Automation testing with Selenium has evolved to become more accessible and efficient, thanks to tools like Selenium IDE.
Overview
What is Selenium Side Runner?
Selenium Side Runner is a command-line tool for running Selenium IDE test cases outside the browser environment using Node.js.
Importance of Selenium Side Runner
It plays a key role in integrating recorded tests into CI/CD pipelines and supports parallel execution, making automation faster and more scalable.
How Selenium Side Runner Works:
- Executes .side project files created in Selenium IDE
- Runs tests from the command line using Node.js
- Supports parallel execution with multiple browsers or configurations
- Allows integration with CI/CD tools for automated workflows
- Offers plugin support for extended capabilities
- Provides detailed reports and logs for test runs
This article explores what Selenium Side Runner is, why it matters, and how it fits into a modern test automation setup.
What is Selenium SIDE Runner?
Selenium SIDE runner is a command-line tool that lets users directly run a .side file on a node.js platform. Anyone familiar with the Selenium IDE is aware that it uses its record and playback features on the web browser and ultimately creates a .side file containing the test logic.
Apart from ease of access and creating test cases Selenium IDE provides access to run tests using the command line runner on the node.js platform.
How Selenium SIDE Runner Works
Selenium SIDE Runner is a command-line tool that executes test cases exported from Selenium IDE. It bridges the gap between the Selenium IDE’s UI-based test creation and full-scale automated test execution in different environments.
Here’s a quick overview of how it works:
- Processes .side Files: It runs tests saved in the .side format, a JSON-based representation of test cases created in Selenium IDE.
- Node.js Integration: SIDE Runner operates through Node.js, allowing test execution through terminal or CI/CD pipelines.
- Uses WebDriver Protocol: It interacts with browser drivers like ChromeDriver or GeckoDriver using the WebDriver protocol to automate browser actions.
- Parallel Execution: Supports parallel test execution across multiple browsers and configurations for faster test runs.
- Cross-Browser Testing: Enables testing across different browsers by simply switching drivers or specifying them via configuration or CLI options.
This setup makes it easier to scale Selenium IDE tests for integration into automated test suites and continuous testing workflows.
Why Should You Use Selenium SIDE Runner?
Selenium SIDE Runner extends the power of Selenium IDE by enabling automated execution of recorded tests from the command line. Here’s why it’s worth using:
- Bridges Manual and Automation: Turns Selenium IDE recordings into runnable test scripts for automation workflows.
- Parallel Test Execution: Run multiple tests simultaneously to save time.
- CI/CD Friendly: Easily integrates with pipelines for automated regression testing.
- Cross-Browser Support: Works with Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and other WebDriver-compatible browsers.
- Customizable Runs: Configure settings like browser options and base URLs via .side.yml or CLI.
- Headless Testing: Supports headless mode for efficient test runs in non-GUI environments.
- Open Source: Actively maintained by the Selenium team with strong community support.
It’s a simple way to scale test automation without writing code.
Prerequisites for running the Selenium SIDE runner
Here are the pre-requises that you will need for Selenium SIDE runner:
- Selenium IDE
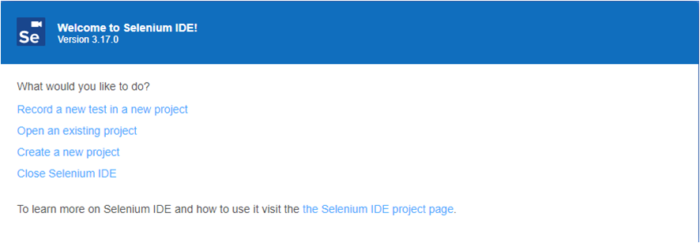
It is easy to install selenium IDE on a web browser. The tool comes as an extension and makes it extremely easy to record test cases. After installation, access the selenium IDE in extensions. Users will see a window like this:
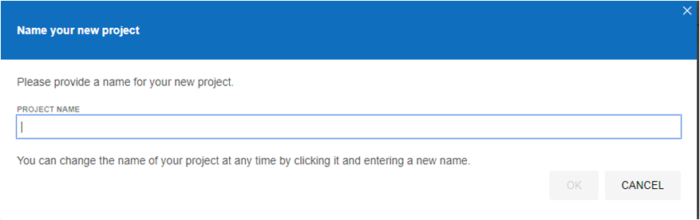
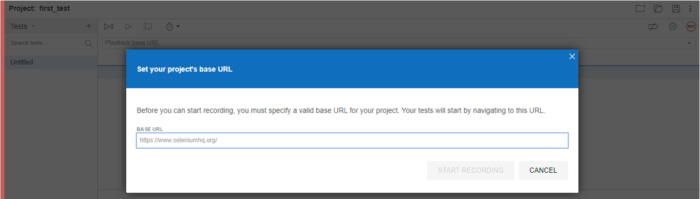
New users should begin with the first option to record a new test in a new project. Here, IDE will ask the user for the project name and the base URL.
