GraphQL and React are powerful tools for building dynamic, data-driven applications. Integrating the two allows for efficient data fetching and seamless UI updates.
Combining GraphQL with React enhances the development experience by enabling efficient data fetching and management within the app. It simplifies state handling, reduces over-fetching, and allows for real-time updates, improving both performance and scalability. Integrating GraphQL with React To integrate GraphQL with React, follow these key steps: Benefits of Using GraphQL with React: This article explores the benefits of combining GraphQL with React to create efficient, scalable, and high-performance applications. Combining GraphQL with React provides a powerful synergy that enhances both development efficiency and application performance. Here’s why this integration is so effective: Setting up a GraphQL server involves defining a schema, creating resolvers to fetch data, and making the server available for requests. Below are the essential steps to set up a basic GraphQL server: You’ll need to install the necessary libraries for setting up a GraphQL server. For a Node.js server, you can use Apollo Server or Express-GraphQL. Here’s how to install Apollo Server: Overview
Why Combine GraphQL with React?
Setting Up a GraphQL Server
1. Install Dependencies
npm install apollo-server graphql
2. Define the GraphQL Schema
The schema defines the types, queries, and mutations available in your API. You’ll define object types and their fields in GraphQL’s Schema Definition Language (SDL).
Example:
const { gql } = require(‘apollo-server’);
const typeDefs = gql`
type Query {
hello: String
user(id: ID!): User
}type User {
id: ID!
name: String
email: String
}
`;
In this example, the schema defines a Query type with two fields: hello and user, which will return a User object.
3. Create Resolvers
Resolvers are functions that fetch data for the fields defined in the schema. They map the schema fields to the actual data sources.
Example:
const resolvers = {
Query: {
hello: () => ‘Hello, world!’,
user: (_, { id }) => {
return { id, name: ‘John Doe’, email: ‘john.doe@example.com’ };
},
},
};
In this case, the hello resolver simply returns a string, while the user resolver returns mock user data based on an id.
4. Set Up the Apollo Server
Now, you can set up the server using the ApolloServer class, passing in the schema and resolvers.
Example:
const { ApolloServer } = require(‘apollo-server’);
const server = new ApolloServer({
typeDefs,
resolvers,
});server.listen().then(({ url }) => {
console.log(`Server running at ${url}`);
});
This sets up the GraphQL server on the default port (4000) and makes it available at http://localhost:4000.
5. Test the Server
Once the server is running, you can test your GraphQL API using a tool like Apollo Studio or GraphiQL, where you can run queries and explore your API interactively.
Example query in GraphiQL:
query {
hello
user(id: 1) {
name
}
}
This will return the mock data defined in the resolver.
Integrating GraphQL with React Using Apollo Client
Integrating GraphQL with React using Apollo Client simplifies data fetching and state management within React applications. Apollo Client provides an easy way to connect React components with a GraphQL server. Here’s how you can set it up.
1. Install Apollo Client and GraphQL
To get started, install the necessary dependencies in your React project:
npm install @apollo/client graphql
2. Set Up ApolloProvider
Wrap your React app with ApolloProvider and provide the Apollo Client instance.
Example:
import { ApolloProvider, ApolloClient, InMemoryCache } from ‘@apollo/client’;
const client = new ApolloClient({
uri: ‘https://your-graphql-endpoint.com/graphql’,
cache: new InMemoryCache(),
});function App() {
return ({/* Your components here */}
);
}
3. Fetch Data with useQuery
Use the useQuery hook to fetch data in your component:
import { useQuery, gql } from ‘@apollo/client’;
const GET_USERS = gql`
query GetUsers {
users {
id
name
}
}
`;function Users() {
const { loading, error, data } = useQuery(GET_USERS);if (loading) return Loading…
; if (error) return Error: {error.message}
;
return ({data.users.map(user => (
{user.name}
))});
}
4. Modify Data with useMutation
Use the useMutation hook to update data:
import { useMutation, gql } from ‘@apollo/client’;
const ADD_USER = gql`
mutation AddUser($name: String!) {
addUser(name: $name) {
id
name
}
}
`;function AddUser() {
const [addUser] = useMutation(ADD_USER);const handleSubmit = async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
const name = e.target.name.value;
await addUser({ variables: { name } });
};return (
Add User
);
}
Best Practices for Efficient Data Fetching
To ensure optimal performance and scalability in your GraphQL-based applications, it’s important to follow best practices for efficient data fetching. Here are some key strategies:
- Fetch Only the Data You Need: Request only the specific fields necessary for your component. Avoid querying unnecessary data, which reduces payload size and improves performance.
