One essential aspect of accessibility testing is ensuring compatibility with screen readers, which are vital tools for individuals with visual impairments.
Overview
What are Screen Readers?
Screen readers are assistive tools that convert on-screen text and elements into speech or Braille, enabling users with visual or cognitive impairments to navigate digital content without seeing it.
Importance of Screen Reader Testing
- Ensures visually impaired users can access and navigate your website seamlessly.
- Identifies accessibility issues that automated tools often miss.
- Expands reach to a growing audience with visual impairments.
- Helps avoid legal risks by supporting WCAG compliance.
- Reveals usability gaps analytics tools may not detect.
Top Tools for Screen Reader Testing
- BrowserStack Accessibility Tool: Test on real devices and browsers with actionable insights for ADA and WCAG compliance.
- JAWS (Job Access With Speech): A powerful Windows screen reader with advanced features for professional users.
- NVDA (NonVisual Desktop Access): A free, open-source Windows screen reader with broad language and web support.
- VoiceOver: Apple’s built-in screen reader offering seamless accessibility across macOS and iOS devices.
- ChromeVox: A Chrome browser extension that enables basic screen reading with easy integration and navigation.
This article will explore how to test websites with screen readers to create a more inclusive online experience.
What are Screen Readers?
Screen readers are assistive tools that convert on-screen text and elements into speech or Braille, enabling users with visual or cognitive impairments to navigate digital content without seeing it.
They do more than just read text; they also convey webpage structure, such as headings, links, and image descriptions, allowing meaningful interaction with websites and applications.
Screen readers make digital environments accessible to millions of users worldwide by translating interfaces into audio or tactile feedback.
Who uses Screen Readers?
Screen readers are commonly used by:
- Individuals who are partially sighted or suffering from blindness use screen readers. It can also be helpful for individuals with cognitive or learning difficulties (such as dyslexia).
- Anyone trying to learn a language or experiencing difficulty reading text online can also utilize such technology. It is ideal for people who prefer to consume content auditorily, for any reason whatsoever.
How to Navigate Websites Using Screen Readers
Screen readers help visually impaired users interact with web content through audio feedback. Here’s how navigation typically works:
- Activating the Screen Reader: Users launch screen reader software (e.g., NVDA, JAWS, VoiceOver) and open a web browser. The tool begins reading page content immediately.
- Interpreting Page Content: The screen reader reads the page title, headings, and landmarks, interpreting the HTML structure (DOM) to understand elements like paragraphs, links, and forms.
- Navigating and Interacting: Users navigate using headings, landmarks, and keyboard shortcuts. The screen reader announces interactive elements like links, buttons, and form fields, guiding users through interaction.
- Reading and Receiving Feedback: Text is read aloud at various levels (character, word, line), and screen readers notify users of alerts, errors, or validation messages during interaction.
- Customizing the Experience: Advanced users can adjust voice settings, speed, and use custom commands or shortcuts to streamline navigation, especially on complex or dynamic websites.
Importance of Screen Reader Testing
Below are the key benefits and importance of screen reader testing:
- Screen reader testing ensures users with visual impairments can access and navigate your website effectively, improving inclusivity.
- Manual testing with screen readers helps identify obstacles that automated tools may miss, offering a more thorough accessibility audit.
- As the number of individuals with sight loss continues to rise, screen reader compatibility is vital for reaching an underserved and growing market.
- Failing to meet accessibility standards could result in legal consequences, as many countries have laws requiring compliance with Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG).
- Analytics tools often do not track screen readers, so you may overlook a significant portion of your audience without realizing it.
Why are Screen Readers Important in the Accessibility Testing of a Website?
Screen reader testing, though not explicitly mentioned in WCAG compliance, is a best practice for accessibility testing.
Below are some key reasons why they are important inthe accessibility testing of a website:
- Testing with screen readers confirms that all content, including non-visual elements like images and buttons, is accessible to visually impaired users.
- It helps ensure that the website’s structure, such as headings and links, is properly announced, improving navigation for screen reader users.
