Test automation accelerates QA, but false failures can undermine its reliability.
Overview
What are false failures?
False failures occur when automated tests report issues that don’t actually exist in the application. These misleading results waste time and reduce trust in automation.
Reasons for false failures in test automation:
- Flaky or unstable test scripts
- Environmental inconsistencies
- Timing or synchronization issues
- Outdated dependencies or selectors
- Third-party service delays or failures
How to reduce false failures in test automation?
- Regularly maintain and refactor test scripts
- Stabilize and isolate test environments
- Use retry logic and wait mechanisms
- Run tests on real browsers and devices
This article explains what false failures are, their common causes, and actionable strategies to prevent them for more accurate and dependable automated testing.
What are False Positives?
False positives occur in test automation when a test case incorrectly flags a defect for functionality that is working as intended.
This phenomenon can lead to unnecessary debugging efforts and wasted resources.
Key Factors Leading to False Positives:
- Test Script Errors: Incorrect conditions or assertions in test scripts can result in false positives.
- Timing Issues: Delays or improper synchronization between the application and test script may cause failures.
- Testing Environment Issues: Configuration mismatches or failure of external dependencies can also trigger false positives.
Reducing false positives involves thoroughly validating test scripts, ensuring proper synchronization, and maintaining a stable test environment.
What are False Negatives?
False negatives happen when a test case fails to detect a genuine issue in the application. This creates a blind spot, leaving critical defects unnoticed, which can escalate into severe problems in production.
Common Causes of False Negatives:
- Incomplete Test Coverage: Missing test cases for edge scenarios may allow defects to go undetected.
- Incorrect Assertions: Flawed logic in test validations can fail to identify actual failures.
- Data Dependency Issues: Using incorrect or hardcoded test data may prevent accurate defect discovery.
Must Read: How to ensure Maximum Test Coverage?
Addressing false negatives requires improving test coverage, refining assertions, and using comprehensive, dynamic test data.
What are False Failures?
False failures occur when test outcomes incorrectly indicate a failure, not because of application defects but due to external factors in the testing process.
This term often overlaps with false positives but is broader in scope.
Examples of False Failures:
- Automation Tool Glitches: Limitations or bugs in the automation framework can cause unexpected results.
- Environment Instabilities: Network fluctuations or unstable test environments may lead to inconsistent test outcomes.
- Third-party Interference: External systems or integrations not functioning properly can falsely signal failures.
Minimizing false failures requires rigorous environment control, frequent framework updates, and isolating external dependencies during test execution.
What is Software Test Automation?
Software test automation uses specialized tools to control the execution of tests and compares the actual results and expected results to produce the output. The checkpoint or assertions are used to define the pass/fail criteria. Some of the most used software test automation frameworks are Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, Puppeteer, etc.
In automation testing, the actions are simulated using specialized commands to replicate the user actions and workflows. Automation tests can run on their own without any human interaction.
Failures in Test Automation
There are two scenarios in which test cases fail in software test automation:
- There is an actual defect in the application under test – valid failures/true failures
- Something wrong with the test automation code – false failures
The first type of failure is valid, as the application is not behaving in an expected way, so the test case failed. This is called a valid failure or true failure.
The second type of failure is a most faced challenge in software test automation. In this scenario, the application might be working as expected in reality, but the code written to automate test cases are somewhat not working in an expected way, so the test cases are failing. The failures of test cases without any actual defect in the application but because of automation code are called False Failures.
Did you know How Test Failure Analysis Can Drive Smoother Releases? Check out the guide to know more about it.
Reasons for false failures
Here are the key reasons for false failures in test automation:
- Browser Interaction: The automation test code simulates the user actions using specialized commands. There is a high chance that the commands might be executed before the page load. There is also a chance that the executed command could not be interpreted by the browser as expected at that point of time for some reason.
- Change in locator: The locator uniquely identifies the HTML element, and automated scripts are instructed to execute the action on the specific locator. There are many reasons why the locator might change. For example, a developer has updated the identifiers such as id, class name, etc., or there might be a change in third-party modules that the application is using. In such cases, the automation scripts need to be updated. Otherwise, the failures will be reported.