After giving the base URL, the IDE will start recording the first test. Interacting in the window with the base URL will create a test case. Save it with a .side extension. The .side extension is what the SIDE runner will be executing on the node.js platform.
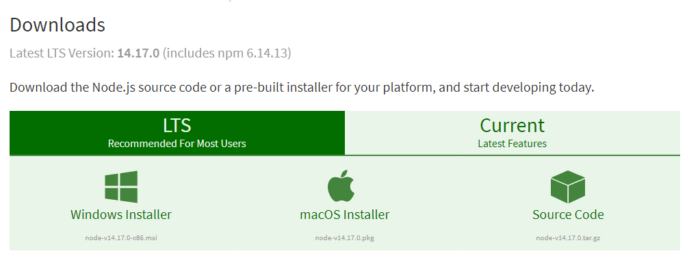
- Node.js
To successfully run Selenium test cases using the SIDE runner, users need the node.js platform. Directly download the node.js version suitable for the OS being used from the official website.
- Node.js package manager
The node.js package manager or npm is a command-line tool that is used to update, install, and delete the node.js packages in an application. To install any necessary packages like web driver, use the npm or node.js package manager. The npm will be automatically installed with the node.js installer.
The other dependencies are the selenium-side-runner npm package and the web driver dependency that it comes with.
Understanding Browser Drivers
Browser drivers like ChromeDriver, GeckoDriver, and EdgeDriver are essential for running Selenium tests. They act as a bridge between the test commands and the browser.
- Enable Browser Control: Drivers translate Selenium commands into browser actions.
- Mandatory for Execution: Each browser requires its corresponding driver.
- Version Match is Crucial: Driver and browser versions must align for compatibility.
- Easy Setup: Install and add to system PATH or configure via command-line.
How to Install Selenium SIDE Runner
Installing the selenium SIDE runner is an easy and systematic task. Follow the steps below to successfully do so:
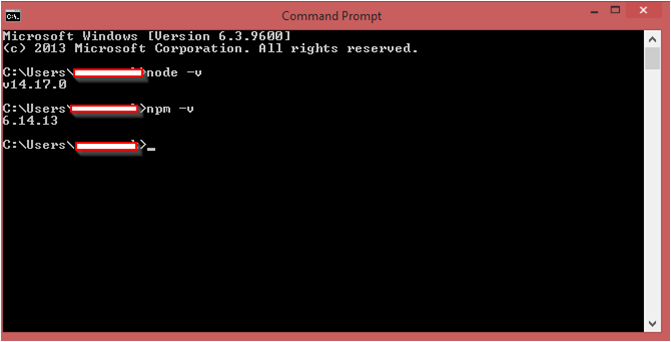
1. Open the Command prompt and check whether node.js and npm have been installed.
2. Install selenium-side-runner using the following command:
>npm install -g selenium-side-runner
3. Installing and Configuring Browser Drivers
To run Selenium tests with the SIDE Runner, appropriate browser drivers must be installed and properly configured. These drivers allow the SIDE Runner to communicate with browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and Edge.
Key steps:
- Install ChromeDriver: Use npm to install globally:
npm install -g chromedriver
- Install GeckoDriver (for Firefox): Download from Mozilla’s GitHub releases or use a package manager like brew (macOS):
brew install geckodriver
- Install EdgeDriver: Download from Microsoft’s Edge Developer site. Choose the driver version that matches your Edge browser.
- Ensure driver executables are accessible by placing them in a system PATH directory or specifying their locations using environment variables or SIDE Runner flags.
- Verify Driver Installation: Run the driver name (e.g., chromedriver, geckodriver) in your terminal to confirm it responds correctly.
How to Run Selenium from the Command Line
Selenium tests created with the IDE can be executed directly from the terminal using the Selenium SIDE Runner.
This is ideal for integrating test execution into CI/CD pipelines or local automation.
Basic Test Execution
Run the following command to execute a .side project file:
selenium-side-runner /path/to/your-test.side
Note: Ensure the appropriate browser driver (e.g., chromedriver) is available in your system’s PATH or explicitly configured.
Specifying Target Browsers for Execution
Use the -c flag to define the target browser:
Run tests in Firefox:
selenium-side-runner -c "browserName=firefox" /path/to/your-test.side
Run tests in Microsoft Edge:
selenium-side-runner -c "browserName=edge" /path/to/your-test.side
This allows cross-browser testing with a single command-line interface.
