As applications scale, managing complex data fetching and efficient pagination becomes challenging. GraphQL Relay simplifies this process, but setting it up and optimizing its performance requires a deep understanding of its core concepts and best practices.
Overview
Relay is a JavaScript framework developed by Facebook for building data-driven React applications. It works with GraphQL to efficiently fetch, cache, and manage data, while simplifying complex data-fetching patterns like pagination and mutations.
Core Concepts of Relay
- Relay Store: Manages local cache and application state for efficient data access.
- Connections and Edges: Handles pagination and lists of data using a standardized format.
- Fragments: Breaks down queries into reusable pieces, improving query efficiency.
- Mutations: Manages server-side changes and updates to the client’s store.
- Node Interface: Provides a global identifier for objects, allowing for unified data fetching.
Best Practices with GraphQL Relay
- Efficient Fragment Usage: Use fragments for reusable query logic and reduced data redundancy.
- Proper Pagination: Use Relay’s connection model for efficient forward and backward pagination.
- Cache Management: Ensure data consistency by leveraging Relay’s built-in cache and garbage collection.
- Optimistic UI Updates: Implement optimistic updates to provide faster user feedback during mutations.
- Avoid Over-fetching: Request only necessary data to minimize payload size and optimize performance.
This article explores how to effectively use GraphQL Relay for managing complex data fetching, pagination, and mutations in React applications.
What is GraphQL Relay?
GraphQL Relay is a JavaScript framework developed by Facebook that works in conjunction with GraphQL to simplify and optimize data fetching in React applications. It provides a set of conventions and utilities for managing complex data requirements, such as pagination, mutations, and caching, while ensuring that data-fetching operations are efficient and scalable.
Relay leverages the GraphQL query language and integrates seamlessly with React components, enabling developers to build highly interactive and performant applications. Its main features include:
- Efficient Pagination using Relay’s connection model to handle large datasets with smooth navigation.
- Automatic Data Caching and management through the Relay store, ensuring minimal network requests.
- Optimistic Updates for real-time UI feedback during mutations, making the app feel faster.
- Global Data Identification using the Node interface, ensuring data consistency across components.
Core Concepts of Relay
Relay introduces several key concepts that help manage data fetching, caching, and state in React applications using GraphQL. Understanding these concepts is essential for working with Relay effectively.
- Relay Store: The Relay Store is a centralized cache that holds data fetched via GraphQL, enabling efficient reuse and ensuring minimal network requests.
- Connections and Edges: Relay uses Connections and Edges for pagination. A connection represents a list of items, and edges are individual items, enabling efficient handling of large datasets with forward and backward pagination.
- Fragments: Fragments are reusable parts of a query, reducing redundancy and ensuring consistency when requesting the same data across different components.
- Mutations: Mutations handle server-side changes like creating or updating records. Relay automatically updates the store after a mutation, ensuring the UI reflects changes without needing to refetch data.
- Node Interface: The Node interface provides unique IDs for all objects, enabling global data identification and simplifying data fetching across different types.
- Pagination with Connection Model: Relay uses cursor-based pagination to manage large datasets efficiently, with pageInfo providing details on available data for easy navigation.
- Relay Environment: The Relay Environment manages queries, cache, and network requests, serving as the core object for data interactions in Relay.
Setting Up Relay with GraphQL
Setting up Relay with GraphQL involves configuring the Relay environment, connecting it to your GraphQL server, and ensuring that your React application can efficiently fetch and manage data. Below are the key steps to get started:
1. Install Dependencies
To begin, you’ll need to install the necessary dependencies for both Relay and GraphQL:
npm install react-relay relay-runtime graphql
These libraries include:
- react-relay: Provides hooks and components to integrate Relay with React.
- relay-runtime: Core runtime for Relay to manage data fetching and caching.
- graphql: The GraphQL query language and utilities.
2. Set Up the Relay Environment
Relay uses the Relay Environment to manage data, queries, and mutations. You’ll need to set up the environment, configure the network layer, and establish the store.
import { Environment, Network, RecordSource, Store } from ‘relay-runtime’;
// Create a function to fetch data from the GraphQL endpoint
function fetchQuery(operation, variables) {
return fetch(‘https://your-graphql-endpoint.com/graphql’, {
method: ‘POST’,
headers: {
‘Content-Type’: ‘application/json’,
},
body: JSON.stringify({
query: operation.text, // GraphQL text
variables,
}),
}).then(response => response.json());
}// Create the Relay Environment
const environment = new Environment({
network: Network.create(fetchQuery),
store: new Store(new RecordSource()),
});export default environment;
This code sets up the Network Layer to handle GraphQL queries and the Store to manage and cache data.
