Modern software ecosystems depend heavily on API integrations to enable seamless data flow between systems, services, and applications. From payment gateways and CRM platforms to weather apps and IoT devices, APIs act as the glue that binds the digital world. Over 85% of organizations say API integration is crucial for achieving digital transformation goals.
Yet, developers often struggle with understanding how API integrations actually work in practice – from setting up endpoints and handling authentication to debugging and optimizing performance.
This article explores real-world API integration examples, their types, implementation process, and best practices for building scalable, secure integrations.
What Is API Integration?
An API integration is the process of connecting two or more software systems through their Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) so they can exchange data and functionality. APIs define rules for communication, allowing applications to request and send information without manual intervention.
For example, when a website fetches weather data from a third-party weather service, it’s performing an API integration. The front-end sends a request (via HTTP methods like GET or POST) to the weather API’s endpoint, which returns structured data (usually JSON or XML) for display.
In essence, API integration enables:
- Automation: Eliminates manual data transfer by syncing systems automatically.
- Real-time communication: Data updates occur instantly across platforms.
- Scalability: Developers can extend functionality without rebuilding from scratch.
Why use an API Integration (Real-World Value)?
API integrations power much of today’s software functionality. Businesses and developers use them to streamline workflows, enhance performance, and improve user experience.
Key real-world benefits include:
- Unified Data Access: APIs bridge applications like CRMs, ERPs, and analytics tools, ensuring consistent data flow across all systems.
- Improved Efficiency: Integrations allow software to share operations-e.g., e-commerce platforms syncing inventory data with warehouse management systems.
- Cost Reduction: Building from existing APIs reduces development time and infrastructure overhead.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Users benefit from unified, responsive systems such as social login features (Google, Facebook) or integrated payment systems (Stripe, PayPal).
A simple example is integrating a payment API in an e-commerce app. When a customer checks out, the front-end sends a POST request to a payment API endpoint. The API then communicates with the payment processor, validates the transaction, and returns a confirmation response-all within milliseconds.
Types of API Integration (REST, SOAP, GraphQL, gRPC, etc.)
Different APIs use different architectural styles and communication protocols. Each serves a unique purpose depending on complexity, speed, and interoperability requirements.
1. REST (Representational State Transfer):
- Uses HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) for communication.
- Commonly returns JSON, making it lightweight and easy to integrate.
- Example: A REST API call to https://api.example.com/users retrieves user data.
2. SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol):
- XML-based protocol with strict message structure.
- Better suited for enterprise-level systems requiring high security and transaction integrity (e.g., banking APIs).
3. GraphQL:
- Developed by Facebook, it allows clients to query specific data fields, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching.
- Example query:
{ user(id: “123”) {
name
email
}
}4. gRPC (Google Remote Procedure Call):
- Uses Protocol Buffers for compact and fast data serialization.
- Ideal for microservices communication and real-time streaming APIs.
Each integration type must be chosen based on project needs-REST for flexibility, SOAP for reliability, GraphQL for efficiency, and gRPC for high-performance environments.
Read More:How to test redirect with Cypress
Anatomy of an API Integration Example
To understand an API integration end-to-end, consider a scenario where a web application fetches user data from a CRM API.
1. Request: The application sends a GET request to an endpoint like /api/users/123 with authentication credentials (API key or OAuth token).
2. Authentication: The API verifies the client’s identity.
3. Response: The server returns a JSON payload with user details.
4. Processing: The front-end parses and displays the data.
5. Error Handling: If the API fails, error codes like 401 Unauthorized or 404 Not Found guide debugging.
Example Request:
GET https://api.crmexample.com/users/123Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9
Example Response:
{ “id”: 123,
“name”: “Emma Johnson”,
“email”: “emma.johnson@example.com”,
“status”: “active”
}This structure highlights how an API integration bridges applications while maintaining data security and structure.
Step-by-Step Guide: Building an API Integration Example
Here’s how developers can build a simple integration using a RESTful API:
1. Identify the API Endpoint: Read the API documentation to locate the endpoint (e.g., /users, /products, /orders).
2. Obtain Authentication Credentials: Most APIs use API keys, OAuth tokens, or JWTs to verify requests.
3. Make a Request: Use tools like fetch() in JavaScript or requests in Python to send requests.
fetch(‘https://api.example.com/users’, { headers: { ‘Authorization’: ‘Bearer ‘ }
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data));4. Handle Responses: Check for status codes: 200 (OK), 201 (Created), or errors like 401, 404, or 500.
5. Parse and Display Data: Process the JSON data for visualization in the front-end.
6. Implement Error Handling: Always include fallback logic for failed API calls or network errors.
Common Challenges in API Integration & How to Overcome Them?
While APIs simplify integration, developers face challenges such as:
- Authentication Errors: Invalid or expired tokens cause 401 errors. Use token refresh mechanisms.
- Rate Limits: Many APIs cap requests per minute. Implement retries or caching strategies.
