Smoke testing became necessary the moment I realized how often a “ready” build wasn’t actually usable. I had spent time running detailed tests, only to find the app crash on launch or fail at a basic login. Those failures raised an obvious question: why dive deep when the fundamentals aren’t even stable?
That’s exactly what smoke testing addresses. It acts as a quick checkpoint to confirm that core functionality works before moving on to deeper testing. This article explains why smoke testing is needed, what it validates, and how it prevents wasted effort later in the test cycle.
Overview
What is Smoke Testing?
Smoke testing is a preliminary testing process that checks if the critical features of an application work properly before proceeding with more detailed testing.
Benefits of Smoke Testing
- Identifies critical issues that could prevent further testing or development.
- Saves time by ensuring only stable builds are tested in-depth.
- Helps catch basic functionality problems before investing in more detailed tests.
- Provides early feedback to developers and allows for faster fixes.
- Reduces testing time by focusing on high-risk areas first.
Levels of Smoke Testing
- Unit Testing: Checks the basic functionality of individual components.
- Integration Testing: Verifies that different components work well together.
- System Testing: Ensures the entire system functions as expected.
- Acceptance Testing: Confirms that the system is ready for user acceptance testing.
- Build Verification Testing (BVT): Checks the stability of new builds before further testing.
- Regression Testing: Ensures core features remain intact after updates or bug fixes.
This guide discusses Smoke Testing, its types, how it differs from other types of Testing, and how to perform Smoke Testing.
What is Smoke Testing?
Smoke Testing is a software testing technique that basically determines whether a new build delivered by the Development team is bug-free or not. It gives the go-ahead to the QA team to move further with their testing rounds.
It is also known as Confidence Testing or Build Verification / Build Promotion Testing and is made up of a collection of tests that are performed on each build received during the software development life cycle to determine its health.
In simple words, Smoke tests verify whether the most important features work as expected and that there are no showstopper issues in the build that can potentially lead to blocking the entire testing team. It helps in deciding if the build is flawed or not and hence, prevents the entire team from wasting time or resources.
Why is Smoke Testing important?
Smoke Testing is important because it:
- Ensures that the product is testable and doesn’t let the QA teams get blocked.
- Uncovers major issues at the beginning of the sprint itself. This ensures that both Development and QA teams have enough time to fix and test the issue further.
- Makes sure that the critical or acute functionalities of the product are working fine.
- Helps determine the system or the application’s stability.
Goals of Smoke Testing
Smoke testing serves as a quick initial check to ensure that an application’s core functionality is stable before deeper testing begins. Here are the key goals:
- Verify Critical Functionality: Ensure core features work as expected before more detailed testing.
- Identify Major Defects Early: Catch show-stopping issues early in the development cycle to save time.
- Ensure Build Stability: Confirm that the new build does not break essential functionality.
- Improve Testing Efficiency: Quickly assess an application’s health to determine whether it’s ready for further testing.
- Provide Quick Feedback: Offer developers fast insights about the build’s stability.
Michael Bolton — Software testing author, international speaker, and context-driven testing advocate, consistently explains smoke testing as a decision-making tool that helps teams determine whether continued testing is worthwhile, especially in early build validation.
Also Read: Manual Testing vs Automation Testing
Types of Smoke Testing
There are three different types of Smoke Testing:
- Manual Testing: As the name suggests, in the case of Manual Testing, QA teams conduct Smoke Testing manually. QA teams write, develop and execute their smoke tests manually for existing as well as new features. Although this is very time taking, Manual Testing omes in with the benefit of human intelligence and acumen.
- Automated Testing: In this case, QA teams use automation tools to perform the tests instead of doing the tests on their own manually. Automation Testing can be a boon to the entire organization, as it saves a significant amount of time and resources. Additionally, it saves the testers from doing the mundane tasks of doing the same tests over and over again.
- Hybrid Testing: Hybrid Testing, as the name suggests, is a combination of both Manual and Automated tests. It involves automation in some cycles of Smoke Testing as well as some amount of Manual intervention by the testers to test the application. Hybrid Testing is said to be better than the other two as it has the attributes of both methods and hence, can prove to be advantageous.
