Appium installation is straightforward and simple, however, there are a few nuances that decide how smooth the setup feels for first-time testers. Most guides list the commands, but they rarely explain the small checks that help avoid version issues, missing prerequisites, or unexpected command failures.
Overview
To install Appium,
- Install Node.js: Download it from the official website and complete the setup.
- Verify Node and npm: Run node -v and npm -v to confirm both are installed.
- Install Appium: Run npm install -g appium.
- Check Appium version: Confirm installation with appium –version.
- Start the server: Launch Appium by running appium in the terminal.
In this guide, I will expand on these steps, call out the nuances that matter, and help you avoid the common setup issues new testers usually run into.
What is Appium Server?
Appium Server is the component that receives your test commands, translates them into actions the device understands, and sends the responses back to your test script. It acts as the bridge between your automation code and the real mobile device or emulator. The server must be running before any Appium test can execute.
While the Appium server is essential for automation, setting it up and maintaining devices can be time-consuming. Platforms like BrowserStack allows you to skip these steps and run Appium tests directly on real devices in the cloud.
How to Download and Install Appium in 2026
Appium enables seamless cross-platform mobile testing, ensuring consistent performance on both iOS and Android devices. Follow these steps to download and install Appium, and get your environment ready for efficient testing.
There are 2 methods to install Appium –
- From the terminal using Node.js
- Directly from the Appium desktop client
Let’s discuss both methods in detail.
Method 1: Install Appium using Node.js
The first step is to verify whether Node.js is already installed in the system.
To do so, open the terminal and run the following command:
node --version
If Node.js is already installed in the system, it’ll return the Node version, else it throws an error stating – ‘node is not recognized’, which means Node.js is not installed in the system.
- To install Node.js, visit the official Node.js download section.
- Choose the Node installer per the underlying operating system (Mac or Windows).
- Windows users can verify the bit size (32-bit or 64-bit) by checking computer properties. Download the installer accordingly.
- Once the installer is downloaded, run it and proceed with the installation. Define the path explicitly if required.
- Once the installation is complete, restart the terminal and run the command -> node –version again. It will return the Node version.
This indicates the successful installation of Node.js. The Node.js installation also covers the installation of npm (node package manager).
Mac users can use the node -v and npm -v commands to verify the installation and version details.
- To install Appium, run the following command.
npm install -g appium
The command above will download and install Appium. Once done, verify the Appium installation on macOS or Windows by running the command below:
appium --version
This will return the latest Appium version installed in your system.
- To start the Appium server directly from the terminal, enter “appium” as a command. It will begin on the Appium server on Port number 4723.
Read More: How to Run Your First Appium Test Script
Method 2: Install Appium using Appium Desktop Client
The Appium Desktop app is a powerful GUI for developers or QA engineers to run automated mobile tests. It is compatible with macOS, Windows, and Linux. The Appium Desktop app provides an intuitive user interface for controlling and configuring the Appium server.
The installation of the Appium Desktop Client is bundled with Node runtime, so users do not need to install Node or npm explicitly.
To get started with Appium Desktop installation, follow the steps below:
1. Visit the official Appium site and Click on the Download Appium button
2. The Download button redirects the user to the GitHub page
3. From the GitHub page, Windows users need to download the .exe file, and Mac users need to download the .dmg file.
Clicking on the Appium link present on the top right corner. This directs you to the GitHub page.
4. Once the Appium Desktop file for the respective OS is downloaded, start the installation by double-clicking on that file. Mac users must drag the Appium logo to the Applications folder to initiate the installation.
5. Once the installation is complete, start the Appium Desktop Client.
6. Users can start or stop the Appium server using this user interface.
They can also configure their test environments using the Appium Desktop Client.
Also Read: How to set up your Appium Grid
Before proceeding with any test scenarios, developers or QAs must consider installing and running Appium doctor. It is a tool that identifies and resolves common configuration issues in Node, iOS, and Android before Appium automation.
- Install Appium Doctor using the following command:
npm install appium-doctor -g
Once the tool is installed, one can view the list of inspections available by running the command below:
appium-doctor -h
The image below represents the available commands one can use to verify the dependencies for a particular test environment before test automation.
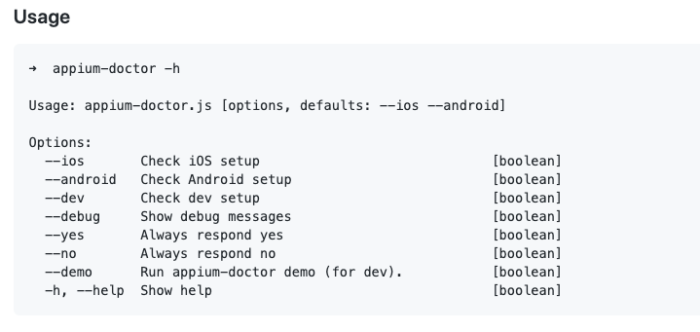
For example, before starting with automation on Android devices, QAs must run the command – appium doctor –android. This will display all missing and existing dependencies required for Android automation.
Master Appium in 2026
Here are a few useful quides that will help you master Appium in 2026
Setup
- Appium Tutorial for Mobile Application Testing
- How to perform Parallel Test Execution in Appium?
- How to Run Your First Appium Test Script
- How to set up your Appium Grid
- Understanding Appium Desktop: Tutorial
Actions
- How to perform Debugging in Appium
- How to report bugs in Appium UI Testing?
