Authentication is a critical component of securing GraphQL APIs, ensuring that only authorized users can access protected resources.
Overview
GraphQL is an open-source query language and runtime for APIs that enables clients to request precise data through a strongly typed schema and a single endpoint.
Why GraphQL Authentication is Important:
- Prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data exposed through flexible queries.
- Protects mutations from being misused to alter or delete critical information.
- Ensures field-level or type-level access control for different user roles.
- Reduces risks of API abuse, data leaks, and malicious queries.
Common Authentication Strategies in GraphQL:
- JWT (JSON Web Tokens): Pass signed tokens in headers to verify user identity.
- OAuth2: Delegate authentication to trusted providers like Google or GitHub.
- API Keys: Use static keys for service-to-service communication or simple apps.
- Session-Based Authentication: Store user sessions in cookies for stateful logins.
This article explores how authentication works in GraphQL, common strategies, and best practices.
What is GraphQL Authentication?
GraphQL authentication is the mechanism used to verify a client’s identity before granting access to data or operations within a GraphQL API.
Unlike REST, where different endpoints can be secured individually, GraphQL exposes a single endpoint capable of handling all queries, mutations, and subscriptions. This design makes authentication a critical safeguard to prevent unauthorized access.
In practice, authentication is usually implemented by attaching credentials, such as JSON Web Tokens (JWTs), OAuth tokens, API keys, or session cookies, to each request.
The GraphQL server processes these credentials within its context, which is then passed to resolvers. Resolvers use this context to determine whether the requester is authenticated and what actions they are permitted to perform.
By establishing trust at the authentication layer, GraphQL ensures that:
- Only verified users can query sensitive data.
- Mutations that modify or delete records are restricted to authorized clients.
- Subscriptions for real-time updates are delivered securely.
Authentication, therefore, is not just a gatekeeping step, it is a foundation for building reliable and secure GraphQL APIs.
Read More: Cypress API Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
How Authentication Works in GraphQL
Authentication in GraphQL is typically managed at the server level, using the request context to carry user identity across queries, mutations, and subscriptions. The process generally follows these steps:
- Client Sends Credentials: The client includes authentication details, such as a JWT, OAuth token, API key, or session cookie, in the HTTP request headers.
- Server Validates Credentials: The GraphQL server intercepts the request and verifies the credentials against its authentication mechanism (e.g., token validation, session store, or external identity provider).
- Context Is Enriched: Once validated, the server attaches the user’s identity and permissions to the GraphQL execution context. This context is then passed to all resolvers handling the request.
- Resolvers Enforce Access: Resolvers check the context to determine whether the authenticated user has the right to access or modify the requested fields. Unauthorized requests are rejected with appropriate error messages.
This model allows authentication to be applied consistently across the schema while still offering flexibility for field-level and role-based access control, making GraphQL both secure and adaptable to diverse application needs.
Common Authentication Strategies in GraphQL
Securing a GraphQL API can be achieved using several authentication approaches, depending on the application’s architecture and security requirements:
- JWT (JSON Web Tokens): A widely used method where clients send a signed token in the request header. The server verifies the token and extracts the user identity and roles from its payload.
- OAuth 2.0 / OpenID Connect: Delegates authentication to trusted third-party providers (e.g., Google, GitHub). Tokens issued by the provider are validated by the GraphQL server before granting access.
- API Keys: Simple and effective for service-to-service communication or lightweight applications. Each request includes a key that is validated against the server’s configuration.
- Session-Based Authentication: Uses cookies to manage user sessions. The server stores session data and checks the cookie on each request to authenticate the user.
Each strategy can be adapted to GraphQL by embedding the credentials in HTTP headers or cookies and validating them inside the GraphQL server’s context before executing resolvers.
Implementing Authentication in GraphQL
Authentication in GraphQL is generally applied at the server level and passed through the context, which makes user information available to all resolvers. A typical implementation follows these steps:
- Client Sends Credentials: The client attaches an authentication token, API key, or session cookie with each GraphQL request.
- Server Validates the Credentials: Middleware or server logic verifies the credentials against the chosen strategy (e.g., JWT, OAuth, sessions).
- Context Propagation: Once validated, the user’s identity is stored in the request context. This context is then accessible in resolvers to determine permissions.
- Resolver-Level Checks: Resolvers use the context to enforce authentication and authorization, ensuring that only authenticated users can access protected fields or perform mutations.
This approach keeps authentication centralized, ensures consistency across queries, mutations, and subscriptions, and allows fine-grained access control at the field level when necessary.
Read More: What is API Testing? (with Examples)
Best Practices for Secure GraphQL Authentication
Implementing authentication in GraphQL requires careful attention to both transport security and schema-level safeguards. The following practices help ensure that authentication remains robust and consistent across environments:
- Enforce Transport Security: All GraphQL requests should be transmitted over HTTPS to prevent credential exposure. Use secure cookie attributes (HttpOnly, Secure, SameSite) when sessions are employed.
