Fetching too much or too little data is a common headache in mobile apps. By integrating GraphQL with Flutter, developers can request exactly what’s needed, reduce network strain, and deliver a smoother user experience.
Overview
Flutter is a cross-platform framework for building mobile, web, and desktop apps from one codebase. Its customizable widgets and reactive model make creating high-performance, responsive UIs seamless.
On the other hand, GraphQL is a modern API query language that lets clients fetch exactly the data they need from a single endpoint, avoiding the inefficiencies of REST and reducing network overhead.
GraphQL adds several advantages when paired with Flutter, including:
- Fetch only the required data, avoiding over- or under-fetching common with REST
- Interact with all resources through a single flexible endpoint
- Reduce network calls, improving performance on mobile connections
- Enable real-time updates with subscriptions for dynamic apps
- Strongly typed schemas improve reliability and make code generation easier
- Simplifies client–server communication, leading to cleaner and more maintainable code
The article covers Flutter & GraphQL fundamentals, their advantages together, setup steps, core operations, advanced techniques, and best practices for building efficient apps.
Flutter & GraphQL Basics
Flutter is Google’s open-source framework for building cross-platform applications that run on mobile, web, and desktop, all from a single codebase. It offers a rich collection of customizable widgets, fast rendering with the Skia engine, and a reactive programming model that makes building dynamic user interfaces seamless.
Its ability to deliver near-native performance has made it one of the most popular choices for modern app development.
GraphQL is a query language and runtime for APIs that provides a more efficient alternative to REST. Instead of making multiple requests to different endpoints, GraphQL allows developers to query exactly the data they need from a single endpoint.
This eliminates issues like over-fetching or under-fetching data, reduces network overhead, and improves performance, especially critical in mobile environments. It also provides strongly typed schemas, making APIs predictable and easier to maintain.
Together, Flutter and GraphQL create a powerful combination. Flutter handles expressive, performant UIs while GraphQL ensures precise and efficient data communication. This synergy not only speeds up development but also leads to applications that are highly responsive, scalable, and easier to evolve over time.
Why Use GraphQL with Flutter
Flutter provides the tools to craft beautiful, high-performance UIs, but the way your app fetches and manages data can make or break the experience. This is where GraphQL adds tremendous value.
By replacing traditional REST endpoints with flexible queries, GraphQL ensures smoother communication between your Flutter app and backend services.
Key reasons to use GraphQL with Flutter include:
- Single endpoint: Simplifies API design by handling queries, mutations, and subscriptions through one endpoint.
- Precise data fetching: Fetch exactly what the UI needs, no more under-, or over-fetching.
- Optimized performance: Fewer network requests and smaller payloads improve app responsiveness, especially on mobile connections.
- Real-time capabilities: Subscriptions allow live updates for chats, notifications, and dashboards.
- Type safety: Strongly typed schemas reduce runtime errors and make integration more predictable.
- Clean codebase: Simplifies data management, keeping Flutter projects easier to maintain and scale.
Together, Flutter and GraphQL strike a balance: expressive front-end design paired with efficient, predictable backend communication.
Getting Started: Core Setup
To use GraphQL in a Flutter project, the most popular option is the graphql_flutter package. It provides the essential tools, like a client, provider, and ready-to-use widgets, for connecting your app to a GraphQL backend.
1. Add Dependencies
In your pubspec.yaml, include:
dependencies: flutter: sdk: flutter graphql_flutter: ^5.1.2 # check pub.dev for the latest version
2. Initialize the Client
Create a GraphQL client with an HTTP link (your API endpoint) and caching strategy:
final HttpLink httpLink = HttpLink('https://example.com/graphql');
ValueNotifier<GraphQLClient> client = ValueNotifier(
GraphQLClient(
link: httpLink,
cache: GraphQLCache(store: InMemoryStore()),
),
);3. Wrap Your App with GraphQLProvider
This makes the client available throughout your widget tree:
GraphQLProvider( client: client, child: MyApp(), );
4. Use Query or Mutation Widgets
The package provides Query, Mutation, and Subscription widgets to fetch or modify data easily:
Query(
options: QueryOptions(
document: gql('query { users { id name } }'),
),
builder: (result, {fetchMore, refetch}) {
if (result.isLoading) return CircularProgressIndicator();
if (result.hasException) return Text(result.exception.toString());
final users = result.data?['users'];
return ListView.builder(
itemCount: users.length,
itemBuilder: (_, i) => Text(users[i]['name']),
);
},
);This setup forms the foundation for working with queries, mutations, and subscriptions in Flutter apps using GraphQL.
