Geo-Location Testing is a critical step in mobile app testing for global users. Today’s world-class apps are expected to function seamlessly from any part of the globe. However, app behavior can vary depending on the user’s location, language, time zone, or regional settings. Testing for geo-specific scenarios ensures that apps perform consistently and provide a localized experience.
Overview
Why Geo-Location Testing?
- Ensures apps behave consistently across countries and regions.
- Validates functionality dependent on geographic location, language, and regional settings.
- Key for localization, internationalization, and global user experience.
Factors to Consider for iOS Apps
- Device Location (via GPX files or GPS coordinates)
- Language & Locale
- Region settings
- Calendar & Time format
- Time zone
- App permissions for location
- Monitoring app performance from different geo-locations
XCUITest Geo-Location Configuration in Xcode
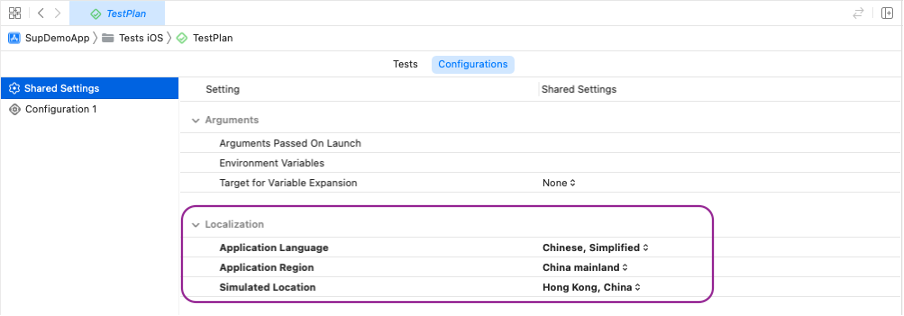
1. Test Plan
- Create a test plan and configure localization under Configurations → Localization.
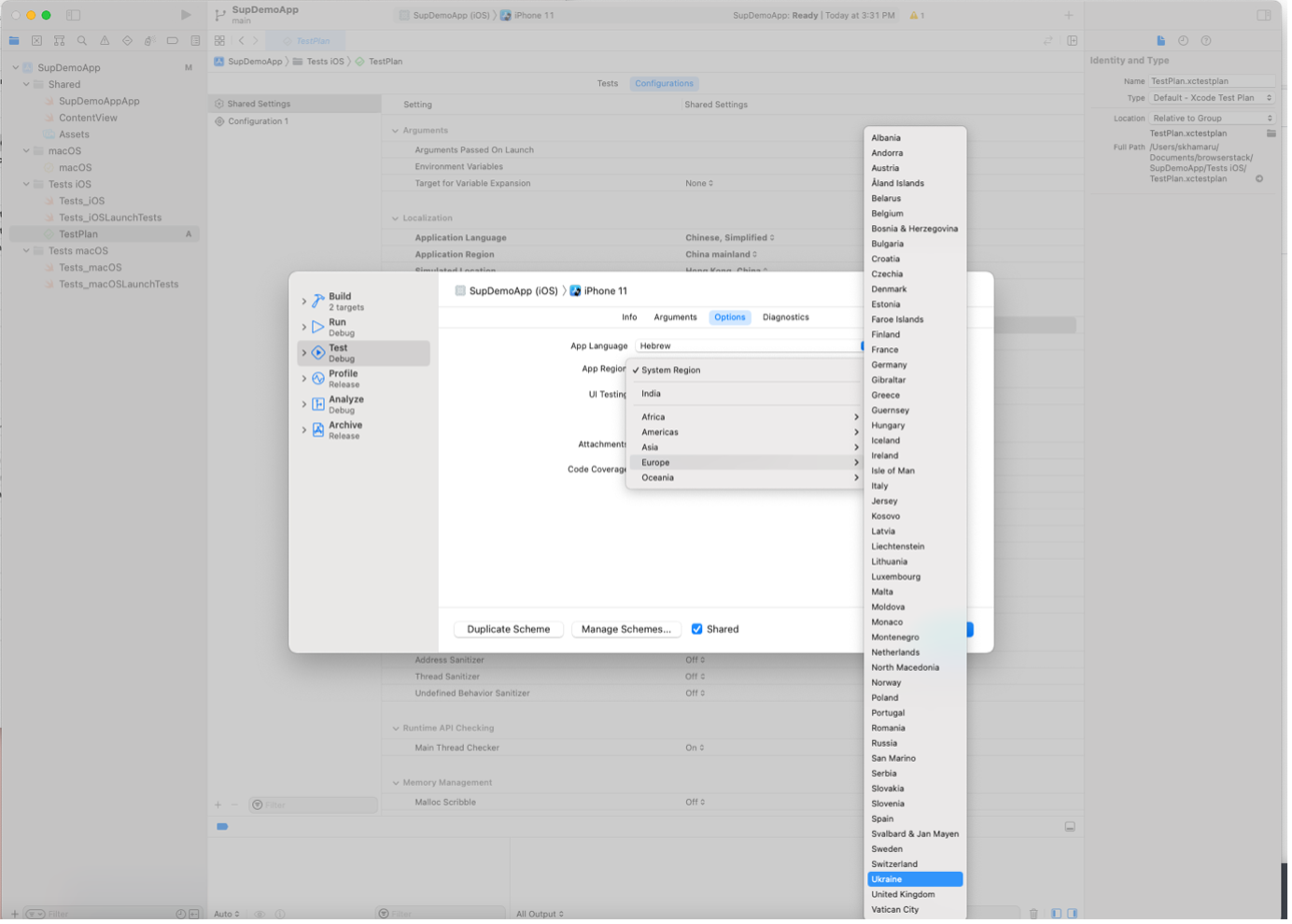
2. Scheme
- Navigate: Product → Scheme → Edit Scheme → Options → App Region.
