In web development and SEO, redirects are a crucial component for ensuring users are guided to the correct content when URLs change. A 307 Temporary Redirect is a specific HTTP status code used to temporarily redirect a user from one URL to another while maintaining the original request method (e.g., GET or POST).
Unlike permanent redirects (301), a 307 redirect signals that the change is temporary and that the client should continue using the original URL in the future.
Overview
- Temporary Site Maintenance and Downtime
- A/B Testing and User Experience Experiments
- Website Maintenance and Temporary Unavailability
- Redirecting Language or Location-Specific Content
Tools for Managing and Testing 307 Redirects
- Requestly HTTP Interceptor
- Redirect Path Chrome Extension
- Redirect Checker Tools
- Bulk Redirect Management Solutions
This article dives deep into 307 redirects, how they work, when to use them, best practices, and the SEO implications of their implementation.
What is a 307 Redirect?
A 307 Temporary Redirect is an HTTP response status code that indicates the requested resource has been temporarily moved to a different URL. This type of redirect tells browsers and search engines that the move is temporary, and the client should continue to use the original URL for future requests.
Difference Between 307 and Other Redirect Types (301, 302)
Unlike a 301 (permanent redirect), which tells search engines and browsers that the original page has permanently moved, a 307 redirects users temporarily. 302 redirects are also temporary, but they don’t guarantee that the HTTP method (such as GET or POST) will be preserved, which is a key difference with a 307 redirect.
How 307 Temporary Redirects Work
Here is how 307 redirect works:
The Role of HTTP Headers in 307 Redirects
When a 307 redirect is triggered, the server sends an HTTP response with a “Location” header containing the new URL. This tells the client (browser, search engine, etc.) to temporarily access the specified location while keeping the original HTTP method intact.
Server-Side vs. Client-Side Redirects
A 307 redirect is typically implemented server-side, which means that the server responds with the redirect command. Client-side redirects, such as those implemented via JavaScript, may not always preserve the HTTP method and can be less reliable in terms of SEO and user experience.
SEO Implications of 307 Redirects
When implementing 307 Temporary Redirects, it’s crucial to understand their implications for Search Engine Optimization (SEO). Unlike 301 Permanent Redirects, which signal a permanent move, 307 redirects are temporary, meaning search engines will typically continue indexing the original URL.
This distinction can have both positive and negative consequences for your website’s SEO performance. Here’s a breakdown of how 307 redirects impact SEO:
Preserving Link Equity with 307 Redirects
Unlike 301 redirects, which pass link equity (or PageRank) from the old URL to the new URL, 307 redirects do not permanently transfer link equity. Search engines will continue to associate the original URL with the page’s link equity. This means that if you’re temporarily redirecting users to a different page, the redirected URL won’t receive the SEO benefits from incoming backlinks and may not rank as well as the original URL.
For example, if your website undergoes a temporary promotion and you use a 307 redirect to point visitors to a special landing page, the SEO value (backlinks, authority, etc.) stays with the original page. Once the promotion ends, and the redirect is removed, the original page can continue to benefit from the link equity it has accumulated over time.
Impact on Search Engine Indexing and Ranking
307 redirects are designed to be temporary, so search engines typically continue indexing the original URL. This means that search engines don’t treat the redirected URL as a replacement for the original one. They will retain the original URL in their index, and it will continue to receive rankings associated with it, rather than the redirected URL.
This behavior is beneficial for temporary changes but can be a downside if you’re planning a permanent change and don’t want the original URL to be indexed. For instance, if you permanently migrate your content or rebrand your website, a 301 redirect would be more suitable because it passes the ranking signals to the new page, whereas a 307 would keep the original URL in the index.
Risks of Misusing 307 Redirects
Misusing 307 redirects can lead to several SEO challenges. If 307 redirects are used for permanent content moves, search engines may continue to index the original URL instead of the redirected URL, which can result in poor SEO performance. Additionally, if the 307 redirect points to irrelevant or low-quality pages, it can harm your site’s reputation and rankings.
Another risk arises when search engines fail to understand the temporary nature of the redirect and continue indexing the temporary destination URL. This can create confusion and result in indexing errors, causing delays in search engine crawls and potential issues with rankings.
Crawl Budget Considerations
Crawl budget refers to the number of pages that search engines crawl on your site during each visit. If a 307 redirect is not configured properly or leads to unnecessary redirections, search engines may end up wasting crawl budget on these redirects instead of crawling your content.