- Dynamic behaviour: It can be handled to some extent using automation, but achieving 100% is difficult. Dynamic behaviour may fail if the data is changing in real-time and the automation script is trying to validate with some assumptions.
- Adding new features or changes in existing features: If the application has added a new feature or if any changes in the existing workflow may cause false failures. For example, in the e-commerce application, the earlier feature was after adding the item to the cart. The next page is the payment page for the improvement of the product. If they introduce a new feature like the review cart items page, then the automation test fails as the automation test doesn’t know the newly added feature unless the script is modified. In this case, the automation test causes false failures.
- Version upgradation and dependencies: Whenever the new version of the automation tool is released, there might be a chance that some commands will be deprecated. When the automation script encounters such commands, a false failure will be reported. Similarly, the automation tests are closely tied with browser and browser versions and other dependencies if any API changes might also cause false failures.
How to reduce the false failures in test automation?
Here are the key methods that you can use to reduce false failures in test automation:
1. Stack traces: The stack traces are like proof of your test failures. The stack trace helps to trace back the errors. In most cases, you can judge whether the failure is a false or valid failure just by looking at the stack traces. Whenever you expect an exception or an error add a code to capture the stack trace.
try
{
//some automation code
}
catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}2. Loggers and .log File: Log every detail into a separate log file. Just like any development practice, have loggers defined in your automation framework. Log interactions and other useful information in a simple log file will help you quickly analyze and fix failures. Many logger frameworks make your job easy. For example, log4j can be used for Java-based frameworks.
The log file provides information about where it failed, and which interaction or action caused the failure of the test. This information helps to narrow down the problem or failures.
driver.get("https://www.browserstack.com/users/sign_in");
log.info("Open browserstack");
driver.manage().window().maximize();
log.info("Maximize window size");
js.executeScript("document.getElementById('user_email_login').value='rbc@xyz.com';");
log.info("enter username");3. Enable console logs: Most of the test automation tool provides the console logs feature, the console logs are shown based on the default log level or that set by the user. The detailed console.log helps to understand the problem and where it originated from.
For example, if you are using Selenium, you can enable all logs to get detailed logs.
LoggingPreferences logPrefs = new LoggingPreferences(); logPrefs.enable(LogType.BROWSER, Level.ALL);
4. Update the script more often: Many think that automation tests can be written once and forget it, but this is not true. The automation tests need timely maintenance for accurate results. One of the reasons for false failure is unknown feature changes or addition.
Have a frequent sync-up with the development and product team to understand the changes. Any changes in the application need to be updated in automation scripts as well. This helps to reduce any false failures because of feature changes.
5. Version Upgrades: Before upgrading the automation framework and dependencies, analyze the new version changes. The release notes usually state the changes that are made in the latest version. Understanding changes and modifying them in your test scripts eliminates false failures.
6. Rerun or Retry mechanism: Many factors can impact test automation, such as tools used, browser version, browser name, configuration settings, the application’s behavior, performance like response time, the execution environment, etc. So having the retry failed test mechanism helps to run the test multiple times and helps reduce the false failures.
For example, the TestNG provides the IRetryAnalyzer. You can write the custom code to implement the IRetryAnalyzer and the number of retries you want to make for failed tests.
@Test(retryAnalyzer=Retry.class)
public void test(){
Assert.assertEquals(1,0);
}Note: Above is a sample code. You need to define and write the logic to implement IRetryAnalyzer before using it in the @Test annotation.
7. Integrate automation tool with messengers : You can integrate the test automation tools or pipelines with tools like Slack, Teams, etc. The messenger tools provide instant results, and whether tests are passed or failed, you can take a quick look immediately and check for errors.
Consider a scenario in which the system where the test automation is configured is running updates. This causes performance degradation and failing automation tests.
Everything might look normal if you look at the automation test results after a few hours. However, if you log in to the system immediately, you can clearly see the update process or tasks which are running, and there is an issue with performance. This helps to understand the problem without the hassle, and you can tune your automation script schedules accordingly.