Learn More: How to move from Manual to Automation Testing
Different Levels of Smoke Testing
Smoke testing can be applied at various levels of the software development lifecycle, ensuring that critical functionalities are working before deeper testing begins. Here are the key levels:
- Unit Testing: Checks the basic functionality of individual modules or components. This ensures they work as intended before integrating with other parts of the system.
- Integration Testing: Tests the interactions between integrated components or modules. The goal is to ensure smooth communication and data flow across the system.
- System Testing: Verifies the critical functionalities of the entire system. This confirms that the system works as expected before moving to more detailed testing.
- Acceptance Testing: Ensures the system is ready for user acceptance testing (UAT). It focuses on verifying that basic workflows function as expected for end-users.
- Build Verification Testing (BVT): Conducted on new builds to check their stability. This determines if the build is ready for further testing and helps identify flaws early.
- Regression Testing: Confirms that critical functionalities remain intact after bug fixes or updates. This ensures that changes do not negatively affect core features.
Smoke Test Cases: Example
The below table illustrates a scenario of an E-Commerce website and some sample Smoke Tests for the same.
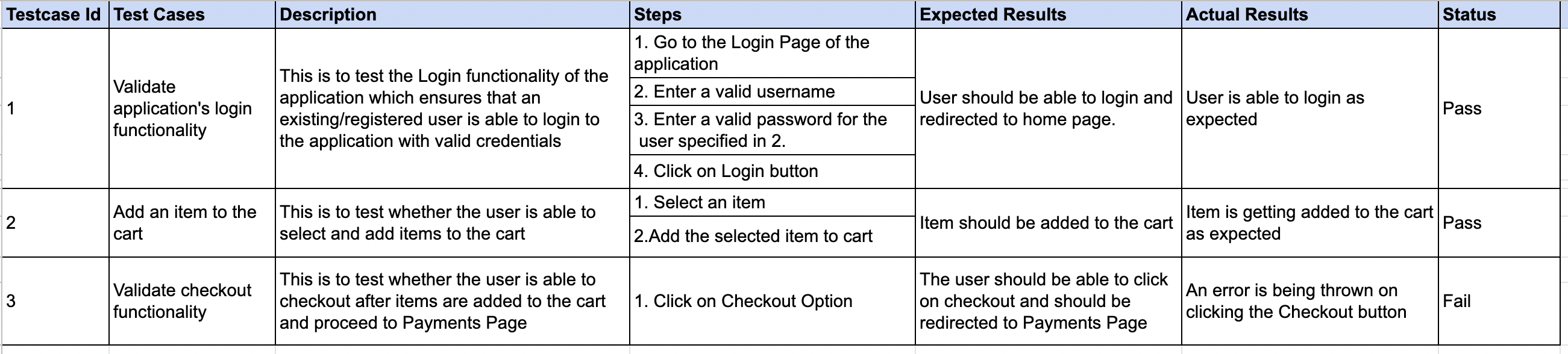
When to perform Smoke Testing?
Smoke testing should be conducted whenever new features or updates are added to the software, and a new build is delivered. It ensures that existing key functionalities are not impacted and that issues do not block new functionalities.
Once a new build is provided, QA teams run smoke tests to verify the stability of essential features. If the tests pass, the build is promoted for further testing. If they fail, the build is rejected, and the previous stable version remains in use until the issues are fixed.
Example: After receiving a build with a fix for the checkout functionality, smoke tests should ensure that login and cart features still work correctly and verify the checkout fix.
What happens if Smoke Testing is not performed?
Skipping smoke testing early on can lead to critical issues being discovered later in the development cycle, resulting in higher costs in terms of time, resources, and money. These issues can also delay the release and negatively impact the product’s reputation.
Learn More: What is Smoke Testing tool?
Differences between Smoke and Sanity Testing
Smoke Testing and Sanity Testing are both important types of software testing, but they differ in their purpose and scope.
