GraphQL and PostgreSQL are a powerful duo for building modern, data-driven applications. While Postgres offers reliability and advanced querying, GraphQL provides a flexible API layer to fetch exactly the data you need.
GraphQL is a query language for APIs that lets clients request exactly the data they need, making data fetching more efficient and flexible compared to REST. PostgreSQL, on the other hand, is a powerful, open-source relational database known for its reliability, scalability, and advanced features like JSON support and complex queries. Benefits to use PostgreSQL with GraphQL This article explores how GraphQL and PostgreSQL work together, the different ways to integrate them, and best practices to build efficient, scalable applications. Combining GraphQL with PostgreSQL unlocks a powerful stack for building modern applications. While GraphQL ensures flexibility in fetching data, PostgreSQL brings proven reliability and advanced database features to the backend. Together, they provide the perfect balance of performance, scalability, and developer productivity. Key Reasons to Use PostgreSQL with GraphQL There are multiple ways to connect GraphQL with PostgreSQL, and the right choice depends on your project’s needs, complexity, and team expertise. 1. Custom Resolvers with SQL/Query Builders You can write your own GraphQL resolvers that directly query PostgreSQL using libraries like pg (Node.js) or query builders such as Knex. 2. ORM-Based Integration Use ORMs like Prisma, TypeORM, or Sequelize to map database models to GraphQL resolvers. 3. Auto-Generated GraphQL APIs Tools like Hasura and PostGraphile generate a GraphQL API automatically from your PostgreSQL schema. Getting started with GraphQL and PostgreSQL is easier than it seems. In this section, we’ll set up a simple project that connects a GraphQL server to a PostgreSQL database. Prerequisites First, create a new Node.js project and install the required dependencies: Next, set up a simple users table inside your PostgreSQL database: Overview
Why Use PostgreSQL with GraphQL?
Approaches to Integrating GraphQL with PostgreSQL
Setting Up a Basic GraphQL + PostgreSQL Project
1. Initialize the Project
mkdir graphql-postgres-demo && cd graphql-postgres-demo
npm init -y
npm install apollo-server graphql pg2. Create the Database and Table
CREATE TABLE users (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100),
email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE
);
INSERT INTO users (name, email)
VALUES (‘Alice’, ‘alice@example.com’), (‘Bob’, ‘bob@example.com’);
This gives us a basic dataset to query from GraphQL.
3. Define the GraphQL Schema
Now, define a GraphQL schema that represents the data in your database:
const { gql } = require(‘apollo-server’);
const typeDefs = gql`
type User {
id: ID!
name: String!
email: String!
}
type Query {
users: [User!]!
}
`;
module.exports = typeDefs;
This schema tells GraphQL that you have a User type and a query to fetch all users.
4. Write the Resolver
Resolvers are the functions that fetch data for each GraphQL field. Connect PostgreSQL with GraphQL by creating a resolver that queries the database:
const { Pool } = require(‘pg’);
const pool = new Pool({
user: ‘postgres’,
host: ‘localhost’,
database: ‘demo’,
password: ‘password’,
port: 5432,
});
const resolvers = {
Query: {
users: async () => {
const result = await pool.query(‘SELECT * FROM users’);
return result.rows;
},
},
};
module.exports = resolvers;
5. Start the GraphQL Server
Finally, tie everything together in an entry point file and launch your server:
const { ApolloServer } = require(‘apollo-server’);
const typeDefs = require(‘./schema’);
const resolvers = require(‘./resolvers’);
const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers });
server.listen().then(({ url }) => {
console.log(`Server ready at ${url}`);
});
Run the server:
node index.js
6. Test Your GraphQL API
Open the Apollo Playground at the printed server URL and run:
query {
users {
id
name
email
}
}You should see the data from your PostgreSQL table returned as JSON.
Best Practices for Security Performance Considerations
When combining GraphQL with PostgreSQL, it’s important to think about both security and performance early in the development process.
Security Best Practices
- Least-privilege database roles: Use dedicated DB users with only the permissions they need (e.g., read-only vs. write).
- Row-Level Security (RLS): Enforce per-user or per-tenant data access directly in Postgres.
- Protect against over-fetching: Apply query depth and complexity limits to prevent abusive queries.
- Authentication & Authorization: Use short-lived tokens (e.g., JWTs) and implement fine-grained access control in resolvers.
- Secure by default: Always use TLS, manage secrets properly, and enable logging/auditing for sensitive operations.