- How to run Appium Tests on macOS?
- How to run Appium iOS Tests on Real Devices?
- XPath in Appium: Tutorial
- How to Analyze Appium Logs
- How to perform Drag and Drop using Appium
- How to test mobile app in Landscape or Portrait mode using Appium
- How to Run Same Script in Multiple Devices using Appium
- How to change Time Zones for Mobile App Testing using Appium
- How to Perform Localization of Mobile Apps using Appium
- What is Appium Inspector? (Benefits & How to Use it?)
- How to run Appium tests on Android devices
- How to scroll down to an element in Appium
- How to test Biometric authentication using Appium?
- How to use touch actions in Appium?
- How to Automate a Real E2E User Flow involving App and Browser with Appium
- How to Inspect Element using UIAutomatorViewer in Appium
- How to Test Flutter Apps Using Appium Automation
- Understanding FindElements in Appium
- Appium Visual Testing: The Essential Guide
- React Native and Appium Tutorial
Best Practices, Tips, and Tricks
- Appium Best Practices Every Developer Must Know
- Effective Locator Strategies in Appium
- Top Appium Commands every Developer must know
- Desired Capabilities in Appium
- Overcoming Top Challenges faced in Appium Automation
Common Issues Testers Face When Installing Appium
Even though Appium installation is usually straightforward, testers often encounter a few recurring issues that can disrupt the setup or initial test execution.
1. Environment Setup Issues
Appium relies on several external tools such as Node.js, Android SDK, and Xcode (for iOS). Errors often occur when these dependencies are missing, incorrectly installed, or misconfigured.
- Missing Dependencies: If Node.js, Android SDK, or Xcode is not properly installed, Appium cannot run. Use Appium Doctor to identify missing or misconfigured components and follow the suggested fixes.
- Path Variables: Incorrect environment variables prevent Appium from locating the required executables. Ensure that the system PATH includes Node.js, Java, and Android SDK paths. On macOS, update the .bash_profile or .zshrc; on Windows, update the system environment variables.
- Permissions Issues: On macOS or Linux, lack of proper permissions can block installation or execution. Run installation commands with proper privileges or use sudo when required, and ensure directories have appropriate read/write access.
Read More: How to Setup Appium Tests on macOS?
2. Compatibility and Version Mismatches
Appium relies on the correct combination of server, client, and driver versions. Mismatches can cause session failures or unexpected errors.
- Appium Server/Client Version Mismatch: Using incompatible server and client libraries often leads to session creation errors. Align the versions of Appium server and client libraries in your test framework. Verify compatibility in the Appium release notes.
- Driver Issues: Using outdated or incompatible drivers can result in failed tests. Regularly update drivers and configure them according to your OS and device versions.
- Android/iOS Version Compatibility: Certain versions of Android or iOS may not work with older drivers or specific Appium features. Update the drivers (e.g., UIAutomator2 for Android, XCUITest for iOS) and check Appium documentation for platform-specific requirements.
Read More: Android App Automation using UIAutomator
3. Session Creation and Capability Issues
Many Appium errors occur during session initiation due to misconfigured desired capabilities or server communication issues.
- Incorrect Desired Capabilities: Incorrect or incomplete capabilities, such as platformName, deviceName, appPackage, or appActivity, prevent sessions from starting. Double-check the values against your device and app configurations.
- SessionNotCreatedException: This indicates failure to establish a session, often due to environment or capability issues. Verify server logs, capabilities, and Appium version compatibility.
- Socket Hang Up Errors: These typically occur after failed session attempts and suggest communication issues between the client and server. Restart the Appium server and the virtual device, and retry the session.
4. Test Execution and Element Interaction
Once the session is established, test failures can occur due to unstable element locators or timing issues.
- Element Not Found Exceptions: Fragile XPaths or incorrect locators prevent Appium from finding UI elements. Use robust locators such as accessibility IDs or stable resource IDs, and validate them with Appium Inspector.
- Synchronization Issues: Tests often attempt actions before elements are fully loaded. Implement explicit waits, use WebDriverWait, or incorporate proper synchronization strategies to ensure elements are interactable.
Why Run Appium Tests on Real Devices?
Running Appium tests only on local devices or emulators has limitations. Local setups often fail to cover device fragmentation, OS versions, screen sizes, or network conditions that apps encounter in the real world.
Emulators cannot replicate real hardware behavior, performance issues, or gestures like pinch, swipe, and rotation precisely. This gap can result in tests passing locally but failing in production.
BrowserStack addresses these challenges by providing access to real devices in the cloud, ensuring tests run under conditions that mirror real users. Key features include:
- Real Device Cloud: Access 3,500+ real Android and iOS devices with different OS versions, screen sizes, and manufacturers.
- Instant Setup: No need to maintain physical devices or configure complex environments locally.
- Parallel Testing: Run multiple tests across devices simultaneously to reduce execution time.
- Real Device Interactions: Test gestures, touch, GPS, camera, and network conditions exactly as on real hardware.
Conclusion
Setting up Appium is straightforward, but paying attention to a few key steps ensures success. Installing Node.js correctly, verifying npm and Appium versions, configuring environment variables, and using compatible drivers are essential to avoid errors and run tests smoothly on the first try.
At the same time, use tools like BrowserStack to run Appium tests on real devices in the cloud. It overcomes the limitations of local setups and allows tests to run in parallel across multiple devices and OS versions. This ensures that test results reflect real user conditions, making mobile automation faster, more reliable, and scalable.