Speed is one of the most essential variables that determine a website’s ranking on Google, its traffic, and its conversion rate. Statistics indicate that 40% of visitors will leave a website if it takes longer than 3 seconds to load. In order to increase website traffic and conversions, it is crucial for all businesses to keep their websites running quickly.
Overview
Why does a Fast Loading Website matter?
- Faster Load Time Leads to a Better Ranking on Search Engines
- Reduction of Bounce Rate
- Improve Overall Conversions
- Improve Brand Credibility
Metrics to track for evaluating Page Load Speed
- Time to First Byte (TTFB)
- Page Load Time
- Server Response Time
- First Contentful Paint (FCP)
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- First Input Delay (FID)
- User Engagement Metrics
- Time Required to Parse HTML into a DOM and Execute the Script
- Round Trips
How to Improve Your Page Load Time?
- Optimising the Size of High-Resolution Images
- Using a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Minify HTML, CSS and JavaScript
- Boost Server Response Time
- Incorporate Browser Caching
- Reduce Redirects
This guide delves into Page Load Speed, why it matters and how to evaluate and improve it.
Why should a Website Load Fast?
Users prefer websites with quick load speeds over those with slow ones. But loading speed is not merely a matter of personal preference; it also has a significant impact on a website’s success.
The longer it takes a website to load, the higher its bounce rate will be. A high bounce rate indicates to search engines that readers do not find the page’s content useful, resulting in a drop in ranking. And ecommerce businesses will lose customers if their checkout page is even a fraction of a second slower than the competition.
And this brings forth the subject of this article – How fast should a website load?
A Statista Survey shows that the longer the wait time, the more an user is willing to leave the site unchecked. In fact it significantly increases around the 5 second mark.
As per some recent statistics,
- 1 in 4 visitors would leave a site that takes more than 4 seconds to load
- Every 1 second delay reduces user satisfaction by 16%
- 64% of dissatisfied shoppers do not visit a slow website again
- Seventy percent of consumers indicate that page speed influences their purchasing decisions from online retailers.
- Each additional second of load time decreases conversion rates by an average of 4.42 percent (in the first five seconds).
What is Website Load Time?
Website load time, also known as web page load time, is the amount of time it takes for a website or web page to completely load and appear on the screen. This covers all content on the page such as text, photos, and videos. Essentially, it is the rate at which all of a website’s content loads.
Page performance can depend on a lot of elements – some examples include: Page type, user behaviour, file sizes, website server/host, inefficient coding, hotlinking, and too many plugins and/or widgets.
Note: Page Speed and Site Speed are often used interchangeably, but technically, Page Speed focuses on individual pages (e.g., “page-load time” or “time to first byte”), whereas Site Speed is an aggregated average across multiple pages.
How is Web Page Speed Measured: Key Metrics
Website speed is the rate at which your site loads for visitors. This is based on an average of numerous page speeds; page speed, or page load time, refers to the amount of time it takes for a web page’s elements, such as text and graphics, to fully load.
Research indicates that website users are likely to leave if it takes more than 400 milliseconds – the blink of an eye — to load.
Some key metrics that allow enterprises to monitor Web Page Speed are enlisted as below:
- Time to First Byte (TTFB): This measure helps to determine how long it takes for web browsers or mobile devices to obtain the first response from the server following a request.
- Page Load Time: This assists in determining the time required to completely load a certain page.
- Server Response Time is used to determine how long it takes to receive a complete response from a server.
- First Contentful Paint (FCP) is the time it takes for the first piece of content (text, image, etc.) to appear on the screen.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This statistic is used to determine the amount of time required to load the largest piece of content (text or image).
- First Input Delay (FID) is used to track the time between when a user submits a request (such as clicking a button or link) and when the browser begins to function.
- User Engagement Metrics like bounce rate, session duration, and conversion rates.
- Time Required to Parse HTML into a DOM and Execute the Script
- Round Trips: This metric measures the time from HTTP request to server and from server to HTTP response, calculating the total round trip time.
Must Read: How to test Website Loading Speed
How Fast should your Website Load?
The short answer to the question how fast should your website load is simply, as fast as possible.
The average page load time on desktop is 2.5 seconds and 8.6 seconds on mobile, according to a survey of the top 100 websites globally. Top browsers like Google strives for load times of less than 0.5 seconds.
The average load time for mobile websites over 3G connections is 19 seconds. Models indicate that publishers whose mobile sites load in five seconds earn up to twice as much mobile advertising revenue as those whose sites load in nineteen seconds.
If industry-wise averages are checked –
- On average, automotive retail websites take six seconds to load.