- Screen readers highlight issues that can’t be detected by automated tools, like improper reading order or lack of context for non-text elements.
- It provides hands-on insight into how real users with visual impairments experience the website, making it easier to optimize for accessibility.
How to perform screen reader testing?
Below are some important steps on how to perform screen reader testing:
- Learn the Basics: Familiarize yourself with screen reader basics, key commands, and common navigation shortcuts, or involve someone experienced with assistive tech.
- Combine with Other Testing Methods: For a complete accessibility evaluation, use screen reader testing alongside manual and automated checks.
- Verify HTML Structure and Alt Text: Ensure semantic HTML is used for headings, lists, and forms, and add descriptive alt text for images and icons for clear screen reader interpretation.
- Test Keyboard Navigation: Confirm that users can fully navigate the site with keyboard commands, which is essential for those who rely on keyboard-only input.
- Review Dynamic Content and Visual Cues: Make sure interactive content like carousels and videos are controllable and understandable without visual instructions, such as colors or shapes.
Also Read: How to Create a Website using HTML and CSS
Top Accessibility Testing Tools for Screen Reader Testing
Here is the list of Top Accessibility Testing Tools for Screen Reader Testing:
1. BrowserStack Accessibility Tool
BrowserStack’s Accessibility Tool is an excellent choice for ensuring your website complies with ADA standards. It enables testing across more than 3,000 real browsers and device combinations, delivering unparalleled accuracy and coverage.
The tool identifies key accessibility issues, including color contrast, keyboard navigation, and screen reader compatibility, and provides clear, actionable insights to address these concerns.
Key Features :
- Real Device Testing: Access over 3,500 real devices and browsers to ensure cross-platform accessibility and identify device-specific issues that simulators might miss.
- Live Debugging: Get real-time feedback on accessibility issues during testing for immediate fixes, aiding rapid development and iteration.
- CI/CD Integration: Automate accessibility testing within CI/CD pipelines using tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and CircleCI to ensure ongoing compliance.
- Detailed Reports: Receive comprehensive reports highlighting WCAG and ADA compliance issues with actionable remediation suggestions, including code snippets and guideline links.
- Cross-Browser Testing: Test across various browsers, including legacy versions, to ensure accessibility for users on different browser configurations.
Pro Tip : You can also use the BrowserStack Accessibility Toolkit, a browser extension for Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge, to assess and improve your website’s accessibility. Available from the Chrome Web Store, it’s ideal for developers and QA teams.
With real device testing, real-time insights, and easy integration into development workflows, it’s a top choice for ensuring ADA compliance.
2. JAWS (Job Access With Speech)
A robust screen reader for Windows, JAWS is widely used by individuals with visual impairments.
- Supports various applications and browsers
- Customizable voice and navigation settings
- Integrates with Microsoft Office and productivity tools
- Advanced scripting for specialized tasks
JAWS is good for professional users needing extensive features across applications but can be costly and complex for beginners.
3. NVDA (NonVisual Desktop Access)
NVDA is a free, open-source screen reader for Windows that converts text to speech.
- Supports multiple languages and web navigation
- Customizable keyboard shortcuts
- Community support and regular updates
NVDA is good for Windows users seeking a free, customizable screen reader, but cannot be used on non-Windows systems.
Read More: NVDA Screen Reader Testing
4. VoiceOver
VoiceOver is built into macOS and iOS, offering screen reader support across Apple devices.
- Pre-installed on Apple devices; no download needed
- Supports gestures and keyboard navigation
- Describes images and visual elements
VoiceOver is good for Apple users due to seamless integration, but cannot be used on non-Apple devices.
5. ChromeVox
ChromeVox is a screen reader extension explicitly designed for the Chrome browser.
- Integrated with Chrome; no installation needed
- Supports keyboard shortcuts and real-time web feedback
- Customizable voice and navigation settings
ChromeVox is good for Chrome browser users who need easy, browser-based screen reading, but it cannot fully support non-Chrome applications.