Read More: How to Test Flutter Apps on Real iOS Devices
Understanding Queries, Mutations & Subscriptions
GraphQL revolves around three core operations, queries, mutations, and subscriptions, each serving a specific purpose in how your Flutter app interacts with the backend.
Queries: Fetching Data
Queries are used to retrieve data. Instead of calling multiple REST endpoints, you can fetch exactly the fields you need in a single request.
query {
users {
id
name
email
}
}In Flutter, this can be executed using the Query widget to display data directly in the UI.
Mutations: Modifying Data
Mutations allow the client to create, update, or delete data on the server. They also support returning updated objects, making UI updates seamless.
mutation {
addUser(name: "Alice", email: "alice@mail.com") {
id
name
}
}In Flutter, you can wrap actions like button presses with the Mutation widget, making it easy to trigger changes and reflect updates in the UI.Subscriptions: Real-Time Updates
Subscriptions: Real-Time Updates
Subscriptions are used for live data streams, ideal for chat apps, notifications, or dashboards. They keep the client updated automatically whenever the server data changes.
subscription {
messageAdded {
id
content
sender
}
}In Flutter, the Subscription widget allows you to listen to these real-time events and update widgets instantly.
Together, these three operations form the backbone of GraphQL. By combining them, your Flutter app can not only fetch and update data efficiently but also deliver real-time, interactive experiences.
Advanced Patterns & Tooling
Once the basics of GraphQL integration are in place, Flutter developers can take advantage of advanced patterns and tooling to make apps more efficient, reliable, and maintainable.
1. Caching Strategies
GraphQL in Flutter supports multiple caching policies such as CacheFirst, NetworkFirst, and CacheAndNetwork. Choosing the right policy ensures faster load times while keeping data fresh. For example, lists of items can be served instantly from cache while critical updates always fetch from the network.
2. Optimistic UI Updates
With optimistic responses, your app can update the UI immediately after a mutation is triggered, without waiting for the server’s response. This creates a smooth user experience, especially for actions like sending messages or liking posts.
3. Code Generation & Type Safety
Tools like Ferry and Artemis generate Dart models directly from GraphQL schemas. This eliminates repetitive boilerplate, ensures type safety, and reduces runtime errors when schemas evolve.
4. State Management Integration
Combining GraphQL clients with Flutter state management libraries (Provider, Riverpod, Bloc) makes data handling more predictable. Queries and mutations can be wrapped into providers or blocs, ensuring consistent updates across the app.
5. Offline Support
For mobile apps, offline-first is often critical. Libraries such as Brick or even built-in caching mechanisms allow data persistence when a network isn’t available, syncing automatically once the connection is restored.
6. Developer Tooling
- GraphQL Playground / Apollo Studio: for testing queries outside the app.
- GraphQL Code Generator: to streamline type-safe client code.
- Flutter DevTools: for profiling performance when combining GraphQL with heavy UI rendering.
By applying these advanced patterns and tools, Flutter GraphQL apps can achieve near-native performance, resilience against network issues, and developer-friendly workflows that scale with project complexity.
Read More: How to test Flutter Apps on Android Devices?
