When managing a website, it is inevitable that some pages will move or need to be permanently replaced. One of the most common and essential tools to handle this situation is the 301 Permanent Redirect.
A 301 redirect informs web browsers and search engines that a page has been permanently moved to a new URL. Properly using 301 redirects can help preserve the user experience and SEO value, ensuring that both users and search engines know where to find content.
Overview
- Website or Page Restructuring: Redirect users to new pages when URLs change during a redesign.
- Domain Name Change: Direct traffic from the old domain to the new one, preserving SEO.
- Consolidating Content: Redirect old pages to a new, consolidated page.
- Removing or Replacing Old Pages: Guide users to relevant content when pages are removed.
- Optimizing URL Structure: Redirect old URLs to new, SEO-friendly ones after restructuring.
This article explores the workings of 301 redirects, their SEO implications, best practices for implementing them, and the tools available to manage them effectively.
What is 301 Permanent Redirect?
A 301 Permanent Redirect is an HTTP status code that tells the browser or search engine that the page has been permanently moved to a new location. It is the most commonly used type of redirect for URL changes, as it indicates that the original URL is no longer valid and the content is now available at a new address.
This type of redirect transfers the full SEO value (such as link equity and ranking signals) from the old URL to the new one, making it essential for preserving the website’s search engine rankings. Unlike temporary redirects (like 302), a 301 redirect tells search engines and browsers that the change is permanent, so the original URL should be removed from the index.
How 301 Redirects Work?
When a user or search engine visits a URL that has been permanently redirected with a 301 status code, the web server sends the new URL’s location in the response header. The browser or search engine will then automatically navigate to the new location. Here’s a simplified flow of how a 301 redirect works:
- User or Search Engine Requests the Original URL: The user clicks a link or searches for the original URL.
- Server Responds with 301 Status Code: The server sends the 301 status code along with the new URL location.
- User is Redirected to the New URL: The browser automatically redirects to the new URL.
- Search Engines Update Their Index: The search engine updates its index and transfers the SEO value to the new URL, replacing the old URL. By doing this, a 301 redirect ensures that the user’s browsing experience remains seamless, and the SEO benefits of the original URL are preserved.
SEO Implications of 301 Redirects
One of the main reasons for using 301 redirects is to preserve SEO rankings. Here’s how they affect SEO:
- Link Equity Transfer: A key benefit of 301 redirects is the transfer of link equity (also known as “link juice”) from the old URL to the new one. This helps the new page retain much of the SEO value, including backlinks and social signals that the original page had accumulated.
- Prevents Loss of Traffic: Without a 301 redirect, a page that has been moved would lead to a “404 Not Found” error, causing users and search engines to lose access to the content. A 301 redirect ensures that users are automatically taken to the new page, maintaining the user experience and preventing traffic loss.
- Search Engine Ranking Preservation: Google and other search engines understand that the 301 redirect is a permanent move, and as such, they will update their indexing to reflect the new page’s location. The SEO rankings of the old page are transferred to the new one, which prevents the new page from losing its search engine visibility.
- Indexing of New URL: Once a 301 redirect is implemented, search engines will gradually replace the old URL with the new URL in their index. This helps ensure that the new page gets indexed correctly and that its SEO value is preserved.
Read More:How to test redirect with Cypress
Common Use Cases for 301 Redirects
301 redirects are versatile and have several use cases. Here are some of the most common scenarios where they are used:
- Website or Page Restructuring: When a website undergoes a redesign or restructuring and URLs are changed, 301 redirects ensure that users and search engines are sent to the correct new pages.
- Domain Name Change: If a website changes its domain name, 301 redirects are used to direct all traffic from the old domain to the new one, preserving SEO value and avoiding broken links.
- Consolidating Content: If two or more pages with similar content are combined into one, a 301 redirect can be used to send traffic from the old pages to the new consolidated page.
- Removing or Replacing Old Pages: When an outdated or irrelevant page is removed or replaced, a 301 redirect ensures that users and search engines are directed to a new, relevant page without encountering a “404 Not Found” error.
- Optimizing URL Structure: If a website undergoes a URL structure optimization, 301 redirects ensure that the old URLs seamlessly lead users to the new, more SEO-friendly ones.
Best Practices for Implementing 301 Redirects
To maximize the effectiveness of 301 redirects and ensure a smooth user experience, follow these best practices:
- Implement 301 Redirects on All Moved Pages: Always use a 301 redirect for any page that has been permanently moved. Failing to do so will result in a poor user experience and loss of SEO value.
- Avoid Redirect Chains: A redirect chain occurs when a URL redirects to another URL, which then redirects to yet another URL. This can slow down page load times and negatively impact SEO. Keep redirects as simple and direct as possible.
- Use a Single 301 Redirect for Each URL: Redirecting a URL to multiple destinations can confuse search engines and degrade SEO performance. Each URL should only have one clear 301 redirect.
