CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) errors occur when a browser blocks requests to a resource from a different origin due to security restrictions.
These obstacles can interrupt data flow between applications and servers, making it essential for developers to identify and correct issues promptly for secure and reliable service integration.
CORS errors present a distinctive challenge in API testing and web development, surfacing when browsers block requests between different origins due to missing or misconfigured headers.
Overview
How to Identify CORS Errors
- Check browser console logs for CORS policy error messages.
- Use network tab in DevTools to inspect blocked requests.
- Look for HTTP status codes like 403 or 401.
- Verify if the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header is missing.
How to Fix CORS Errors
- Configure the server to include CORS headers (Access-Control-Allow-Origin).
- Allow specific HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) in server settings.
- Enable CORS for required origins only (avoid * in production).
- Use proxies or API gateways to handle cross-origin requests safely.
This article explores CORS errors, their causes, types, and the methods to identify and resolve them.
What are CORS Errors?
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) errors, commonly known as CORS errors, arise when a web application attempts to request resources from a different domain or origin without the necessary permissions.
These errors are enforced by browsers as a security measure called the same-origin policy, which restricts web pages from making requests to a different origin to prevent malicious attacks.
When the server does not include the necessary CORS headers, such as Access-Control-Allow-Origin, in its response to explicitly allow the requesting domain, the browser blocks the request, leading to a CORS error.
These errors often occur during API testing or when a frontend tries to communicate with a backend hosted on a different domain, port, or protocol.
Why Do CORS Errors Occur?
When a web application tries to access resources from another origin without explicit permission, the browser blocks the request and throws a CORS error.
The primary reasons CORS errors happen include:
- Misconfigured CORS headers: The server fails to send the correct Access-Control-Allow-Origin header or sends an incorrect value that does not match the requesting origin.
- Preflight request failures: For HTTP methods other than simple GET or POST, browsers send a preflight OPTIONS request to check permissions. If this preflight fails due to missing or incorrect headers, a CORS error results.
- Different origins: If the client’s origin (domain, port, or protocol) doesn’t align with what the server allows, requests are blocked.
- Missing or invalid API keys: Servers may reject requests lacking valid credentials or API keys, causing CORS errors.
- Use of unsupported request protocols: Requests sent over non-HTTP(S) schemes like local files (file://) generate CORS errors since CORS applies only to HTTP/HTTPS.
- Multiple conflicting CORS headers: Sending more than one Access-Control-Allow-Origin header leads to errors, as only one is allowed.
How to Identify CORS Errors
Detecting CORS errors effectively is the first step toward resolving them and ensuring smooth cross-origin communication. Here are key approaches developers use to identify these errors:
- Monitor Browser Console for Error Messages: Modern browsers clearly report CORS errors in the developer console, often stating missing or disallowed Access-Control-Allow-Origin headers or failed preflight requests.
- Inspect Network Requests: Use the Network panel in browser developer tools to examine requests and responses. Look specifically at the response headers to check if required CORS headers like Access-Control-Allow-Origin, Access-Control-Allow-Methods, and Access-Control-Allow-Headers are present and correctly configured.
- Check Preflight Request Status: For HTTP methods such as PUT or DELETE, browsers issue a preflight OPTIONS request. Identifying if these requests fail or lack proper headers is crucial.
- Look for Multiple or Conflicting CORS Headers: Browsers reject responses with duplicate Access-Control-Allow-Origin headers or headers that do not match the requesting origin.
- Confirm Request Origins and Protocols: Verify that requests are made over supported protocols (HTTP/HTTPS) and that the origin specified matches what the server allows.
How CORS Helps to Prevent CORS Errors
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is a security mechanism implemented by web browsers that dictates how resources can be requested from a domain different from the one that served the web page.
It acts as a controlled relaxation of the strict Same-Origin Policy, enabling legitimate cross-origin requests while protecting users from malicious activities.
When a web application initiates a cross-origin request, the browser automatically includes an Origin header that specifies the domain of the requesting site.
