Integrating TestNG with Eclipse, which is one of the most commonly used IDEs among developers and testers, helps streamline the testing workflow. This guide walks you through the various ways of installing TestNG in Eclipse, helping you set up your test automation environment quickly and efficiently.
What is TestNG Framework?
TestNG is a Unit testing framework for Java inspired by JUnit and NUnit, which allows you to run your tests using TestNG Annotations. It is popular because of the Annotations range it supports as compared to JUnit.
Features that make TestNG Framework so popular are:
- Wide range of Annotations Support.
- Support Data-driven tests
- Flexible execution model via Testng.xml configuration
- Concurrent testing: TestNG runs tests in arbitrarily big thread pools with various policies available (all methods in their own thread, one thread per test class, etc.) and tests whether the code is multithread safe.
- Parallel Run support: With parallel testing, multiple tests can be run simultaneously, supporting testing at scale in lesser time.
Features of TestNG
Here are the main features of TestNG:
1. Test Configuration: TestNG offers a set of annotations to configure pre-test and post-test conditions efficiently. Annotations like @BeforeSuite, @BeforeTest, and @BeforeMethod help set up the environment or initialize resources before tests run. Similarly, @AfterSuite, @AfterTest, and @AfterMethod are used for clean-up activities after the test execution. This structured setup makes test configuration simple and organized.
2. Test Data Management: TestNG supports data-driven testing through the @DataProvider annotation, letting you run the same test method with multiple input data sets. This is useful for testing input combinations like positive, negative, and random values, making your test scenarios more robust and comprehensive.
3. Parallel Test Execution: TestNG enables parallel test execution, significantly reducing total execution time. This feature is handy when executing large test suites, as it improves efficiency by executing tests concurrently across threads or machines.
4. Managing Test Dependencies and Groups: TestNG helps define dependencies between test methods. For instance, if a login test depends on successful user registration, and the registration test fails, the login test will be skipped.
Additionally, TestNG supports grouping of tests based on features or modules, enabling easy organization and management of complex test cases.