Performance Considerations
- Avoid N+1 queries: Use batching techniques or tools like DataLoader to reduce repeated lookups.
- Efficient pagination: Prefer cursor-based pagination over offset-based for large datasets.
- Indexing strategy: Create indexes that match your most common filters and sorts.
- Connection pooling: Use a pool manager (e.g., PgBouncer) to handle concurrency efficiently.
- Caching layers: Combine short-lived in-memory caching, database-level optimizations (like materialized views), and CDN caching for queries where possible.
- Monitoring & observability: Track slow queries, GraphQL resolver performance, and database load to spot bottlenecks early.
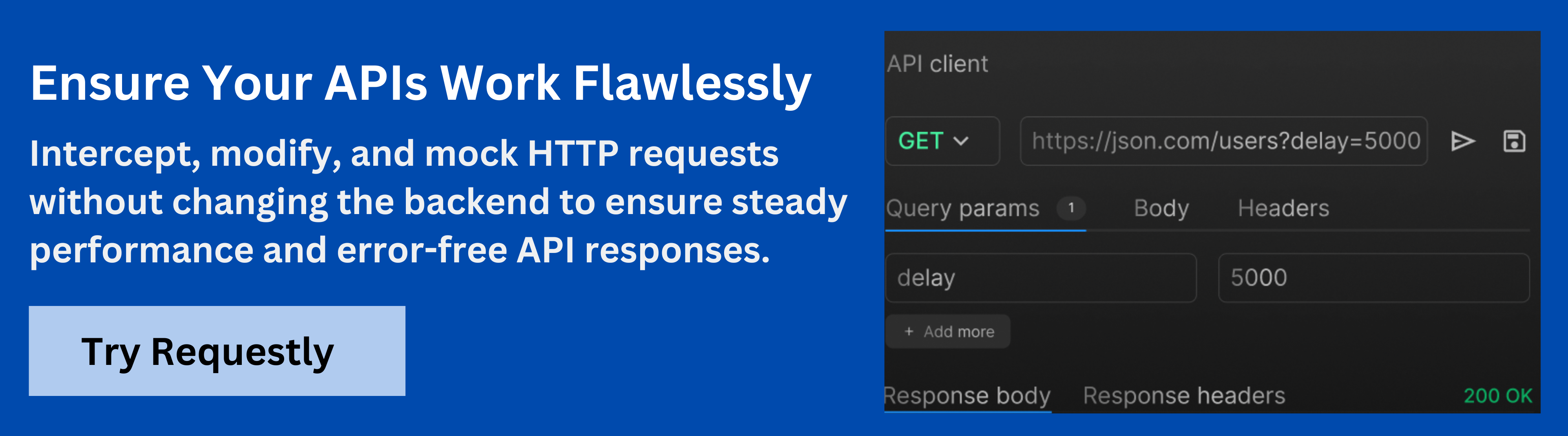
Debug GraphQL APIs with Requestly
Building a GraphQL API on top of PostgreSQL is powerful, but debugging queries and responses can often be tricky. This is where Requestly by BrowserStack comes in, it lets you intercept, modify, and test GraphQL requests directly in your browser, speeding up development and troubleshooting.
How Requestly Helps
- Inspect requests and responses: Easily view and tweak GraphQL queries, variables, and headers without changing backend code.
- Mock APIs: Simulate responses to test UI states, error handling, and edge cases before the backend is ready.
- Test authentication flows: Swap tokens or headers to validate role-based access and row-level security policies.
- Simulate network conditions: Reproduce slow queries, timeouts, or failures to see how your application behaves under stress.
- Share rules with your team: Keep debugging consistent by sharing mocks, rewrites, or redirects.
Since Postgres often powers multi-tenant and complex relational data, debugging authorization, query performance, and error paths is crucial. Requestly acts as a companion tool to your stack, helping developers quickly test different scenarios without touching backend logic.
Conclusion
GraphQL and PostgreSQL together form a powerful foundation for building modern, data-driven applications. PostgreSQL offers reliability, rich data modeling, and advanced querying capabilities, while GraphQL provides the flexibility to fetch exactly the data your clients need. Whether you choose to integrate through custom resolvers, ORMs, or auto-generated APIs, the key is balancing control, speed, and scalability.
By following best practices for security and performance, and using tools like Requestly to debug and test GraphQL APIs efficiently, developers can ship robust features faster while keeping applications secure and optimized.