The server receiving this request evaluates the Origin and responds with specific CORS headers indicating whether the request is permitted. Key headers include:
- Access-Control-Allow-Origin: Specifies which origins are allowed to access the resource.
- Access-Control-Allow-Methods: Lists allowed HTTP methods such as GET, POST, or PUT.
- Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Indicates which custom headers can be used in the request.
- Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: Indicates whether the browser can include credentials like cookies.
For certain types of requests, such as those using methods like PUT or DELETE or including custom headers, browsers perform a preflight OPTIONS request to verify permissions before sending the actual request.
The server must respond positively to this preflight request with the appropriate CORS headers for the browser to proceed.
If the server’s response permits the origin, methods, and headers from the request, the browser allows the web application to access the resource. Otherwise, it blocks the request and triggers a CORS error, preventing unauthorized cross-origin access.
This robust handshake between the browser and server ensures that cross-origin communications are both secure and flexible, reducing the risk of malicious cross-site attacks while enabling legitimate resource sharing in modern web applications.
Read More: What is CORS, and How to Bypass It?
How to Fix CORS Errors
Fixing CORS errors involves ensuring correct configuration on the server side and sometimes implementing workarounds on the client side to accommodate cross-origin policies. Below are key approaches to resolve these errors:
Configure Server to Allow CORS
The most effective way to fix CORS errors is by configuring the backend server to include the appropriate CORS headers in responses. This typically involves adding the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header to specify which origins can access the resources. The server may also need to send headers such as Access-Control-Allow-Methods, Access-Control-Allow-Headers, and Access-Control-Allow-Credentials depending on the request type. For example:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https://example.com
Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET, POST, PUT
Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Content-Type, Authorization
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
Use a Proxy Server
If the server cannot be modified (e.g., third-party APIs), a proxy server can be used to relay requests. The client sends requests to the proxy, which then makes calls to the external server. This bypasses CORS restrictions since the proxy and client typically share the same origin.
Serverless Functions as a Proxy
Cloud serverless functions (e.g., AWS Lambda, Azure Functions) can act as middleware to safely perform cross-origin requests and serve data to the client without hitting CORS restrictions.
Development Workarounds
During development, browser extensions like CORS Unblock can be used temporarily to bypass CORS restrictions, though this is not recommended for production since it only affects the local environment.
Handle Preflight Requests Properly
Ensure the server correctly responds to preflight OPTIONS requests with necessary CORS headers, especially for methods like PUT, DELETE, or when custom headers are used.
Avoid Wildcard with Credentials
When using credentials (cookies, HTTP authentication), never use a wildcard (*) in Access-Control-Allow-Origin. Instead, explicitly specify the allowed origin.
By implementing these strategies, developers can effectively eliminate CORS errors, enabling smooth and secure communication between web applications and APIs across different origins.
