Timeouts in Selenium help manage wait times for elements or page loads, ensuring tests don’t fail abruptly. Optimizing timeouts improves user experience by handling delays gracefully and avoiding premature test failures.
Overview
Types of Selenium Timeout
Timeout with Wait:
- implicitlyWait()
- Explicit Wait (via WebDriverWait)
- Fluent Wait
Timeout without Wait:
- setScriptTimeout()
- pageLoadTimeout in Selenium
Common Causes of TimeoutException
- Slow Loading Elements
- Dynamic Content Issues
- Network Latency
- Incorrect Locators
- Application Errors
- Overly Aggressive Timeouts
- Conflicting Waits
This article explains how testers can configure different types of timeouts in Selenium to handle delays effectively before triggering exceptions.
What are Selenium Timeouts?
Selenium Timeouts are the longest periods of time for which a WebDriver should wait for specific actions or events to occur during a webpage interaction before it throws any error.
Consider a situation in which WebDriver fails to execute the test case as the webpage takes too long to load. In such cases, it is essential to mention the wait time for the page load to avoid test case failure. This is where Timeouts play an essential role. They are used to set an interval between actions performed on the test.
Timeouts are usually performed using Selenium wait commands.
The various Selenium Webdriver timeouts used while testing an application are as follows:
- implicitlyWait()
- setScriptTimeout()
- pageLoadTimeout()
This article will explain how testers can set these timeouts with examples in Java and Python.
Difference between Wait and Timeout in Selenium
While often used interchangeably in casual conversation, “wait” and “timeout” have distinct meanings in the context of Selenium:
Wait
A wait mechanism is a conditional pause in the script execution. It is designed to wait for a specific condition to be met (for example, an element to be visible, clickable, or a certain text to appear) before proceeding with the next step. Selenium offers both implicit and explicit waits to handle the dynamic loading of web elements.
Timeout
A timeout is the maximum duration for which a wait mechanism (either implicit or explicit) will attempt to satisfy the specified condition. If the condition is not met within this defined timeframe, a TimeoutException is raised, halting the script execution. Timeouts act as a safeguard to prevent the script from waiting indefinitely.
In essence, a wait is the action of pausing and checking for a condition, while a timeout limits how long that action will be performed.
Types of Selenium Timeout
Here are the types of Selenium Timeouts:
Timeout with Wait
These timeouts are associated with the wait mechanisms in Selenium, defining the maximum duration to wait for a specific condition.
1. implicitlyWait()
Implicit Wait directs the Selenium WebDriver to wait for a certain measure of time before throwing an exception. Once this time is set, WebDriver will wait for the element before the exception occurs.
Once the command is run, Implicit Wait remains for the entire duration for which the browser is open. It’s default setting is 0, and the specific wait time needs to be set by the following protocol.
implicitlyWait() timeout is used to specify the time the driver should wait while searching for an element if it is not immediately present.
The syntax is as follows:
implicitlyWait(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit);
- time – The amount of time to wait for
- unit – The unit of measure for time
When searching for a particular single element, the driver should pause page loading until the element has been found. If it doesn’t wait, the timeout expires before throwing a NoSuchElementException.
When searching for multiple elements, the driver should pause the page until at least one element has been found or the timeout has expired.
Example:
implicitlyWait(20, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
In this statement, the WebDriver will wait for 20 seconds before proceeding to the next action.
Code Snippet:
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
public class TimeoutExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "Path of Chrome Driver");
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.get("https://www.ebay.com/");
// Implicit wait timeout for 20seconds
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(20, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='gh-ac']")).sendKeys("Mobile");
//xpath for search button
WebElement search = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='gh-btn']"));
search.click();
}
}
On executing the code above, the driver will wait for 20 seconds on the particular website even if the web element is not found.
Note: If a user wants to increase the implicit wait timeout, it should be done carefully, as this will affect the test run time.
