Mobile applications must function smoothly across devices, networks, and operating systems. Even a minor glitch can lead to poor user reviews or uninstalls. That’s why mobile app testing is crucial to ensure your app delivers a smooth and reliable experience.
Overview
Mobile app testing involves evaluating an application’s functionality, performance, user experience, and security across various devices, platforms, and network conditions
Approaches to Testing Mobile Applications
- Manual Testing: Testers manually explore and test mobile applications for functionality, usability, and design accuracy.
- Automated Testing: Automated scripts run repetitive and complex tests on mobile applications, improving speed and efficiency.
What to Test in Mobile Applications
- Functionality: Ensure all app features work as intended.
- Compatibility: Validate performance across devices, screen sizes, and OS versions.
- Performance: Check responsiveness and stability under various conditions.
- Usability: Ensure intuitive navigation and accessibility.
- Security: Protect user data and prevent vulnerabilities.
- Network Handling: Confirm app stability across different network conditions (Wi-Fi, 4G, 5G).
- Interrupt Handling: Ensure the app handles calls, messages, and notifications smoothly.
This article explores how to test mobile applications effectively, covering approaches, tools, strategies, and best practices for ensuring app quality.
What is Mobile App Testing?
Mobile app testing is the process of evaluating a mobile application to ensure it works as intended across different devices, operating systems, and network conditions. It verifies the app’s functionality, performance, usability, and security, ensuring a seamless user experience.
The aim of mobile app testing is to identify and fix issues such as crashes, slow load times, or broken features, before they impact users. A well-tested app delivers consistent performance and meets user expectations, helping businesses retain users and build trust.
Why is Mobile App Testing Important?
Mobile app testing is vital for several reasons that directly impact user satisfaction and business success:
- Ensures app works smoothly across different devices, screen sizes, and operating systems.
- Prevents crashes, slow performance, and bugs that frustrate users.
- Protects against security vulnerabilities and data breaches.
- Validates app reliability under varied network conditions and interruptions.
- Enhances user experience, leading to positive reviews and higher retention.
- Helps maintain brand reputation and drives business growth.
Types of Mobile Apps
Mobile applications come in different types, each with unique characteristics that influence how they should be tested and where users can access them:
Web Apps
These types of mobile apps are websites optimized for mobile devices and accessed via web browsers like Chrome or Safari. Web apps do not require installation and work across all platforms but have limited access to device hardware and features. Because they run in browsers, users can access them simply by visiting a URL.
Example: Google Docs can be used as a web app by accessing docs.google.com on any mobile browser.
Native Apps
These are built specifically for one operating system, such as iOS or Android, using platform-specific programming languages like Swift for iOS or Kotlin for Android.
These apps provide the best performance and have full access to different device features like GPS, camera, and sensors.
Example: Instagram is a native app available for download on the Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
Hybrid Apps
Hybrid apps blend features of both native and web apps. Built using web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, they are packaged in a native shell that enables installation and execution across various platforms.
Hybrid apps offer a balance between cross-platform compatibility and access to some native device features, though performance may not be as smooth as fully native apps. These apps are also available on app stores.
Example: Airbnb’s mobile app is a hybrid app available on the Apple App Store and Google Play Store.
Read More: Native vs hybrid app: Which one to choose?
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
PWAs are advanced web applications that deliver an app-like experience through browsers. PWAs can work offline, send push notifications, and be added to the home screen without needing to be downloaded from an app store.
They combine the ease of access of web apps with features traditionally reserved for native apps, making them highly versatile.
Example: Twitter Lite is a PWA accessible by visiting mobile.twitter.com in a browser.
Understanding these different app types is essential for tailoring testing strategies that ensure each app delivers a seamless user experience across platforms.
Types of Mobile Application Testing
Testing mobile applications involves multiple testing types to ensure the app functions flawlessly and meets security standards.
- Functional Testing: Focuses on verifying that every app feature works as intended. This includes checking user interactions like tapping buttons, filling forms, navigating screens, and ensuring that all workflows produce the expected results.
- Compatibility Testing: Ensures the app performs consistently across various devices, screen sizes, operating systems, and network types. Since mobile devices vary greatly, this testing confirms the app works well regardless of hardware or software differences.
