Blocking a URL in your browser means stopping specific websites or resources from loading. This is useful not only for avoiding specific sites but also for testing how web apps behave when resources are unavailable.
Developers often block URLs to check how their applications handle failures like missing APIs, broken images, or unavailable third-party services. Chrome, Firefox, and Safari offer different ways to block URLs, either through built-in tools or browser extensions.
Why Block URLs in Browsers?
Developers often block URLs as part of testing to check how apps handle broken or missing resources. Others block URLs to control access, improve focus, or protect users. Below are detailed reasons why you might block URLs:
- Test error handling in web apps: Developers block URLs to simulate API failures, missing scripts, or broken image links. This helps check how well an app handles errors and fallback conditions so that users do not face issues during real outages.
Read More: Bug vs Error: Key Differences
- Simulate missing third-party services: Many apps depend on external services like analytics, ads, or payment gateways. Blocking these URLs lets developers see if the app continues to function correctly when these services are unavailable or slow to respond.
Also Read: Payment Gateway Test: A Complete Guide
- Avoid distractions: People block social media sites, video platforms, or news portals to stop themselves from getting sidetracked during work or study. This helps maintain focus and improve productivity.
- Protect children: Parents often block inappropriate or harmful websites to create a safer online environment for children. This reduces the risk of exposure to unsafe content while browsing.
- Prevent security threats: Blocking known malicious URLs protects users from phishing, malware, or other security risks. This adds a layer of defense against unsafe sites that could compromise data.
- Control bandwidth or network use: In offices, schools, or shared spaces, blocking certain sites helps reduce unnecessary traffic. This ensures that the network is used for priority tasks and not wasted on unrelated browsing.
How to Block a URL in Chrome Using DevTools
You can temporarily block a URL in Chrome by using the Developer Tools. This method blocks the URL only while DevTools is open.
Step 1: Open Chrome and navigate to the webpage where the URL request occurs.
Step 2: Press Ctrl + Shift + I (Windows) or Cmd + Option + I (Mac) to open Chrome DevTools.
Step 3: Click on the Network tab in DevTools.
Step 4: Reload the webpage to capture network requests.
Step 5: Find the request with the URL you want to block in the list of network requests.
Step 6: Right-click the request and choose Block request URL from the context menu.
Step 7: Reload the page. The URL you blocked will not load as long as DevTools stays open.
Step 8: To remove the block, open DevTools, click the three-dot menu in the Network tab, select Blocked URLs, and delete the blocked URL from the list.
How to Block a URL in Firefox Using DevTools
You can temporarily block a URL in Firefox with its Developer Tools. The block lasts only while DevTools is open.
Step 1: Open Firefox and go to the webpage where the request you want to block occurs.
Step 2: Press Ctrl + Shift + I (Windows) or Cmd + Option + I (Mac) to open Firefox DevTools.
Step 3: Click on the Network tab to view all network requests.
Step 4: Reload the page to capture the requests.
Step 5: Locate the network request with the URL you want to block.
Step 6: Right-click on that request and select Block URL from the context menu.
Step 7: Reload the page. The blocked URL will not load while DevTools remains open.
Step 8: To unblock the URL, right-click any request in the Network tab, select Manage Blocking, then remove the URL from the blocked list.
Also Read: How to Perform Remote Firefox Debugging
How to Block a URL in Safari Using Web Inspector
Safari’s Web Inspector lets you temporarily block URLs. The block works only while the Web Inspector is active.
Step 1: Open Safari and go to the webpage where the request occurs.
Step 2: Enable the Develop menu if it’s not already enabled: Go to Safari > Preferences > Advanced and check Show Develop menu in menu bar.
Step 3: Press Cmd + Option + I to open the Web Inspector.
Step 4: Click the Network tab to see network requests.
Step 5: Reload the page to capture network activity.
Step 6: Find the request with the URL you want to block.
Step 7: Right-click the request and select Block Request URL.
Step 8: Reload the page. The URL will be blocked as long as the Web Inspector is open.
Step 9: To unblock, right-click any request, choose Manage Blocked URLs, then remove the URL from the list.
