In the world of web development, HTTP status codes serve as a vital communication tool between the client (browser) and the server. They provide information about the status of the requested resource, helping users and web developers troubleshoot issues efficiently.
Among these status codes, the 4xx series represents client-side errors, indicating that the problem lies with the request sent by the client, not the server. Understanding these errors, their causes, and how to resolve them is crucial for maintaining smooth and error-free user experiences on the web.
Overview
- User Input Mistakes: Typos or incorrect URLs, leading to errors like 404.
- Authentication Failures: Incorrect credentials triggering 401 or 403 errors.
- Broken Links: Outdated links without proper redirects causing 404 errors.
- Request Formatting Issues: Invalid headers or unsupported methods resulting in request rejection.
- Rate Limiting: Exceeding request limits leading to 429 Too Many Requests.
- Browser Cache & Cookies: Corrupted cache or cookies causing 400 errors, resolved by clearing them.
This article will explore the most common 4xx error codes, their causes, impacts on SEO and user experience, troubleshooting steps, and tools to manage and resolve these errors effectively.
Understanding 4xx Client Errors
4xx Client Errors are HTTP status codes that indicate an issue with the client’s request. When a client sends a request to a server, the server responds with a status code. If the status code falls within the 4xx range (400-499), it means there was a problem with the request, which prevents the server from fulfilling it. These errors usually occur because the client has made a bad request, whether it’s due to invalid syntax, missing credentials, or a request that the server cannot process.
While the server is functioning correctly, the client needs to correct the issue in their request for the interaction to succeed. Common 4xx error codes include: 400 Bad Request, 401 Unauthorized, 403 Forbidden, 404 Not Found.
Common 4xx Error Codes and Their Meanings
The 4xx error codes cover a broad range of issues. Here are some of the most common ones:
400 Bad Request
This error typically occurs when the request sent by the client is malformed or contains invalid syntax. This could be due to a typo in the URL, incorrect query parameters, or corrupted data being sent.
401 Unauthorized
A 401 error indicates that the request lacks proper authentication credentials or that the credentials provided are invalid. For example, when a user tries to access a protected page without logging in, the server responds with a 401 error.
403 Forbidden
Unlike the 401 error, a 403 status code signifies that the server understands the request but refuses to authorize it. This could happen when the user doesn’t have permission to access the requested resource.
404 Not Found
The 404 error is one of the most well-known and occurs when the server cannot find the requested resource. This could be due to an incorrect URL, a deleted page, or a broken link.
405 Method Not Allowed
This error occurs when the client tries to use an HTTP method (such as POST, GET, DELETE) that is not supported by the server for the requested resource.
406 Not Acceptable
A 406 error occurs when the requested resource is only available in a format that the client cannot accept. For example, the client may request JSON data when the server only supports HTML.
429 Too Many Requests
This error appears when the client has sent too many requests in a given amount of time, often due to rate limiting enforced by the server.
Causes of 4xx Errors
4xx errors typically arise from issues related to the client’s request. Understanding the common causes can help web developers prevent or resolve these errors.
User Input Mistakes
The most common cause of 4xx errors is user input mistakes, such as misspelled URLs, incorrect query parameters, or wrong credentials. For example, typing “http://example.com/page” when the correct URL is “http://example.com/products/page” will result in a 404 error.
Authentication and Authorization Failures
Authentication errors, such as providing the wrong login credentials or failing to authenticate properly, can trigger 401 Unauthorized or 403 Forbidden errors. These errors occur when a server requires specific user validation before granting access.
Broken or Outdated Links
Broken or outdated links can lead to 404 errors, especially when pages are removed or moved without proper redirects. This is often a problem with websites that don’t update their internal links or external backlinks after a page is changed or deleted.
Request Formatting Issues
Sometimes, 4xx errors arise from improperly formatted requests. This could include invalid headers, incorrect content types, or unsupported HTTP methods, causing the server to reject the request.
Rate Limiting and Throttling
To prevent abuse or overloading, many websites and APIs implement rate limiting, which restricts the number of requests a user can make in a set time period. When these limits are exceeded, a 429 Too Many Requests error is returned.
Browser Cache and Cookie Problems
Sometimes, cached files or corrupted cookies in the client’s browser can interfere with requests, leading to errors like 400 Bad Request. Clearing the browser cache and cookies can often resolve such issues.
Read More:How to test redirect with Cypress
Impact of 4xx Errors on SEO and User Experience
4xx errors can have significant consequences, both for user experience and search engine optimization (SEO).
- Effects on Search Engine Crawling and Indexing: When search engine bots encounter 4xx errors, they may stop crawling and indexing the affected pages, which can harm the site’s visibility in search results. A high number of 4xx errors may lead to a reduction in search engine ranking.
- Influence on User Engagement and Conversion Rates: From a user experience perspective, encountering 4xx errors can frustrate visitors, leading to higher bounce rates and lower conversion rates. For instance, when users cannot access a page due to a 404 error, they may leave the site and turn to a competitor.
- Best Practices for Handling 4xx Errors:To minimize the impact of 4xx errors, it’s essential to implement custom error pages, use redirects for moved or deleted pages, and regularly check for broken links. Additionally, ensuring proper authentication mechanisms are in place can help reduce 401 and 403 errors.
Troubleshooting and Resolving 4xx Errors
Addressing 4xx errors requires a systematic approach to identify and resolve the root cause.
- Verifying URLs and Request Syntax: Start by checking the URL for typos or errors in the query parameters. Ensure the syntax is correct and the resource being requested exists on the server.