How to Test Websites with Screen Readers using BrowserStack Accessibility Testing Tool
BrowserStack’s Accessibility Testing tool offers three testing methods:
- Automatic Scanning with Workflow Analyzer to detect static issues
- Assisted Tests for identifying complex accessibility problems
- Manual Testing with Screen Readers to check usability for visually impaired users
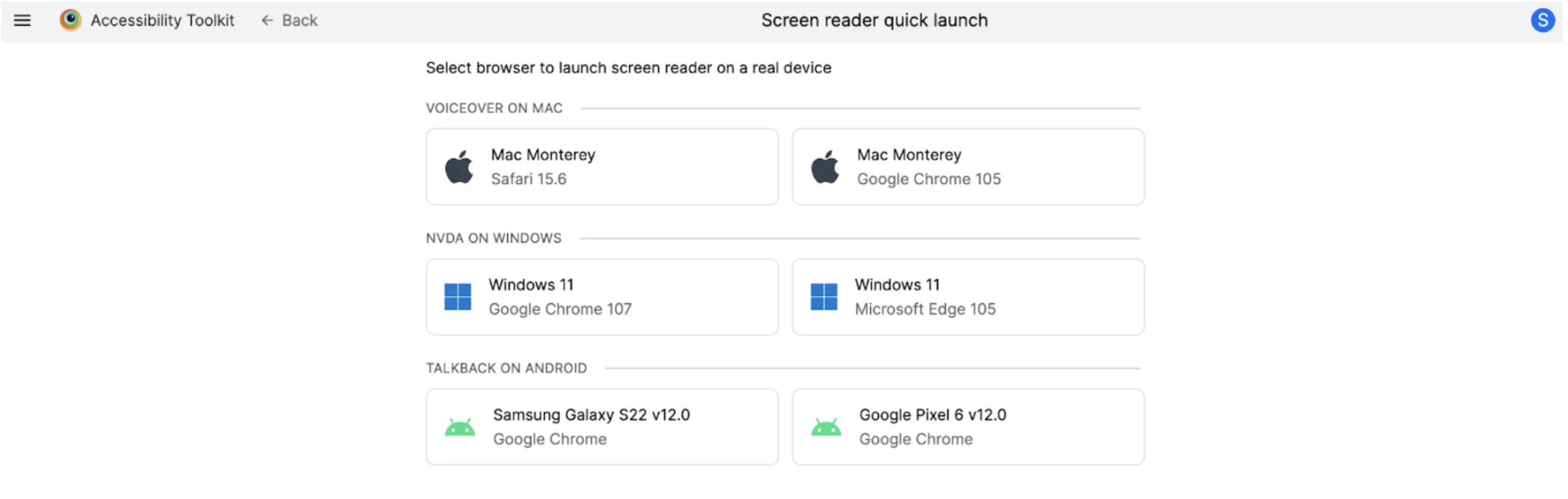
The BrowserStack Screen Reader feature lets you test on real devices with screen readers. It currently supports VoiceOver (Mac), NVDA (Windows), and TalkBack (Android).
Prerequisite: Ensure the BrowserStack Accessibility Toolkit is installed and open before starting a screen reader test.
Step 1. Open the BrowserStack Accessibility Toolkit.
Step 2. Click on the “Select browser” option in the Screen reader tile.
Step 3. Choose the desired operating system and browser combination to start the screen reader test session.