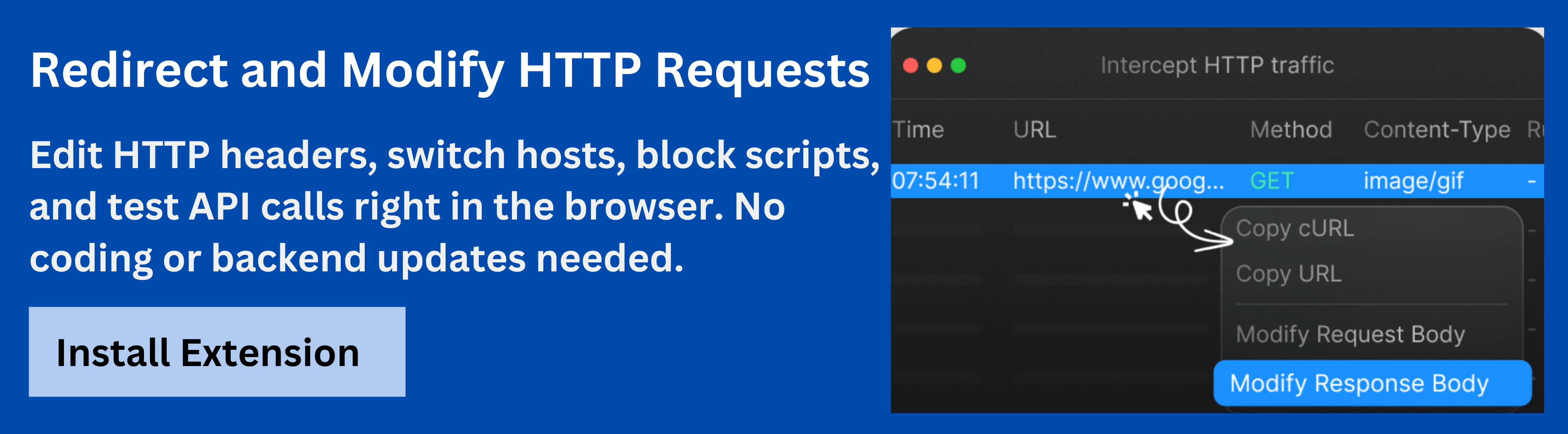
- Test Redirects After Implementation: After setting up a 301 redirect, it’s crucial to test it to ensure that it works correctly. Use tools like Requestly’s HTTP Interceptor (discussed below) to validate your redirects in real-time.
- Update Internal Links: If possible, update internal links to point directly to the new URL instead of relying solely on redirects. This helps reduce the number of redirects and improves site performance.
Tools for Managing 301 Redirects
There are several tools available to help manage and implement 301 redirects effectively. Here’s a look at some of the best options:
Requestly: HTTP Interceptor for Testing 301 Redirects
Requestly’sHTTP Interceptor is an essential tool for developers, particularly because of its feature. This tool allows you to intercept, modify, and simulate HTTP requests and responses, including 301 redirects, in real-time. With Requestly, you can:
- Test Redirects: Before deploying changes, you can use Requestly’s HTTP Interceptor to simulate 301 redirects and see how they affect your site in a staging environment.
- Create Custom Redirect Rules: You can create custom rules to intercept and modify URLs, which is particularly useful for testing various redirection scenarios.
- Monitor in Real-Time: Monitor how your site responds to 301 redirects without affecting the live version of your website, helping to identify issues before they go live.
Requestly’s HTTP Interceptor is an invaluable tool for managing redirects during the development and testing phases of website changes.
Testing and Monitoring 301 Redirects
Once 301 redirects are implemented, regular testing and monitoring are crucial to ensure they are working correctly. Here’s how to effectively monitor and test 301 redirects:
- Use Redirect Testing Tools: Tools like Requestly’s HTTP Interceptor can help you test redirects in real-time before they go live. You can simulate user requests and ensure that the redirects behave as expected.
- Monitor Server Logs: Checking your server logs is another way to monitor how 301 redirects are functioning. You can identify any potential errors or issues related to the redirects.
- Track SEO Performance: Monitor your SEO performance using tools like Google Search Console to track the impact of your 301 redirects. Ensure that the old URLs are being replaced in search engine results and that the new pages are indexed correctly.
- Check for Redirect Loops: Redirect loops can harm both user experience and SEO. Use tools like Redirect Path or Screaming Frog SEO Spider to detect any redirect loops or chains on your website.
Read More: What Is API Automation Testing?
Advanced Topics in 301 Redirects
For advanced users and web developers, here are a few additional topics to consider when working with 301 redirects:
- Handling Redirects in Single Page Applications (SPAs): SPAs often use client-side routing, which can make managing 301 redirects more complex. You’ll need to handle redirects properly to ensure that both users and search engines are directed to the right content.
- International SEO and 301 Redirects: For websites targeting multiple countries or languages, you may need to use 301 redirects in combination with hreflang tags to ensure that users are sent to the appropriate localized content.
- Redirects in E-commerce Websites: E-commerce websites often need to manage product URL changes or category reorganizations. Implementing proper 301 redirects ensures that users and search engines are not left with broken links, preserving SEO and sales.
Conclusion
301 Permanent Redirects are an essential tool for maintaining SEO value, user experience, and site performance when moving or restructuring web pages. By properly implementing 301 redirects, you can ensure that your website retains its rankings, backlinks, and user traffic.
Whether you’re moving content, consolidating pages, or making URL structure changes, following best practices and using the right tools like Requestly’s HTTP Interceptor will ensure that your redirects work smoothly and effectively. With proper planning and monitoring, 301 redirects will keep your website running smoothly without compromising its SEO performance.