- Use Variables in Queries: Use variables to dynamically pass values into queries instead of hardcoding them. This makes queries reusable and adaptable to different conditions.
- Implement Pagination: For large datasets, use pagination to limit the amount of data fetched at once. This prevents performance issues and keeps the response size manageable.
- Leverage Caching: GraphQL clients like Apollo automatically cache query results. Use this feature to avoid redundant requests and speed up your app by serving cached data when possible.
- Use Fragments for Reusability: Fragments allow you to define reusable parts of a query. This helps reduce redundancy and maintain consistency across different parts of your application.
- Avoid Deep Nesting: Minimize deeply nested queries. While GraphQL allows nested fields, excessive nesting can increase complexity and reduce performance. Keep queries as flat as possible.
- Batch Multiple Queries: If your app requires multiple independent queries, consider batching them together in a single request to reduce the number of round trips to the server.
- Handle Errors Gracefully: Ensure proper error handling in your queries to prevent unnecessary re-fetching of data. Use tools like Apollo Client’s built-in error handling to manage exceptions efficiently.
Error Handling and Optimistic UI Updates
Effective error handling ensures that users experience minimal disruption when something goes wrong with a GraphQL request. Apollo Client offers built-in support for handling errors in queries and mutations.
- Error Boundaries: Use React’s error boundaries to catch runtime errors in React components.
- Apollo Error Handling: Apollo Client provides error messages that you can use to display specific errors, such as network issues or invalid queries.
- Handling Errors in Queries: You can handle errors returned by the useQuery and useMutation hooks by checking the error state.
Example:
const { loading, error, data } = useQuery(GET_USER);
if (loading) return Loading…
;if (error) return Error: {error.message}
;
By displaying user-friendly error messages, you can enhance the user experience even when something goes wrong.
Optimistic UI Updates
Optimistic UI updates help improve user experience by showing immediate feedback during mutation operations, such as adding, updating, or deleting data, even before the server responds. This makes the app feel faster and more responsive.
- Optimistic Response: Apollo Client allows you to define an optimistic response to simulate a server’s response right after a mutation is called.
- Update Cache Optimistically: You can also update the Apollo Client cache before the mutation is complete, providing immediate visual feedback to the user.
Example:
const [addUser] = useMutation(ADD_USER, {
optimisticResponse: {
addUser: {
id: -1, // Temporary ID
name: ‘New User’,
email: ‘newuser@example.com’,
},
},
update(cache, { data: { addUser } }) {
const data = cache.readQuery({ query: GET_USERS });
cache.writeQuery({
query: GET_USERS,
data: {
users: […data.users, addUser],
},
});
},
});
This approach ensures that users immediately see the changes (such as a new user being added) without waiting for the server response, creating a smoother experience.
