Images are vital to delivering engaging and visually appealing web experiences. However, when images fail to load properly, they can disrupt usability, undermine site credibility, and negatively impact SEO performance.
Overview
Image loading failure occurs when an image on a website does not load or display correctly for users, impacting the visual experience and site performance.
Common Causes:
- Broken or Incorrect URL: The image source link is incorrect, missing, or points to a non-existent file.
- Server or Network Issues: The server hosting the image is down, or there is a connectivity issue preventing the image from loading.
- Unsupported Format or Size: The image is in an unsupported format or too large to load efficiently.
- File Permissions: Restricted access or permissions on the server prevent the image from being served to the user.
- Browser or Device Compatibility: The image may not be compatible with certain browsers or devices, causing display issues.
- Cache Issues: Cached versions of the page may be showing outdated or broken image links.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check the Image URL: Ensure the path to the image is correct and there are no typos or broken links.
- Test Server and Network: Confirm the server is online, and the network connection is stable to ensure the image can be retrieved.
- Optimize Image Format and Size: Verify the image is in a standard, supported format (e.g., JPG, PNG, WebP) and reduce the file size if it’s too large.
- Inspect File Permissions: Make sure the image file has the correct permissions on the server, allowing public access.
- Clear Browser Cache: Clear the browser cache to ensure that outdated or corrupted files aren’t causing issues.
- Test Across Browsers and Devices: Check the image loading across different browsers and devices to spot compatibility issues.
- Check for CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) Issues: If the image is hosted on a different domain, ensure proper CORS headers are set.
This article explores the common causes behind these issues, provides effective diagnostic methods, and offers practical solutions to ensure smooth image rendering.
What is an Image Loading Failure?
An image loading failure occurs when a web page is unable to display an image as intended. Instead of showing the expected visual content, the browser may display a broken image icon or leave an empty space where the image should appear. This happens because the browser could not retrieve or render the image file specified in the webpage’s code.
Image loading failures can significantly disrupt the user experience by making a site look incomplete or unprofessional.
They can also harm the website’s credibility and negatively impact search engine rankings, as users may leave the site in frustration. Such failures can result from a wide range of issues, from simple mistakes like incorrect file paths or file names, to more complex problems such as server downtime or corrupted image files.
Understanding what constitutes an image loading failure is the first step toward diagnosing and fixing these issues to maintain a smooth and visually appealing website.
Read More:How to make images responsive
Common Causes of Image Loading Failures
Image loading failures can result from a variety of technical issues, many of which are common pitfalls when managing website assets. Some of the most frequent causes include:
- Incorrect File Path or Broken Links: One of the primary reasons images fail to load is an incorrect or broken file path in the website’s code. If the browser cannot locate the image file using the specified path, it will not display the image.
- Case-Sensitivity in File Names: Many servers (especially Linux-based) treat file names as case-sensitive, meaning “Image.jpg” and “image.jpg” are considered different files. Mismatched capitalization can cause loading failures.
- Misspelled or Wrong File Names: Any typo or mismatch between the image file name in the code and the actual file name on the server can prevent images from showing.
- Incorrect File Extensions: Using the wrong file extension (e.g., labeling a JPG image as PNG in the HTML) causes browsers to misinterpret the file, leading to errors.
- Missing or Deleted Images: Images that have been deleted or never uploaded properly will naturally fail to load.
- Host Website Downtime or Server Issues: If the server hosting the images is down or slow, or if an external Content Delivery Network (CDN) faces issues, images won’t load as expected.
- Browser Caching Problems: Sometimes browsers load cached versions of webpages where images may be outdated or missing, causing loading errors.
- Security Settings (Mixed Content): Loading images over HTTP when the rest of the site uses HTTPS triggers browser security blocks, leading to image failures.
- Plugin or Theme Conflicts: Particularly in CMS platforms like WordPress, conflicts from plugins or themes can interfere with how images load.
- Large Image File Sizes: Oversized images take longer to load and can sometimes fail, especially over slow connections.
- Incorrect URLs in CSS: Background images and other CSS-embedded images can fail if the URLs specified are wrong.
How to Diagnose Image Loading Problems
Diagnosing image loading issues involves a systematic approach using browser tools and manual checks to identify the root cause. Here are key steps to diagnose image loading problems effectively:
- Use Browser Developer Tools: Open the browser’s developer tools (usually by pressing F12 or right-clicking and selecting “Inspect”). The Console and Network tabs show detailed error messages and HTTP status codes related to image requests. Failed requests often appear in red, indicating broken links or permission issues.
- Check Image URLs Directly: Copy the image URL from the webpage code and open it in a new browser tab to verify if the image is accessible. If it doesn’t load, the file path may be incorrect or the image might be missing.
- Verify File Paths and Names: Ensure that the file paths and image file names in the HTML or CSS code exactly match those on the server, including case sensitivity and file extensions.
- Test Across Multiple Browsers and Devices: Load the website on different browsers and devices to check if the issue is browser-specific or universal.
- Clear Browser Cache: Sometimes a cached version of the page can cause outdated images to display or not display at all. Clearing the browser cache and reloading the page can resolve this.
