Developers often face delays when backend services are incomplete, unstable, or evolving, which slows frontend development and testing. Mocking API responses helps teams build, test, and debug applications independently of live servers.
Overview
GraphQL mocking is the process of creating simulated responses for a GraphQL API based on its schema, without needing a live backend. It helps developers test queries, explore API behavior, and validate application logic early in the development cycle.
GraphQL Mocking Techniques
- Schema-Based Mocking: Generate mock data directly from the GraphQL schema using tools like @graphql-tools/mock.
- Resolver-Level Mocking: Override specific resolvers to return custom or dynamic data for targeted testing.
- Request Interception: Intercept API requests and return predefined responses, useful for frontend testing.
- Subscription Mocking: Simulate real-time data streams for testing GraphQL subscriptions.
- Custom Scalar and Complex Types: Define mocks for non-standard scalars or nested objects to reflect realistic data structures.
This article explores key GraphQL mocking techniques, best practices for implementing them, and strategies to streamline API testing and development workflows.
Implementing Mocking in Development Workflows
Implementing GraphQL mocking effectively within development workflows requires careful planning to ensure that both frontend and backend teams can work efficiently, even when the backend services are incomplete or evolving.
Mocking can be introduced at multiple stages of development to create a stable, predictable environment for testing and feature building.
- Local Development: Set up a mock server or use schema-based mocks to simulate API responses, enabling frontend development without waiting for real endpoints.
- Continuous Integration and Testing: Integrate mocks into CI/CD pipelines to provide consistent test data for automated tests, ensuring reliability regardless of backend availability.
- Team Collaboration: Frontend and backend teams can work in parallel: frontend uses mocks while backend implements real services, reducing delays.
- Maintaining Mock Configurations: Keep mocks updated with schema changes to ensure realistic and consistent data, using reusable mock resolvers where possible.
Embedding GraphQL mocking in workflows accelerates development, improves testing, and maintains progress despite backend dependencies.
Advanced Mocking Techniques
For complex applications, basic mocking may not be enough. Advanced GraphQL mocking techniques help simulate real-world scenarios, test edge cases, and ensure that APIs behave correctly under various conditions.
- Resolver-Level Mocking: Instead of mocking the entire schema, override specific resolvers to return dynamic or context-specific data. This allows testing particular queries or mutations with customized responses.
- Mocking Subscriptions: Simulate real-time data streams by mocking GraphQL subscriptions. This is useful for testing features like live updates, notifications, or chat functionality without a live backend.
- Handling Custom Scalars and Complex Types: Define mocks for non-standard scalar types (e.g., Date, JSON) and deeply nested objects to reflect realistic data structures and maintain test accuracy.
- Conditional and Dynamic Mocking: Create mocks that change based on query arguments, variables, or request context. This enables testing of different API responses for various input scenarios.
- Combining Multiple APIs: Use tools like GraphQL Mesh to stitch multiple APIs together and provide unified mocks, which is helpful when an application depends on multiple data sources.
Advanced mocking techniques make testing more realistic, reduce surprises during integration, and ensure applications handle complex data and interactions correctly.
Testing Strategies with Mocked GraphQL APIs
Mocked GraphQL APIs provide a controlled environment to test application behavior before the backend is fully available. Implementing effective testing strategies ensures that both frontend components and the overall system function correctly.
- Unit Testing: Use mocks to isolate individual components and test their behavior against predictable responses. This helps verify that each part of the application handles data correctly without depending on a live API.
- Integration Testing: Test how different modules interact by combining multiple mocked queries and mutations. This ensures that components communicate properly and handle data flow as expected.
- End-to-End Testing: Simulate user journeys using mocked APIs to validate complete workflows. This allows QA teams to test UI interactions, error handling, and edge cases without relying on a live backend.
- Performance Testing: Leverage mocks to simulate large datasets or high-frequency queries, helping identify potential performance bottlenecks and optimize data handling before production.
- Regression Testing: Maintain mocks that mirror previous API behavior to ensure new changes don’t break existing functionality. This helps catch unintended side effects early.
Using these strategies with mocked GraphQL APIs accelerates testing, improves reliability, and reduces dependency on backend availability, enabling faster and more confident development cycles.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
While GraphQL mocking accelerates development and testing, certain pitfalls can reduce its effectiveness if not addressed. Being aware of these challenges helps maintain accurate and reliable mocks.