2. Explicit Wait (via WebDriverWait)
Explicit wait allows the configuration of a timeout for a specific condition to be met before proceeding with the next step in the script. It uses the WebDriverWait class in conjunction with ExpectedCondition to define the condition to wait for. This provides more granular control over the waiting process compared to implicit wait.
Code:
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait;
import java.time.Duration;
public class ExplicitWaitExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Set the path of the ChromeDriver
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "C:\\Path\\To\\chromedriver.exe");
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(); // Initialize WebDriver
driver.get("https://www.ebay.com/"); // Navigate to eBay
// Create an explicit wait instance with 20 seconds timeout
WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver, Duration.ofSeconds(20));
// Wait until the search input field is visible and enter the search term
WebElement searchInput = wait.until(ExpectedConditions.visibilityOfElementLocated(By.id ("gh-ac")));
searchInput.sendKeys("Mobile");
// Wait until the search button is clickable and click it
WebElement searchButton = wait.until(ExpectedConditions.elementToBeClickable(By.id("gh-btn")));
searchButton.click();
driver.quit(); // Close the browser
}
}Note:
On Windows: “C:\\Path\\to\\ chromedriver.exe”
On macOS/Linux: “/path/to/ chromedriver”
Explanation:
When the code is executed,
- Necessary Selenium classes for web automation are imported, including By, WebDriver, and WebDriverWait.
- The ExplicitWaitExample class is defined as the main method by which the program’s execution begins.
- In the main method, the path to the ChromeDriver is set using System.setProperty(), and a new instance of ChromeDriver is created to control the Chrome browser.
- The browser navigates to https://www.ebay.com/ using the get() method of the driver object.
- An instance of WebDriverWait with a 20-second timeout is created, allowing the program to wait for specific conditions to be met before proceeding.
- The program waits for the search input field to be visible on the page using ExpectedConditions.visibilityOfElementLocated(), and then enters the search term “Mobile” into the input field.
- Now, the program waits for the search button to be clickable using ExpectedConditions.elementToBeClickable(), and then clicks the button to initiate the search.
Finally, the browser is closed automatically using driver.quit().
3. Fluent Wait
Fluent Wait is an extension of explicit wait that allows the configuration of the polling frequency (how often to check for the condition) and ignoring specific types of exceptions while waiting for a condition. This offers maximum flexibility in defining the waiting strategy.
Code:
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.FluentWait;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.Wait;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.function.Function;
public class FluentWaitExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Set the path of the ChromeDriver
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "C:\\path\\to\\chromedriver.exe");
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(); // Initialize WebDriver
driver.get("https://www.ebay.com/"); // Navigate to eBay
// Create a FluentWait with a maximum wait time of 20 seconds and a polling interval of 2 seconds
FluentWait<WebDriver> wait = new FluentWait<>(driver)
.withTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(20))
.pollingEvery(Duration.ofSeconds(2))
.ignoring(Exception.class);
// Wait for the search input field to be visible and then enter the search term
WebElement searchInput = wait.until(new Function<WebDriver, WebElement>() {
public WebElement apply(WebDriver driver) {
return driver.findElement(By.id("gh-ac"));
}
});
searchInput.sendKeys("Mobile");
// Wait for the search button to be clickable and then click it
WebElement searchButton = wait.until(new Function<WebDriver, WebElement>() {
public WebElement apply(WebDriver driver) {
return driver.findElement(By.id("gh-btn"));
}
});
searchButton.click();
driver.quit(); // close the browser
}
}Highlights:
Timeout: 20 seconds max
Polling frequency: every 2 seconds
Exception ignored: NoSuchElementException
Explanation
When the code is executed,
- Necessary Selenium classes for web automation are imported, including By, WebDriver, and FluentWait.
- The FluentWaitExample class is defined as the main method where execution begins.
- The path to the ChromeDriver is set, and a new instance of ChromeDriver is created to control the browser.
