More than 89% of developers rely on APIs daily, with many organizations managing hundreds of endpoints across multiple services.
This high dependency means that even a single malfunctioning API endpoint can break critical user experiences. API endpoint testing ensures each endpoint behaves exactly as expected, handling both intended and unexpected inputs reliably.
Here are the extracted headings for the two sections:
Overview
Types of API Endpoint Testing
- Functional Testing
- Integration Testing
- Contract Testing
- Performance & Load Testing
- Security Testing
- End-to-End Testing
Why Perform API Endpoint Testing?
- Improved Reliability
- Better User Experience
- Lower Debugging Costs
- Compliance Assurance
- Performance Stability
This article delves deep into what API endpoints are and why performing API Endpoint testing is essential.
What are API Endpoints?
An API endpoint is a specific URL or URI within an API where a client application can access resources or perform operations. Each endpoint represents a distinct function or data source, often tied to HTTP methods such as GET, POST, PUT, or DELETE.
For example, in an e-commerce API:
- GET /products retrieves a list of products.
- POST /cart adds an item to the shopping cart.
- DELETE /cart/{itemId} removes a specific item.
Well-designed endpoints follow consistent naming conventions, respect HTTP method semantics, and return responses in structured formats like JSON or XML. They may also include parameters for filtering, sorting, or pagination, and must handle errors gracefully with clear status codes and messages.
Types of API Endpoint Testing
API endpoints can be validated through multiple testing methods, each addressing a different quality dimension.
- Functional Testing: Confirms the endpoint performs the correct action with valid inputs, returning expected status codes, response bodies, and headers.
- Integration Testing: Checks how an endpoint interacts with other components like databases, queues, and third-party services, ensuring end-to-end functionality.
- Contract Testing: Validates that the endpoint adheres strictly to its defined API specification (e.g., OpenAPI), catching breaking changes early.
- Performance & Load Testing: Measures latency, throughput, and error rates under normal and peak load, identifying bottlenecks before production.
- Security Testing: Detects vulnerabilities such as injection flaws, insufficient authorization, or insecure data transmission.
- End-to-End Testing: Simulates real-world workflows across multiple endpoints to ensure overall system behavior matches expectations.
Why Perform API Endpoint Testing?
Thorough testing of API endpoints delivers both technical and business benefits.
- Improved Reliability: Reduces the risk of outages and broken features by catching defects early.
- Better User Experience: Ensures users receive fast, accurate, and consistent responses.
- Lower Debugging Costs: Resolves issues before production, saving time and resources.
- Compliance Assurance: Meets industry and regulatory standards for data handling and security.
- Performance Stability: Maintains predictable response times and behavior under different loads.
How to Conduct API Endpoint Testing?
Conducting API endpoint testing requires a structured, step-by-step approach to ensure completeness and accuracy.
- Understand Requirements: Review API documentation, sample payloads, authentication methods, and expected outputs.
- Identify Endpoints: List every endpoint and its associated HTTP methods, noting those critical to business operations.
- Select Test Types: Determine whether functional, performance, security, or a mix of tests is needed for each endpoint.
- Create Test Scenarios: Cover positive, negative, and edge cases, including rate limit boundaries, payload extremes, and invalid tokens.
- Prepare Test Data: Use realistic, sanitized datasets to mimic production conditions without exposing sensitive information.
- Execute Tests: Run manually for ad-hoc checks or automate for repeatable regression coverage.
- Analyze & Report: Document failures, performance metrics, and suggested fixes for developers.
Preparing for API Endpoint Testing
Good preparation helps prevent false positives, reduce test flakiness, and ensure meaningful results.
- Review and Maintain API Specifications: Keep OpenAPI/Swagger definitions current and stored in version control to ensure tests align with the latest contracts.
- Configure Test Environments: Use staging or sandbox environments that closely mirror production, isolating dependencies to avoid interference.
- Manage Test Data: Create synthetic datasets with unique identifiers to avoid collisions, while ensuring they cover normal, edge, and error conditions.
- Mock or Virtualize Dependencies: For third-party services or unstable components, use mocks to stabilize test results and simulate rare failure scenarios.
- Secure Access & Secrets: Store API keys and tokens securely, rotate them regularly, and test both valid and expired credential cases.
Designing Effective Test Cases
Well-designed test cases increase coverage, reliability, and maintainability.
- Positive Scenarios: Validate correct outputs when given valid inputs, ensuring full compliance with contracts.
- Negative Scenarios: Test invalid data formats, missing parameters, or unauthorized access, confirming proper error codes and messages.
- Boundary Conditions: Check input extremes, such as maximum string lengths, minimum values, and high payload volumes.
- Idempotency Checks: For PUT or POST with idempotency keys, verify that repeated requests produce the same result without duplication.
- Pagination and Sorting: Ensure list endpoints return stable and predictable ordering across multiple pages.
- Security Validations: Test for injection vulnerabilities, weak authentication handling, and correct enforcement of permissions.
Automating API Endpoint Tests and Execution Strategy
Automation enables consistent execution, scalability, and faster feedback loops.
- Select Appropriate Frameworks: Use tools like REST Assured for Java-based projects, Newman for Postman collections, or JMeter for load testing.
- Organize Tests Logically: Group by endpoint and HTTP method, and share reusable fixtures for setup and teardown steps.
- Integrate into CI/CD: Run automated tests on every code change, blocking deployments if critical endpoints fail.