For example, if you are using the Jenkins and MS teams, you can easily configure the integration using the connectors.
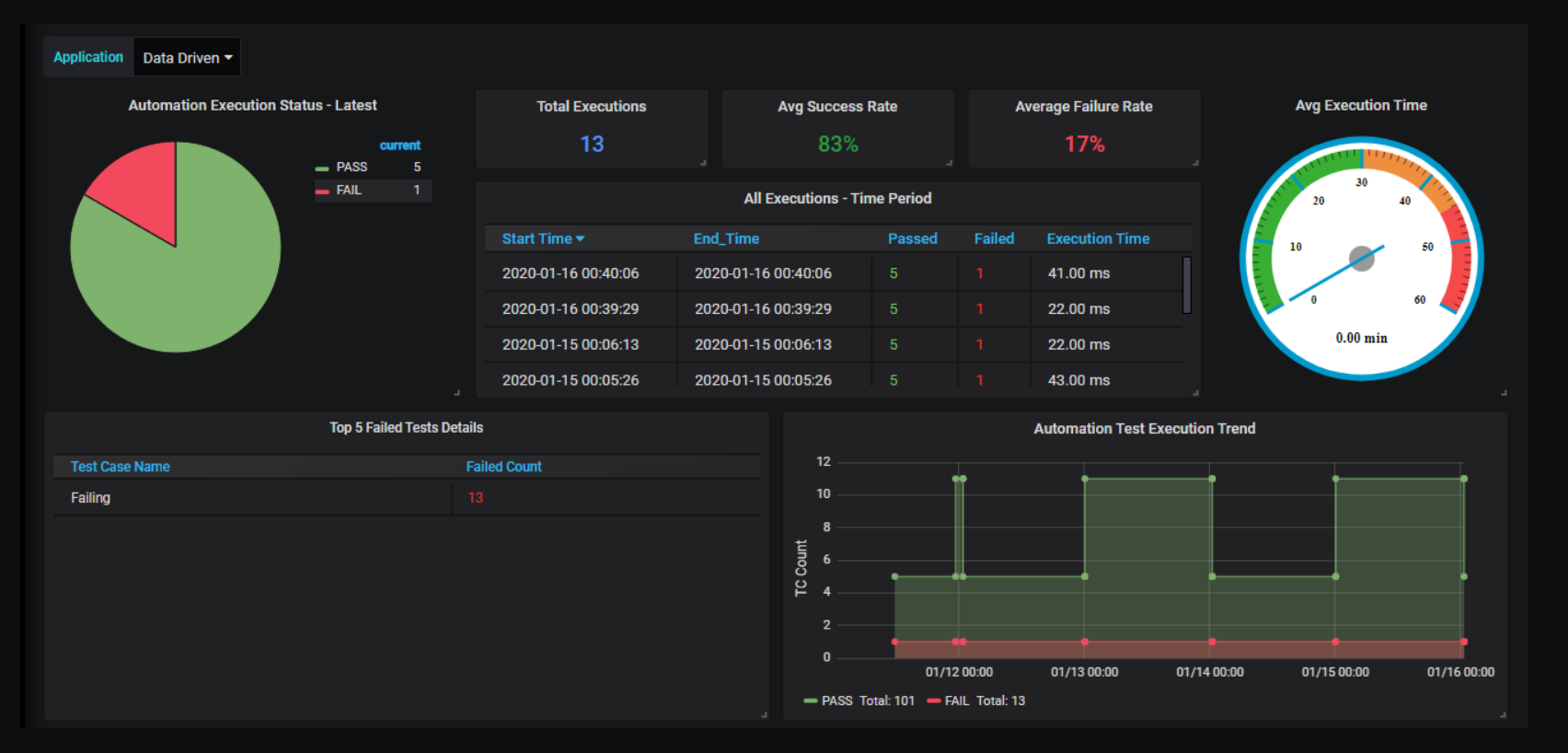
8. Integration with analytics Platform: An analytics platform like Grafana can provide you with trend analysis of tests. Though it requires advanced configuration knowledge, it can help analyze inconsistent test cases, execution time, server performance, application health, etc. You can also create a custom dashboard, trend analysis, alerting, etc., using Grafana.
