The HTTP 426 Upgrade Required status code is a relatively uncommon error, but it plays a crucial role in ensuring the web’s evolving standards and protocols are upheld. This error signifies that the requested resource can only be accessed using a different protocol, often a newer or more secure one.
Whether you’re a developer, administrator, or someone managing a web application, understanding how to handle and resolve this issue is essential to maintaining a smooth user experience and optimizing website performance.
Overview
Common Causes of the 426 Status Code
- Protocol Obsolescence: Server requires a newer protocol (e.g., HTTPS, HTTP/2), but client uses an older version (e.g., HTTP/1.0).
- Server Policy Enforcements: Servers enforce secure protocols like HTTPS, rejecting outdated HTTP requests.
- Client-Side Misconfigurations: Client errors due to outdated or misconfigured browsers or applications.
- Legacy System Compatibility: Older systems or APIs may use outdated protocols, causing the 426 error when connecting to modern servers.
This article dives into the HTTP 426 Upgrade Required error, explore its causes, discuss troubleshooting tips, and highlight the SEO implications of this status code.
What is HTTP 426 Upgrade?
The HTTP 426 status code indicates that the client needs to upgrade its protocol in order to complete the request. This could happen because the server requires a higher version of the protocol (such as HTTP/2 or HTTPS) than what the client is using. The error is typically accompanied by a message that specifies which protocol is needed to successfully process the request.
For instance, if a server is configured to only handle HTTPS requests (to ensure secure communication) but a client tries to access the page using HTTP, the server will respond with a 426 status code and inform the client to switch to HTTPS. In simpler terms, the HTTP 426 Upgrade Required is a way for servers to enforce the use of more secure or modern communication protocols that benefit both users and the website’s security.
Common Causes of the 426 Status Code
Several scenarios can trigger the 426 Upgrade Required status code. Below are the most common causes:
- Protocol Obsolescence: This occurs when a server is configured to require a newer or more secure protocol, like HTTPS or HTTP/2, but the client uses an older version such as HTTP/1.0 or HTTP/1.1. Websites today often enforce HTTPS for security reasons, which is a common cause for encountering this error.
- Server Policy Enforcements: Servers may enforce certain protocols to meet security standards or avoid vulnerabilities. For example, a website might reject HTTP requests in favor of HTTPS to prevent data interception during transmission.
- Client-Side Misconfigurations: Sometimes, the error can arise from misconfigurations on the client side, such as a browser or application requesting a page without properly supporting the necessary protocol version.
- Compatibility Issues with Legacy Systems: In some cases, older systems or APIs may still rely on outdated protocols and thus generate the 426 error when attempting to communicate with a server that requires newer standards.
The Main Differences Between 426 vs Other Error Codes
It’s important to understand how HTTP 426 compares to other common HTTP error codes, especially those within the 3xx (Redirection) and 4xx (Client Error) families.
- 426 vs 301/302 Redirects: The key difference between a 426 status code and redirection codes like 301 (Moved Permanently) or 302 (Found) is that the 426 error doesn’t indicate a resource has moved. Instead, it requires a protocol upgrade to successfully process the request. Redirection codes typically point to a new URL, while the 426 error focuses on protocol compatibility.
- 426 vs 400 Bad Request: A 400 error indicates that the request is malformed or invalid, whereas the 426 error indicates that the request is valid, but the client needs to upgrade its protocol to proceed. In both cases, the server cannot fulfill the request, but the reasons differ.
- 426 vs 405 Method Not Allowed: A 405 Method Not Allowed error occurs when the HTTP method (like GET, POST) is not allowed for the requested resource. On the other hand, 426 implies that the correct method is being used but needs a protocol upgrade to function.
Troubleshooting and Resolving 426 Errors
When you encounter a 426 error, here are the steps to troubleshoot and resolve the issue:
Upgrade Client Protocol: The first step in resolving a 426 error is ensuring that the client (browser, application, etc.) supports the protocol requested by the server. This may involve:
- Enabling HTTPS in your browser or application if the website requires it.
- Updating the client’s software or application to support HTTP/2 or HTTP/3.
Update Server Configurations: If you are the server administrator, ensure that the server is correctly configured to support modern protocols while maintaining backward compatibility where possible. For instance:
- Configure your server to support both HTTP/1.1 and HTTP/2 to accommodate a wider range of client requests.
- If using HTTPS, ensure your SSL/TLS certificates are up-to-date and properly configured.
Check for Legacy Systems or APIs: If your site is communicating with legacy systems that use outdated protocols, consider upgrading those systems to newer standards. For APIs, this may involve upgrading the API versions or adjusting configurations to support the required protocols.
Use a 3xx Redirect as a Temporary Fix: If the issue arises from protocol incompatibility between your server and older clients, you can consider temporarily redirecting requests to a URL that uses a supported protocol.
SEO Implications of Encountering 426 Errors
Encountering HTTP 426 errors can have SEO implications if not handled properly:
- Impact on Search Engine Crawlers: If search engines like Google attempt to crawl a page and encounter a 426 error, they may not be able to index the page properly, which could affect its rankings.