3. Configure Relay in the React App
Wrap your React application with the RelayEnvironmentProvider to provide the Relay environment to the entire app.
import React from ‘react’;
import ReactDOM from ‘react-dom’;
import { RelayEnvironmentProvider } from ‘react-relay’;
import App from ‘./App’;
import environment from ‘./RelayEnvironment’; // import Relay environmentReactDOM.render(
,
document.getElementById(‘root’)
);
This ensures that all components within the app have access to the Relay environment for fetching and managing data.
4. Set Up GraphQL Server (if not already done)
Make sure your GraphQL server supports Relay’s specifications, particularly the Node interface and Connection model for pagination. Relay expects certain structures in your GraphQL schema, such as using the id field to uniquely identify nodes and defining paginated results with edges and pageInfo.
5. Test Your Setup
Now that the environment is set up, you can start writing queries using GraphQL fragments and fetch data in your React components.
import { useLazyLoadQuery, graphql } from ‘react-relay’;
const UsersQuery = graphql`
query UsersQuery {
users(first: 10) {
edges {
node {
id
name
}
}
}
}
`;function Users() {
const data = useLazyLoadQuery(UsersQuery, {});return (
{data.users.edges.map(({ node }) => (
{node.name}
))});
}
This will fetch a list of users from the server, and Relay will manage the data caching and pagination automatically.
Querying Data with Relay
Relay simplifies data fetching by leveraging GraphQL queries and fragments, ensuring efficient and optimized data handling. Here’s how data querying works with Relay:
1. Using GraphQL Fragments
Relay queries are built using GraphQL fragments, which allow components to specify exactly which fields they need from the data. This helps reduce redundancy and ensures that only relevant data is fetched, improving performance and maintainability.
2. Fetching Data with useLazyLoadQuery
Relay uses the useLazyLoadQuery hook to fetch data when a component is mounted. This hook ensures that data is fetched only when necessary and helps to optimize rendering. It supports declarative fetching, making it easier to manage asynchronous data requests.
3. Querying Data on Demand
For more flexible data fetching, Relay provides the useQuery hook, which can be used to trigger data fetching based on specific events or interactions. This allows for more control over when and how data is fetched within the application.
4. Pagination with Relay Connections
Relay’s Connection model supports efficient pagination, allowing you to handle large datasets with minimal performance impact. By using connections, Relay provides an optimized way to manage fetching and rendering large lists of data in manageable chunks.
Handling Pagination with Relay
Relay simplifies pagination with its Connection model, which is designed to efficiently manage large datasets. The Connection model uses cursors to paginate through data, allowing you to easily implement both forward and backward pagination.
1. Connections and Edges
In Relay, data is structured into Connections and Edges:
- Connection: Represents a list of items, such as users or posts.
- Edge: Represents an individual item in the list. Each edge contains the item data (referred to as a node) and a cursor, which is used for pagination.
2. Cursor-based Pagination
Relay uses cursor-based pagination to navigate through large datasets. The cursor points to a specific item in the list, allowing for forward and backward pagination. The pageInfo object contains information about the pagination state, such as:
- hasNextPage: Indicates whether more data is available to load.
- hasPreviousPage: Indicates whether there’s data available before the current page.
- endCursor: Points to the last item on the current page, used for the next page query.
3. Forward and Backward Pagination
- Forward Pagination: Fetches data starting from the current position and moves forward in the dataset.
- Backward Pagination: Allows users to load previous items in the dataset by using the startCursor and endCursor.
Relay’s Connection model makes it easy to implement both types of pagination with minimal effort, ensuring that large datasets are handled efficiently without unnecessary re-renders or excessive network requests.
Relay and GraphQL Optimizations
Relay is designed to optimize data fetching and performance when using GraphQL. By leveraging various features and techniques, it ensures that data is managed efficiently, reducing unnecessary network requests and improving overall application responsiveness.
1. Persistent Queries
Relay supports persistent queries, which allow you to store and reuse GraphQL queries on the server. Instead of sending the full query each time, the client sends a hash of the query, reducing the payload size and speeding up query execution.