5. Test Assertions: In TestNG, assertions validate expected outcomes against actual results. With built-in assertion methods like assertEquals(), assertTrue(), and assertFalse(), testers can verify application behavior efficiently and ensure that the system under test performs as expected.
Read More: What is Assertion Testing?
What is Eclipse
Eclipse is a popular open-source Integrated Development Environment (IDE), essentially used for Java development. However, it supports many other programming languages through plugins.
Different ways to run TestNG Test
TestNG tests can be run using two different methods as follows:
- Inside IDE (Like Eclipse)
- Via Maven Profile through Command Line
Running tests within IDE is needed during the development and debugging of the TestNG test. While, Maven Profile is used when you need to execute all the tests outside the IDE, like executing the TestNG tests from Jenkins.
How to install TestNG in Eclipse
To configure Eclipse you need to perform the following:
- Add TestNG to Eclipse using TestNG Plugin configuration and Run
- Creating Sample Maven Project by adding TestNG dependency
How to Install and Add TestNG in Eclipse
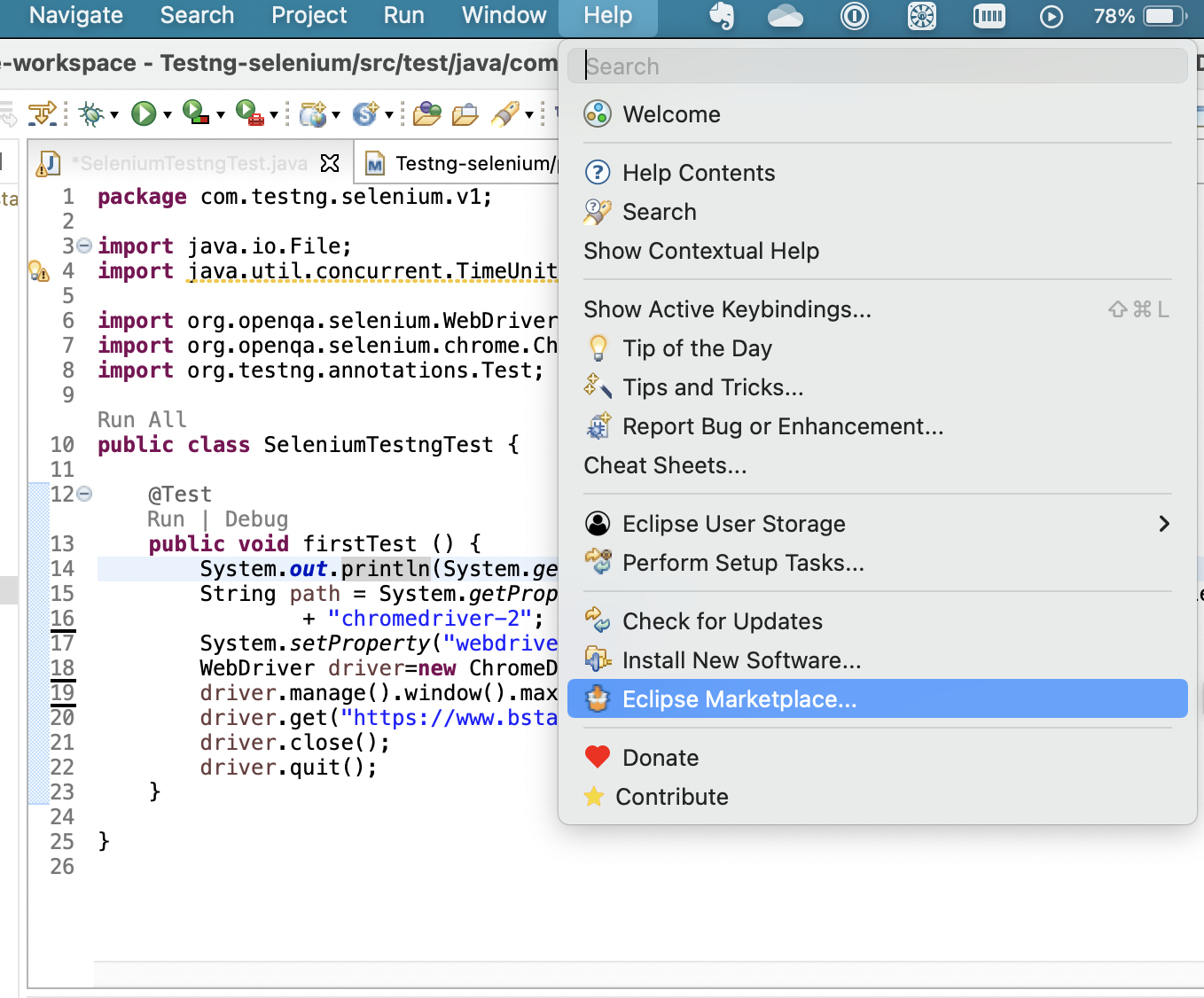
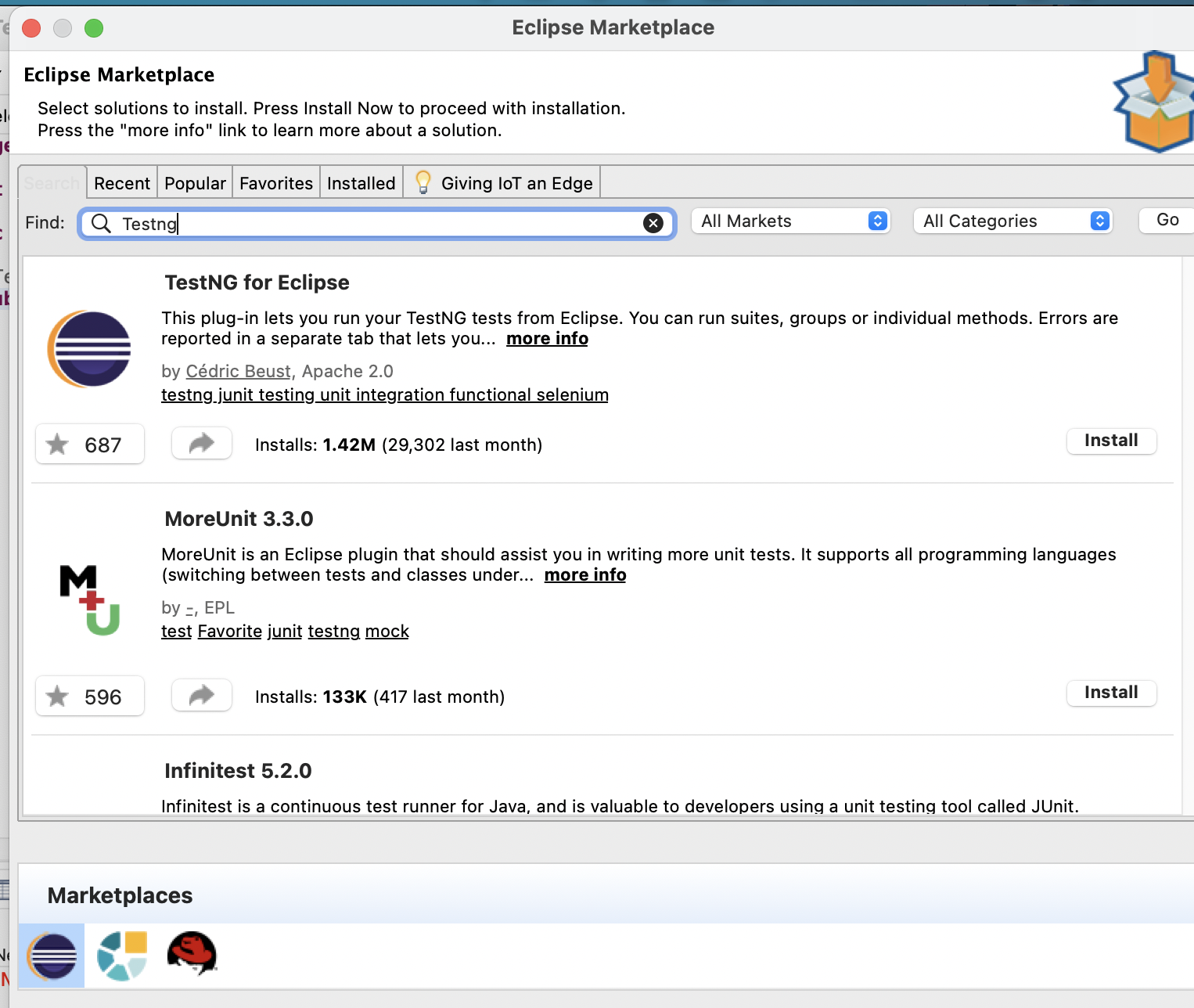
Step 1: Navigate to Eclipse Marketplace