- Preventing SEO Penalties: Consistently encountering 426 errors might lead to SEO penalties or a drop in rankings if search engines cannot access the page. Ensuring your website uses modern protocols (especially HTTPS) is critical for maintaining optimal SEO health.
Read More:How to test redirect with Cypress
Resolving 426 Errors in SEO
Follow these steps for resolving 426 errors in SEO:
- Ensure that all pages are accessible via HTTPS and support HTTP/2 or HTTP/3.
- Use 301 redirects to guide search engines and users to updated pages that comply with the server’s protocol requirements.
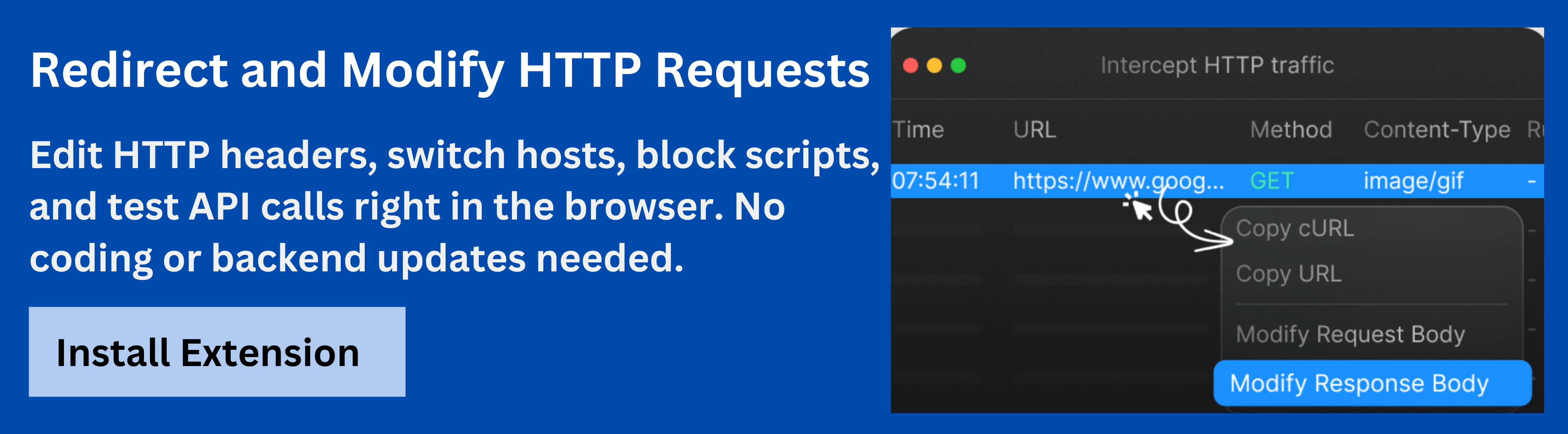
Requestly HTTP Interceptor Tool: Mocking and Testing Redirects
For developers dealing with protocol issues like HTTP 426, tools like Requestly’s HTTP Interceptorare invaluable. Requestly allows you to simulate different types of HTTP responses, including 3xx redirects and 426 errors, to test how your server and application handle these scenarios.
Key Features:
- Mock Protocol Upgrades: Use Requestly to simulate the 426 status code and test how your application responds to protocol upgrade requests, allowing you to debug and resolve issues before they affect end users.
- Test Redirect Scenarios: Requestly can help test how redirects are handled during protocol upgrades, ensuring users are smoothly transitioned to the correct protocol without interruption.
- Real-Time Testing: Easily mock and inspect responses without modifying your live environment, making it simpler to troubleshoot and resolve errors.
By integrating Requestly into your workflow, you can ensure that your web application handles 426 errors effectively and provide a seamless user experience even during protocol transitions.
Best Practices for Implementing Protocol Upgrades
To avoid encountering HTTP 426 Upgrade Required errors, consider the following best practices when implementing protocol upgrades:
- Gradual Rollouts: Implement protocol changes gradually to ensure users are not abruptly impacted by the transition. Inform users about necessary protocol updates well in advance.
- User Notifications: If certain clients cannot access your site due to outdated protocols, consider providing clear notifications explaining how to upgrade or switch protocols.
- Monitoring and Logging: Keep an eye on error logs and monitor user access patterns to quickly identify if clients are encountering protocol issues. Use tools like Requestly to simulate different scenarios during testing.
- Educating Users: Inform your users about the importance of modern protocols (like HTTPS) and guide them on how to upgrade their browsers or systems.
Read More: What Is API Automation Testing?
Conclusion
The HTTP 426 Upgrade Required error plays a vital role in enforcing modern web standards and ensuring secure communication. By understanding its causes, troubleshooting effectively, and using tools like Requestly for testing, you can minimize its impact on user experience and maintain your site’s SEO health.
Properly implementing protocol upgrades and ensuring that both your clients and servers support the necessary protocols will keep your website running smoothly and securely.