- Outdated Mock Data: Mocks that aren’t updated with schema changes can produce misleading results. Regularly reviewing and synchronizing mock configurations with the latest schema ensures consistency.
- Over-Simplified Mocks: Mocks that always return the same static data fail to reflect real-world scenarios. Using dynamic and conditional mocking helps simulate varied responses and edge cases.
- Ignoring Error Scenarios: Testing only successful responses can hide potential issues. Including error responses, timeouts, and invalid data in mocks ensures the application handles failures gracefully.
- Over-Reliance on Mocks: Relying solely on mocks may miss integration issues with the real backend. Combining mocked testing with real API tests once the backend is available provides more comprehensive coverage.
- Complex Setup: Intricate mocking setups can become difficult to maintain. Keeping mocks modular, reusable, and focused on critical paths simplifies management and improves reliability.
Read More: Top 10 Python REST API Frameworks
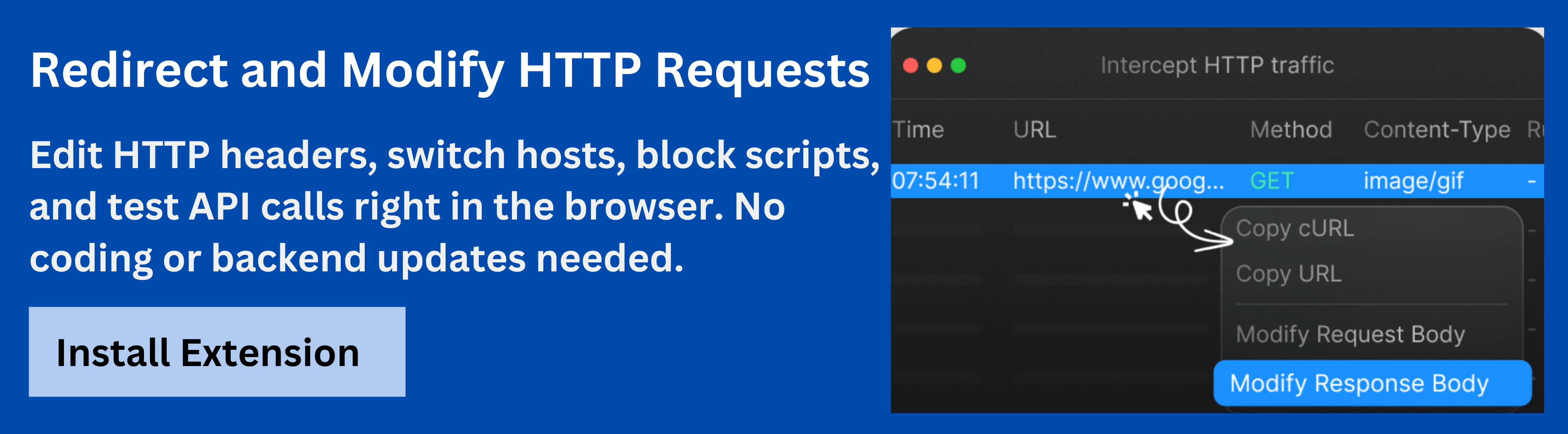
Boost API Testing and Debugging with Requestly HTTP Interceptor
Requestly HTTP Interceptor is a versatile tool that helps developers monitor, modify, and debug API requests in real time. It simplifies testing workflows by allowing teams to simulate different scenarios without altering the backend, making it particularly useful when working with mocked or evolving GraphQL APIs.
- Intercept and Modify Requests: Capture outgoing GraphQL requests and modify headers, query parameters, or request payloads on the fly to test different conditions and edge cases.
- Mock API Responses: Return custom responses for specific requests to simulate backend behavior, test error handling, or validate frontend logic against different data scenarios.
- Monitor and Debug: Track all API calls, inspect request/response details, and detect issues early, helping developers identify inconsistencies and optimize the API integration process.
Try Requestly HTTP Interceptor Now
By using Requestly HTTP Interceptor alongside GraphQL mocking, teams can accelerate testing, improve debugging efficiency, and ensure applications handle a wide range of scenarios reliably.
Conclusion
GraphQL mocking is a powerful approach to accelerate development, testing, and debugging by simulating API responses without relying on a live backend. When implemented effectively, it enables teams to work independently, test edge cases, and catch issues early.
By combining robust mocking techniques with tools like Requestly HTTP Interceptor, developers can ensure more reliable APIs, smoother workflows, and faster delivery of high-quality applications.