. | 95% reduction in debugging time. |
| Native Scenarios | Securely test FaceID/TouchID, QR scans, and SMS/OTP 2FA on real hardware. | End-to-end automation of critical user journeys. |
| Build Inefficiency | Test Selection AI Agent identifies and executes only the tests impacted by your specific code changes. | Up to 50% cut in build times and costs. |
App Automate empowers mobile teams to achieve genuine continuous delivery with complete confidence in their application’s performance. It accomplishes this by moving beyond reactive troubleshooting to utilize AI-powered orchestration.
Best Practices for Android App Automation Testing
To ensure effective and reliable automation, it’s essential to follow proven best practices throughout the testing lifecycle:
- Define a Clear Testing Scope: Set an achievable and well-defined scope to align expectations across development, QA, and product teams. Focus on high-impact areas to maximize test coverage and efficiency.
- Choose the Right Framework: Select automation tools based on project requirements, not just popularity. Consider app type, team expertise, testing goals, and integration needs to pick the most suitable framework from the options available.
- Test on Real Android Devices: With Android’s diverse device ecosystem, emulators alone are not enough. Real devices reveal issues emulators miss, like battery drain, network instability, or hardware-specific bugs. Use a real device cloud like BrowserStack to test across thousands of Android phones and tablets in real user conditions.
- Follow Consistent Scripting Standards: Maintain clean, uniform scripts with proper indentation, naming conventions, and comments. This improves readability, collaboration, and long-term maintainability.
- Update and Maintain Test Suites: Android OS updates are frequent. Regularly review and update your test cases to remain compatible with new versions and avoid test failures due to platform changes.
- Track Automation Metrics: Measure success through key metrics like execution time, pass rate, test coverage, and build stability. Tools like BrowserStack Test Observability offer real-time insights to optimize your automation strategy.
- Don’t Compare Manual and Automated Testing: Automation isn’t a replacement for manual testing. Each serves a different purpose; manual testing excels at exploratory and UI/UX validation, while automation ensures speed and consistency in repetitive scenarios.
- Strengthen Debugging with Rich Test Reports: Enhance debugging by using detailed reports with screenshots, logs, and video recordings. This helps pinpoint failures quickly and improves overall test reliability.
Conclusion
With Android holding over 71% of the mobile market share, testers need a reliable and scalable approach to ensure app quality. Automating the testing process is key to increasing device coverage and accelerating release cycles.
While there are numerous Android automation tools and frameworks available, teams must carefully choose the right ones based on their project needs and set realistic expectations across engineering teams.
It’s also crucial to move beyond APK emulators and test on real Android devices to simulate actual user conditions. Emulators can’t replicate scenarios like incoming calls, battery drain, or network variability.
A real device cloud like BrowserStack enables seamless integration with frameworks like Appium and Espresso, allowing you to run automated tests on thousands of real Android devices for more accurate and reliable results.