- Data Format Mismatch: Ensure correct content types (e.g., application/json).
- Network Failures: Use retry logic and exponential backoff for transient issues.
- Versioning Issues: Always specify API versions to maintain compatibility.
Read More: What Is API Automation Testing?
Debugging & Testing API Integrations
Testing is crucial for verifying endpoint responses, data accuracy, and security compliance. Manual and automated testing methods ensure reliable integration.
Manual Testing Tools:
- Postman: Popular tool for sending requests and visualizing responses.
- Curl: Command-line utility for quick testing.
Automated Testing:
Integration tests validate API workflows within CI/CD pipelines. Frameworks like Jest (JavaScript) or PyTest (Python) are often used.
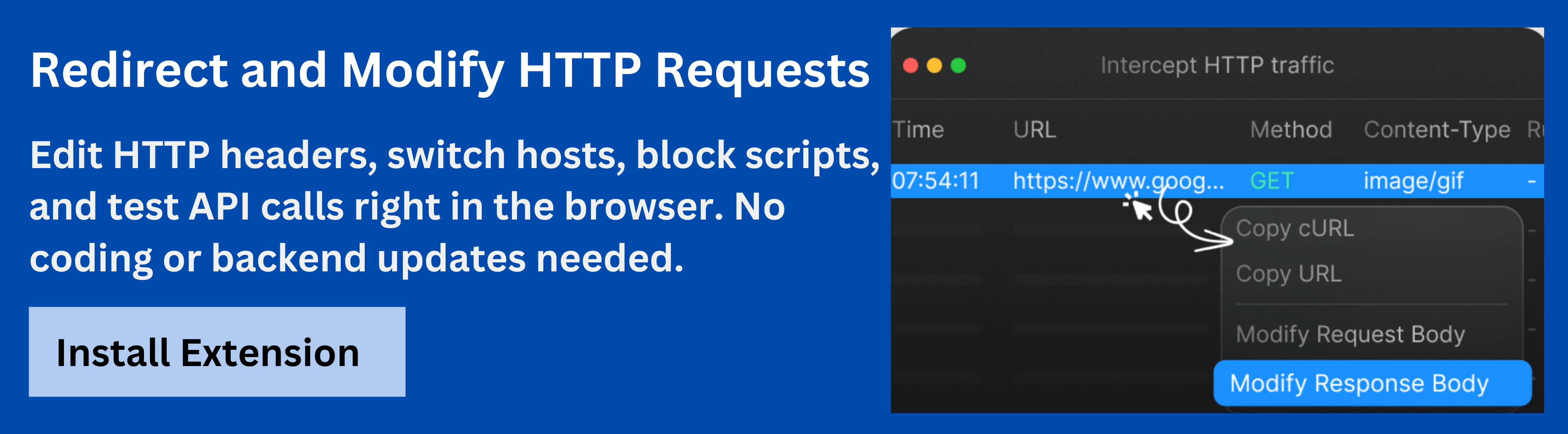
Using Requestly API Client for Debugging and Simulation
TheRequestly API Client is an advanced tool for developers who need to debug, intercept, and test APIs directly within the browser. It allows developers to:
- Intercept API requests and responses in real-time.
- Mock APIs without needing backend availability.
- Modify request parameters, headers, or responses dynamically to simulate different test conditions.
- Visualize API responses for quick debugging.
For instance, when testing a payment integration, developers can use Requestly to alter response codes or payloads to observe how the frontend reacts. This makes it an invaluable addition to the developer toolkit for building and maintaining stable API integrations.
Best Practices for API Integration
To ensure efficient and secure integrations:
- Use HTTPS: Always encrypt communication between client and server.
- Handle Errors Gracefully: Provide meaningful error messages and fallback mechanisms.
- Implement Caching: Reduce redundant API calls to improve performance.
- Respect Rate Limits: Adhere to the API provider’s request quota.
- Monitor and Log: Track request failures and performance metrics.
- Maintain Version Control: Specify API versions in URLs or headers.
Future Trends & Advanced Topics for API Integration Example
API integrations continue to evolve with modern technologies:
- Serverless APIs: Using platforms like AWS Lambda or Google Cloud Functions for cost-effective scalability.
- Event-Driven Integrations: Employing webhooks and streaming APIs for real-time data synchronization.
- AI-Powered Integrations: Leveraging AI APIs (like OpenAI or AWS AI Services) to enhance functionality.
- API Security Enhancements: Implementing OAuth 2.1, mutual TLS, and API gateways for secure communication.
- Low-Code Integration Platforms: Tools like Zapier and Make are simplifying integration development for non-coders.
Summary
API integration forms the backbone of interconnected digital systems, driving automation, scalability, and innovation. Whether connecting internal microservices or external third-party APIs, understanding the fundamentals-request handling, authentication, error management, and testing-is key to success.
By leveraging tools like Requestly API Client for debugging and BrowserStack for cross-environment testing, developers can create robust, efficient, and secure integrations that perform flawlessly across use cases.