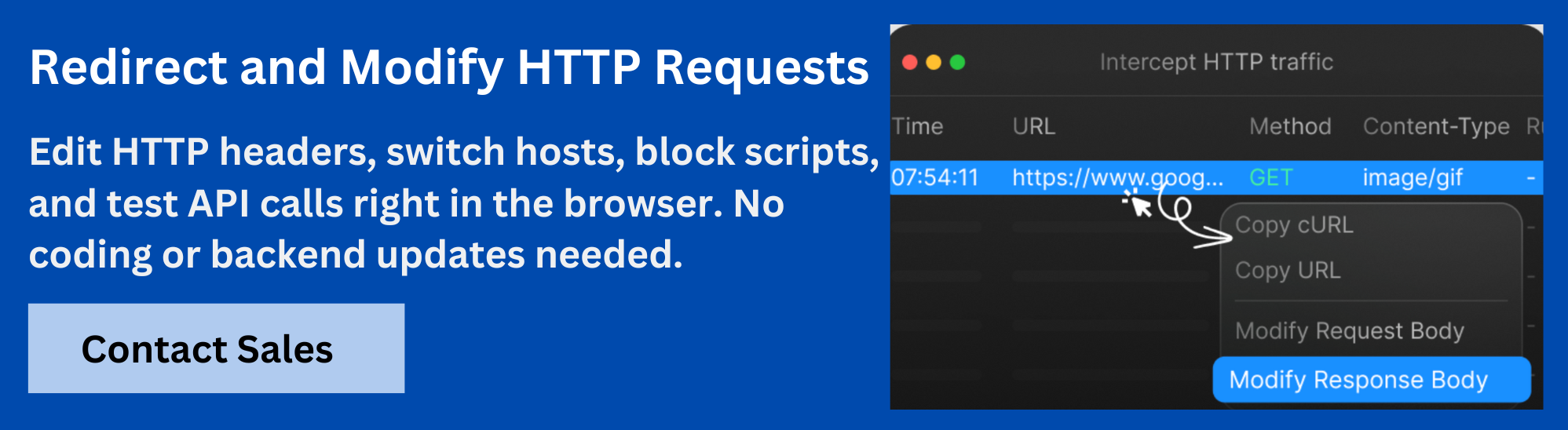
How to Block URLs Across All Browsers With Requestly?
Requestly is a browser extension that lets you block URLs by creating rules to cancel network requests. It works across multiple browsers and gives you control to block specific URLs, domains, or request patterns easily.
To block a URL using Requestly, follow these steps:
- Install Requestly extension: Add the Requestly browser extension from the Chrome Web Store or the Firefox Add-ons site.
- Create a Cancel Rule: Open Requestly and click Create your first rule. Select Cancel Request and click Create Rule.
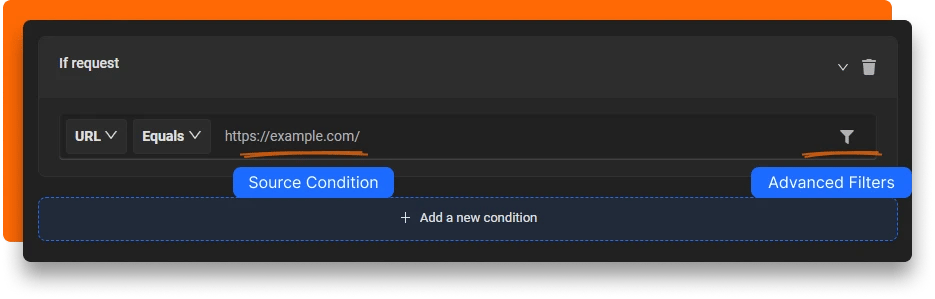
- Set the Source Condition: Enter the URL or pattern you want to block. You can use options like URL, Host, or Path with matching types such as Regex, Contains, Wildcard, or Equals.
- Configure Source Filters (Optional): Narrow down the rule’s scope by specifying which webpages, domains, request types, methods, or payloads it applies to.
- Save the rule: Once configured, save the rule. Requestly will automatically block matching URLs in your browser.
Conclusion
Blocking URLs in browsers helps control access, improve focus, protect users, and test how web applications respond to missing or failed resources. Chrome, Firefox, and Safari all offer ways to block URLs temporarily using their developer tools.
For more flexible and persistent blocking across multiple browsers, use Requestly by BrowserStack, which allows you to block URLs by creating custom rules. You can block specific URLs, domains, or request patterns without affecting other networks.