Step 2: Search for TestNG and click on install.
Note: After the plugin is installed, restart the Eclipse IDE
As the plugin is installed, you can see Options like Run All, Run | Debug in the editor itself, and clicking on Run above the TestNG Test will execute the test likewise Debug will allow debugging the test.
Adding a TestNG plugin within the Eclipse IDE helps in making the test execution easier by directly running the tests inside the Text Editor itself. Hence, it is recommended to configure the TestNG Plugin in Eclipse to run Unit Tests.
Creating Sample Maven Project by adding TestNG dependency
Here are the steps to create Sample Maven Project and how to add TestNG Dependencies:
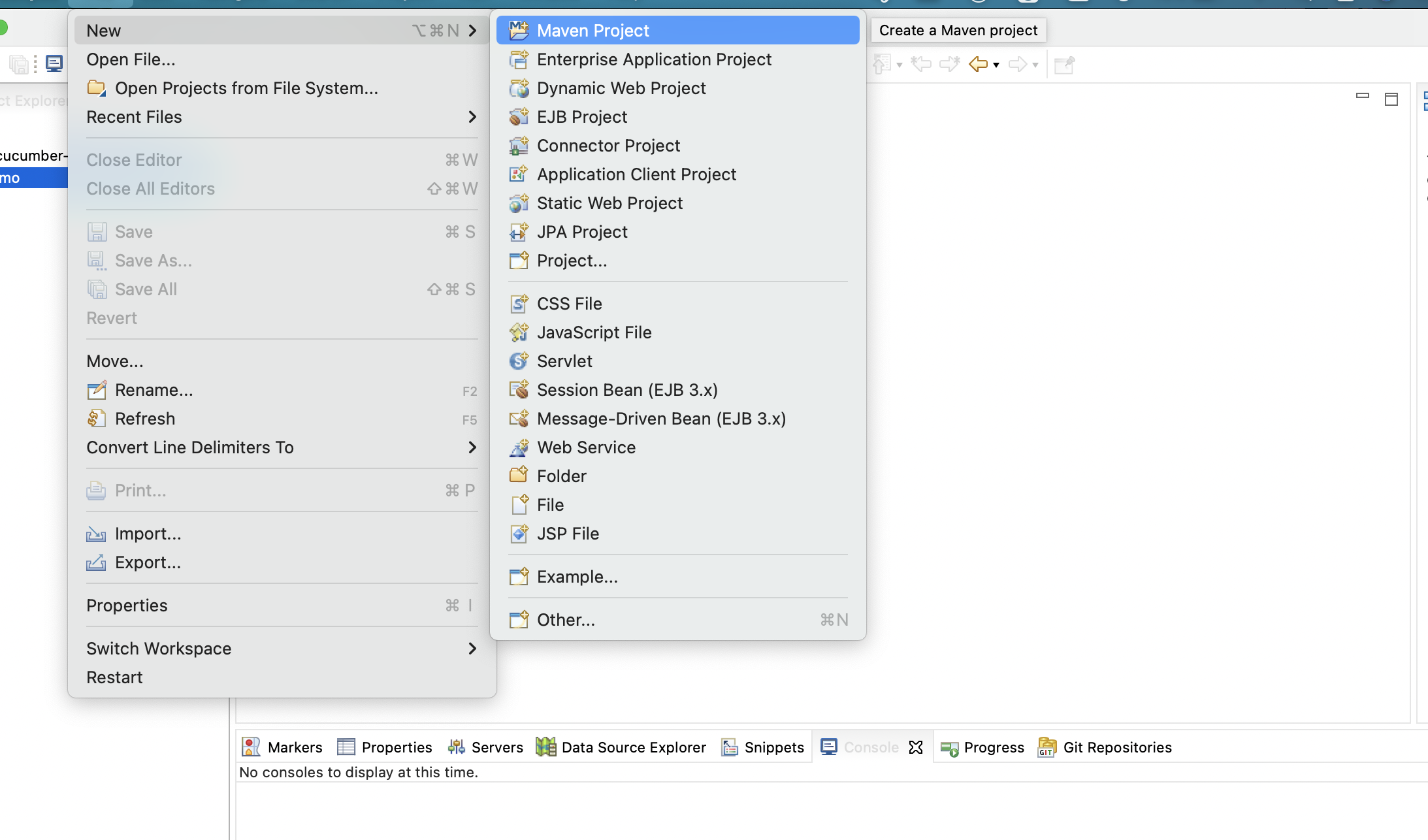
Step 1: Create a new Maven Project by opening eclipse. Click on New > Select Maven Project
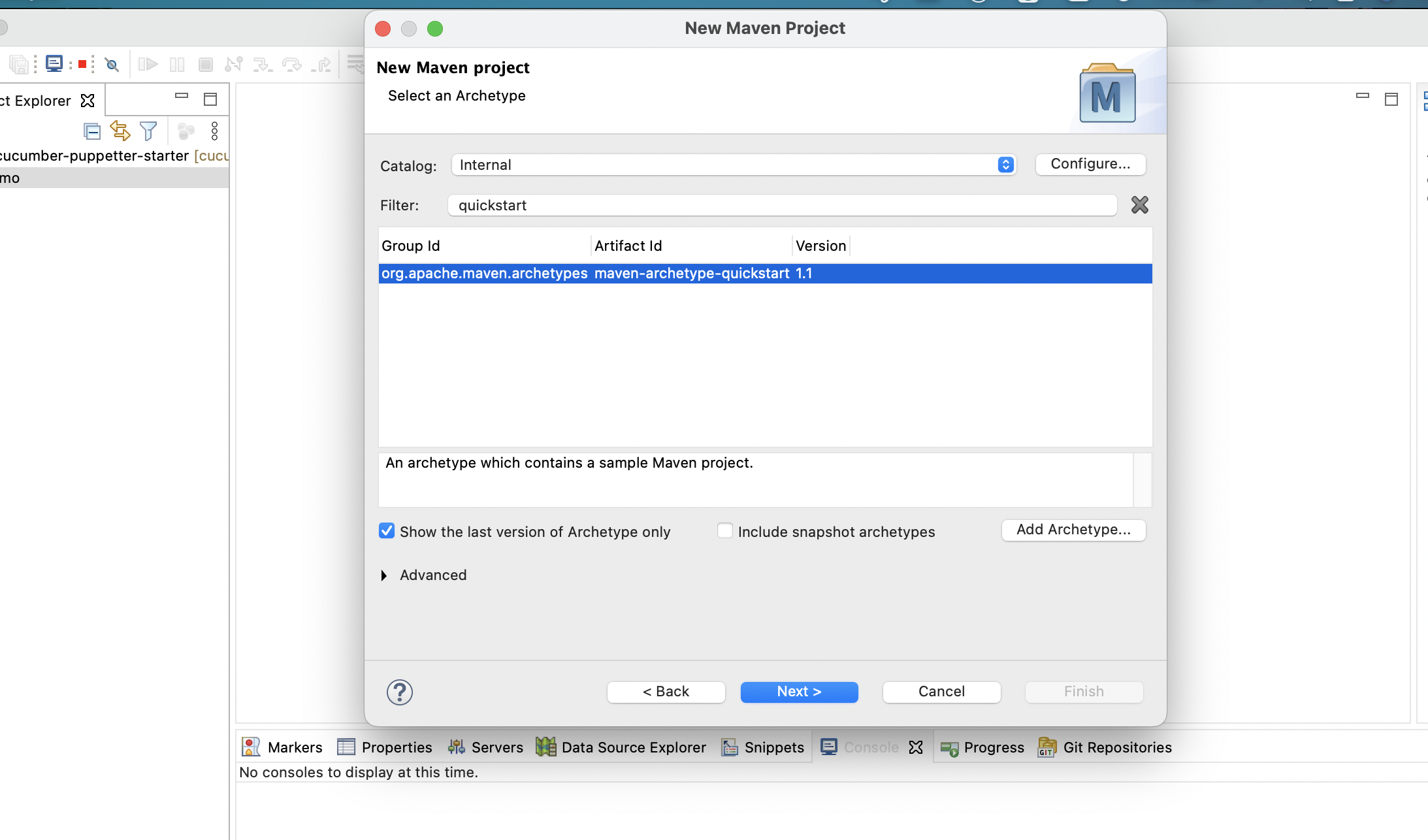
Step 2: Select the quickstart Archetype
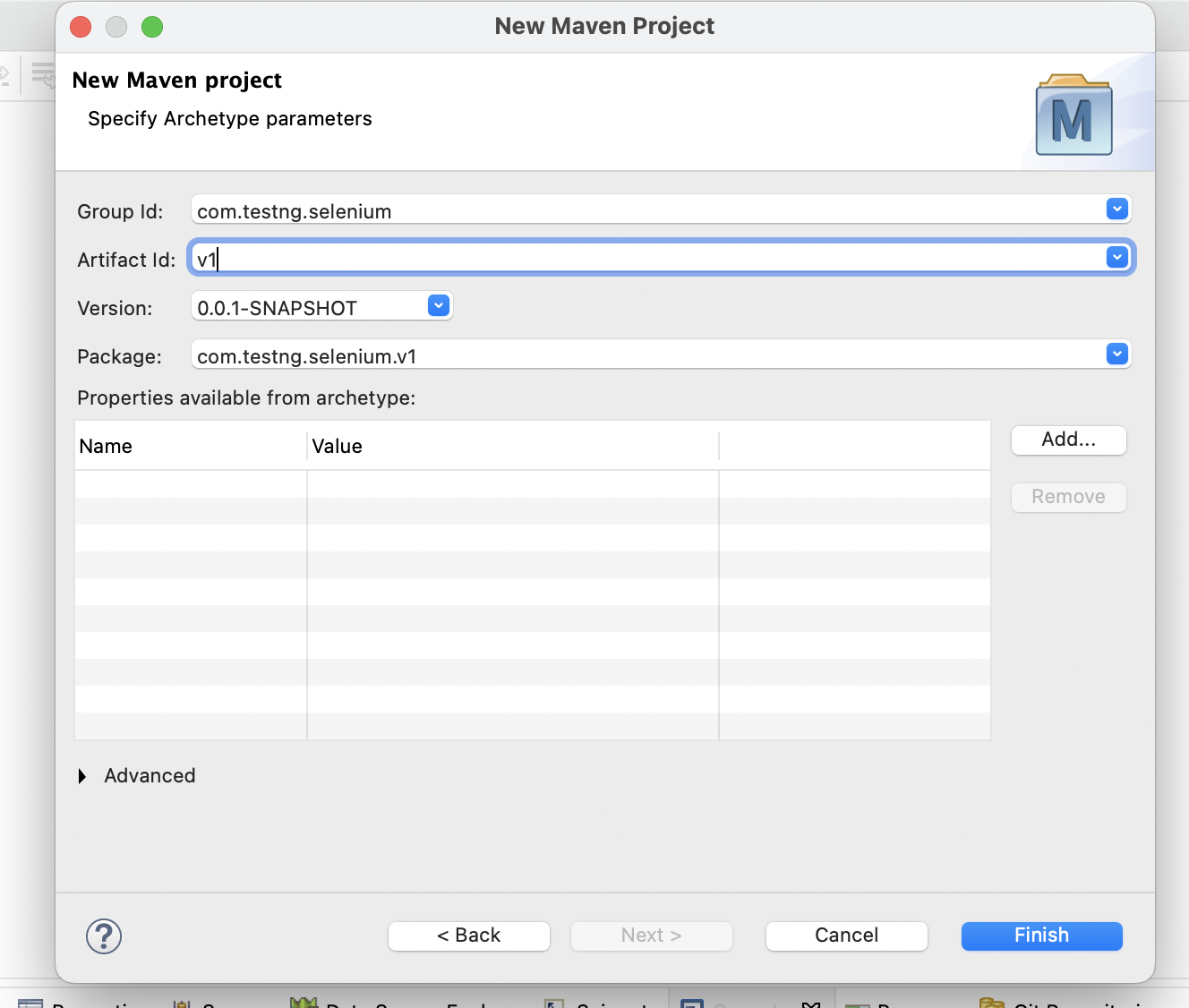
Step 3: Enter Group ID, Artifact ID, and Finish the setup process
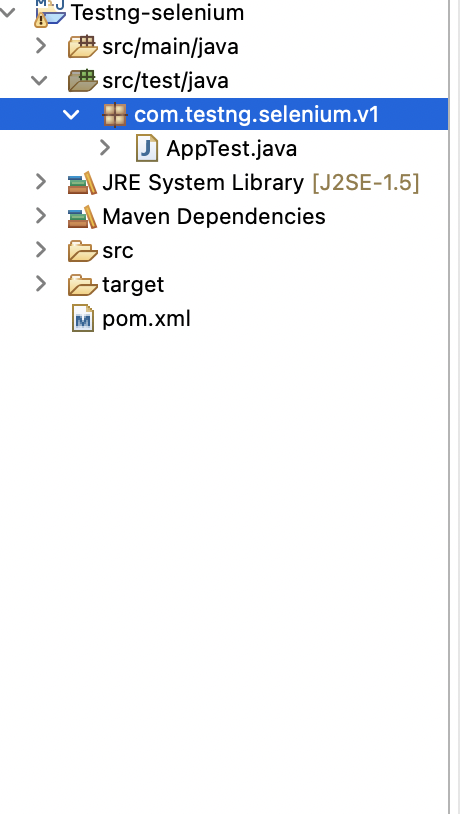
Step 4: New Maven project is created and all our tests will be written inside folder src/test/java and package com.test.selenium.v1
Step 5: Add dependencies to the POM.xml file
Add the below dependencies to the POM.xml file