- Check Server and Network Status: Confirm that the server hosting the images is operational and that there are no connectivity issues. If using a CDN, ensure it is functioning correctly.
- Disable Conflicting Plugins or Themes: On CMS platforms like WordPress, temporarily disable plugins or switch to a default theme to rule out conflicts affecting image loading.
- Validate Security Settings: Ensure that HTTPS is used consistently for image URLs to avoid browser blocking images due to mixed content security policies.
Effective Solutions to Fix Image Loading Failures
Fixing image loading failures involves addressing the root causes and implementing best practices to ensure reliable image delivery and optimal website performance. Here are some effective solutions:
- Verify and Correct File Paths and Names: Double-check the file paths, names, and extensions in your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code to confirm they exactly match the image files on the server, including case sensitivity.
- Set Default Fallback Images: Use the onerror attribute in image tags to specify a fallback image if the primary image fails to load. Example:
<img src=”image.jpg” onerror=”this.onerror=null;this.src=’default.jpg’;”> - Upload or Restore Missing Images: Ensure all images referenced by your site are properly uploaded and accessible on the server or CDN.
- Use Reliable Hosting and CDN Services: Host images on stable servers or Content Delivery Networks to reduce downtime and improve loading speed globally.
- Clear and Manage Cache: Clear browser and server caches regularly to avoid loading outdated or corrupted image versions.
- Resolve Plugin and Theme Conflicts: Especially in CMS platforms like WordPress, disable or update plugins/themes that may interfere with image loading.
- Ensure HTTPS Consistency: Fix mixed content issues by serving images over HTTPS if your website uses HTTPS to prevent browsers from blocking image loads.
- Optimize Image Size and Format: Compress images without compromising quality using tools like TinyPNG, ImageOptim, or cloud services. Use modern formats like WebP for faster performance.
- Implement Lazy Loading: Load images only when they enter the viewport to speed up initial page load. Use native HTML loading attribute (loading=”lazy”) or JavaScript libraries.
- Configure Server to Handle Missing Files Gracefully: Use server settings (e.g., .htaccess on Apache) to serve default images for missing files, preventing broken image icons.
- Check and Fix Hotlinking Settings: Disable hotlink protection if it is blocking legitimate image requests.
- Enable JavaScript: Make sure JavaScript is enabled in the browser if images are loaded dynamically using scripts.
Conclusion
Image loading failures disrupt the visual appeal and functionality of a website, leading to poor user experience and potential SEO setbacks. By understanding what causes these failures, diagnosing problems using practical tools, and applying effective solutions such as correcting file paths, optimizing images, and managing server or plugin issues, website owners can ensure flawless image rendering.
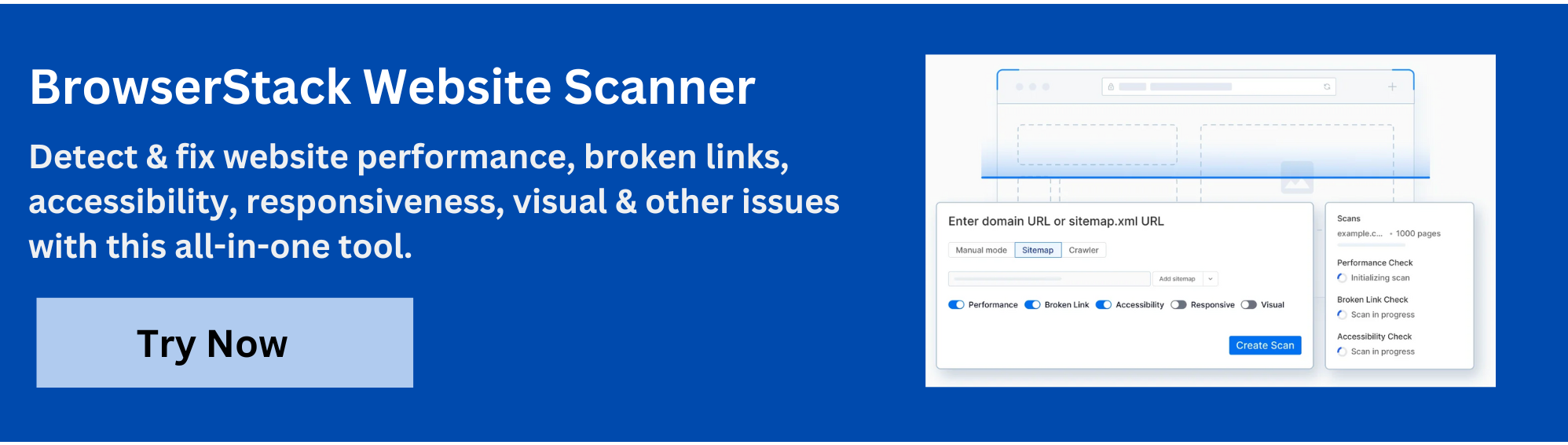
To keep your website running smoothly and efficiently, consider using BrowserStack Website Scanner. This tool allows you to automatically scan your website for issues like broken images, layout problems, and performance bottlenecks. Get detailed reports with actionable insights to fix defects before they affect your users, ensuring a seamless and visually complete browsing experience.