Redirects are a common and essential feature of web development, used to guide users and search engines from one URL to another. One such redirect is the 302 Temporary Redirect, often used when a webpage is temporarily moved. Unlike a 301 redirect, which signals a permanent move, a 302 redirect informs browsers and search engines that the move is temporary and the original page will return soon.
Understanding how 302 redirects work and how to implement them correctly can significantly impact your website’s user experience and SEO.
Overview
- Temporary Website Maintenance
- A/B Testing or User Experiments
- Regional Content Redirection
- Seasonal or Limited-Time Promotions
This article dives into the details of 302 temporary redirects, their functionality, SEO implications, and best practices for managing them effectively.
What is a 302 Temporary Redirect?
A 302 Temporary Redirect is an HTTP status code that tells the browser or search engine to temporarily redirect the user to a different URL. This redirect suggests that the original URL will eventually be restored, and search engines should continue to index the original URL rather than the redirected page. The main difference between a 302 and a 301 redirect is that a 302 is not considered a permanent change. When a browser encounters a 302 redirect, it temporarily redirects the user to the new location, but keeps the original URL intact in the address bar.
302 Redirect Flow:
- User requests the original URL.
- The server responds with a 302 status code and a new location URL.
- The browser redirects the user to the new location.
- The search engine keeps the original URL indexed.
How 302 Redirects Work?
When a 302 redirect is triggered, the web server sends a response with the 302 status code, along with the new location where the user or search engine should be directed. The browser then automatically navigates to this new location while keeping the original URL intact.
For instance, if you have a webpage at www.example.com/old-page and you temporarily want to redirect visitors to www.example.com/new-page, the server will send the 302 status code with the new URL as the location.
While this redirects the user to new-page, the original URL is still expected to be valid once the temporary move ends.
SEO Implications of 302 Redirects
302 redirects have unique SEO implications due to their temporary nature. Here’s what you need to know:
- Search Engine Indexing: Since 302 redirects are temporary, search engines will continue to index the original URL, assuming it will be restored. Unlike a 301 redirect, which tells search engines that the page has permanently moved and to transfer SEO value, a 302 tells search engines to wait and not transfer the SEO authority to the redirected page.
- Link Equity: A 302 redirect generally does not pass as much link equity as a 301 redirect. Search engines understand the content might return to the original URL soon, so the link equity is preserved for that page rather than being passed to the redirected URL.
- User Experience: For users, 302 redirects help maintain a seamless experience when the original page is temporarily unavailable, without affecting SEO. However, too many temporary redirects can lead to confusion if users find themselves repeatedly redirected.
When Not to Use a 302 Redirect:
- When the move is permanent, use a 301 redirect to ensure SEO benefits are transferred.
- When there’s no need to keep the original URL indexed, such as in the case of a completely removed page, use a 410 (Gone) status code.
Common Use Cases for 302 Redirects
Here are some of the most common scenarios where a 302 redirect is used:
1. Temporary Website Maintenance: When a website or page is under maintenance, a 302 redirect can temporarily redirect users to a maintenance page while keeping the original URL for future use.
2. A/B Testing or User Experiments: For marketing or optimization experiments, 302 redirects allow you to test different versions of a page while keeping the original URL intact for search engine purposes.
3. Regional Content Redirection: Websites that serve content in multiple languages or for different geographical locations might use 302 redirects to temporarily redirect users to the correct version of a page based on location or language preferences.
4. Seasonal or Limited-Time Promotions: When running a seasonal campaign or limited-time offer, a 302 redirect can be used to redirect users to a special landing page without affecting the original page’s SEO value.
Best Practices for Implementing 302 Redirects
To ensure that 302 redirects are implemented correctly and effectively, follow these best practices:
- Use Only for Temporary Changes: A 302 redirect should only be used when the page or content is temporarily unavailable. If the change is permanent, use a 301 redirect.
- Ensure Proper HTTP Headers: The 302 status code should be set correctly in the HTTP header, along with the new location URL.