- Select the desired country from the dropdown list.
3. Launch Arguments
- Set locale and language in setup() method of the test suite.
4. GPX File
- Simulate location using latitude and longitude.
- Supports multiple coordinates for advanced testing.
This guide explains how to configure and execute Geo-Location Testing for iOS apps using XCUITest in Xcode and via BrowserStack’s real device cloud.
How to configure Geo-Location for Testing in XCUITest?
For mobile app testing, there are different ways to configure Geo-Location in XCode while testing using XCUITest:
Test Plan
Users can create a test plan and configure the localization section in the Configurations tab:
Scheme
To update geo-location settings in XCode via Scheme, the below setting is to be configured by navigating to
Product → Scheme → Edit Scheme → Options -> App Region -> Select a country from the dropdown list.
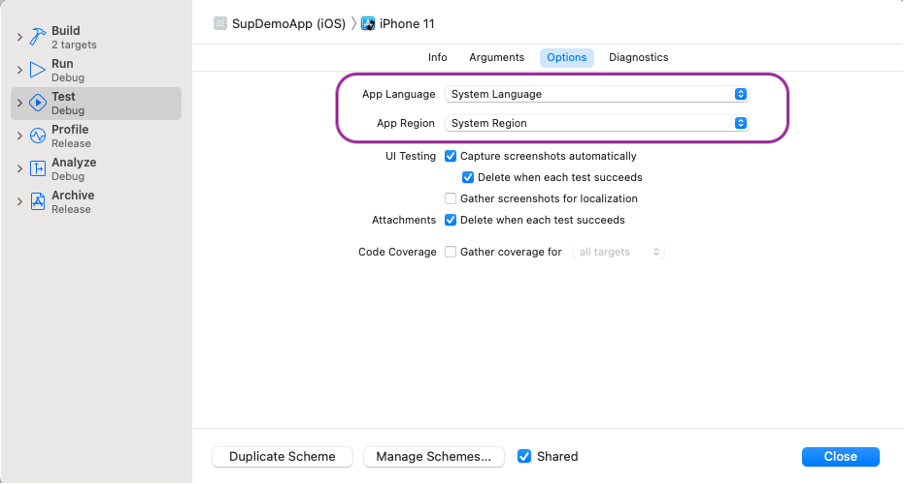
An example is provided below for reference:
Launch Arguments
Apple provides a setup method for all test suite classes. We can pass our launch arguments through code in the setup method to launch the test app for the localized region required for our test app.
In the example below, we observe the syntax of the launch argument where the France locale is passed to the app.
app.launchArguments += ["-AppleLocale", "fr_FR"]
Usually a setup() method would look like below, where the launch arguments are passed:
In Swift Language:
import XCTest
class Tests_iOSLaunchTests: XCTestCase {
override func setUp(){
super.setUp()
continueAfterFailure = false
let app = XCUIApplication()
app.launchArguments += ["-AppleLanguages", "(fr)"]
app.launchArguments += ["-AppleLocale", "fr_FR"]
app.launch()
}
}GPX File
In the GPX File approach, we can pass the latitude and longitude coordinates of the required simulated location. We can create a GPX file through XCode with one or more customized locations.
Example of a GPX file with latitude and longitude of Los Angeles:
<gpx> <wpt lat="34.0625905" lon="-118.36230069999999"></wpt> </gpx>
Running XCUITest Location Testing with BrowserStack
Let us assume we wish to test GeoLocation without trying any of the above approaches of XCode, then we can also configure the same using the below BrowserStack commands in CI.
BrowserStack can be integrated with the XCUITest suite using the following three approaches:
1. Setting Language and Locale
You can configure the language and locale to test a localized app version for your XCUI tests. To do so, you need to pass the language parameter in the REST API request to start the XCUI test execution.
2. Setting IP Geolocation
With BrowserStack’s IP Geolocation feature, it’s easier to simulate website and mobile behavior from different locations by using IP addresses hosted in 45+ countries worldwide. By incorporating this into your XCUITest Location testing, you can verify localized pricing, languages, product listings, and more scenarios.
NOTE – IP geolocation is an Enterprise feature on BrowserStack
3. Setting GPS Location using Latitude and Longitude
GPS geolocation testing makes it easier to simulate the device location to specific GPS coordinates and test location-based scenarios for your mobile app. You will be required to pass the latitude and longitude of the desired location.
Conclusion
Wrapping up, we can see Apple provides effective and flawless ways to help in the localization & internationalization testing of iOS & Mac apps in XCUITest on XCode.
However, with BrowserStack Geo-Location Testing, testing teams can access:
- GeoTargeting: Verify mobile apps for delivering content localized to a user’s location that benefits SEO and app rankings in different countries.
- GeoFencing: Mobile app testing that triggers a proper notification when a user crosses a predefined geographical perimeter.
- GeoTagging: Test if your mobile app tags the right location to media, such as photos, videos, and social posts.
- Localization: Check if language, currency, time, and spelling correctly adapt based on the selected location.
- GeoBlocking: Test and ensure user access to your mobile app is restricted based on user location.