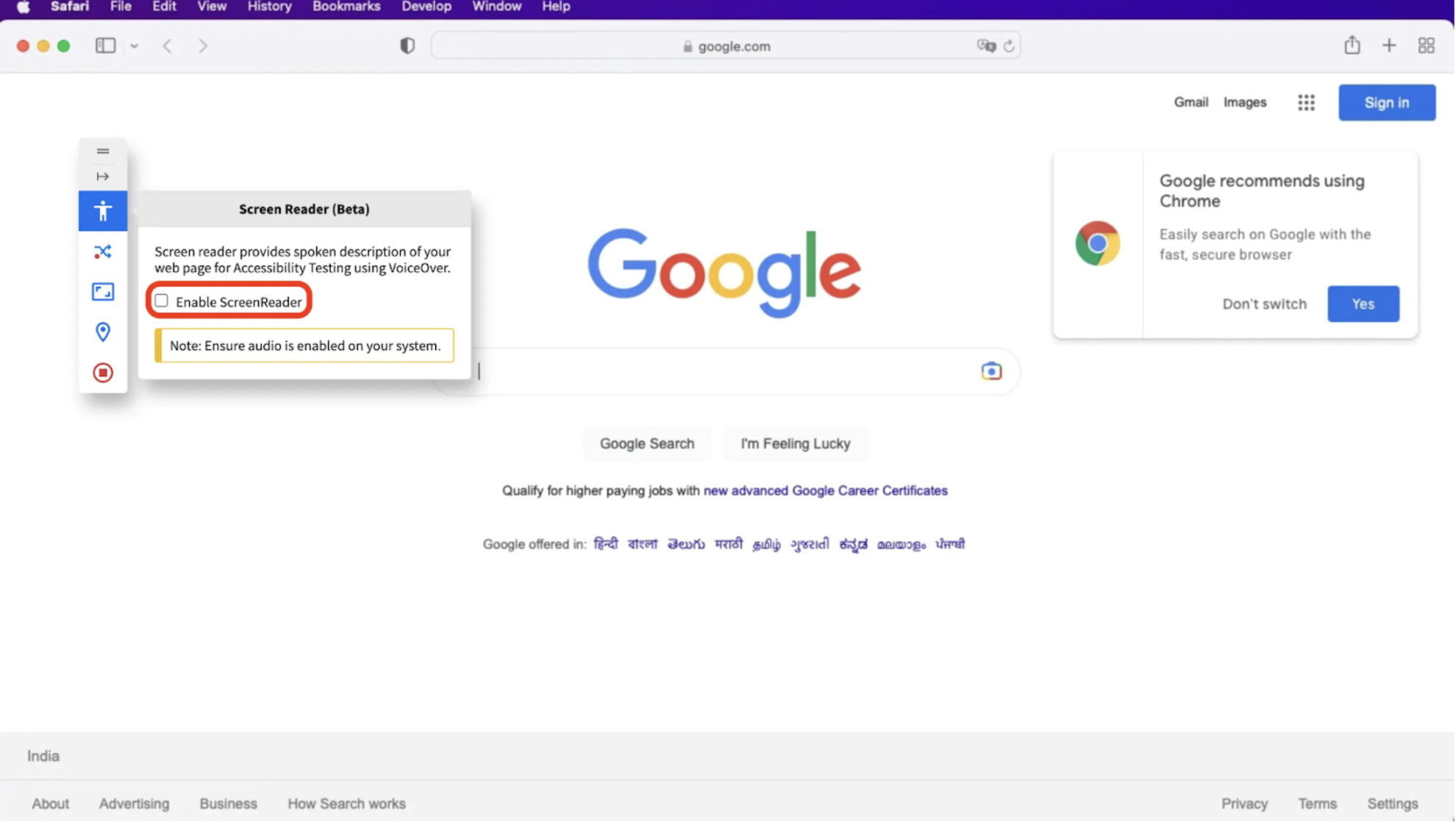
Step 4. In the Screen Reader menu, check the “Enable ScreenReader” box to start the test session.