How Requestly Helps Resolve Corrs Errors
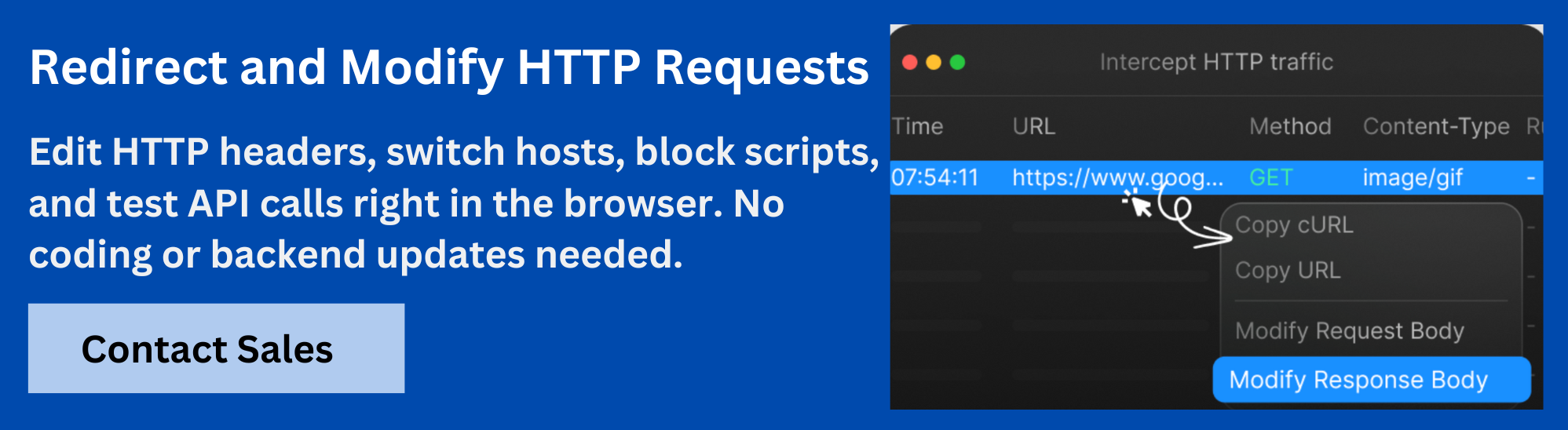
Requestly by BrowserStack offers a range of powerful features that make identifying, troubleshooting, and overcoming CORS errors straightforward and efficient.
Requestly HTTP Interceptor is a lightweight browser extension that lets you inspect, modify, and debug HTTP requests and responses in real time. It helps developers test APIs, simulate scenarios, and troubleshoot issues faster without changing backend code.
- Intercept and modify HTTP requests and responses directly within the browser to troubleshoot CORS issues instantly.
- Add, remove, or override CORS-related headers like Access-Control-Allow-Origin to bypass restrictions during development or testing.
- Redirect API requests or mock responses to replicate scenarios without backend changes.
- Provide real-time debugging capabilities, enhancing productivity by quickly identifying and resolving CORS errors.
- Support various rule types and flexible targeting options for precise control over which requests to modify.
- Include session recording features to reproduce and share debugging steps effectively.
Best Practices to Avoid CORS Errors
To proactively prevent CORS errors and ensure smooth cross-origin communication, developers should adopt the following best practices:
- Specify Allowed Origins Explicitly: Avoid using wildcards (*) in the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header, especially in production environments. Instead, specify exact domains that are permitted to access your resources to enhance security.
- Configure Server to Properly Handle CORS Requests: Ensure your server responds correctly to both simple and preflight (OPTIONS) requests by including all necessary CORS headers such as Access-Control-Allow-Methods and Access-Control-Allow-Headers.
- Limit Allowed HTTP Methods and Headers: Restrict allowed methods and headers to only what the application requires to minimize exposure and reduce potential errors.
- Enable and Handle Credentialed Requests Carefully: If your application needs to send credentials like cookies or HTTP authentication, ensure Access-Control-Allow-Credentials is set to true and do not use wildcard origins.
- Use HTTPS across All Origins: Enforce secure HTTPS connections to prevent security issues and to comply with modern browser requirements for cross-origin requests.
- Validate and Restrict Origins on Server Side: Implement server-side checks to validate the Origin header and reject unauthorized requests even if headers appear correct.
- Test CORS Implementations Thoroughly: Use browser tools, API testing clients, and automated tests to regularly verify that your CORS setup works as expected under different scenarios.
- Avoid Reflecting Unvalidated Origins: Never dynamically echo the Origin header from incoming requests without validation, as this can introduce security vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
CORS errors occur due to browser security policies that restrict cross-origin requests to protect users from malicious actions. Resolving these errors typically involves proper server-side configuration of CORS headers or using tools to modify request and response headers during development.
Tools like Requestly HTTP Interceptor by BrowserStack provide an effective way to troubleshoot and bypass CORS issues by allowing developers to intercept, modify, and test HTTP requests and responses directly within the browser, making cross-origin development smoother and more efficient.