2. Automatic Caching
Relay’s automatic caching ensures that once data is fetched, it is stored in the Relay Store and reused when needed, avoiding redundant network requests. The cache is intelligently updated after mutations, keeping the UI in sync with the server state without needing a full refetch.
3. Fragment Colocation
Relay encourages fragment colocation, where fragments (smaller parts of GraphQL queries) are colocated with React components. This minimizes the need for rerenders by fetching only the data necessary for the component, reducing the overhead of fetching extra data and improving UI performance.
4. Batched Queries
Relay optimizes data fetching by allowing multiple GraphQL queries to be batched into a single network request. This reduces the number of HTTP requests and enhances performance, especially in applications with multiple concurrent data needs.
5. Garbage Collection
Relay implements automatic garbage collection in its store. It cleans up data that is no longer needed, freeing up memory and ensuring that stale or unused data does not unnecessarily occupy space in the cache.
6. Efficient Pagination
Relay uses cursor-based pagination (via the Connection model) to efficiently manage large datasets. By only fetching the data needed for a particular page or list, Relay reduces the load on the server and improves data retrieval times, even with large amounts of data.
7. Batch Updates to Store
Instead of updating the store on every small mutation or query, Relay batches updates to the store. This minimizes the number of updates and ensures more efficient handling of the data layer, improving performance in high-demand applications.
Best Practices with GraphQL Relay
To get the most out of Relay and GraphQL, it’s important to follow best practices that ensure efficient data fetching, state management, and scalability. Here are some key practices to consider when working with Relay in your React applications:
1. Efficient Fragment Usage
Use fragments to avoid redundant queries and ensure that data is requested in a modular way. By colocating fragments with your React components, you ensure that only the required data is fetched for each component.
- Break down complex queries into smaller fragments to keep them reusable and maintainable.
- Ensure that each component queries only the data it needs, which reduces the amount of data being fetched and avoids over-fetching.
2. Optimize Cache Management
Relay’s automatic caching is powerful, but it’s important to ensure that the cache is properly managed. Make sure the cache is invalidated or updated after mutations to prevent stale data from being displayed.
- Use store updates to manually update data after a mutation rather than refetching.
- Regularly clear the cache when necessary to prevent memory leaks or stale data.
// Clear the cache
environment.getStore().clear();
3. Handle Pagination Efficiently
Relay’s Connection model is ideal for handling pagination in large datasets. Always use the first, after, before, and last parameters when dealing with paginated queries to ensure that you’re fetching data efficiently.
- Use cursor-based pagination to load only a small subset of data at a time.
- Implement both forward and backward pagination to provide users with a seamless experience when navigating large lists.
4. Use Optimistic UI Updates
Optimistic UI updates provide an immediate response to user actions before the server responds, making the app feel faster. This is especially useful when performing mutations like creating or updating data.
- Use optimistic responses to immediately reflect changes in the UI.
- Always update the cache after mutations to ensure the UI reflects the most recent data.
// Example of an optimistic update in a mutation
const [addUser] = useMutation(ADD_USER, {
optimisticResponse: {
addUser: {
id: -1, // Temporary ID
name: ‘New User’,
email: ‘newuser@example.com’,
},
},
update(cache, { data: { addUser } }) {
const data = cache.readQuery({ query: GET_USERS });
cache.writeQuery({
query: GET_USERS,
data: {
users: […data.users, addUser],
},
});
},
});
5. Avoid Over-fetching
Ensure that your queries are efficient and don’t request unnecessary data. Relay’s use of fragments and connections makes it easy to structure queries for exactly the data needed. Avoid querying large datasets when only a small subset is required.
- Keep queries minimal and focused on the specific fields required by your component.
- Always use fragment colocation to keep query logic organized and avoid excessive data fetching.
6. Utilize Batch Updates
Relay efficiently batches network requests and cache updates to reduce the number of re-renders and network calls. Make sure you take advantage of these optimizations by batching queries and mutations together when possible.
- When possible, use batched queries to reduce the number of round trips to the server.
- Use store updates for handling data changes within Relay’s store efficiently.
7. Leverage Subscriptions for Real-time Data
Relay supports GraphQL subscriptions, which allow your app to receive real-time data updates. Implement subscriptions for scenarios where data changes frequently, such as live chat or live notifications.