Understanding Command-Line Output and Status Codes
The terminal displays real-time logs, including test steps, assertions, and errors.
Exit codes:
- 0: All tests passed successfully.
- 1: One or more tests failed.
- Other codes may indicate environment or configuration errors.
These outputs help quickly determine the success of a test run and enable automated error handling in pipelines.
Advanced Configuration with Command-Line Options
Selenium SIDE Runner supports powerful CLI options to customize and scale test execution. Below are key flags and use cases for advanced workflows:
- Run Tests in Parallel: Use -w <N> or –workers <N> to control the number of parallel test threads.
- Set Base URL and Filter Tests: Use –base-url <URL> to override the target site, and –filter <regex> to run specific tests by name.
- Use a Configuration File: Pass .side.yml or any config file via –config-file <file_path> to centralize test settings.
- Manage Output Directories and Artifacts: Use –output-directory <path> to save logs, screenshots, or generated reports.
- Execute in Headless Mode: Add capabilities like -c “goog:chromeOptions.args=[headless]” to run without a visible browser window.
- Pass Runtime Parameters and Capabilities: Use –-params key=value to inject dynamic data, or -c for setting advanced browser capabilities.
When to Choose Selenium SIDE Runner
Selenium SIDE Runner is ideal for running recorded tests at scale. Choose it when:
- Need to automate .side files without coding
- Want easy CI/CD integration with parallel test runs
- Prefer fast setup and execution over complex scripting
Use Selenium WebDriver scripts for advanced, customizable tests. Selenium IDE standalone is mainly for recording tests.
Integrating Selenium SIDE Runner with CI/CD Pipelines
Integrating Selenium SIDE Runner with CI/CD ensures automated test execution on every code change, enabling faster feedback, improved quality, and early defect detection.
Example CI Configuration Snippets
GitHub Actions
jobs: test: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - uses: actions/checkout@v3 - name: Install Node.js uses: actions/setup-node@v3 with: node-version: 18 - run: npm install -g selenium-side-runner chromedriver - run: selenium-side-runner tests/sample.side
Jenkins (Shell Step)
npm install -g selenium-side-runner chromedriver selenium-side-runner tests/sample.side
Use –output-directory and –params as needed to customize outputs or support dynamic test data.
Leveraging Selenium SIDE Runner with BrowserStack
Running Selenium IDE tests on BrowserStack’s Real Device Cloud enables scalable, reliable cross-browser testing with real devices and browsers in real user conditions.
Configuring SIDE Runner with BrowserStack involves setting the –server URL and specifying capabilities like project, build, OS, and browser versions using -c.
Benefits of running Selenium SIDE Runner tests on BrowserStack Automate:
- Access to a wide range of real browsers and mobile devices for accurate testing
- Parallel test execution to speed up testing cycles
- Detailed debugging tools including logs, screenshots, and video recordings
- Seamless integration with CI/CD pipelines for automated testing
Troubleshooting Common Selenium SIDE Runner Issues
Troubleshooting Common Selenium SIDE Runner Issues
Common challenges when using SIDE Runner and how to quickly identify them.
- Driver Errors: Issues like Driver executable not found or version mismatches (ChromeDriver, GeckoDriver, EdgeDriver).
- Test Failures and Debugging Tips: Causes of test failures when running .side files and how to read runner logs to diagnose problems.
- Installation and Version Compatibility Problems: Conflicts related to Node.js or SIDE Runner versions that may disrupt execution.
Best Practices for Using Selenium SIDE Runner
Here are some best practcies to maximize reliability and efficiency when working with SIDE Runner.
- Organizing .side Projects and Test Suites: Structure tests logically for smooth command-line runs and easy maintenance.
- Writing Maintainable and Reliable Tests: Create robust Selenium IDE tests that work consistently with the runner.
- Managing Test Configurations: Use .side.yml files to handle multiple environments and streamline test setups.
Conclusion
Selenium SIDE Runner is a powerful tool for executing .side tests across multiple browsers with parallel support and flexible configurations.
For more accurate and scalable testing, running tests on real devices through BrowserStack’s cloud ensures faster feedback and real-world reliability, helping teams catch issues before users do.
Useful Resources for Selenium
Methods, Classes, and Commands
- Selenium Commands every Developer or Tester must know
- Selenium WebElement Commands
- Desired Capabilities in Selenium Webdriver
- Assert and Verify Methods in Selenium
- Understanding System setProperty in Selenium
- Select Class in Selenium : How to select a value in dropdown list?