- Consumer packaged goods websites load in an average of 6.1 seconds.
- On average, financial websites require 5.1 seconds to load.
- On average, healthcare websites require 5.6 seconds to load.
- On average, media websites require 5.5 seconds to load.
- On average, retail websites take six seconds to load.
- On average, technology websites take 6.8 seconds to load.
- On average, travel websites take 6.7 seconds to load.
The average desktop First Input Delay (FID) speed is 12.73 milliseconds, while the average mobile FID speed is 59.73 milliseconds, with pages on mobile taking 70.9% longer to load on average than on desktop.
Slow load times generally lead to negative Google Rankings.
According to studies,
- As Page Load Time grows from 1s to 3s, the likelihood of bounce increases by 32%.
- As Page Load Time grows from 1s to 5s, the likelihood of bounce increases by 90%.
- When Page Load Time grows from 1s to 6s, the likelihood of bounce increases by 106%.
- When Page Load Time climbs from 1s to 10s, the likelihood of a bounce increases by 123%.
Why does a Fast Loading Website matter?
Google said in 2010 that it will examine a website’s speed before assigning a rating. If a website takes more than five seconds to load, Google will not rank it. Numerous organisations employ tools to test their website’s speed, but the results are inaccurate, resulting in a loss of ranking, decreased traffic, and decreased sales. It is necessary, therefore, to accurately assess your website’s speed and determine whether a fast loading speed is required.
So, there are several reasons why a website should load quickly.
Pro Tip : Speed Lab by BrowserStack is one of the solutions that facilitate the evaluation of Website Speed insights. Speed Lab gives you an instantaneous Page Speed Score out of 100 for both Desktop and Mobile platforms. With this information, your website optimization team can create a user-friendly website.
- Faster Load Time leads to a better Ranking on Search Engines
In the modern era, Google will only rank websites that load quickly and in less than five seconds. As you boost your website’s loading speed, Google will give you a higher rating, and you’ll begin receiving high-quality traffic, which will raise your conversions. Visitors will spend more time on your website if it has a fast loading speed that keeps them engaged with the content, resulting in a higher Google page rank. If you wish to expand your business, attract more visitors, and improve your sales, you must increase the speed of your website.
- Reduction of Bounce Rate
Bounce rate is an important aspect that might negatively impact conversion rate. Say your website receives a substantial amount of traffic, but visitors leave quickly because it takes too long to load. In such a scenario, the bounce rate will increase, severely hurting your website, and Google will blocklist your site and reduce its rating. According to Google, a website’s bounce rate increases by 123% if its speed drops from 1s to 10s. So, it is necessary to boost the speed of your website so that clients can immediately interact with it without having to wait for it to load.
- Improve overall conversions
Any website’s primary objective is to attract potential customers, enhance engagement, and boost conversions. Improving the speed of your website improves your site’s rating, attracts more visitors, and facilitates the customer’s journey, hence increasing sales and conversions. A website that loads quickly can improve the consumer experience by allowing them to navigate to any page, acquire information, and make purchasing decisions more quickly. Instead, many people will not wait for the page to load and will simply navigate to a different website.
- Improve brand credibility
The websites of businesses must be quick and responsive. It enhances the brand’s credibility and the customer experience. Customers who visit a website that runs slowly and takes a long time to load will immediately depart and never trust that brand again. Thus, brands must maintain a faster website speed and simplify the purchasing journey.
Reasons for slow load time
Every website must be optimised for the fastest possible speed, regardless of the device-browser-operating system combinations that visit it. To implement appropriate optimization strategies, developers must comprehend these 10 fundamental causes of slow website loading and learn how to address them to increase traffic, revenue, and trustworthiness.
Reasons for slow Load Time:
- Poor Server Performance
- Unsuitable Server Location
- Heavy Traffic
- Excessive Flash Content
- Increased HTTP Requests
- Code Density
- Inadequate Caching Techniques
- Too Many Ads
- Using an Outdated CMS
- Lack of a CDN
- Poor Server Performance
When a user clicks on a website, the browser pings the server, requesting all the necessary information and data to load the website. Consider the analogy of a car key starting the engine.
If the server’s performance is subpar, it takes longer for it to react. Even if every other aspect of a website’s operation is flawless, a subpar server’s performance will slow down the site’s load time.
Bad server performance is typically attributable to the web host’s caliber.
Less expensive web hosts will provide a shared server. This indicates that a website shares space and resources with multiple other websites. In this instance, each site has a low rank because it is behind other sites in the queue.
- Unsuitable Server Location
Long-distance calls require more time to connect because the information required to make the phone ring must travel further. More cables means more satellites for transmission. It is the same when it comes to websites.