- The browser navigates to https://www.ebay.com/ using the get() method.
- A FluentWait instance is created with a maximum wait time of 20 seconds and a polling interval of 2 seconds. This allows the program to check for specific conditions while ignoring Exception errors repeatedly.
- The program waits for the search input field to be visible by using a custom function that attempts to find the element by its ID (“gh-ac”). Once the element is found, the search term “Mobile” is entered into the input field.
- Next, the program waits for the search button to be clickable by using another custom function that locates the button by its ID (“gh-btn”). Once the button is found, it is clicked to initiate the search.
- Finally, the browser is closed automatically using driver.quit().
Timeout without Wait
These timeouts are not directly associated with waiting for specific conditions related to element presence or interactability.
1. setScriptTimeout()
setScriptTimeout is a Selenium Timeout that specifies the time to wait for an asynchronous script to finish execution before throwing an error.
If the timeout is negative, not null, or greater than 2e16 – 1, an error code with invalid argument will be returned.
Syntax:
setScriptTimeout(long time,java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit);
- time – The timeout value.
- unit – The unit of time
The default timeout for setScriptTimeout method is zero. If you do not set time, then there are chances that executeAsyncScript method may fail because the JavaScript code may take more than the time allotted. To avoid such failures, set the setScriptTimeout. This is mainly used for Javascript objects and executors.
Example:
// setScriptTimeout for 10 seconds
driver.manage().timeouts().setScriptTimeout(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
((JavascriptExecutor) driver).executeScript("alert('hello world');");
((JavascriptExecutor) driver).executeAsyncScript("window.setTimeout(arguments[arguments.length - 1], 500);");In the example above, if the time is not used, then there will be an error stating: “Timed out waiting for async script result”. To avoid this error, one should use setScriptTimeout.
2. pageLoadTimeout in Selenium
PageLoadTimeout is a Selenium feature that specifies the maximum time that the WebDriver should wait for the page to render completely before throwing an exception.
When the user navigates to a new page or reloads the current page, WebDriver waits for the web page to load completely. If it fails to load within the specified timeout duration, it throws a Timeout exception.
This sets the time to wait for a page to load completely before throwing an error. If the timeout is negative, page loads can be indefinite.
Syntax:
pageLoadTimeout(long time,java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit);
This timeout is applicable only to driver.manage() and driver.navigate.to() methods.
Example:
public class PageLoadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "Path of driver");
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
// set the time of 30 seconds for page to complete the loading
driver.manage().timeouts().pageLoadTimeout(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
driver.get("https://www.google.com/");
}
}In the code above, if your page does not load within 30 seconds, WebDriverException will be thrown.
Selenium Timeouts must be included to create effective, comprehensive and seamlessly running test cases. This article intends to help in this regard by briefly explaining how Timeouts work, and how they can be incorporated into Selenium test scripts.
To know more about Automation, refer to this piece on Selenium Automation.
Read More: Selenium Wait Commands using Python
Default Timeout in Selenium WebDriver
The default timeout depends on the type of wait command used.
- Default Timeout for Implicit Wait is 0 seconds. Here the Selenium Command reports immediately if it cannot find an element.
- Default Timeout for Page Load is 300 seconds.
- Default Timeout for Script Timeout is 30 seconds.
How to handle a Timeout Exception in Selenium?
TimeOut Exception in Selenium mainly occurs when a given condition is not met in the specified time.
- So one way to handle timeout exceptions is to adjust the wait time according to the application behavior so that the webpage is loaded completely and all web elements are visible.
- You can also use polling, also called a fluent wait in selenium, which polls after a specified amount of time.
- For example, an element is dynamic and might be loaded after 10 seconds,20 seconds or 30 seconds, or even more.
- If You declare an explicit wait of 20 seconds, in this case, it will wait for that time before throwing an exception.
- In this case, the fluent wait is most suitable as it will try to find the element at different frequencies until the final timer runs out.