- SendKeys in Selenium WebDriver
- getAttribute() method in Selenium: What, Why, and How to use
- How does Selenium isDisplayed() method work?
- findElement vs findElements in Selenium
- Types of Listeners in Selenium (with Code Examples)
- How to set Proxy in Firefox using Selenium WebDriver?
Configuration
- How to set up Selenium on Visual Studio
- How to configure Selenium in Eclipse
- Maven Dependency Management with Selenium
- How to Build and Execute Selenium Projects
XPath
- How to use XPath in Selenium?
- How to find element by XPath in Selenium with Example
- Top Chrome Extensions to find Xpath in Selenium
Locators and Selectors
- Locators in Selenium: A Detailed Guide
- CSS Selector in Selenium: Locate Elements with Examples
- How to Create Object Repository in Selenium
Waits in Selenium
- Wait Commands in Selenium C and C#
- Selenium Wait Commands: Implicit, Explicit, and Fluent Wait
- Understanding Selenium Timeouts
- Understanding ExpectedConditions in Selenium
- Understanding Role of Thread.sleep() in Selenium
Frameworks in Selenium
- Data Driven Framework in Selenium
- Implementing a Keyword Driven Framework for Selenium: A Practical Guide
- Hybrid Framework in Selenium
Miscellaneous
- How to create Selenium test cases
- How to set Proxy in Selenium?
- Difference between Selenium Standalone server and Selenium server
- Exception Handling in Selenium WebDriver
- How to use JavascriptExecutor in Selenium
- How to run your first Selenium test script
- Parallel Testing with Selenium
Best Practices, Tips and Tricks
- Top 5 Challenges Faced During Automation Selenium Testing
- 5 Selenium tricks to make your life easier
- 6 Things to avoid when writing Selenium Test Scripts
- Best Practices for Selenium Test Automation
- Why you should pay attention to flaky Selenium tests
- How to start with Selenium Debugging
- How to make your Selenium test cases run faster
- How to upgrade from Selenium 3 to Selenium 4
- Why you should move your testing to a Selenium Cloud?
Design Patterns in Selenium: Page Object Model and Page Factory
- Design Patterns in Selenium
- Page Object Model and Page Factory in Selenium
- Page Object Model and Page Factory in Selenium C#
- Page Object Model in Selenium and JavaScript
- Page Object Model and Page Factory in Selenium Python
Action Class
- How to handle Action class in Selenium
- How to perform Mouse Hover Action in Selenium
- Understanding Click Command in Selenium
- How to perform Double Click in Selenium?
- How to Drag and Drop in Selenium?
- How to Scroll Down or Up using Selenium Webdriver
- How To verify Tooltip Using Selenium
TestNG and Selenium
- Database Testing using Selenium and TestNG
- How to use DataProvider in Selenium and TestNG?
- All about TestNG Listeners in Selenium
- How to run parallel test cases in TestNG
- How to use TestNG Reporter Log in Selenium: Tutorial
- Prioritizing tests in TestNG with Selenium
JUnit and Selenium
- Understanding JUnit assertions for Selenium Testing with Examples
- How to run JUnit Parameterized Test in Selenium
- How to write JUnit test cases
- JUnit Testing Tutorial: JUnit in Java
- How to create JUnit Test Suite? (with Examples)
Use Cases
- Handling Login Popups in Selenium WebDriver and Java
- How to Launch Browser in Selenium
- How to handle Alerts and Popups in Selenium?
- How to get Selenium to wait for a page to load
- How to Find Element by Text in Selenium: Tutorial
- How to Read/Write Excel Data using Apache POI Selenium
- How to handle Captcha in Selenium
- How to handle multiple windows in Selenium?
- How to handle Multiple Tabs in Selenium
- How to find broken links in Selenium
- How to handle Cookies in Selenium WebDriver
- How to handle iFrame in Selenium
- How to handle Web Tables in Selenium
- How To Validate Text in PDF Files Using Selenium Automation
- Get Current URL in Selenium using Python: Tutorial
Types of Testing with Selenium
- Different Testing Levels supported by Selenium
- How to perform UI Testing with Selenium
- Regression Testing with Selenium: Tutorial
- UI Automation using Python and Selenium: Tutorial
- How to Run Visual Tests with Selenium: Tutorial
- How to perform ETL Automation using Selenium
- Cross Browser Testing in Selenium : Tutorial
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I update Selenium SIDE Runner and its browser drivers?
To update Selenium SIDE Runner, run:
npm install -g selenium-side-runner@latest
For browser drivers, download the latest compatible versions (ChromeDriver, GeckoDriver, EdgeDriver) and ensure they’re in your system PATH. Match driver versions with your browser for best results.