- Performance Testing: Measures how the app behaves under different conditions, including load times, responsiveness, and stability. It tests how well the app handles heavy user traffic, limited device resources, and network fluctuations without crashing or slowing down.
- Usability Testing: Evaluates how easy and intuitive the app is for users. It examines the design, navigation, and overall user experience to ensure users can interact with the app efficiently and without confusion.
- Security Testing: Identifies vulnerabilities that could expose data or allow unauthorized access. This includes testing data encryption, secure login processes, safe data storage, and protection against attacks like data breaches or malware.
- Interrupt Testing: Verifies the app’s behavior during unexpected interruptions, such as incoming calls, text messages, or notifications. It ensures the app pauses, resumes, or maintains data correctly without crashing or losing user progress.
- Installation Testing: Checks that the app installs, updates, and uninstalls properly on all supported devices. It ensures the app does not cause errors during these processes and that updates don’t introduce new issues.
- Localization Testing: Confirms the app’s adaptation for different languages, cultures, and regions. It verifies correct translation, formatting, and cultural appropriateness of content and UI adjustments for various languages and regions.
What to Test in Mobile Applications?
Testing a mobile app thoroughly means examining various critical areas to ensure the app is user-friendly and performs well under real-world conditions. Key aspects to focus on include:
- User Interface and User Experience (UI/UX): Test the design elements, navigation flow, responsiveness, and overall ease of use to ensure the app is intuitive and visually consistent across devices.
- Input Methods and Gestures: Verify support for different input types such as touch, swipe, pinch, tap, and voice commands, ensuring all gestures work correctly and consistently.
- Multitasking and Interruptions: Check how the app behaves during interruptions like incoming calls, messages, notifications, or when the user switches between apps, ensuring no data loss or crashes occur.
- Compatibility: Ensure the app functions correctly across various devices, screen sizes, OS versions, and network environments, accommodating the diversity of the mobile ecosystem.
- Installation and Updates: Test the installation process, app updates, and uninstallation to make sure they work without errors and that user data is preserved appropriately during updates.
- Performance: Assess loading times, responsiveness, battery consumption, and memory usage to guarantee smooth and efficient app operation.
- Network Conditions: Test app behavior under different network scenarios, including offline mode, slow connections, and switching between Wi-Fi and mobile data.
Read More: UI Testing: A Detailed Guide
Approaches to Test the Mobile Application
There are two primary approaches to test mobile applications. Choosing the right one depends on different factors like app complexity, release cycles, and testing requirements:
Manual Testing
In manual testing, testers interact with the app just like end-users, following test cases to verify functionality, usability, and visual elements. This approach is ideal for:
- Exploratory Testing: When requirements are unclear, or testers need to explore the app’s behavior.
- Usability Testing: To assess the app’s user interface, user experience, and ease of use.
- Ad-hoc Testing: For testing unexpected scenarios or one-off use cases.
With BrowserStack App Live, teams can manually test mobile apps on different real devices and browsers, ensuring accurate results across real user conditions.
Automated Testing
Automated testing uses scripts and testing tools to execute test cases repeatedly across devices, platforms, and configurations. It’s best suited for:
- Regression Testing: To verify that new changes don’t break existing functionality.
- Performance Testing: To measure app speed, responsiveness, and behavior under load.
- Compatibility Testing: To test the app across various devices, OS versions, and screen sizes.
- Repetitive Test Cases: To test login flows, form submissions, or transactions.
BrowserStack App Automate helps teams run automated tests at scale across thousands of real devices, enabling fast and reliable results for every build. It supports popular frameworks, offers parallel test execution, and integrates seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines for faster release cycles.
Combining both approaches ensures a robust mobile testing strategy, manual testing for user-centric validations, and automated testing for efficiency, speed, and scalability.
Stages of Mobile App Testing
A systematic testing process ensures mobile apps meet user expectations across diverse devices and environments. Here’s how to approach it step by step:
Step 1: Process Outlining
Define the testing scope, objectives, and target devices. Establish the testing goals based on app requirements and end-user needs.