While smoke testing ensures an app’s basic functionality, sanity testing checks whether the new changes work as expected.
| Parameter | Smoke Testing | Sanity Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Ensures critical functionalities are working as expected | Verifies that existing functionalities and bug fixes work as expected |
| Subset of | Acceptance Testing | Regression Testing |
| Performed by | Developers or Testers | Primarily Testers |
| Documentation | Documented | Not Documented |
| Stability | Can be unstable or stable | Always stable |
| Test Scripting | Scripted | Not Scripted |
| Frequency | Performed when a new build is released | Can be done for every new build or daily for environment health checks |
Differences between Smoke Testing and Regression Testing
Smoke Testing and Regression Testing are performed to verify functionality but serve different purposes.
Smoke testing is a preliminary check, while regression testing ensures the changes don’t affect existing functionality.
| Parameter | Smoke Testing | Regression Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Surface-level testing to ensure build and environment stability | Deep-level testing to ensure overall product functionality |
| Performed by | Developers or Testers | Primarily Testers |
| Cost | Low cost and resource-intensive | High cost due to the comprehensive nature of tests |
| Time and Effort | Quick, requires less manpower | Time-consuming, requires more manpower |
| Test Scripting | Scripted | Not Scripted |
| Frequency | Performed on every new build | Performed on stable builds throughout the development lifecycle |
| Acceptance or Rejection | Determines if the build is accepted or rejected | Ensures existing functionality remains intact after changes |
Automation and Smoke Testing
Automated smoke tests are essential for improving efficiency, especially since smoke tests need to be repeated with each new build.
Manual testing for every new build can be time-consuming, particularly for large-scale applications.
Key Benefits of Automated Smoke Testing:
- Faster Execution: Automation reduces the time spent running smoke tests, speeding up the testing cycle.
- Consistency: Automated tests ensure consistent results every time, eliminating human errors.
- Increased Coverage: Automation enables the execution of a larger number of test cases across different environments.
- Quick Feedback: Issues can be identified and addressed immediately, reducing overall testing delays.
- Cost-Efficient: Reduces the burden on testers, allowing them to focus on more complex tests.
Also Read: 6 Testing Tactics for Faster Release Cycles
Automating smoke tests accelerates the development process and ensures a more reliable, efficient workflow, minimizing the chances of bugs making it into production.
How to Perform Automated Smoke Testing?
Automated smoke testing helps ensure basic functionality without manual intervention. Here’s a simplified process:
- Select a Testing Framework: Choose the right framework for the project. Some popular options include:
- Selenium: Supports multiple scripting languages and integrates with Maven, Ant, etc.
- Appium: For mobile app testing across Android and iOS.
- REST Assured: Validates REST services in Java.
- Maven: Manages Java projects and testing dependencies.
- BrowserStack: Provides cloud-based testing on 3500+ real devices and browsers, integrating with various CI tools.
- Select a Test Runner (Optional): If your framework doesn’t come with a test runner, consider options like TestNG or Cucumber for seamless integration.
- Write the Code: Develop test scripts and utilities, then organize them into test suites (e.g., Smoke, Sanity, Regression).
- Integrate with CI Platform: Integrate tests with CI tools like Jenkins, CircleCI, or GitLab CI for automated execution during build processes.
- Schedule or Trigger Tests: To ensure continuous testing, set up automated test execution either at scheduled times or triggered by new builds.
Smoke Testing Tools
Smoke testing tools verify the stability of critical functionalities in an application. These tools offer features like automation, cross-platform compatibility, and detailed reporting to ensure faster detection of issues before further testing.
Here are the top tools for smoke testing:
1. BrowserStack
BrowserStack is a leading cloud-based testing platform that allows teams to perform automated and manual smoke tests across thousands of real devices and browsers. Its seamless integration with popular tools makes it a reliable choice for comprehensive testing.
Key Features:
- Access to over 3,500 real devices and browsers for cross-platform testing.
- Integration with Selenium, Appium, and other automation tools.
- Automated parallel testing to save time.
- Detailed logs, screenshots, and video recordings for debugging.
Pros: Easy to use, no maintenance required, and supports CI/CD pipelines.