- Adopt Token Expiry and Rotation: Short-lived access tokens, such as JWTs should be configured with expiration times. Incorporate refresh tokens or key rotation policies to reduce the risk of token compromise.
- Centralize Authentication Logic: Authentication should be handled at the server level and stored in the execution context. This ensures resolvers consistently have access to user identity and claims when enforcing access rules.
- Apply Fine-Grained Authorization: Beyond verifying identity, enforce role-based or field-level access control to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive operations or data.
- Limit Query Abuse: Configure query depth and complexity limits to mitigate denial-of-service risks from overly nested or expensive queries. Consider persisted queries for untrusted clients.
- Restrict Schema Introspection in Production: Disable or limit introspection queries in production environments to prevent attackers from mapping out the entire schema.
- Standardize Error Handling and Logging: Return clear but generic error codes, such as UNAUTHENTICATED or FORBIDDEN to clients, while maintaining detailed logs internally for auditing and investigation.
By consistently applying these practices, organizations can strengthen the security of their GraphQL APIs while providing a reliable authentication framework for users and services.
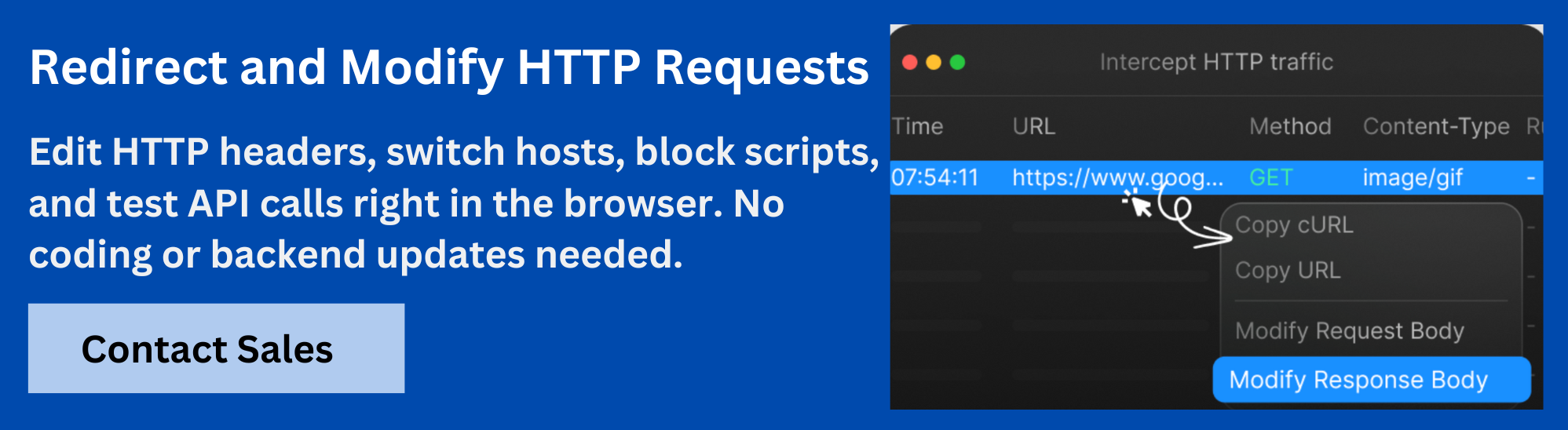
Enhancing Authentication Debugging with Requestly HTTP Interceptor
Authentication issues in GraphQL often depend on the exact combination of headers, tokens, and variables sent with a request. The Requestly HTTP Interceptor simplifies debugging by giving developers full visibility and control over these interactions.
With Requestly, developers can:
- Capture live GraphQL requests to inspect headers, authentication tokens, and payloads in real time.
- Replay or modify requests by altering tokens, cookies, or query variables to test how the server responds under different conditions.
- Simulate edge cases such as expired tokens, missing headers, or invalid credentials without changing client-side code.
- Share reproducible scenarios across teams, ensuring consistent troubleshooting during development and testing.
By integrating Requestly by BrowserStack into the debugging workflow, teams can quickly isolate authentication problems, confirm server-side validation, and strengthen the overall security of their GraphQL APIs.
Conclusion
Authentication is a cornerstone of securing GraphQL APIs, ensuring that only trusted clients and users can access or modify data. Because GraphQL exposes a single, flexible endpoint, strong authentication strategies, combined with fine-grained authorization, are essential to protect sensitive operations.Learn how GraphQL authentication works, explore common strategies, best practices, and debugging methods to secure modern APIs effectively.
By adopting proven approaches such as JWTs, OAuth, or session-based methods, and reinforcing them with best practices like token rotation, query complexity limits, and restricted introspection, teams can maintain both security and performance. Tools like the Requestly HTTP Interceptor further enhance this process by enabling clear visibility into authentication flows during debugging.
When implemented thoughtfully, authentication not only safeguards GraphQL APIs but also builds the foundation for reliable, scalable, and secure applications.