Step 2: Choosing the Test Type: Manual or Automated
Decide whether manual testing, automated testing, or a combination suits the app’s complexity, release frequency, and available resources.
Step 3: Preparing Test Cases for User Functionalities
Write detailed test cases covering all key app features, user journeys, edge cases, and potential error scenarios to ensure complete test coverage.
Step 4: Setting Up the Test Environment
Configure devices, OS versions, network conditions, and real-device clouds (e.g., BrowserStack) for accurate testing across real-world scenarios.
Step 5: Executing Tests
Run the tests manually or via automation tools like BrowserStack Automate, and monitor for issues across various devices, operating systems, and network conditions.
Step 6: Identifying and Logging Defects
Document any bugs, UI issues, crashes, or performance bottlenecks identified during testing, including detailed reproduction steps and screenshots for clarity.
Step 7: Retesting and Regression Testing
After fixes, re-execute relevant test cases to ensure issues are resolved and that no new bugs were introduced.
Step 8: Final Sign-Off
Once all critical test cases pass and the app meets quality standards, provide final approval for release.
How to Test Mobile Apps on BrowserStack
BrowserStack App Live provides access to a Real Device Cloud, allowing testers to manually interact with their mobile apps on real Android and iOS devices from any browser. This helps simulate real user conditions without requiring physical devices.
Below are the steps to perform manual testing using BrowserStack App Live.
Step 1: Create a free account on BrowserStack or log into the App Live dashboard.
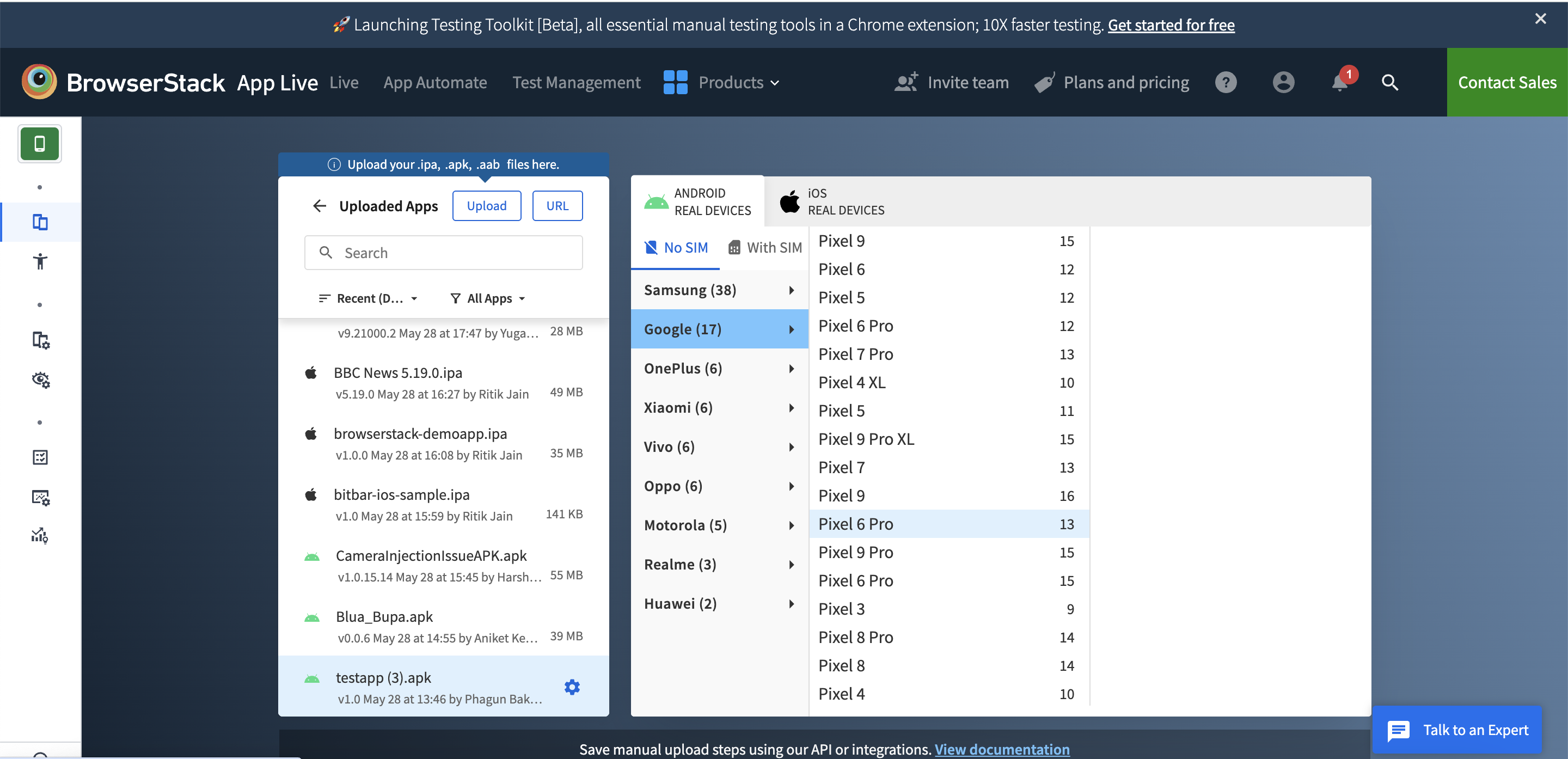
Step 2: Choose App Live
Step 3: Upload your mobile app file (.apk, .aab for Android or .ipa for iOS) to the platform.
