JMeter and Selenium are two of the most popular open-source testing tools, but they serve very different purposes. JMeter is built for performance testing under load, while Selenium is designed for functional automation and cross-browser testing.
Knowing their strengths, limitations, and use cases helps testers pick the right tool—or even combine them.
Overview
What is JMeter and How Does It Work for Performance Testing?
- Open-source Java app for load and stress testing.
- Simulates thousands of virtual users, collects server responses, and generates results (charts, XML, JSON).
- Advantages: Easy setup, Jenkins integration, supports API/DB testing, thread groups, test IDE for recording.
- Limitations: Poor JavaScript/AJAX support, difficult automation, complex output reports.
What is Selenium and How Does It Automate Browser Testing?
- Framework for automation and cross-browser testing of web apps.
- Uses WebDriver to send JSON Wire Protocol requests to browsers.
- Advantages: Highly customizable, supports parallel testing with Grid, integrates with other tools.
- Limitations: Outdated UI, AJAX element waits cause issues, maintenance can be challenging.
What are the Key Differences Between JMeter and Selenium?
- Testing Focus: JMeter → performance; Selenium → functional/cross-browser automation.
- Programming: JMeter is UI-based; Selenium is a robust programming library.
- Cross-Browser: JMeter lacks support; Selenium supports Chrome, Firefox, Edge, etc.
- Best Use Cases: JMeter for load handling, Selenium for user interaction testing.
This guide gives insights on:
JMeter focuses on performance and load testing, while Selenium specializes in automation and cross-browser functional testing. Together, they can be integrated to deliver both speed and accuracy in web application testing.
JMeter vs Selenium: General Differences
Here’s a comparison between JMeter and Selenium based on their key features and use cases:
| Aspect | JMeter | Selenium |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Performance, load, and stress testing | Functional and regression testing of web apps |
| Testing Focus | Measures performance metrics (e.g., response time, throughput) | Automates browser actions for functional testing |
| Supported Protocols | HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, JDBC, and more | Primarily HTTP/HTTPS for web applications |
| Test Type | Load testing, performance testing, stress testing | Functional testing, UI testing, regression testing |
| Integration | Primarily for performance testing in CI/CD | Integrated with automation testing frameworks in CI/CD |
| Output/Reports | Performance-related reports (e.g., response times, server health) | Test execution results (e.g., pass/fail status) |
| Technology Stack | Java-based, supports various protocols | Works with JavaScript, Python, Java, and more |
| Best Use Case | Load testing APIs, databases, and servers | Functional testing of web applications |
What is JMeter?
Apache JMeter is an open source Java application designed to load test functional behavior and gauge software performance. Originally designed for testing web apps, it has since expanded to include other test-related functions. Additionally, JMeter can simulate a heavy load on a server by creating thousands of virtual concurrent users to the web server.
How does JMeter perform tests?
- Creates a request and sends the request to the server
- Collects responses from the server and visualizes the details in a chart or graph
- Processes the response from the server
- Generates test results in several formats such as text, XML, JSON for the tester to analyze data
Advantages and Disadvantages of JMeter
Below are the advantages and disadvantages of using JMeter for performance and load testing:
Advantages of JMeter
- Easy to use without extensive knowledge of programming. It has a user-friendly UI and one can also use CLI.
- Provides integration with Jenkins and reporting
- Easy installation on any operating system
- Key features like the Thread Group, helps to see whether software performance is good.
- Test IDE allows test recording from browsers or native applications
- Allows API testing, Database Testing, and MQ testing with ease
- When there’s a high number of TPS, one can achieve more transactions per second given the hyper-limitations.
Disadvantages of JMeter
- Automation is difficult with JMeter
- JMeter output reports are difficult to understand without training
- It doesn’t support JavaScript and AJAX requests.
- Complex applications that use dynamic content or use JS to alter requests can be difficult to test using JMeter.
- It’s difficult to get data from one place or to perform customizations.
Areas of Application: JMeter
JMeter discovers the maximum number of concurrent users that a website can handle and provides a variety of graphical analyses of performance reports.
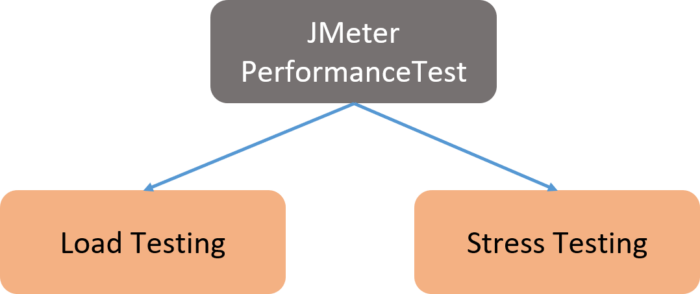
It also includes load and stress testing as shown in the diagram below.
- Load Testing: Modeling the expected usage by simulating multiple user access to the Web services concurrently
- Stress Testing: Every web server has a maximum load capacity. When the load goes beyond the limit, the web server starts responding slowly and produces errors. The purpose of stress testing is to find the maximum load the web server can handle.