2. Selenium
Selenium is an open-source automation tool widely used for testing web applications. It supports multiple programming languages and browsers, making it highly versatile for smoke testing.
Key Features:
- Cross-browser testing support.
- Integration with programming languages like Java, Python, and C#.
- Works seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines.
- Extensive community support and third-party libraries.
Pros: Free, flexible, and highly customizable.
Cons: Requires programming knowledge and lacks built-in reporting tools.
3. Apache JMeter
Primarily a performance testing tool, JMeter is also effective for API and functional smoke testing. It’s especially useful for testing backend systems.
Key Features:
- Load and performance testing capabilities.
- Supports multiple protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP.
- Plugin support for extended functionality.
- Ideal for API testing and backend validations.
Pros: Open-source, scalable, and supports diverse testing needs.
Cons: Steep learning curve for beginners and limited GUI functionalities.
4. TestNG
TestNG is a powerful Java-based testing framework designed for automated functional, unit, and smoke testing. It is ideal for structured testing processes.
Key Features:
- Parallel execution of test cases.
- Built-in annotations for test configuration.
- Detailed reporting with logs and metrics.
- Integration with CI/CD tools like Jenkins and Maven.
Pros: Flexible, efficient, and supports detailed reporting.
Cons: Java-specific and requires programming expertise.
Read More: How to Automate TestNG tests in Selenium
5. Postman
Postman is a popular tool for API testing, but it also serves as an efficient platform for smoke testing API endpoints and integrations.
Key Features:
- Simple API request creation and execution.
- Automated testing with scripting capabilities.
- Comprehensive reports for API responses.
- Collaboration tools for team-based testing.
Pros: User-friendly and robust for API smoke testing.
Cons: Limited functionality for UI-based testing.
These tools offer diverse capabilities, enabling effective and reliable smoke testing across web applications, APIs, and systems.
Metrics to Measure in Smoke Testing
Measuring the right metrics helps determine whether smoke testing is actually preventing unstable builds from moving forward or merely acting as a checkbox activity. The following metrics are commonly used to evaluate the effectiveness of smoke tests.
- Smoke test pass rate: This measures the percentage of smoke test executions that pass for a given build. A consistently low pass rate may indicate unstable builds, poor build quality, or unclear smoke test criteria.
- Build rejection rate due to smoke test failures: This tracks how often builds are rejected after failing smoke tests. A high rejection rate highlights issues earlier in the pipeline, while a sudden spike may point to recent changes impacting core functionality.
- Time to detect critical failures: This metric measures how quickly smoke tests identify blocking issues after a build is deployed. Faster detection reduces wasted effort in downstream testing and speeds up feedback to developers.
- Smoke test execution time: Execution time reflects how long it takes to complete the smoke test suite. Smoke tests should remain short and focused; increasing execution time often signals scope creep or poorly optimized tests.
- Defect leakage beyond smoke testing: This tracks the number of critical defects found later in regression or system testing that should have been caught during smoke testing. High leakage indicates gaps in smoke test coverage.
- Frequency of smoke test runs: This measures how often smoke tests are executed, such as per build, per deployment, or per environment. Infrequent execution reduces their value as an early validation mechanism.
- Environment-specific failure rate: This metric identifies whether smoke tests fail more often in specific browsers, devices, or environments. It helps detect environment-related stability issues early.
- Automation stability of smoke tests: This measures how often smoke tests fail due to test issues rather than product defects. Flaky smoke tests reduce trust and slow down release decisions.
Advantages of Smoke Testing
Smoke testing helps identify major issues early in the development process and ensure that only stable builds move forward to more detailed testing. Here are the key advantages.
- Early Detection of Critical Issues: Smoke testing catches major problems early on, which prevents time from being wasted on more in-depth tests for a broken build. This helps developers focus on fixing the core issues first before moving forward.
- Faster Feedback: With smoke testing, developers receive quick results on whether the essential features of the application are functioning. This helps accelerate the development process and allows developers to resolve issues sooner.
- Improves Test Planning: Smoke testing highlights the critical areas of the application that need more detailed attention. It allows testers to plan subsequent tests more effectively and ensure that efforts are directed where they are most needed.