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.testng.selenium</groupId> <artifactId>Testng-selenium</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>v1</name> <url>http://maven.apache.org</url> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> </properties> <dependencies> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.seleniumhq.selenium/selenium-java --> <dependency> <groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId> <artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId> <version>4.2.1</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.testng/testng --> <dependency> <groupId>org.testng</groupId> <artifactId>testng</artifactId> <version>7.6.0</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
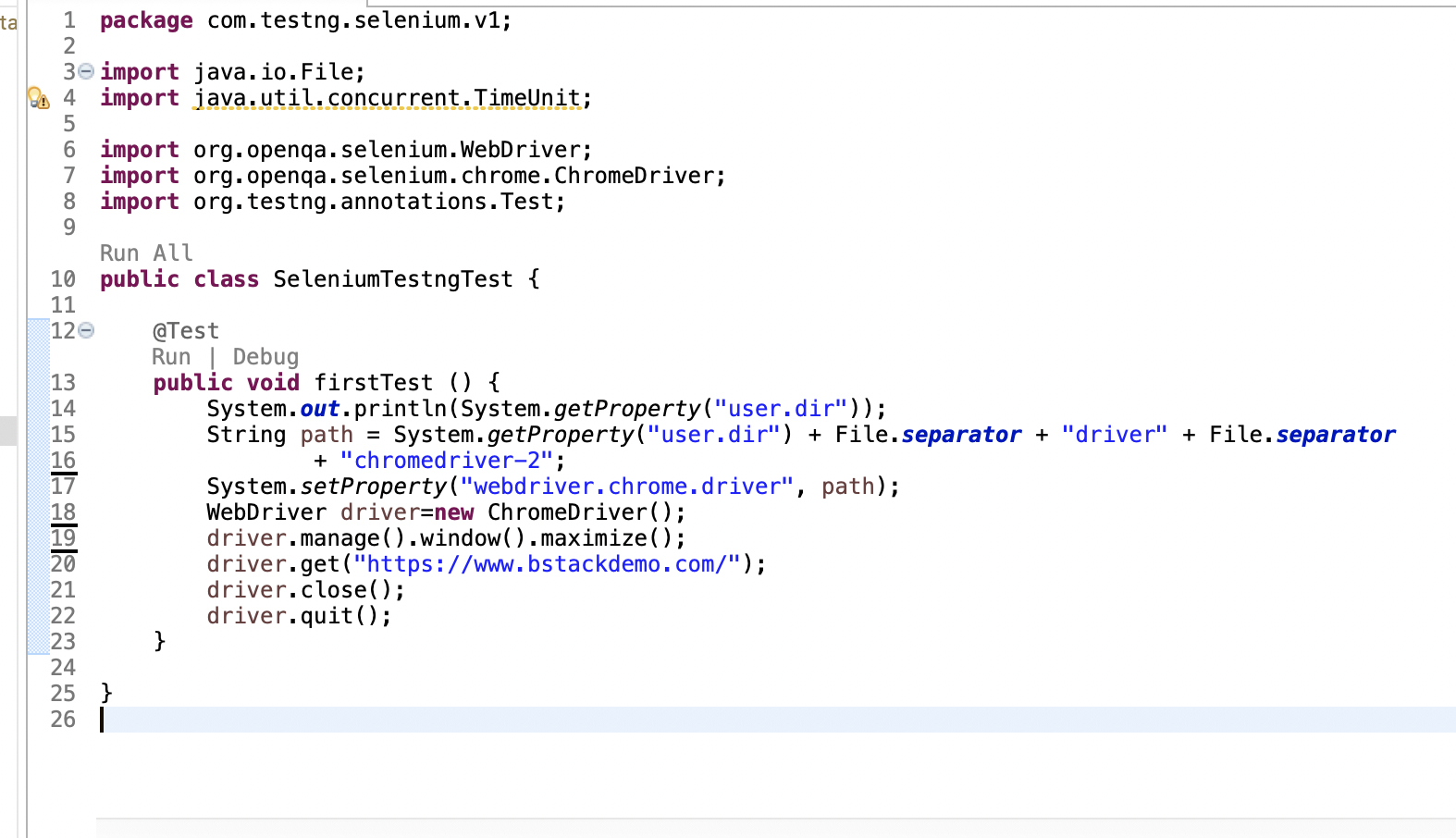
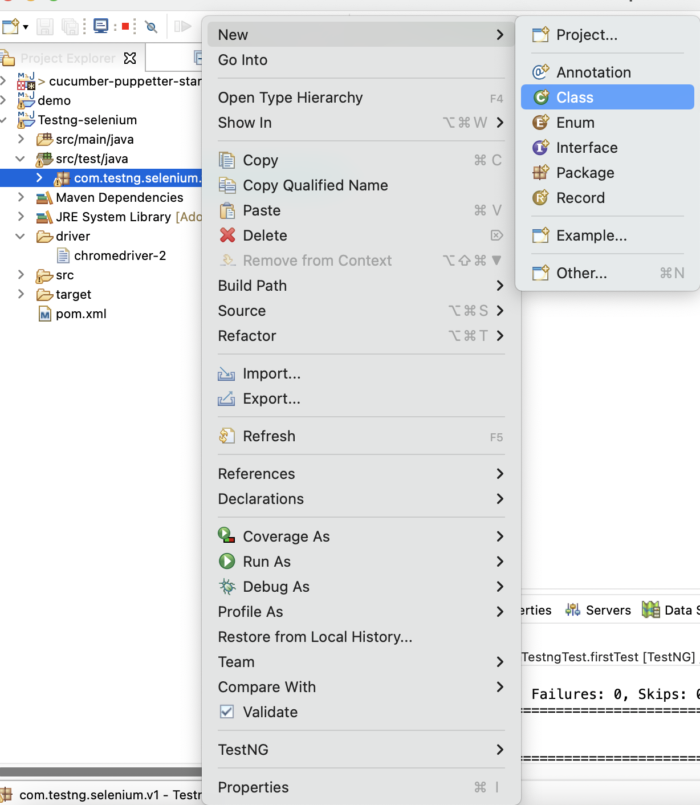
Step 6: Add a new Class to the package
Step 7: Add a TestNG test to the newly created class
import java.io.File;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterTest;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeTest;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class SeleniumTestngTest {
WebDriver driver;
@BeforeTest
public void initDriver() {