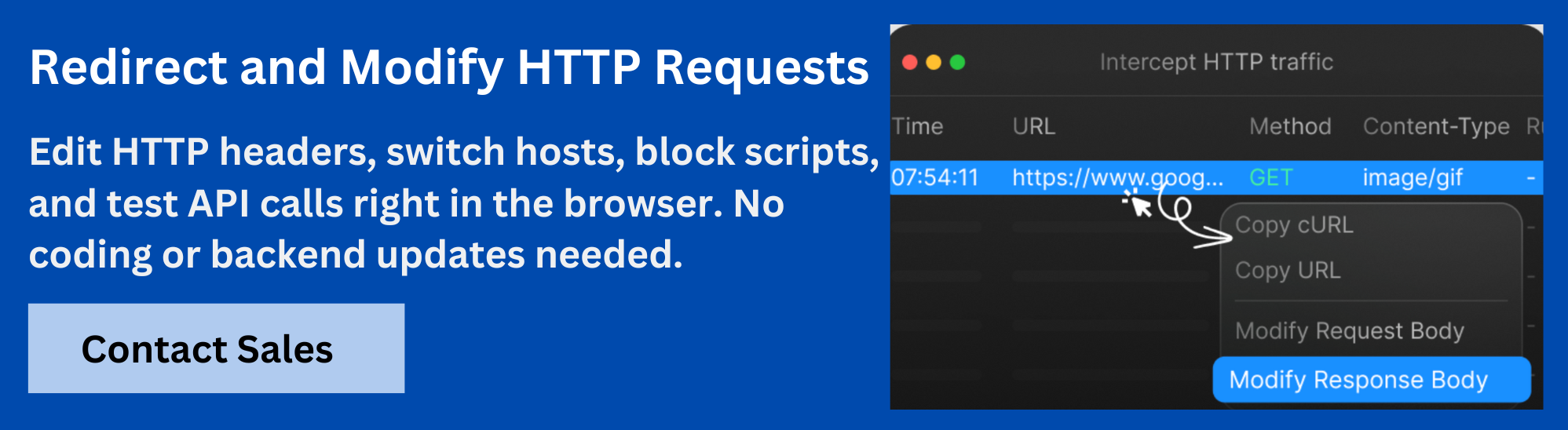
Debugging with Requestly HTTP Interceptor
Testing GraphQL APIs in Flutter can get tricky when you need to simulate edge cases or verify how the UI responds to different scenarios. This is where Requestly HTTP Interceptor by BrowserStack becomes a valuable tool.
With Requestly, developers can:
- Intercept and inspect GraphQL requests to see the exact queries, mutations, and variables being sent.
- Mock responses without changing backend code, making it easy to test loading states, errors, or empty results.
- Simulate failures or latency by modifying responses or adding delays to check how the app handles poor network conditions.
- Modify headers like Authorization to quickly test different user roles or permissions.
By integrating Requestly into the debugging workflow, Flutter developers can catch issues earlier, validate UI states faster, and reduce reliance on backend changes for testing. It streamlines the entire GraphQL development process and makes troubleshooting far more efficient.
Best Practices & Workflow Recommendations
Building apps with Flutter and GraphQL is powerful, but following proven practices ensures your project stays scalable, maintainable, and resilient.
- Organize operations clearly: Keep queries, mutations, and subscriptions in dedicated files or classes instead of scattering them across widgets. This improves readability and makes schema updates easier to manage.
- Leverage code generation: Use effective tools to generate type-safe models from your GraphQL schema. This reduces boilerplate, catches schema mismatches early, and improves refactoring safety.
- Choose caching strategies wisely: Apply policies like CacheFirst or NetworkOnly based on the data type. For example, use cached results for lists while fetching fresh data for user profiles or transactions.
- Test both happy paths and edge cases: Verify not just successful queries but also error states, empty responses, and permission-restricted scenarios. Tools like Requestly can help here.
- Integrate with state management: Combine GraphQL clients with Flutter state management solutions for predictable data flow and consistent UI updates.
- Plan for offline resilience: Mobile apps often face unstable connections. Use caching layers or libraries like Brick to support offline-first experiences and background sync.
- Monitor and log effectively: Add logging for GraphQL requests and errors during development, and track performance metrics in production to detect bottlenecks early.
By applying these practices, you can maintain a clean architecture, reduce technical debt, and ensure that your Flutter + GraphQL apps remain reliable as they grow.
Conclusion
Combining Flutter’s rich UI framework with GraphQL’s efficient data handling creates a powerful stack for building modern, scalable apps. By adopting smart patterns, leveraging the right tools, and following best practices, developers can deliver responsive, reliable experiences that adapt seamlessly to user needs.