The further this distance is, the slower the site will load.
If a person from the United States accesses a website with a Danish server, the browser ping required to load the website must go halfway around the world, request access to the relevant data, and then travel halfway back to the visitor’s device.
- Heavy Traffic
At any given level, a web server can only support requests from a certain number of users. After this threshold is exceeded, the page will load more slowly; for instance, the more traffic on an e-commerce website, the slower the website. With an increase in website traffic, service providers may need to provide additional resources. But, without an upgrade, the current services will fall short, resulting in slower website load times and worse conversion rates.
- Excessive Flash Content
Flash is excellent for enhancing the interactivity of a website, but it can also impede load times. Flash content tends to be heavier, and more of it will slow down a website’s performance. If feasible, minimize or remove the size of the Flash files. Replace old Flash content with HTML5 counterparts, which typically have more manageable file sizes.
- Increased HTTP Requests
If a website contains excessive amounts of JavaScript, CSS, and picture files, HTTP requests will increase. In this situation, every time a user visits the website, the browser sends far too many requests to the server to load numerous files. Obviously, this would result in a slow page load time.
- Code Density
As explained in the preceding sections, large, dense web elements will slow page load speed. Few things are more dense than the website’s coding. For instance, Facebook has approximately 62 million lines of code. Google has two billion users. The Large Hadron Collider, the world’s largest and highest-energy particle collider and the world’s largest machine, employs 50 million lines of code.
If a website lacks the resources to transmit and execute dense, complex code, it will see a performance decrease.
- Inadequate Caching Techniques
Caching is a method by which a browser caches frequently accessed data in its cache. This means that the browser will not need to reload all the data the next time the website is visited. With speedier data retrieval, the loading time is decreased. Without cache, the website must continually load all files. This is needless and will detract from the user experience when it is so simple to resolve.
- Too Many Ads
Although advertisements are a fantastic way to monetize high-traffic websites, they can slow down web pages. Additional advertisements result in additional HTTP requests, and their impact on page load speed has already been described. Rich media advertisements are extremely detrimental in this aspect.
With pop-ups and pop-unders, interstitials, and auto-downloads clogging up a website, the real web content would take significantly longer to load.
- Using an Outdated CMS
Digital material is created, managed, and modified through a Content Management System (CMS). They are typically employed for corporate and website content management.
When utilizing a CMS like WordPress or Wix to manage a website, ensure that the most recent software upgrades and speed optimization plugins have been installed.
By keeping up with the most recent upgrades, the program is free of defects and performance-related issues.
Read More: Top 5 WordPress Plugins to Speed Up Websites
- Lack of a CDN
A content distribution network, or CDN, is a network of geographically dispersed, independently-operating servers. They are utilized to offer web content to website users with enhanced accessibility, visibility, and performance. This article’s second point discusses why server location affects page load speed.
A CDN assigns a website local servers. This provides the website with an American server for its American visitors and a Danish server for its Danish guests. This reduces the online content’s round-trip time (RTT) and speeds up the loading of web pages.
Must Read : 10 Reasons for Slow Website Loading
How to Evaluate Your Load Time
Fortunately, a variety of internet-based tools make it simple to discover speed bottlenecks and speed enhancements, regardless of the technology stack used to construct the website. A user-friendly website is expected to have the following characteristics:
- User-Friendly & Simple to Browse
- Mobile Compatible
- Rapid Device Compatibility Loading
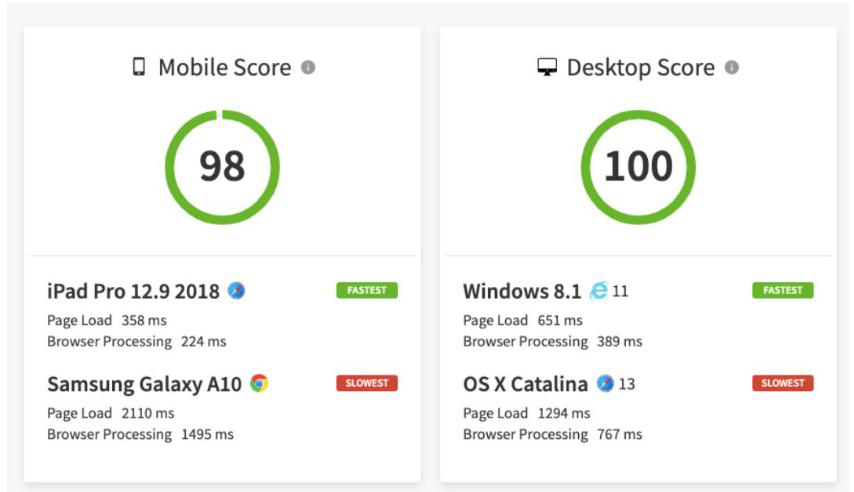
Speed Lab by BrowserStack is one of the solutions that facilitate the evaluation of Website Speed insights. Speed Lab gives you an instantaneous Page Speed Score out of 100 for both Desktop and Mobile platforms. With this information, your website optimization team can create a user-friendly website.