This is especially relevant for large websites with many pages. Ensuring that your 307 redirects are used only when necessary helps prevent search engine crawlers from wasting valuable time on redirects, optimizing the crawl budget for more important pages.
Temporary Nature of 307 Redirects
The key feature of 307 redirects is their temporary nature. This is advantageous when you need to test something, temporarily reroute traffic for marketing purposes, or make changes that will be reverted. However, relying on 307 redirects for an extended period could potentially harm SEO. If search engines detect that the redirect has been in place for a prolonged time, they may treat the original URL as permanently inactive, impacting your site’s overall performance.
It’s essential to periodically evaluate the need for 307 redirects and remove them once they are no longer required. Prolonged use of a temporary redirect can confuse both users and search engines, potentially leading to a loss of SEO value and diminished user experience.
Read More:How to test redirect with Cypress
When to Use 307 Temporary Redirects
Here is a list of use cases on when to use 307 redirects:
Temporary Site Maintenance and Downtime:
A common use case for a 307 redirect is during website maintenance or downtime. If a site is temporarily unavailable, you can use a 307 redirect to point users to a maintenance page while keeping the original URL intact for future use.
A/B Testing and User Experience Experiments
307 redirects are useful for A/B testing, as they allow you to redirect users to different versions of a page while preserving the original URL. This helps marketers test page variants and gather insights without affecting search engine indexing.
Website Maintenance and Temporary Unavailability
For website updates or changes, a 307 redirect ensures users are temporarily directed to an alternate page without impacting long-term SEO. It’s ideal when content is temporarily unavailable or undergoing revisions.
Redirecting Language or Location-Specific Content
If your site serves content in multiple languages or targets specific geographic regions, a 307 redirect can be used to temporarily direct users to the appropriate content based on their language or location, providing a tailored user experience.
Best Practices for Implementing 307 Redirects
Here are the best practices for implementing 307 redirects:
Avoiding Redirect Chains and Loops: Redirect chains and loops, where one redirect leads to another and so on, can significantly slow down your site and affect SEO. It’s essential to implement 307 redirects properly, avoiding unnecessary chains or loops that can confuse users and search engines.
Redirecting to Relevant and High-Quality Pages: Always ensure that the URL you are redirecting to is relevant to the user’s request and offers high-quality content. Redirecting to irrelevant pages can hurt user experience and negatively impact SEO.
Regular Audits and Maintenance of Redirects: It’s important to regularly review your redirects. 307 redirects should only be used temporarily, so performing periodic audits ensures they are still necessary. Over time, remove or replace redirects that are no longer required.
Using Absolute URLs in Redirects: To ensure the correct redirection, always use absolute URLs (complete URLs with the domain) rather than relative URLs, which could cause unexpected issues with redirection.
Implementing Redirects in .htaccess, NGINX, or via CMS: You can implement 307 redirects through server configuration files such as .htaccess for Apache or nginx.conf for NGINX. Additionally, most content management systems (CMS) like WordPress offer plugins to handle redirects more easily.
Tools for Managing and Testing 307 Redirects
Here is a list of tools for managing and testing 307 redirects:
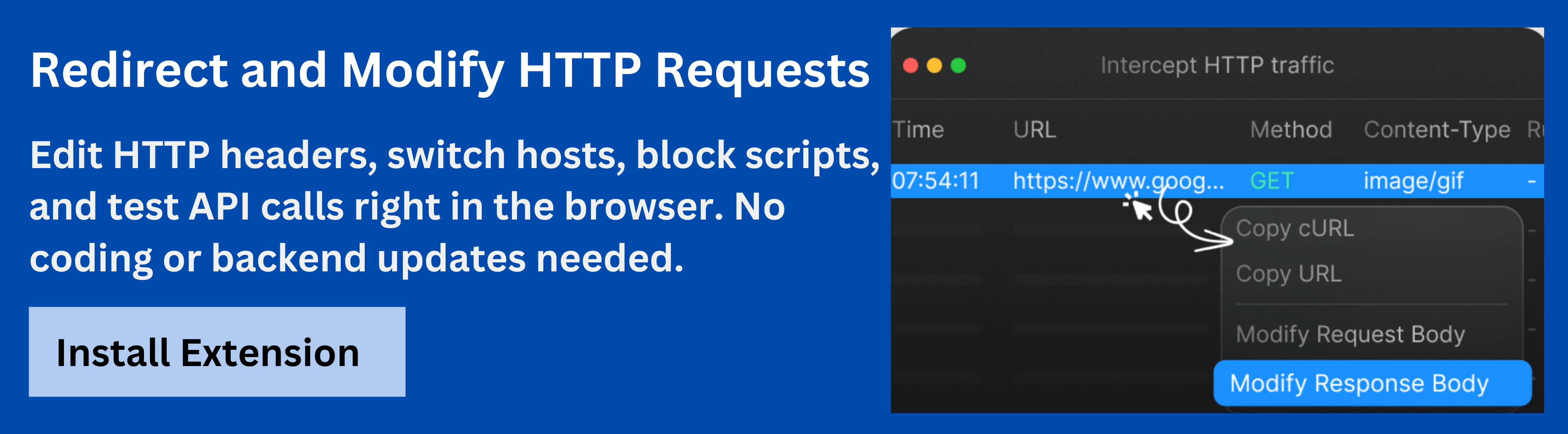
1. Requestly: A Powerful Tool for Managing 307 Redirects
Requestly Https Interceptor is an excellent tool for developers looking to test and manage 307 redirects. With Requestly, you can create custom rules to redirect requests, modify response headers, and simulate different redirection scenarios before they are live. It’s an invaluable tool for validating redirects in a staging environment.