Wait wait = new FluentWait(driver) .withTimeout(timeout, SECONDS) .pollingEvery(timeout, SECONDS) .ignoring(Exception.class);
Timeout Exception in Selenium Java
Timeout exception generally occurs when a Webdriver wait has finished waiting for a particular element to be present or any condition to be satisfied.
To understand this, see an example where You will try to search for an element for a few seconds using webdriver wait.
package com.qa.bs;
import java.time.Duration;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeOptions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class timeOutExample {
@Test
public void timeOutTest()
{
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver","c:\\chromedriver.exe");
ChromeOptions options = new ChromeOptions();
options.addArguments("--remote-allow-origins=*");
ChromeDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(options);
driver.get("https://app.hubspot.com/login");
//This waits up to 10 seconds before throwing a TimeoutException or if it finds the element will return it in 0 - 10 seconds
WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver,Duration.ofSeconds(10));
wait.until(ExpectedConditions.visibilityOfElementLocated(By.id("username1")));
}
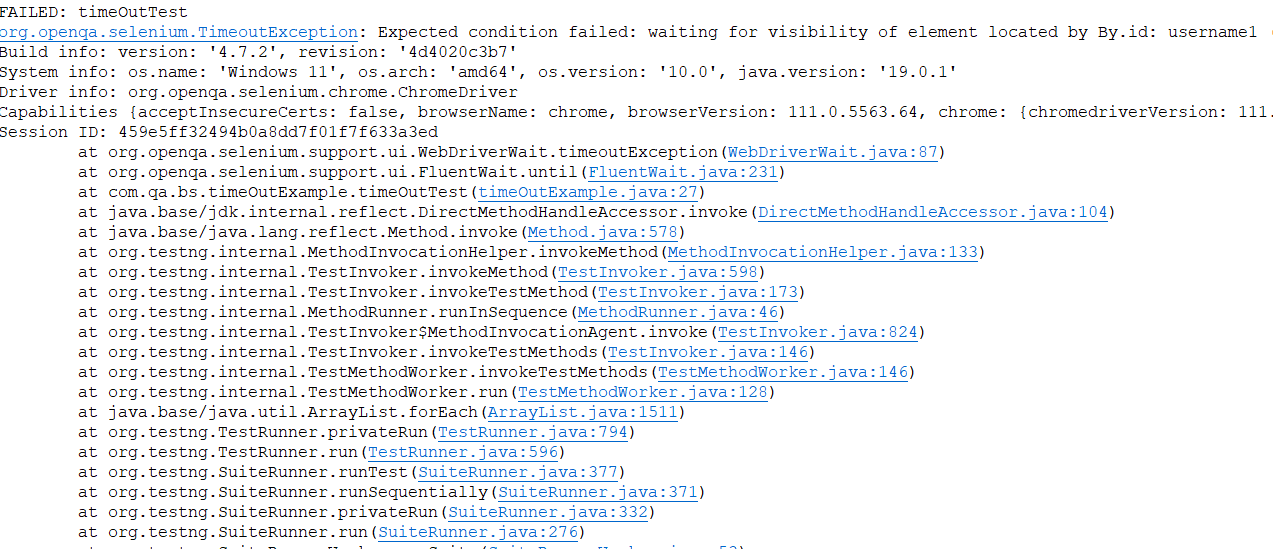
}For the sake of understanding, the ID for the username given in the above example is incorrect. The driver cannot find the element between 10 seconds, and it throws a timeout exception as demonstrated below.
This clearly shows that the driver tried to find the element’s visibility for 10 seconds, and as it could not find the element it threw a timeout exception.