This is a simple three-step approach for testing your website’s loading performance with SpeedLab:
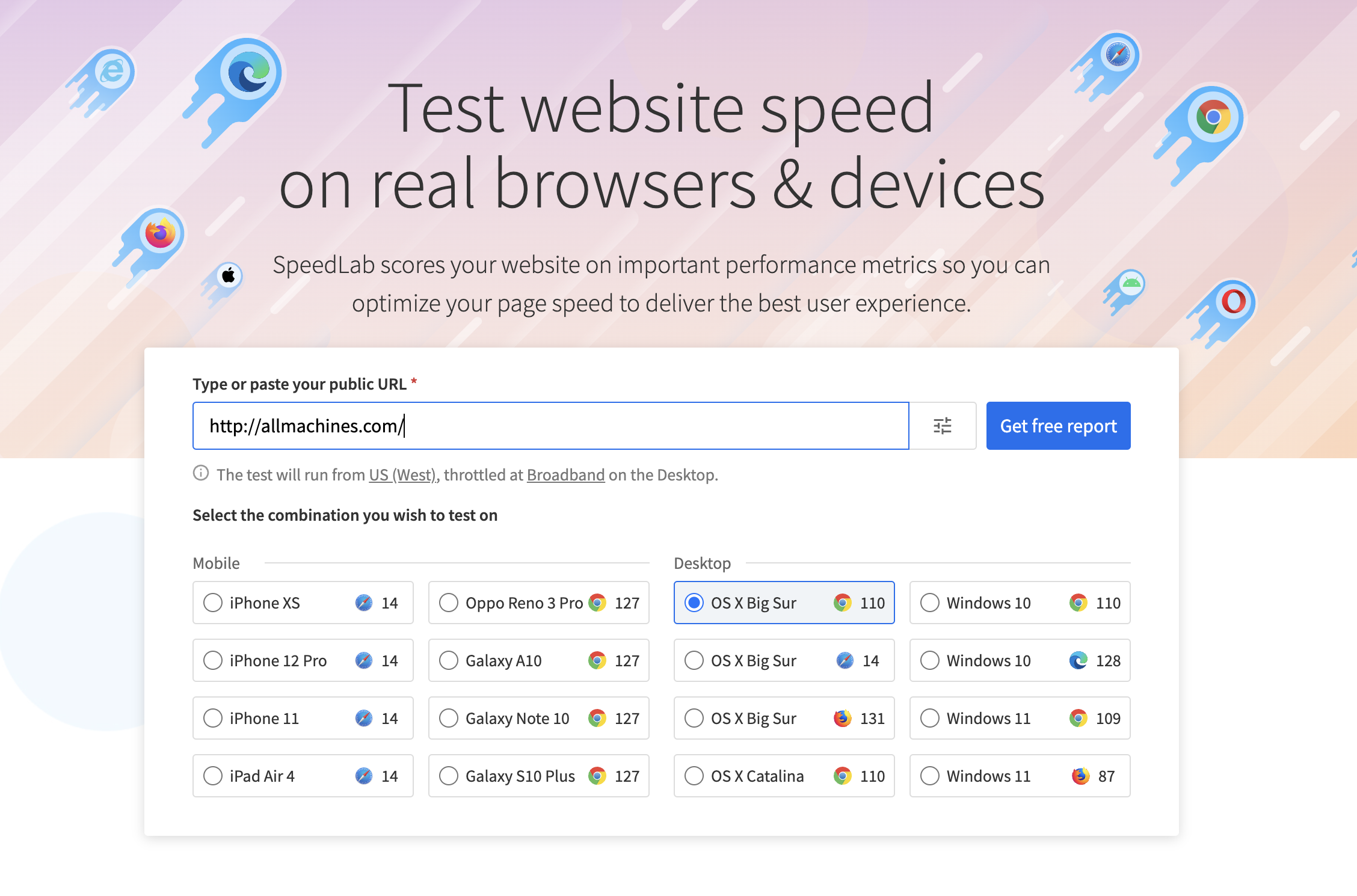
Step 1: Choose your desired testing instrument on SpeedLab. Example: Testing AllMachines website using BrowserStack SpeedLab.