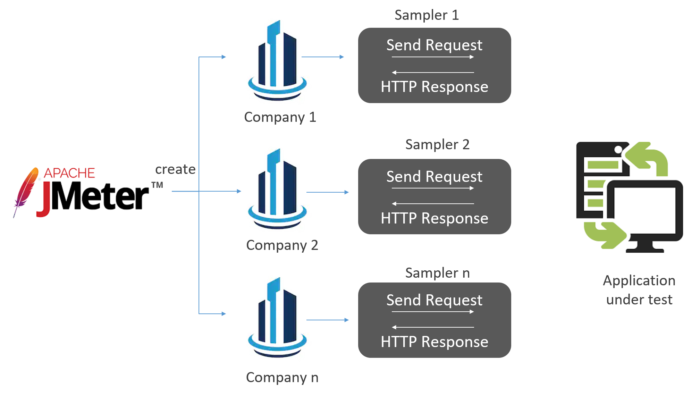
The figure below depicts how JMeter load Testing simulates the heavy load. There are multiple companies that work for a client. Each company sends a request to the client simultaneously and receives the response. Assuming that there is a heavy load of data during the response, JMeter is used to measure and test the performance of an application in such scenarios.
Before testing the performance of a web application, one should determine:
- Normal Load
- Heavy load
- Target in the test
What is Selenium?
Selenium is a framework used for automation testing of web applications. It extends wide support to a majority of browsers, operating systems, and programming languages. It also supports cross browser testing but is limited to web applications. Selenium does not support mobile application testing.
There are various components of Selenium, but the most widely used tool is Selenium WebDriver due to its manifold functionalities. To know, in detail, about the components of Selenium, kindly refer to Selenium Tutorial.
How does Selenium Webdriver perform tests?
- In a Selenium script, every statement will be converted to a URL with the help of the JSON Wire Protocol over HTTP. The URLs will be passed to the Browser Drivers.
- Every Browser Driver uses an HTTP server to receive HTTP requests. Once the Browser Driver receives the URL, it will pass the request to the actual browser over HTTP. The commands in the Selenium script will then be executed on the browser.
- If it is a POST request then there will be an action on the browser.
- If it is a GET request then the corresponding response will be generated at the browser end and it will be sent over HTTP.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Selenium
The following outlines the advantages and disadvantages of Selenium for automating web application testing:
Advantages
- One can build their own framework and can connect with multiple other tools that use frameworks, keywords, etc. That helps make it a stronger solution
- The Selenium Grid, allows testers to execute parallel testing. This speeds up tests and saves time
- Selenium offers users the flexibility to customize or write their own code, create their own features, etc. It is not restricted by licensing.
Disadvantages
- Does not offer enough information for personality testing
- Test maintenance is difficult due to element waits in applications using AJAX
- If proper implementation methods are not followed, testing will be slowed down
- The Selenium UI is outdated
Read More: Selenium WebElement Commands
Areas of Application: Selenium
Selenium is a versatile tool widely used in various areas of web application testing. Some of its key applications include:
- Functional Testing: Selenium automates the process of testing the functionality of web applications, ensuring that all features work as intended across different browsers and devices.
- Regression Testing: It is used to rerun tests after new code changes to ensure that existing functionality has not been affected.
- Cross-Browser Testing: Selenium supports multiple browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, etc.), making it ideal for testing web applications across different browser environments.
- UI Testing: Selenium automates user interface testing by simulating user actions such as clicks, text inputs, and navigation, to ensure that the web pages render and behave as expected.
- Integration with CI/CD: Selenium can be integrated with continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipelines to run automated tests as part of the build process, ensuring the software remains stable with each release.
- Mobile Web Testing: Through tools like Appium, Selenium can be extended to test mobile web applications, ensuring compatibility with different devices and operating systems.
- Data-Driven Testing: Selenium allows for executing tests with different sets of data to verify the functionality of web applications under varying conditions, improving test coverage.
For seamless automation across different browsers and devices, BrowserStack Automate offers an ideal solution, allowing you to run Selenium tests in real-time on a cloud-based platform, ensuring robust and scalable testing across multiple environments.
JMeter and Selenium Integration
Integrating JMeter and Selenium can combine the strengths of both tools, allowing testers to run comprehensive performance and functional tests in one unified testing pipeline.
While JMeter is focused on load and performance testing, and Selenium handles functional testing, their integration helps in creating an end-to-end testing process that covers both user behavior and performance under load.
- Performance Testing with Functional Validation: By integrating Selenium tests into JMeter’s performance test scripts, testers can simulate real-world user interactions and validate application functionality while simultaneously assessing its performance under load.
- End-to-End Testing: With this integration, you can execute Selenium tests within JMeter’s distributed load testing environment. This allows the running of automated functional tests alongside load testing to measure how the system performs during real user interactions.
- Scripting: Selenium WebDriver can be used within JMeter test plans as a sampler to perform tasks like browser actions, while JMeter can simulate multiple virtual users, generating high traffic and load on the application.
- Realistic Load Testing: Integrating the two allows for more realistic load testing by simulating actual user behavior (clicking buttons, navigating pages) while monitoring the system’s performance under various stress conditions.
- Reporting and Analysis: JMeter offers robust reporting features, and when integrated with Selenium, it provides detailed results that include both functional test outcomes and performance metrics, giving a complete view of the application’s behavior.
Integrating JMeter and Selenium streamlines the testing process, ensuring that applications are not only functional but also capable of handling high traffic without performance degradation.
Conclusion
JMeter and Selenium are both used for web application testing. But the main difference is that JMeter is mostly used to test the performance of web applications under load and stress. On the other hand, Selenium is best suited for automation and cross browser testing of a website. Based on what type of testing is necessary for the project, one can choose JMeter or Selenium or integrate both if that serves their purpose.