- Minimize Redirect Chains: Avoid creating redirect chains where a series of redirects lead to the final page, as they can slow down site performance and impact user experience.
- Monitor and Test Redirects: Regularly test your 302 redirects to ensure they are functioning properly and not causing issues like broken links or infinite redirect loops.
Tools and Resources for Managing 302 Redirects
There are several tools available to manage and test 302 redirects, ensuring they function correctly across your site. Here are some of the best tools:
There are several tools available to manage and test 302 redirects, ensuring they function correctly across your site. Here are some of the best tools:
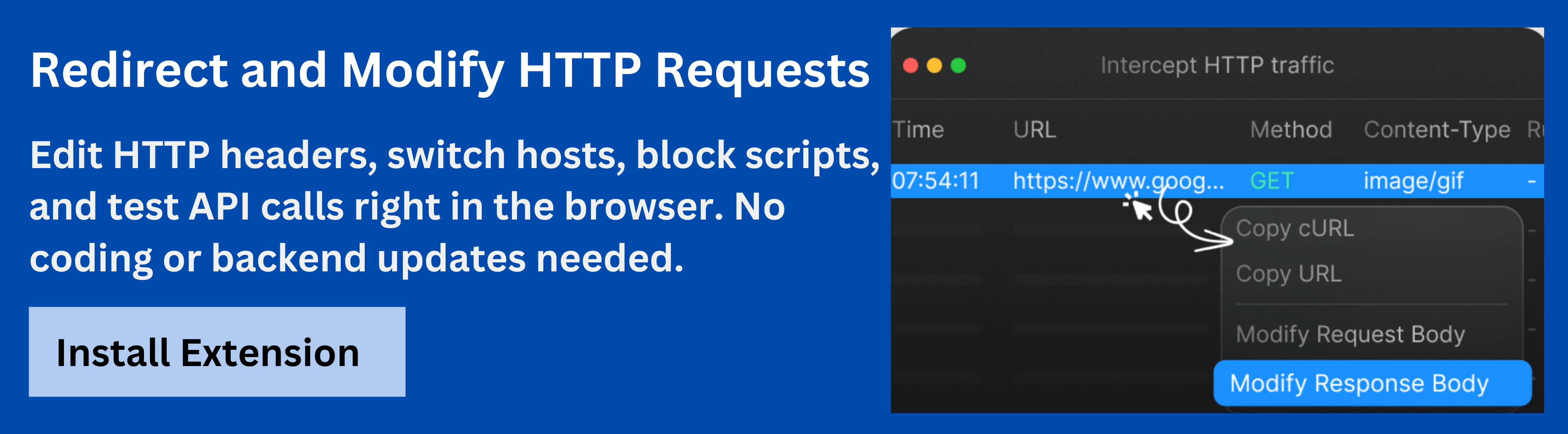
1. Requestly: A Powerful HTTP Interceptor Tool for Managing 302 Redirects
Requestly stands out as an essential tool for developers, especially when it comes to managing and testing redirects like the 302 temporary redirect. At its core, Requestly’s HTTP Interceptorfeature is designed to help developers intercept, modify, and test HTTP requests and responses in real-time, all without affecting the live website.
Key Features of Requestly’s HTTP Interceptor:
- Custom Redirection Rules: Easily set rules to redirect specific requests or simulate different redirection scenarios.
- Modify HTTP Headers: You can change request and response headers to test how they affect the redirect behavior.
- Simulate Redirect Loops or Delays: Helps in testing complex redirect chains or delays, ensuring your site’s behavior aligns with expectations.
- Real-Time Testing: Make changes in real-time to validate redirects without affecting your production environment.
2. Redirect Path Chrome Extension
The Redirect Path Chrome extension provides a quick way to check the HTTP status codes of any URL, including 302 redirects. This tool helps users easily identify if redirects are working as expected and if the status code is properly set.
Key Features of Redirect Path Chrome Extension:
- Instant HTTP Status Codes: View the status code of any URL in real-time while browsing the web.