Read More: How to test Loading Speed of Website
Step 2: Enter your website’s URL and choose a browser to test.
Step 3: Select Get Free Report
Pro Tip : BrowserStack’s geolocation testing ensures that your website is displayed as intended across geographies and targeted regions, hence accelerating your global access.
How to Improve Your Page Load Time
Some general steps to help speed up Page Load Time are as below:
1. Optimising the size of High-Resolution Images
Graphics are a vital aspect of websites and have a significant effect in the loading speed of a page. High-resolution images typically have bigger file sizes. Hence, they can result in slow load times. Site designers must ensure that image sizes are appropriately compressed without sacrificing visual quality.
With tools such as Adobe Photoshop, one may dramatically reduce image file sizes from 3MB to 200KB. WordPress users can compress images using plugins such as WP Smush. For page speed improvement, this will be a straightforward gain for image-heavy websites.
2. Using a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A Content Delivery Network, also known as a Content Distribution Network, is a collection of servers that are geographically dispersed. CDNs assist website owners in hosting their sites on servers located across the globe in accordance with their target audience.
It basically expedites the delivery of all materials required for loading web content (HTML files, photos, videos, etc.) according on the user’s geographic location.
For instance, if a business owner has a website hosted in India, but a significant number of clients access it from the United States, page loading may be delayed. In this situation, it makes sense to host a version of the website in the United States utilizing a content delivery network (CDN). Amazon Cloud Front and Cloudflare are well-known CDN providers.
3. Minify HTML, CSS and JavaScript
Obviously, a file with a reduced file size will load faster. Web developers must now concentrate on minifying the code by removing extraneous lines of code, spaces, commas, and other characters. Gzip allows developers to compress HTML, CSS, and Javascript files greater than 150 bytes. Yahoo claims that employing the Gzip compression method can reduce download time by 70%.
4. Boost Server Response Time
The server’s response time is dependent on numerous variables, including:
- Quantity of website visits
- The amount of assets utilized by each website hosting service and the software employed
- Teams must invest in a server that is both dependable and high-performing.
Web developers must also keep an eye out for performance bottlenecks caused by delayed routing or database queries, which can increase page load times.
5. Incorporate Browser Caching
Using the browser caching feature enables the browser to save information about recently visited web pages. This includes graphics, stylesheets, and even JavaScript. Caching a recently visited web page reduces load time because the browser does not need to reload the complete page when a visitor returns to the site.
6. Reduce Redirects
Redirects are required when there are substantial content modifications (migrating, deleting specific pages). However, having an excessive amount can result in additional HTTP requests. This can have an adverse effect on page load times, especially on mobile devices.
This brings us to an important topic concerning mobile website load times.
It is important to keep in mind that Google ranks webpages using the mobile-first crawling technique.
Conclusion
Having a quick page load time is essential for increasing conversion rates and income. While a few extra seconds may not seem like a big concern, studies indicate that with each passing second, the likelihood of losing potential clients increases.
Conversion rates are influenced by website load times, and as a result, your business as a whole. It does not necessarily take a great deal of time or effort to ensure that your load time is as efficient as possible, but it does require some thought. You will observe an improvement in your UX, conversions, time-on-page, and income if you optimize the speed of your web pages.
Clearly, developers will not spend time and effort optimizing websites if they are not sluggish and difficult to use. If a website is slow and loses users, however, it must be speed up immediately.
It is best to use a tool to assess website speed before it is released into production, rather than waiting for traffic to drop before evaluating whether page load time is slow. Also, as discussed previously, the setup of the device itself might affect the loading speed of the same website on different devices. Thus, a website speed test must be conducted with a tool that utilizes actual devices.
BrowserStack SpeedLab offers precisely this. This free application does a performance test across various genuine browsers, devices, and operating systems when a user inputs their URL. The resulting report will demonstrate not only how quick (or sluggish) the website is, but also how it performs in terms of speed across numerous desktops, mobile devices, and browser versions.
Regardless of how fast the website loads, it will all be to no avail if the core functionality fails to perform as per user expectations. For optimal results, all testing, including unit tests, must be run on actual devices. Testing is only 100 percent effective when conducted under real user situations. Emulators/Simulators and Virtual Machines are incapable of accurately simulating the precise conditions under which devices work; hence, their findings do not instill sufficient confidence to release the code into production.
Real device testing is essential for both manual and automated Selenium Testing in order to receive credible findings. In order to avoid the prohibitive costs of establishing an in-house lab, businesses tend to favour cloud-based testing infrastructure.