Step 4: Select Device or OS
Step 5: Launch the app and start interactive manual testing.
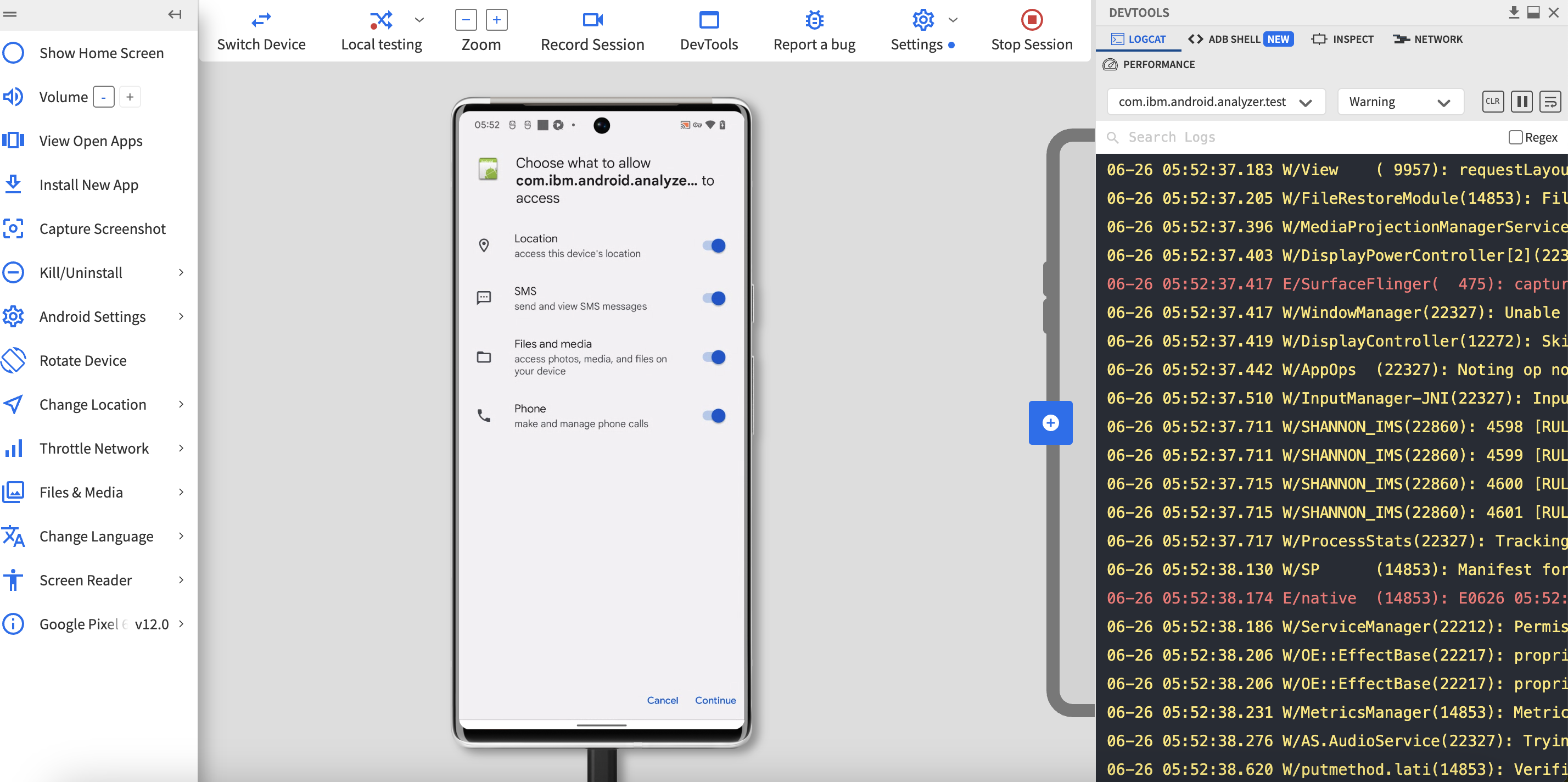
Manually navigate the app, testing UI, UX, gestures, and network conditions (like 3G, 4G, Wi-Fi). Simulate device rotations, multitasking, interruptions, and other real-world scenarios.
Step 6: Capture screenshots, record videos, and take notes to document bugs and unexpected behaviors.
Mobile App Testing Tools and Frameworks
Choosing the right frameworks and tools is crucial for efficient and effective mobile app testing. These tools help automate tests, manage devices, simulate user interactions, and generate detailed reports, making it easier to identify and fix issues quickly.
Here are some of the most popular tools and frameworks used in mobile app testing:
- BrowserStack: A cloud platform that offers manual and automated testing on real devices and supports popular frameworks like Appium and Espresso.
- Appium: An open-source framework for automating hybrid, native, and web apps on Android and iOS, supporting multiple programming languages.
- Espresso: Google’s Android-specific UI testing tool that offers fast and reliable automated testing with simple test script creation.
- XCUITest: Apple’s native testing framework for iOS apps, integrated with Xcode for robust UI and accessibility testing.
- Robotium: A user-friendly Android test automation tool for native and hybrid apps that simplifies writing powerful UI tests.
- Selenium: Primarily for web testing but often combined with Appium to automate mobile web application tests across browsers.
- Calabash: An open-source framework using Cucumber for writing readable automated tests on Android and iOS apps.
Why Choose BrowserStack?