Now try to see the same example with the correct id for the username field, and you shall know the test has passed without throwing a timeout exception.
package com.qa.bs;
import java.time.Duration;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeOptions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class timeOutExample {
@Test
public void timeOutTest()
{
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver","c:\\chromedriver.exe");
ChromeOptions options = new ChromeOptions();
options.addArguments("--remote-allow-origins=*");
ChromeDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(options);
driver.get("https://app.hubspot.com/login");
//This waits up to 10 seconds before throwing a TimeoutException or if it finds the element will return it in 0 - 10 seconds
WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver,Duration.ofSeconds(10));
wait.until(ExpectedConditions.visibilityOfElementLocated(By.id("username")));
}
}Now you can see the same test has passed as the driver was able to find the element within the given time.
Timeout Exception in Selenium Python
Now see the same timeout example in Python. In this example, you have used the presence_of_element_located() function to find the element within the given time.
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
from selenium.webdriver.support.wait import WebDriverWait
driver = webdriver.Chrome('C:/chromedriver.exe')
driver.get("https://app.hubspot.com/login")
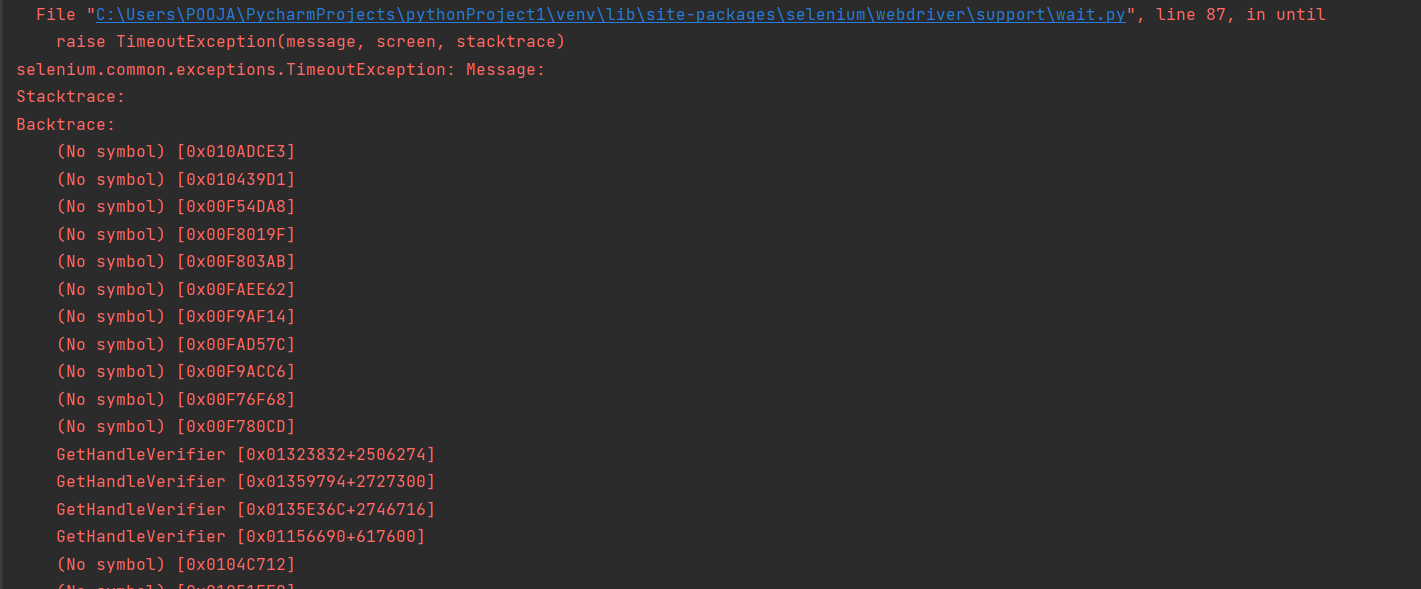
WebDriverWait(driver, 10).until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, 'username1')))Here too, you have deliberately given an invalid ID for the username field so that the driver is unable to find the element and throws a timeout exception as below.