- Reduced Integration Complexity: Smoke testing helps identify integration issues early by ensuring that core components work together. This makes the later integration process smoother and reduces the likelihood of complications as the system grows.
- Increases Overall Testing Effectiveness: Smoke testing ensures essential features work properly before detailed testing begins. By confirming the stability of the core system, it reduces the chances of failures during deeper tests and allows teams to focus on more complex scenarios with greater confidence.
Challenges in Smoke Testing
Smoke testing is essential for verifying a system’s basic functionality, but it has certain challenges and limitations that can impact its effectiveness.
1. Limited Test Coverage: Smoke tests focus only on critical functionalities and do not cover the entire application. This can leave less obvious defects undetected.
Read More: How to ensure maximum Test Coverage
2. Time Constraints: While smoke testing is designed to be quick, tight deadlines might result in rushed execution, potentially overlooking key issues.
3. Dependency on Stable Builds: Smoke testing requires a stable build to be meaningful. Frequent build failures or incomplete builds can disrupt the testing process.
4. Inadequate Depth: These tests check only the surface-level functionality without delving into edge cases or detailed scenarios, risking unnoticed bugs.
5.Lack of Automation: If not automated, repeated execution of smoke tests for every build can become time-consuming and error-prone.
6. High Setup Costs for Automation: Automating smoke tests can require significant initial effort and resources, particularly in complex systems with frequent changes.
7. Environment-Specific Issues: Differences in environments (for example, development, staging, production) can result in undetected issues that only surface in later stages.
8. Overlooking Non-Critical Components: Non-critical features or backend processes might be skipped during smoke testing, leading to unnoticed bugs in those areas.
9. Subjectivity in Test Case Selection: Deciding which functionalities are “critical” can vary between teams, potentially missing vital components in the test suite.
10. Reliance on Correct Test Scripts: Inaccurate or poorly written smoke test scripts can produce false positives or negatives, undermining confidence in the results.
Best Practices for Smoke Testing
To maximize Smoke Testing’s efficiency and effectiveness, adopt a set of best practices to streamline the process, improve accuracy, and quickly identify major issues before deeper testing begins.
- Define Critical Features to Test: Focus on the most important functionalities of the application, such as login, navigation, and basic workflows, to ensure they work before proceeding to detailed testing.
- Automate Repetitive Smoke Tests: Use automation tools like BrowserStack or Selenium to execute smoke tests consistently and quickly for each new build or release.
- Perform Smoke Tests on Stable Builds: Ensure the build is stable enough to execute tests; unstable or incomplete builds may lead to misleading results.
- Run Tests Early and Frequently: Conduct smoke tests as soon as a new build is deployed and repeat them after any significant updates or fixes to detect critical issues early.
- Use Real Environments and Devices: Test on environments and devices that closely replicate real-world usage to identify environment-specific issues early. Tools like BrowserStack can be useful for cross-platform testing.
- Prioritize Speed Over Depth: Keep smoke tests lightweight and fast, focusing on essential workflows rather than in-depth testing of edge cases.
- Maintain a Reusable Test Suite: Regularly update the test suite to reflect changes in critical features and workflows, ensuring relevance and reusability over time.
- Integrate with CI/CD Pipelines: Automate smoke testing as part of your CI/CD pipeline to quickly validate new builds and ensure continuous delivery quality.
- Monitor and Analyze Results: Use logs, screenshots, and reports to review failures and quickly identify build stability issues. Maintain proper documentation for debugging and improvement.
- Communicate Results Promptly: Share the outcomes of smoke testing with the development and QA teams immediately to address critical issues without delay.
Conclusion
Smoke testing is crucial in the software development lifecycle, but is often overlooked due to time and resource constraints. However, investing in smoke testing and its automation yields long-term benefits, especially as the product scales.
QA teams should prioritize automating smoke testing to save time, improve resource management, and ensure a stable product.
Testing on real devices is essential for accurate results. BrowserStack offers access to 3500+ real devices and browsers, ensuring comprehensive and realistic testing.