BrowserStack is a comprehensive mobile app testing platform that helps teams deliver high-quality apps faster by enabling testing on real devices and browsers in real-world conditions.
Key Features of BrowserStack for Mobile App Testing:
- Access to 3500+ Real Devices and Browsers: Test mobile applications across a wide range of Android and iOS devices without maintaining an in-house lab.
- Instant Manual and Automated Testing: Use App Live for manual testing and App Automate for automated testing with frameworks like Appium and Espresso.
- No Setup or Maintenance: Get started immediately, no device setup, configuration, or updates required.
- Real User Conditions: Test mobile apps under varying network profiles (3G, 4G, 5G, Wi-Fi) and device settings to ensure real-world performance.
- Geolocation Testing: Simulate app behavior from different locations worldwide.
- CI/CD Integration: Seamlessly integrate with CI/CD pipelines using plugins for Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and other popular tools.
- Interactive Debugging Tools: Access logs, videos, and screenshots to quickly identify and resolve issues.
- Secure Testing: Run tests on a secure, private cloud with enterprise-grade security standards.
Conclusion
Thorough testing is crucial for delivering high-quality mobile applications that meet user expectations. By understanding the different testing types, approaches, and strategies, teams can ensure their apps function seamlessly across devices, operating systems, and network conditions.
Using robust platforms like BrowserStack enables teams to streamline both manual and automated testing on real devices, ensuring comprehensive test coverage without the overhead of managing device labs.
Adopting the right tools and frameworks, along with a structured testing process, empowers teams to build reliable, user-friendly mobile applications that deliver exceptional user experiences.