- Parallelize Execution: Speed up test suites by running independent cases concurrently, keeping rate limits in mind.
- Set Performance Gates: Fail builds when latency or error rates exceed defined thresholds.
- Control Flakiness: Add timeouts, retries for idempotent operations, and dependency mocks to keep results stable.
Analyzing Results & Reporting
Interpreting and communicating results effectively is as important as running the tests themselves.
- Measure Response Metrics: Track average, p95, and p99 latencies, payload sizes, and status code distributions.
- Identify Error Trends: Detect recurring issues across specific endpoints or time periods.
- Report Coverage: Show which endpoints and scenarios are tested, including both functional and non-functional checks.
- Provide Reproducible Failures: Include logs, request/response samples, and cURL commands to help developers debug quickly.
- Visualize Trends: Maintain dashboards that show API health and performance over time for stakeholders.
Common Challenges in API Endpoint Testing
Several recurring challenges can reduce testing accuracy or stability.
- Changing Specifications: API updates can invalidate tests unless specs and tests are tightly coupled.
- Unstable Dependencies: Third-party services can cause false failures without proper mocking.
- Authentication Complexity: Multi-step or token-based authentication can complicate automated tests.
- Flaky Results: Network latency or environmental inconsistencies can produce intermittent failures.
- Rate Limiting: High-volume test runs can hit API throttling rules, causing false negatives.
- Eventual Consistency: Asynchronous processes can cause delayed data availability, requiring smart polling strategies.
Best Practices for API Endpoint Testing
Following proven best practices improves both the effectiveness and maintainability of testing efforts.
- Test Early and Often: Incorporate API tests into early development stages to catch defects sooner.
- Balance Test Types: Combine functional, performance, security, and contract testing for comprehensive coverage.
- Prioritize Negative Testing: Ensure APIs handle invalid inputs and edge cases gracefully.
- Use Realistic Data: Simulate actual usage patterns to uncover real-world issues.
- Maintain Test Reliability: Fix flaky tests immediately to preserve confidence in results.
- Keep Documentation Synced: Ensure that public API docs reflect tested behavior and examples.
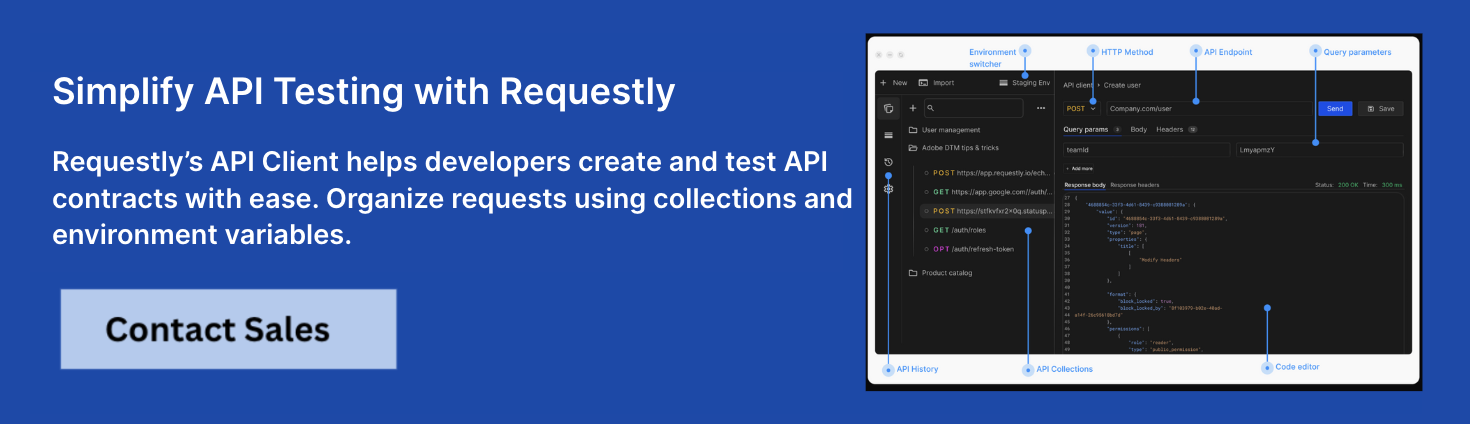
Why Test APIs Using Requestly?
Requestly provides flexible traffic interception, modification, and mocking capabilities that enhance API endpoint testing.
- Mock Unavailable Services: Simulate responses for endpoints still under development.
- Inject Edge Cases: Modify payloads and headers to test handling of unusual scenarios.
- Debug Live Traffic: Intercept and inspect API calls to pinpoint the root cause of failures.
- Collaborate Easily: Share mock configurations and request rules across teams.
Beyond traffic manipulation, Requestly’s API Client allows you to send requests, inspect responses, and organize endpoint collections directly within the tool—eliminating the need to switch between multiple applications like Postman or cURL. It supports advanced features such as environment variables, request history, and saved test suites, streamlining both manual and automated API endpoint testing workflows.
Conclusion
API endpoint testing is not just a quality assurance activity—it’s a safeguard for the stability, performance, and security of modern software. By validating every aspect of an endpoint’s behavior, from functional correctness to performance under load, teams can deliver APIs that are predictable and resilient, even in complex environments. A well-structured testing strategy, supported by tools like Requestly for simulation, creates a feedback loop that catches issues before they impact end users.