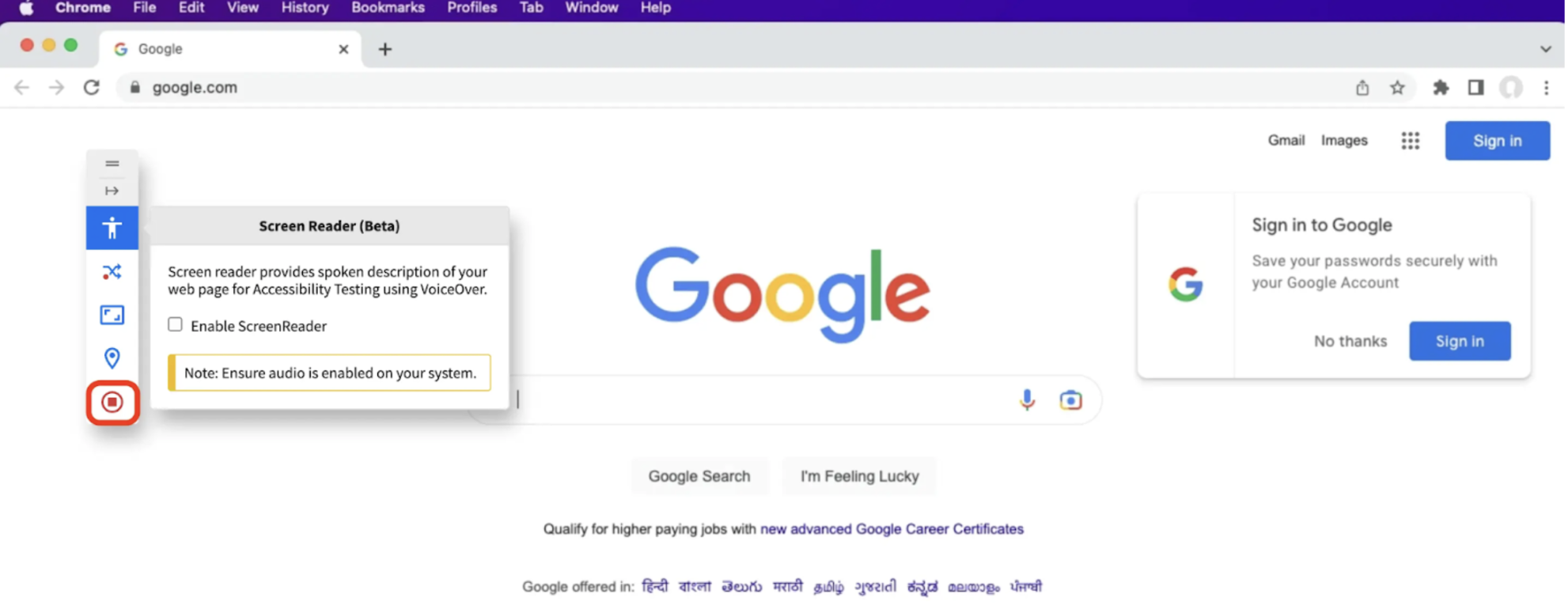
Step 5. Once the test is finished, uncheck the “Enable ScreenReader” box in the Screen Reader menu to end the session.
Step 6. Click “Stop Session” in the navigation menu to return to the Accessibility Testing Dashboard, where you can relaunch a screen reader session if needed.
How to Ensure WCAG Compliance with Screen Reader Testing?
Ensuring WCAG compliance with screen reader testing involves verifying that your website or application meets Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) standards through practical scenarios. Here’s how to approach it:
1. Keyboard Navigation and Focus Management
Scenario: A user navigates through a form using only keyboard controls.
- Action: Confirm that all interactive elements (links, buttons, input fields) are reachable and focusable via keyboard.
- Screen Reader Check: Ensure the screen reader announces the current focus and provides sufficient context for smooth navigation.
2. Form Accessibility
Scenario: A user completes a form with multiple fields.
- Action: Verify that each input field has a corresponding label and that any validation errors are clearly communicated.
- Screen Reader Check: Ensure the screen reader correctly reads out field labels and validation messages, helping users understand and correct errors.
3. Image and Media Descriptions
Scenario: A user encounters images and media on a webpage.
- Action: Make sure all images have descriptive alt text and that media content includes captions or descriptions where necessary.
- Screen Reader Check: Confirm the screen reader reads the alt text for images and provides relevant media descriptions, including captions or transcripts.
4. Headings and Page Structure
Scenario: A user examines the content layout of a webpage.
- Action: Check that headings are used correctly to organize content logically.
- Screen Reader Check: Verify that the screen reader announces headings in the right order, giving a clear overview of the page structure.
5. Link and Button Descriptions
Scenario: A user interacts with links and buttons on a page.