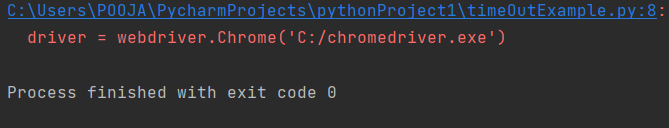
If you give the correct ID for the username element, the driver can find the element of the specified time, and the test passes as below.
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
from selenium.webdriver.support.wait import WebDriverWait
driver = webdriver.Chrome('C:/chromedriver.exe')
driver.get("https://app.hubspot.com/login")
WebDriverWait(driver, 10).until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, 'username')))Common Causes of TimeoutException
Several factors can lead to TimeoutException in Selenium:
- Slow Loading Elements: The web element being waited for takes longer to load than the specified timeout.
- Dynamic Content Issues: The logic for dynamically loading elements on the page might have errors, preventing the element from appearing.
- Network Latency: Slow or unstable network connections can delay the loading of resources and elements.
- Incorrect Locators: If the locator used to find the element is incorrect, Selenium will keep searching until the timeout is reached.
- Application Errors: Underlying issues in the web application can prevent elements from loading or behaving as expected.
- Overly Aggressive Timeouts: Setting timeouts too low might cause false failures even when the application is functioning correctly under normal conditions.
- Conflicting Waits: Mixing implicit and explicit waits can lead to unexpected timeout behaviour.
Best Practices when using Selenium Timeout
To effectively manage timeouts in Selenium and create robust test scripts, consider the following best practices:
- Prefer Explicit Waits: Explicit waits provide more precise control over the waiting conditions and are generally preferred over implicit waits for handling dynamic elements.
- Use Implicit Wait Judiciously: If used, set the implicit wait to a reasonable maximum that accommodates the slowest loading elements across the application. Avoid setting it too low, which can lead to unnecessary timeouts.
- Avoid Mixing Implicit and Explicit Waits: Combining implicit and explicit waits can lead to unpredictable behaviour and longer overall wait times. Choose one strategy and stick to it.
- Set Appropriate Timeout Values: Analyse the application’s performance and set timeout values that are sufficient to handle normal loading times but are not excessively long.
- Implement Proper Exception Handling: Use try…except blocks to catch TimeoutException and implement logging or other error reporting mechanisms to aid in debugging.
- Consider Fluent Wait for Complex Scenarios: For situations where the polling frequency or specific exceptions need to be ignored during the wait, leverage the flexibility of Fluent Wait.
- Monitor Application Performance: Regularly monitor the performance of the application under test to identify and address slow-loading elements that may require longer timeouts.
- Use Specific Expected Conditions: When using explicit waits, choose the most specific ExpectedCondition that accurately reflects the state being waited for (for example, element_to_be_clickable, visibility_of_element_located).
Why use BrowserStack Automate for Selenium Tests?
Here’s why you should use BrowserStack Automate for running Selenium tests:
- Diverse environment testing: With BrowserStack one can automate Selenium tests across different devices, operating systems and browsers.
- Real Devices and Browsers: It is always wiser to test the application on real devices and browsers to simulate a real user experience. Testing on real devices gives the actual confidence about the application performance.
- Concurrent test execution: Simultaneous test execution of multiple Selenium tests can be achieved which reduces the total execution time, gives quicker feedback and accelerates deployment cycles.
- Custom Reports with Artifacts: In Automate, custom reports can be generated to provide detailed and customized reports for the automated test execution.
- Easy Integration with CI/CD Pipeline: BrowserStack’s Automate product can be seamlessly integrated with popular CI/CD tools such as Jenkins, TeamCity, TravisCI
Conclusion
Handling timeouts effectively is crucial for building reliable and efficient Selenium tests. By understanding the types of timeouts and addressing common causes, testers can minimize failures, improve test stability, and ensure faster feedback cycles.
You can run your Selenium tests across real browsers and devices with BrowserStack Automate, helping you catch timeout issues early and deliver a smoother user experience.