2. Redirect Path Chrome Extension
The Redirect Path Chrome extension allows users to quickly view the HTTP status codes of any URL, including 307 redirects, making it easy to identify if redirects are working as expected.
Redirect Checker Tools
There are various tools like httpstatus.io and Redirect Detective that can check the status of URLs and track redirection chains. These tools help ensure that 307 redirects are functioning correctly and not creating unnecessary issues.
Bulk Redirect Management Solutions
For larger websites, tools like Screaming Frog SEO Spider or Ahrefs are valuable for managing and auditing redirects in bulk. These tools crawl your site and identify potential redirect problems, making it easier to maintain proper redirection practices.
Monitoring and Maintaining Redirects
Follow these steps for monitoring your redirects:
1. Setting Up Redirect Monitoring
Regular monitoring is crucial to ensure your 307 redirects continue to function properly. Tools like Google Search Console can alert you to crawl errors related to redirects, allowing you to fix issues quickly.
2. Handling 404 Errors and Broken Links
When a 307 redirect points to a non-existent page or encounters a 404 error, it’s important to address the problem immediately. Regular checks for broken links will help maintain a positive user experience.
3. Analyzing Redirect Performance
After implementing 307 redirects, you should monitor their performance to ensure they aren’t negatively impacting user engagement or SEO. Tools like Google Analytics and SEMrush provide insights into traffic flow and page performance, helping you make adjustments as needed.
Read More: What Is API Automation Testing?
Advanced Topics in 307 Redirects
Here are some advanced topics in 307 redirects:
- Handling 307 Redirects with Load Balancers and CDNs: For large websites using load balancers or Content Delivery Networks (CDNs), handling 307 redirects at multiple points can be tricky. It’s important to configure these systems properly to ensure the redirect doesn’t interfere with performance or caching.
- Redirecting with Query Parameters and Dynamic URLs: If you need to preserve query parameters or dynamic content during a 307 redirect, ensure that the redirect properly passes this data to the new URL. This is particularly important for forms and dynamic content that need to be handled in real-time.
- 307 Redirects in Mobile and Serverless Environments: In mobile-first indexing and serverless environments, 307 redirects may behave differently depending on the architecture. Ensure proper testing to guarantee that redirects function correctly across all platforms.
Real-World Applications of 307 Redirects
Here are some examples of real world applications of 307 redirects:
- Using 307 Redirects for E-commerce Site Promotions: E-commerce websites often use 307 redirects during sales events or promotional campaigns to redirect users to special landing pages temporarily without altering the original product URLs.
- Redirecting Temporarily for Marketing Campaigns: Marketing campaigns often require temporary content changes. 307 redirects ensure that users are sent to campaign-specific pages while preserving the original URLs for long-term use.
- Implementing 307 for Content Migration or Updates: For sites migrating content or undergoing updates, 307 redirects ensure users are directed to the new content while preserving search engine indexing for the original pages.
Conclusion
307 Temporary Redirects are a useful tool for temporary URL changes, maintenance, and testing. They preserve the original request method and ensure users are redirected correctly without affecting long-term SEO.
While 307 redirects are helpful for temporary moves, they should be used judiciously. Ensure they are implemented correctly, audited regularly, and removed once the temporary move is no longer necessary. By following best practices, you can maintain a seamless user experience and avoid SEO pitfalls.