9. Execute Tests on Real Devices: Many times you try to emulate browser settings and perform the automation on emulated devices. For example, you can execute the mobile browser testing by changing the viewport, but this doesn’t guarantee that result will be the same on real devices.
At times, testing on emulators and simulators is not as accurate as that of real devices since the real user conditions are not taken into account. It is pivotal to decipher why test on real devices compared to emulators or simulators.
The tests can be executed on real devices and browsers using tools like BrowserStack, which helps to avoid false failures.
What is a Test Report in Software Test Automation?
Test Reports are the end results or output of the testing written in a human-readable format. Test reports contain screenshots of failed scenarios/test cases, graphs, etc. Sometimes additional stack traces will be mentioned to analyze the failed scenarios.
Read More: How to write a good Test Summary Report
When not to choose Test Automation?
However, test automation might not always fit into every testing requirement. Test automation is not a good choice when:
- The application is undergoing frequent changes
- The application development doesn’t follow standard architectural practices
- Tests are not required to run frequently
- No proper or stable infrastructure exists to execute automation scripts
- The application has a lot of third-party integrations/gateways, and there are restrictions around their usage.
Importance of Testing on Real Device Cloud with BrowserStack Automate
Using a real device cloud like BrowserStack Automate is vital for reducing false failures in test automation workflows.
It replicates real user conditions to ensure accurate and reliable test outcomes.
Here’s why it’s essential:
- Real Device Cloud: Get instant access to thousands of real devices and browsers, eliminating inconsistencies in emulators or simulators.
- Faster Testing with Parallel Execution: Run multiple test cases simultaneously to identify and isolate failures, improving efficiency quickly.
- Real-world Environment Simulation: Test under real conditions like varying networks, locations, and device behaviors to reduce false positives and negatives.
- Seamless Tool Integration: Integrates smoothly with automation frameworks like Selenium and CI/CD tools, ensuring consistent and error-free workflows.
- Advanced Debugging Tools: Use features like screenshots, videos, and logs to pinpoint and fix issues quickly.
With BrowserStack Automate, testing becomes more dependable, leading to faster deployment and higher confidence in software quality.
Software Test Automation Best Practices to Reduce False Failures
Implementing the right practices in test automation helps minimize false failures, save time, and ensure test reliability.
Below are key best practices to adopt:
- Stabilize Test Environments: Ensure that the test environment closely mirrors the production environment to reduce environment-specific issues.
- Use Explicit Waits and Synchronization: Handle dynamic elements and load times with proper wait strategies (e.g., explicit waits) instead of relying on arbitrary delays.
- Maintain and Update Test Scripts Regularly: Keep test scripts aligned with the latest UI and functional changes in the application to avoid outdated validations.
- Implement Retry Logic for Flaky Tests: To reduce noise in test results, use retry mechanisms for tests known to fail intermittently.
- Isolate Test Cases: Make tests independent so that a failure in one test doesn’t cascade into others.
- Use Reliable Locators: Prefer stable and unique identifiers like data-testid attributes to reduce locator-based failures.
- Mock External Dependencies: Stub or mock third-party services (e.g., APIs, payment gateways) during tests to avoid reliance on their availability.
- Continuously Monitor and Analyze Failures: Review test results frequently to identify patterns in false failures and take corrective action quickly.
- Use Real Device & Browser Testing Platforms: Leverage tools like BrowserStack Automate to test in real-world conditions and catch failures specific to actual devices and browsers.
Conclusion
False failures are a major challenge in test automation, often caused by outdated scripts, unstable environments, or flaky tests.
Reducing them requires regular script maintenance, robust test design, and continuous monitoring.
Testing on real devices is essential to minimize false positives. While building an in-house lab is costly, cloud-based solutions like BrowserStack offer a more scalable, cost-effective alternative.