- Detailed Redirect Chain Information: See the entire redirect chain from the original URL to the final destination.
- Quick Identification of Redirect Issues: Easily identify if redirects are set up properly, including 302 redirects, and spot any issues in the chain.
- Visual Redirect Indicators: The extension visually indicates redirects directly in the Chrome browser toolbar, allowing for quick and easy analysis.
- SEO Insights: Helps identify misconfigured redirects or issues that might impact SEO performance, such as unnecessary redirect loops or incorrect status codes.
3. Redirect Checker Tools
Tools like HTTPStatus.io and Redirect Detective help test URLs and track redirection chains. They ensure that 302 redirects are set up correctly and identify any issues, like redirect loops or missing status codes.
Key Features of Redirect Checker Tools:
- Comprehensive URL Testing: Test any URL to track its redirection path and ensure the correct status codes, including 302, are returned.
- Redirect Path Visualization: See the full sequence of redirects, from the initial URL to the final destination, helping to identify issues in the chain.
- Status Code Identification: Quickly spot if 302 redirects or other status codes (like 301 or 404) are properly set.
- Identify Redirect Loops: Help detect infinite or cyclic redirects that could cause major issues with user experience and SEO.
- Detailed Reports: Generate reports on URL status codes and redirection issues for quick analysis and troubleshooting.
4. Screaming Frog SEO Spider
For larger websites, Screaming Frog SEO Spider is a comprehensive tool that crawls your site, identifies redirect issues, and helps you manage redirects in bulk.
Key Features of Screaming Frog SEO Spider:
- Crawl Your Entire Site: Automatically crawl your website to identify any redirect issues across all pages.
- Bulk Redirect Management: Manage and analyze 302 redirects in bulk, making it ideal for large-scale websites.
- Redirect Reporting: Generate detailed reports of all redirects, including 302, to ensure they’re set up correctly.
- Identify Redirect Loops: Automatically detect redirect loops and chains that could negatively affect user experience and SEO.
- SEO Performance Insights: Provides insights into how redirects might be affecting your site’s SEO performance, including issues like broken redirects or misconfigured status codes.
- Customizable Crawl Options: Customize the crawl to include specific pages or types of content, helping to fine-tune redirection analysis.
Read More: How to test redirect with Cypress
Testing and Monitoring 302 Redirects
Testing and monitoring 302 redirects are critical steps to ensure they function as intended. Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Use Redirect Testing Tools: Leverage tools like Requestly, Redirect Path, and Screaming Frog to test 302 redirects across your site. Monitor them periodically to identify any errors or changes in the redirect behavior.
- Check for Redirect Loops: Redirect loops occur when URLs point back to each other, causing infinite redirection. This can be detrimental to user experience and SEO. Ensure your redirects are configured correctly.
- Monitor User Impact: Track user behavior and engagement metrics to ensure the redirects are providing a smooth experience. High bounce rates after a redirect might indicate issues with the user flow.
Advanced Topics in 302 Redirects
For more advanced use cases, consider the following topics:
1. Handling Redirects in Single Page Applications (SPAs): In SPAs, redirects can be more complex due to the way content is dynamically loaded. Handling 302 redirects in such environments requires careful attention to ensure they work as expected without breaking the user flow.
2. Handling Redirects in Mobile Apps: For mobile apps that rely on deep linking, 302 redirects need to be properly configured to ensure users are redirected to the correct content within the app without disrupting their experience.
3. International SEO and 302 Redirects: When dealing with international SEO, ensure 302 redirects are used correctly to serve the right content to users in different countries. Be mindful of how search engines treat these redirects for international pages.
Conclusion
302 Temporary Redirects are a useful tool for managing temporary page changes or redirections without affecting the long-term SEO value of the original page. When used correctly, they can improve user experience, help with A/B testing, and support internationalization efforts. However, it is important to follow best practices, monitor their performance, and utilize the right tools to ensure they are working effectively.
By understanding how 302 redirects work and using them appropriately, you can maintain a seamless user experience and preserve SEO rankings without unintended consequences.