- Checking Server Logs and Headers: Review the server logs to understand why a request is failing. Pay attention to request headers, payloads, and response codes, which can provide insights into the error’s cause.
- Implementing Proper Authentication and Authorization: For 401 and 403 errors, ensure that the correct authentication credentials are being sent with the request and that the server is configured to allow access to the requested resource.
- Utilizing Redirects and Custom Error Pages: For pages that have moved or been deleted, implement 301 redirects or create custom error pages (such as a 404 page) to guide users to relevant content.
- Monitoring and Analyzing Error Patterns: Use analytics tools to monitor error rates and patterns, helping identify recurring issues that require fixing.
Tools for Managing and Resolving 4xx Errors
Several tools can help developers manage and resolve 4xx errors efficiently. These tools are useful for debugging, testing, and optimizing the client-server communication process.
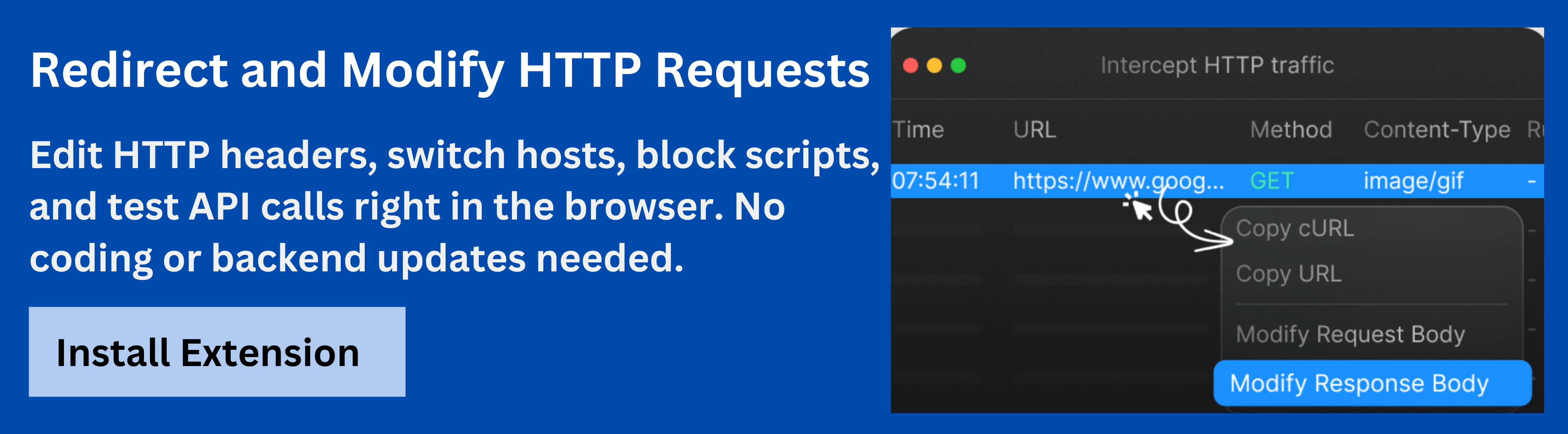
Requestly’s HTTP Interceptor Tool
One powerful tool for developers working with HTTP requests is Requestly’s HTTP Interceptor Tool. Requestly allows users to modify HTTP requests and responses in real time, making it easier to diagnose and fix 4xx errors.
Requestly enables developers to intercept, modify, and debug HTTP requests and responses, which is especially useful for simulating different error scenarios.
- Setting Up Requestly: Installing and configuring Requestly is straightforward, allowing developers to create custom rules for intercepting requests and debugging issues.
- Capturing and Modifying Requests: With Requestly, you can capture and modify requests before they reach the server, which is helpful for testing how the server handles different types of client errors.
- Integrating Requestly into Your Development Workflow: Requestly seamlessly integrates into your workflow, providing valuable insights that help prevent and resolve 4xx errors in real time.
Advanced Techniques for Handling 4xx Errors
To prevent recurring 4xx errors, consider implementing the following advanced techniques:
- Implementing Custom Error Handling Logic: Custom error handling logic allows you to intercept errors and handle them in a way that improves the user experience. For example, you could redirect users to an alternative page or display a helpful message when an error occurs.
- Using API Gateways and Proxies: API gateways and proxies can help manage 4xx errors at scale. These tools allow you to route requests and handle errors centrally, providing better control over your application’s error responses.
- Leveraging Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs can help minimize 4xx errors by caching content closer to the end user, reducing the likelihood of broken links and improving load times.
- Automating Error Detection and Resolution: Implement automated systems to detect and resolve 4xx errors in real time, minimizing their impact on user experience and SEO.
Read More: What Is API Automation Testing?
Conclusion
4xx Client Errors are common issues in web development, but they can be effectively managed with the right tools and strategies. By understanding their causes, impacts, and troubleshooting methods, developers can enhance user experience, improve SEO, and ensure smoother website functionality.
Using tools like Requestly’s HTTP Interceptor can streamline the debugging and resolution of these errors, making web development more efficient and less error-prone.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the difference between 4xx and 5xx errors?
4xx errors indicate a problem with the client’s request, while 5xx errors suggest issues with the server.
Q2: How can I prevent 4xx errors from affecting my website?
Regularly check for broken links, implement proper redirects, and ensure correct authentication and authorization mechanisms.
Q3: What tools can help in diagnosing 4xx errors?
Requestly’s HTTP Interceptor tool, browser developer tools, and server logs are excellent tools for diagnosing 4xx errors.
Q4: How do I handle 4xx errors in a RESTful API?
Ensure proper input validation, use status codes accurately, and provide helpful error messages to guide the client.