- Action: Ensure that links and buttons have descriptive text or accessible names.
- Screen Reader Check: Confirm that the screen reader provides clear descriptions of link and button functions, avoiding vague labels like “Click here.”
6. Dynamic Content and Live Regions
Scenario: A user interacts with elements that update dynamically, such as AJAX content.
- Action: Verify that changes in dynamic content are announced to users.
- Screen Reader Check: Ensure the screen reader provides updates about content changes and alerts users to new or updated information.
7. Error Handling and User Feedback
Scenario: A user submits a form with errors.
- Action: Ensure error messages and feedback are clear and helpful.
- Screen Reader Check: Verify that the screen reader announces errors and alerts, providing users with the information needed to resolve issues.
8. Tables and Data Presentation
Scenario: A user views a data table.
- Action: Check that tables have proper headers and clear relationships between rows and columns.
- Screen Reader Check: Confirm that the screen reader reads table headers and data accurately, helping users understand the table’s content.
Best Practices for Testing Websites with Screen Readers
By following the best practices, you can make sure that your site is navigable, comprehensible, and usable for those relying on screen readers.
Proper testing helps identify and address potential barriers, ensuring an inclusive experience and compliance with accessibility standards. This not only enhances user satisfaction but also broadens your audience and meets legal and ethical obligations for digital accessibility.
- Test with Multiple Screen Readers: Use different screen readers (e.g., VoiceOver, NVDA, TalkBack) to ensure broad compatibility.
- Verify Keyboard Navigation: Ensure all interactive elements are accessible via keyboard and that focus management is consistent.
- Check Alt Text for Images: Confirm that all images have descriptive alt text that conveys their purpose.
- Ensure Proper Form Labels: Verify that form fields have clearly associated labels and that error messages are announced.
- Test Heading Structure: Ensure headings are used correctly and in a logical order to provide a clear content hierarchy.
- Review Link and Button Descriptions: Check that links and buttons have descriptive text or accessible names that convey their functions.
- Monitor Dynamic Content Updates: Ensure that changes in dynamic content (e.g., AJAX updates) are announced promptly by the screen reader.
- Evaluate Table Accessibility: Verify that tables are structured with appropriate headers and that data is clearly communicated.
- Check for Clear Focus Indicators: Make sure focus indicators are visible and distinguishable to help users track their position on the page.
- Test Usability and Feedback: Ensure that the screen reader provides meaningful feedback and that users can understand and interact with the content effectively.
Checklist for Screen Reader Testing
A comprehensive checklist for screen reader testing ensures that your website is accessible, functional, and user-friendly for individuals relying on assistive technologies.
- Verify all images have descriptive alt text.
- Ensure form fields have clear and properly associated labels.
- Check that error messages are announced by the screen reader.
- Confirm that headings are used in a logical and hierarchical order.
- Test that links and buttons have descriptive, functional text.
- Ensure focus indicators are visible and clearly distinguishable.
- Check that dynamic content updates are announced in real-time.
- Verify that tables have headers and are announced correctly.
- Ensure all interactive elements are accessible via keyboard navigation.
- Test that the screen reader provides clear and understandable feedback.
Conclusion
By conducting Screen Reader tests, using tools like BrowserStack Accessibility Testing, you can verify compliance with established standards like WCAG Compliance. This ensures that the web content you deliver is readily accessible to all users, regardless of their abilities.
It helps you check that your website can be easily accessed using Screen Readers on different real devices making it easier for people with visual impairments to access the content.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How often should I perform screen reader testing?
Screen reader testing should be carried out whenever there are major updates to your website, such as a redesign, migration, or during an accessibility audit. It’s best to test before going live to catch usability issues early. For ongoing accessibility, include screen reader checks in your routine site maintenance.
2. Is screen reader testing required for WCAG compliance?
WCAG doesn’t explicitly require screen reader testing, but it’s a recommended best practice. Many WCAG guidelines support screen reader usability, such as requiring alt text and language identification. Combining manual screen reader testing with automated tools ensures broader compliance and better accessibility.