String path = System.getProperty("user.dir") + File.separator + "driver" + File.separator
+ "chromedriver-2";
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", path);
WebDriver driver=new ChromeDriver();
driver.manage().window().maximize();
}
@Test
public void firstTest () {
driver.get("https://www.bstackdemo.com/");
}
@AfterTest
public void tearDown() {
driver.close();
driver.quit();
}
}Follow Up Read: Maven Dependency Management with Selenium
Install TestNG using Install New Software
The “Install New Software” option in Eclipse can be opted when the Eclipse Marketplace does not offer the plugin you require or when you prefer installing directly from a plugin’s update site URL.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to installing TestNG in Eclipse using the “Install New Software” option:
Step 1: Open Eclipse IDE and Navigate to:
Help > Install New Software
Step 2: In the “Work with” field, input the official TestNG update site URL:
https://testng.org/testng-eclipse-update-site
Step 3: Press Enter. Eclipse will then fetch the available software.
Step 4: Select “TestNG” from the list.
Step 5: Click Next. Eclipse will calculate dependencies.
Step 6: Click Next again on the review screen.
Step 7: Accept the license agreement. Then, Click Finish
Step 9 : Installation will begin. You may see a warning about unsigned content. Click “Install Anyway”.
Step 10 : Once installation is complete, restart Eclipse when prompted.
Step 11: Verify TestNG Installation:
After restarting:
- Go to Window > Preferences
- Look for TestNG in the left panel
- If it appears, TestNG is successfully installed
How to Set Up TestNG Eclipse Tests From Your Existing Java Projects
Here’s a step-by-step to set up TestNG Eclipse Tests From Your Existing Java Projects:
Step 1: Open Your Existing Java Project
Make sure that you have TestNG involved before you start with the following:
- Launch Eclipse.
- Open your existing Java project from the Project Explorer.
Step 2: Add TestNG to the Project Build Path
- Right-click on your project> Build Path>Configure Build Path
- Then, navigate to the Libraries tab. Click Add Library > Select TestNG > Next > Finish
- Click Apply and Close
With this, you have linked TestNG to your project.
Step 3: Create a New TestNG Class
- Right-click on src folder >New > Other
- Search for TestNG Class, click Next
- Name your class (e.g., LoginTests)
- Select desired annotations like @BeforeMethod, @Test, etc.
- Click Finish
This will generate a skeleton test class with TestNG annotations.
Step 4: Run the Test
- Right-click the TestNG class > Run As > TestNG Test
- Get results in the TestNG Results tab
Optional: Convert Existing Java Class to TestNG
If you already have a test class written in plain Java:
- Right-click the class file > Convert to TestNG
Conclusion
By installing TestNG in Eclipse, testers can streamline their automation workflows and fully utilize the framework’s robust capabilities.
When used along with tools like BrowserStack, you can run your TestNG test suites on a wide range of real devices and browsers (3500+) in the cloud. This ensures broader test coverage and speeds up the testing cycle, enabling faster and reliable releases.
Useful Resources for TestNG
- What is TestNG: Advantages, Annotations, & Best Practices
- TestNG Groups
- What are TestNG Parameters?
- What does the test timeOut mean in TestNG?
- How to run parallel test cases in TestNG
- TestNG vs Cucumber: Core Differences
- JUnit Vs TestNG
- Database Testing using Selenium and TestNG
- How to use DataProvider in Selenium and TestNG?
- All about TestNG Listeners in Selenium
- How to run parallel test cases in TestNG
- How to use TestNG Reporter Log in Selenium: Tutorial
- Prioritizing tests in TestNG with Selenium
- How to run failed test cases using TestNG in Selenium Webdriver?