Use subscriptions to ensure that your app reflects changes in real-time, providing users with up-to-date information without the need to poll the server.
8. Error Handling and Fallbacks
Ensure that your app gracefully handles errors and provides useful feedback to the user. Relay’s error handling mechanisms allow you to catch and display errors from GraphQL operations.
- Display friendly error messages and fallback UI in case of failed queries or mutations.
- Use error boundaries in React to handle and recover from errors in the UI.
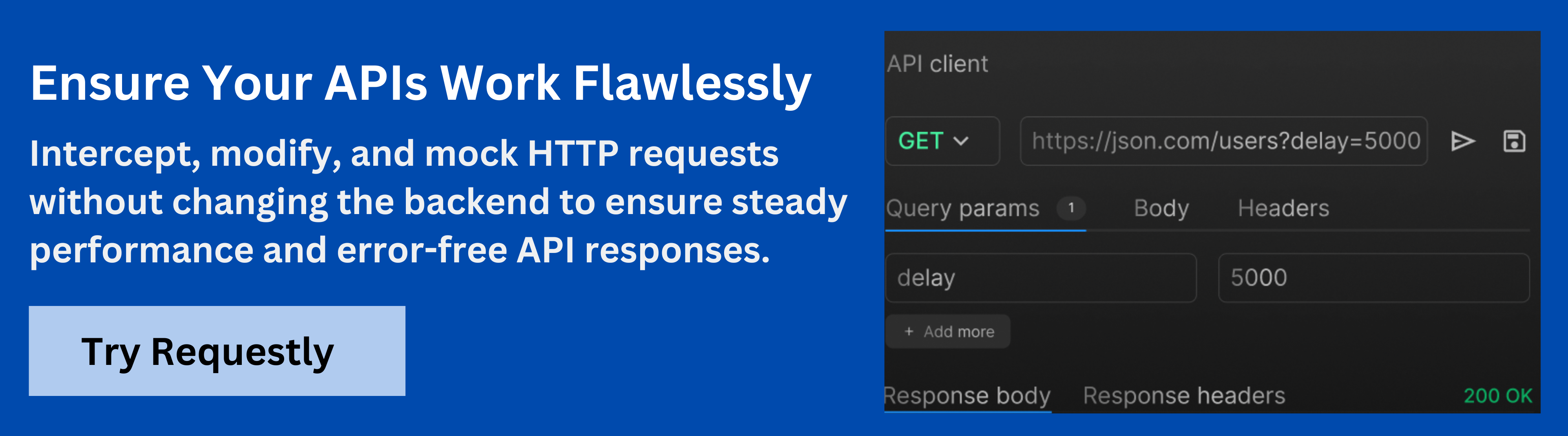
Enhance GraphQL Relay Debugging with Requestly
Requestly is a powerful tool that allows developers to intercept, modify, and mock HTTP requests and responses in real-time. It helps in debugging, testing, and optimizing network requests by giving full control over request data and response handling during development.
Requestly simplifies debugging GraphQL Relay applications by allowing you to intercept, modify, and inspect requests and responses. Here’s how it can help:
- Intercept and Inspect Requests: Monitor GraphQL queries, variables, and headers to ensure they are sent correctly and match expectations.
- Modify Requests and Responses: Change query variables or modify responses to simulate different scenarios, test edge cases, or handle errors without changing your app’s code.
- Mock Responses: Simulate server responses when the backend is incomplete, enabling you to continue development with mock data or simulate failure conditions.
- Analyze Network Traffic: Track the performance of GraphQL requests, identify slow queries, and spot errors in requests or responses.
- Optimize Query Performance: Detect redundant or over-fetched queries, and optimize them to reduce unnecessary network calls and improve performance.
Requestly streamlines the debugging process, helping you quickly resolve issues and optimize performance in GraphQL Relay applications.
Conclusion
Integrating GraphQL with Relay provides a robust solution for handling complex data fetching and state management in React applications. By leveraging Relay’s powerful features like efficient pagination, optimistic UI updates, and fragment colocation, developers can build scalable and performant applications.
Tools like Requestly further enhance the debugging and optimization process, allowing developers to easily inspect, modify, and optimize their GraphQL queries and responses. With these tools and best practices in place, building data-driven applications becomes more efficient, leading to a smoother and faster development process.