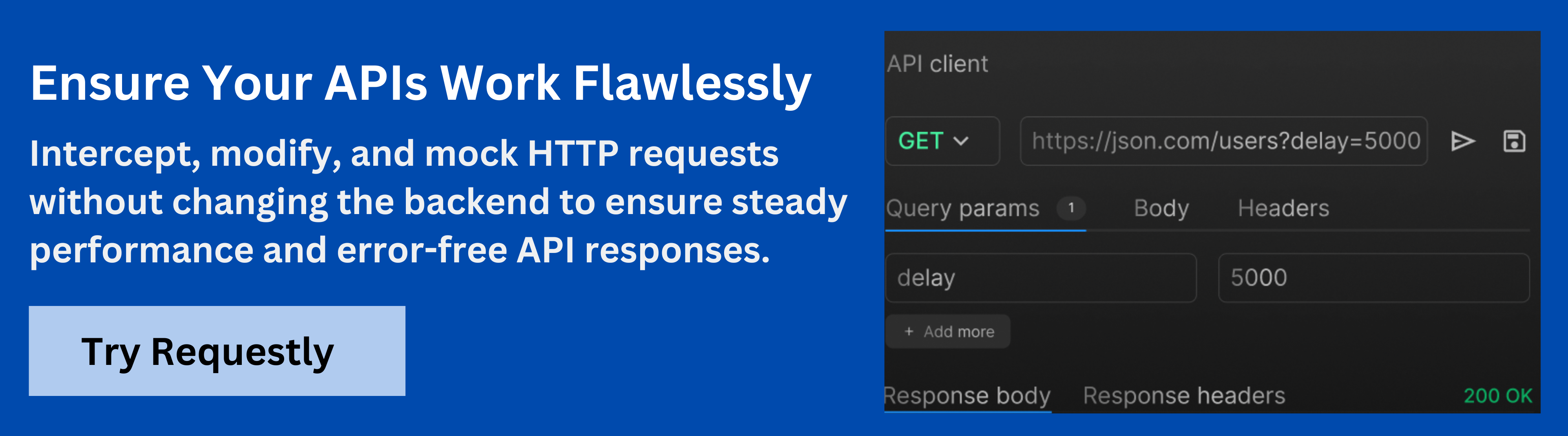
Enhance GraphQL Debugging with Requestly
Requestly by BrowserStack is a powerful tool that simplifies the debugging process of GraphQL queries. By allowing you to intercept, modify, and monitor GraphQL requests and responses, Requestly makes it easier to identify and resolve issues during development. Here’s how it can enhance your debugging workflow:
- Intercept and Inspect GraphQL Requests: Requestly enables you to inspect the details of GraphQL requests, including the query, variables, and headers, to ensure that your data is being sent correctly. You can quickly verify whether the correct data is being requested from the server, making it easier to debug malformed queries.
- Modify Requests and Responses: With Requestly, you can modify GraphQL requests and responses in real time, which is especially helpful when testing different scenarios without modifying your actual code. You can change query variables, headers, or even the response data to simulate various use cases, such as error handling or data changes, without needing to rely on the backend.
- Mock GraphQL Responses: Requestly allows you to mock GraphQL responses, which is particularly useful during development when the backend is incomplete or unavailable. By defining mock data for specific queries, you can continue working on the frontend without waiting for the server, ensuring smoother progress and UI development.
- Monitor Network Traffic and Query Performance: Requestly provides a visual interface to monitor network traffic, which helps in identifying slow or inefficient queries. You can track the performance of your GraphQL requests, see response times, and determine if any optimizations are needed to improve the performance of your queries.
Using Requestly’s features for monitoring, modifying, and mocking GraphQL requests can streamline the debugging process, making it easier to optimize your GraphQL queries and ensure smoother application performance.
Conclusion
Integrating GraphQL with React significantly enhances the efficiency and scalability of modern web applications. By allowing precise data fetching, reducing over-fetching, and simplifying state management, GraphQL streamlines the development process.
Tools like Requestly further enhance the debugging experience, enabling developers to easily inspect, modify, and mock GraphQL requests and responses.
By following best practices for efficient data fetching and implementing strategies like error handling and optimistic UI updates, you can build high-performance applications that deliver seamless user experiences. Combining these technologies equips developers with the tools needed to create fast, dynamic, and scalable web applications.